Abstract
The brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål; BPH) has become a severe constraint on rice production. Identification and pyramiding BPH-resistance genes is an economical and effective solution to increase the resistance level of rice varieties. All the BPH-resistance genes identified to date have been from indica rice or wild species. The BPH12 gene in the indica rice accession B14 is derived from the wild species Oryza latifolia. Using an F2 population from a cross between the indica cultivar 93-11 and B14, we mapped the BPH12 gene to a 1.9-cM region on chromosome 4, flanked by the markers RM16459 and RM1305. In this population, BPH12 appeared to be partially dominant and explained 73.8% of the phenotypic variance in BPH resistance. A near-isogenic line (NIL) containing the BPH12 locus in the background of the susceptible japonica variety Nipponbare was developed and crossed with a NIL carrying BPH6 to generate a pyramid line (PYL) with both genes. BPH insects showed significant differences in non-preference in comparisons between the lines harboring resistance genes (NILs and PYL) and Nipponbare. BPH growth and development were inhibited and survival rates were lower on the NIL-BPH12 and NIL-BPH6 plants compared to the recurrent parent Nipponbare. PYL-BPH6 + BPH12 exhibited 46.4, 26.8 and 72.1% reductions in population growth rates (PGR) compared to NIL-BPH12, NIL-BPH6 and Nipponbare, respectively. Furthermore, insect survival rates were the lowest on the PYL-BPH6 + BPH12 plants. These results demonstrated that pyramiding different BPH-resistance genes resulted in stronger antixenotic and antibiotic effects on the BPH insects. This gene pyramiding strategy should be of great benefit for the breeding of BPH-resistant japonica rice varieties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam SN, Cohen MB (1998a) Detection and analysis of QTLs for resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, in a doubled-haploid rice population. Theor Appl Genet 97:1370–1379
Alam SN, Cohen MB (1998b) Durability of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, resistance in rice variety IR64 in greenhouse selection studies. Entomol Exp Appl 89:71–78
Barloy D, Lemoine J, Abelard P, Tanguy AM, Rivoal R, Jahier J (2007) Marker-assisted pyramiding of two cereal cyst nematode resistance genes from Aegilops variabilis in wheat. Mol Breed 20:31–40
Chen H, Wang SP, Xing YZ, Xu CG, Hayes PM, Zhang QF (2003) Comparative analysis of genomic locations and race specificities of loci for quantitative resistance to Pyricularia grisea in rice and barley. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2544–2549
Chen JW, Wang L, Pang XF, Pan QH (2006) Genetic analysis and fine mapping of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph19(t). Mol Genet Genomics 275:321–329
Cohen MB, Alam SN, Medina EB, Bernal CC (1997) Brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, resistance in rice cultivar IR64: mechanism and role in successful N. lugens management in Central Luzon, Philippines. Entomol Exp Appl 85:221–229
Deen R, Ramesh K, Gautam SK, Rao YK, Lakshmi VJ, Viraktamath BC, Brar DS, Ram T (2010) Identification of new gene for BPH resistance introgressed O. rufipogon. Rice Genet Newsl 25:70–72
Du B, Zhang WL, Liu BF, Hu J, Wei Z, Shi ZY, He RF, Zhu LL, Chen RZ, Han B et al (2009) Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:22163–22168
Edwards OR (2001) Interspecific and intraspecific variation in the performance of three pest aphid species on five grain legume hosts. Entomol Exp Appl 100:21–30
Fujita D, Yoshimura A, Yasui H (2010) Development of near-isogenic lines and pyramided lines carrying resistance genes to green rice leafhopper (Nephotettix cincticeps Uhler) with the Taichung 65 genetic background in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed Sci 60:18–27
Heinrichs EA (1986) Perspectives and directions for the continued development of insect-resistant rice varieties. Agric Ecosyst Environ 18:9–36
Heinrichs EA, Aquino GB, Chelliah S (1982) Resurgence of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) populations as influenced by method and timing of insecticide applications in lowland rice. Environ Entomol 11:78–84
