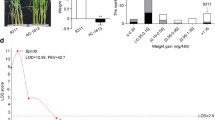
Abstract
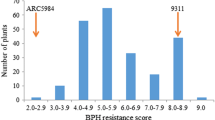
Brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål, BPH) is one of the most destructive insect pests of rice. Exploring resistance genes from diverse germplasms and incorporating them into cultivated varieties are critical for controlling this insect. The rice variety Swarnalata was reported to carry a resistance gene (designated Bph6), which has not yet been assigned to a chromosome location and the resistance mechanism is still unknown. In this study, we identified and mapped this gene using the F2 and backcrossing populations and characterized its resistance in indica 9311 and japonica Nipponbare using near isogenic lines (NILs). In analysis of 9311/Swarnalata F2 population, the Bph6 gene was located on the long arm of chromosome 4 between the SSR markers RM6997 and RM5742. The gene was further mapped precisely to a 25-kb region delimited between the STS markers Y19 and Y9; and the distance between these markers is 25-kb in Nipponbare genome. The Bph6 explained 77.5% of the phenotypic variance of BPH resistance in F2 population and 84.9% in BC2F2 population. Allele from Swarnalata significantly increased resistance to the BPH, resulted in a reduced damage score. In characterization of Bph6-mediated resistance, the BPH insects showed significant preference between NIL-9311 and 9311 in 3 h and between NIL-NIP and Nipponbare in 120 h after release. BPH growth and development were inhibited, and the insect’s survival rates were lower on Bph6-NIL plants, compared with the parents 9311 and Nipponbare. The results indicate that the Bph6 exerted prolonged antixenotic and antibiotic effects in Bph6-NIL plants, and NIL-9311 plants showed a quicker and stronger effect toward BPH than NIL-NIP plants.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam SN, Cohen MB (1998) Detection and analysis of QTLs for resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, in a doubled-haploid rice population. Theor Appl Genet 97:1370–1379
Athwal DS, Pathak MD, Bacalangco EH, Pura CD (1971) Genetics of resistance to brown planthoppers and green leafhoppers in Oryza sativa L. Crop Sci 11:747–750
Bird DA, Franceschi VR, Facchini PJ (2003) A tale of three cell types: alkaloid biosynthesis is localized to sieve elements in opium poppy. Plant Cell 15:2626–2635
Cao YL, Ding XH, Cai M, Zhao J, Lin YJ, Li XH, Xu CG, Wang SP (2007) The expression pattern of a rice disease resistance gene Xa3/Xa26 is differentially regulated by the genetic backgrounds and developmental stages that influence its function. Genetics 177:523–533
Chen JW, Wang L, Pang XF, Pan QH (2006) Genetic analysis and fine mapping of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph19(t). Mol Genet Genomics 275:321–329
Cohen MB, Alam SN, Medina EB, Bernal CC (1997) Brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, resistance in rice cultivar IR64: mechanism and role in successful N. lugens management in Central Luzon, Philippines. Entomol Exp Appl 85:221–229
Du B, Zhang WL, Liu BF, Hu J, Wei Z, Shi ZY, He RF, Zhu LL, Chen RZ, Han B et al (2009) Identification and characterization of Bph14, a gene conferring resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:22163–22168
Edwards OR (2001) Interspecific and intraspecific variation in the performance of three pest aphid species on five grain legume hosts. Entomol Exp Appl 100:21–30
Hao PY, Liu CX, Wang YY, Chen RZ, Tang M, Du B, Zhu LL, He GC (2008) Herbivore-induced callose deposition on the sieve plates of rice: an important mechanism for host resistance. Plant Physiol 146:1810–1820
Hirabayashi H, Ogawa T (1995) RFLP mapping of Bph-1 (brown planthopper resistance gene) in rice. Breed Sci 45:369–371
Hirabayashi H, Angeles ER, Kaji R, Ogawa T, Brar DS, Khush GS (1998) Identification of brown planthopper resistance gene derived from O. fficinalis using molecular markers in rice. Breed Sci 48(Suppl):82 (in Japanese)
Huang Z, He GC, Shu LH, Li XH, Zhang QF (2001) Identification and mapping of two brown planthopper resistance genes in rice. Theor Appl Genet 102:929–934
Inukai T, Zeigler RS, Sarkarung S, Bronson M, Dung LV, Kinoshita T, Nelson RJ (1996) Development of pre-isogenic lines for rice blast-resistance by marker-aided selecting from inbred population. Theor Appl Genet 93:560–567