Huang N, Angeles ER, Domingo J, Magpantay G, Singh S, Zhang G, Kumaravadivel N, Bennett J, Khush GS (1997) Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice: marker-assisted selection using RFLP and PCR. Theor Appl Genet 95:313–320
Huang Z, He GC, Shu LH, Li XH, Zhang QF (2001) Identification and mapping of two brown planthopper resistance genes in rice. Theor Appl Genet 102:929–934
Jairin J, Phengrat K, Teangdeerith S, Vanavichit A, Toojinda T (2007) Mapping of a broad-spectrum brown planthopper resistance gene, Bph3, on rice chromosome 6. Mol Breed 19:35–44
Jena KK, Kim SM (2010) Current status of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance and genetics. Rice 3:161–171
Jena KK, Jeung JU, Lee JH, Choi HC, Brar DS (2006) High resolution mapping of a new brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene, Bph18(t) and marker-assisted selection for BPH resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 112:288–297
Kennedy GG, Gould F, Deponti OMB, Stinner RE (1987) Ecological, agricultural, genetic and commercial considerations in the deployment of insect-resistant germplasm. Environ Entomol 16:327–338
Klingler J, Creasy R, Gao LL, Nair RM, Calix AS, Jacob HS, Edwards OR, Singh KB (2005) Aphid resistance in Medicago truncatula involves antixenosis and phloem-specific, inducible antibiosis, and maps to a single locus flanked by NBS-LRR resistance gene analogs. Plant Physiol 137:1445–1455
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu YB, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu BY, Maghirang R, Li ZK, Xing YZ, Zhang QF, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Myint KKM, Hideshi Y, Masami T, Masaya M (2009) Virulence of long-term laboratory populations of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), and whitebacked planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) (Homoptera: Delphacidae), on rice differential varieties. Appl Entomol Zool 44(1):149–153
Normile D (2008) Reinventing rice to feed the world. Science 321:330–333
Palloix A, Ayme V, Moury B (2009) Durability of plant major resistance genes to pathogens depends on the genetic background, experimental evidence and consequences for breeding strategies. New Phytol 183:190–199
Park DS, Lee SK, Lee JH, Song MY, Song SY, Kwak DY, Yeo US, Jeon NS, Park SK, Yi G, Song YC, Nam MH, Ku YC, Jeon JS (2007) The identification of candidate rice genes that confer resistance to the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) through representational difference analysis. Theor Appl Genet 115:537–547
Qiu YF, Guo JP, Jing SL, Zhu LL, He GC (2010) High-resolution mapping of the brown planthopper resistance gene Bph6 in rice and characterizing its resistance in the 9311 and Nipponbare near isogenic backgrounds. Theor Appl Genet 121:1601–1611
Rahman ML, Jiang WZ, Chu SH, Qiao YL, Ham TH, Woo MO, Lee J, Khanam MS, Chin JH, Jeung JU, Brar DS, Jena KK, Koh HJ (2009) High-resolution mapping of two rice brown planthopper resistance genes, Bph20(t) and Bph21(t), originating from Oryza minuta. Theor Appl Genet 119(7):1237–1246
Ram T, Deen R, Gautam SK, Ramesh K, Rao YK, Brar DS (2010) Identification of new genes for brown planthopper resistance in rice introgressed from O. glaberrima and O. minuta. Rice Genet Newsl 25:67–69
Renganayaki K, Fritz AK, Sadasivam S, Pammi S, Harrington SE, McCouch SR, Kumar SM, Reddy AS (2002) Mapping and progress toward map-based cloning of brown planthopper biotype-4 resistance gene introgressed from Oryza officinalis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Crop Sci 42:2112–2117
Sharma PN, Torii A, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C (2004) Marker-assisted pyramiding of brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance genes Bph1 and Bph2 on rice chromosome 12. Hereditas 140:61–69
Singh S, Sidhu JS, Huang N, Vikal Y, Li Z, Brar DS, Dhaliwal HS, Khush GS (2001) Pyramiding three bacterial blight resistance genes (Xa5, Xa13 and Xa21) using marker-assisted selection into indica rice cultivar PR106. Theor Appl Genet 102:1011–1015
Sun LH, Su CC, Wang CM, Zhai HQ, Wan JM (2005) Mapping of a major resistance gene to the brown planthopper in the rice cultivar Rathu Heenati. Breed Sci 55(4):391–396
Tan MYA, Hutten RCB, Visser RGF, van Eck HJ (2010) The effect of pyramiding Phytophthora infestans resistance genes R Pi-mcd1 and R Pi-ber in potato. Theor Appl Genet 121(1):117–125
Tanaka K, Endo S, Kazana H (2000) Toxicity of insecticides to predators of rice planthoppers: spiders, the mirid bug and the dryinid wasp. Appl Entomol Zool 35:177–187
Temnykh S, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartinhour S, Hauck N, Lipovich L, Cho YG, Ishii T, McCouch SR (2000) Mapping and genome organization of microsatellite sequence in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:697–712
Van Ooijen JW (2004) MapQTL 5.0, software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, The Netherlands Plant Research International, Wageningen
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap 3.0, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Kyazma BV, The Netherlands Plant Research International, Wageningen
Watanabe T, Kitagawa H (2000) Photosynthesis and translocation of assimilates in rice plants following phloem feeding by planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae). J Ecol Entomol 93:1192–1198
Way MJ, Heong KL (1994) The role of biodiversity in the dynamics and management of insect pests of tropical irrigated rice—a review. Bull Entomol Res 84:567–587
Yang CJ, Yang ZH, Hu JF, He GC, Shu LH (1999) Study on the brown planthopper resistance introgressive lines from wild rice. Acta Phytophy Sinica 26:197–202
Yang HY, Ren X, Weng QM, Zhu LL, He GC (2002) Molecular mapping and genetic analysis of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene. Hereditas 136(1):39–43
Yang HY, You AQ, Yang ZF, Zhang FT, He RF, Zhu LL, He GC (2004) High-resolution genetic mapping at the Bph15 locus for brown planthopper resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 10:182–191
Yara A, Phi CN, Matsumura M, Yoshimura A, Hideshi Y (2010) Development of near-isogenic lines for BPH25(t) and BPH26(t), which confer resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål.) in indica rice ‘ADR52’. Breed Sci 60:639–647
Yoshimura S, Yoshimura A, Iwata N, McCouch SR, Abenes ML, Baraoidan MR, Mew TW, Nelson RJ (1995) Tagging and combining bacterial-blight resistance genes in rice using RAPD and RFLP markers. Mol Breed 1:375–387
Zhang JF, Li XH, Jiang GH, Xu YB, He YQ (2006) Pyramiding of Xa7 and Xa21 for the improvement of disease resistance to bacterial blight in hybrid rice. Plant Breed 125:600–605
Zhou YL, Xu JL, Zhou SC, Yu J, Xie XW, Xu MR, Sun Y, Zhu LH, Fu BY, Gao YM, Li ZK (2009) Pyramiding Xa23 and Rxo1 for resistance to two bacterial diseases into an elite indica rice variety using molecular approaches. Mol Breed 23:279–287
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 30671287), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant no. 1104002), the Projects from the Ministry of Agriculture of China for transgenic research and the National Major Project of Breeding for New Transgenic Organisms (grant no. 2009ZX08009-047B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Tai.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2011_1722_MOESM2_ESM.tif
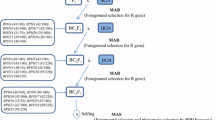
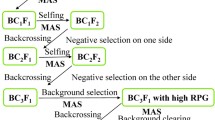
Supplementary Figure S1 The pedigree NILs and PYLs containing BPH resistance genes BPH6 and BPH12 developed using marker-assisted selection (MAS). * The BC4F1 individual with BPH6 was developed by Qiu et al. (2010). (TIFF 9996 kb)
122_2011_1722_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary Figure S2 The graphical genotype of the selected BC4F1 plant (4Y1249-53-2). The white squares show the chromosomal segment of Nipponbare, while the black squares show the chromosomal segment of B14. (TIFF 2640 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, Y., Guo, J., Jing, S. et al. Development and characterization of japonica rice lines carrying the brown planthopper-resistance genes BPH12 and BPH6 . Theor Appl Genet 124, 485–494 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1722-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1722-5