Jairin J, Phengrat K, Teangdeerith S, Vanavichit A, Toojinda T (2006) Mapping of a broad-spectrum brown planthopper resistance gene, Bph3, on rice chromosome 6. Mol Breed 19:35–44
Jena KK, Jeung JU, Lee JH, Choi HC, Brar DS (2006) High resolution mapping of a new brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene, Bph18(t), and marker-assisted selection for BPH resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 112:288–297
Kabir MA, Khush GS (1988) Genetic analysis of resistance to brown planthopper in rice, Oryza sativa L. Plant Breed 100:54–58
Kaloshian I, Kinsey MG, Ullman DE, Williamson VM (1997) The impact of Meu1-mediated resistance in tomato on longevity, fecundity and behavior of the potato aphid, Macrosiphum euphorbiae. Entomol Exp Appl 83:181–187
Kawaguchi M, Murata K, Ishii T, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C (2001) Assignment of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph4 to the rice chromosome 6. Breed Sci 51:13–18
Khush GS, Brar DS (1991) Genetics of resistance to insects in crop plants. Adv Agron 45:223–274
Khush GS, Rezaul Karim ANM, Angeles ER (1985) Genetic analysis of rice cultivar ARC 10550 to Bangladesh brown planthopper biotype. J Genet 64:121–125
Klingler J, Creasy R, Gao LL, Nair RM, Calix AS, Jacob HS, Edwards OR, Singh KB (2005) Aphid resistance in Medicago truncatula involves antixenosis and phloem-specific, inducible antibiosis, and maps to a single locus flanked by NBS-LRR resistance gene analogs. Plant Physiol 137:1445–1455
Lakshminarayana A, Khush GS (1977) New genes for resistance to the brown planthopper in rice. Crop Sci 17:96–100
Li RB, Li LS, Wei SM, Wei YP, Chen YZ, Bai DL, Yang L, Huang FK, Lu WL, Zhang XJ et al (2006) The evaluation and utilization of new genes for brown planthopper resistance in common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Mol Plant Breed 4(3):365–371
Marcel TC, Gorguet B, Ta MT, Kohutova Z, Vels A, Niks RE (2008) Isolate specificity of quantitative trait loci for partial resistance of barley to Puccinia hordei confirmed in mapping populations and near-isogenic lines. New Phytol 177:43–755
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu YB, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu BY, Maghirang R, Li ZK, Xing YZ et al (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Monna L, Lin HX, Kojima S, Sasaki T, Yano M (2002) Genetic dissection of a genomic region for quantitative trait locus Hd3, into two loci, Hd3a and Hd3b, controlling heading date in rice. Theor Appl Genet 104:772–778
Murai H, Hashimoto Z, Sharma PN, Shimizu T, Murata K, Takumi S, Mori N, Kawasaki S, Nakamura C (2001) Construction of a high-resolution linkage map of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph2. Theor Appl Genet 103:526–532
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nemoto H, Ikeda R, Kaneda C (1989) New genes for resistance to brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stål, in rice. Jpn J Breed 39:23–28
Normile D (2008) Reinventing rice to feed the world. Science 321:330–333
Palloix A, Ayme V, Moury B (2009) Durability of plant major resistance genes to pathogens depends on the genetic background, experimental evidence and consequences for breeding strategies. New Phytol 183:190–199
Park DS, Lee SK, Lee JH, Song MY, Song SY, Kwak DY, Yeo US, Jeon NS, Park SK, Yi G et al (2007) The identification of candidate rice genes that confer resistance to the brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) through representational difference analysis. Theor Appl Genet 115:537–547
Rahman ML, Jiang WZ, Chu SH, Qiao YL, Ham TH, Woo MO, Lee J, Khanam MS, Chin JH, Jeung JU et al (2009) High-resolution mapping of two rice brown planthopper resistance genes, Bph20(t) and Bph21(t), originating from Oryza minuta. Theor Appl Genet 119(7):1237–1246
Ramalingam J, Vera Cruz CM, Kukreja K, Chittoor JM, Wu JL, Lee SW, Baraoidan M, George ML, Cohen MB, Hulbert SH (2003) Candidate defense genes from rice, barley, land maize and their association with qualitative and quantitative resistance in rice. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16(1):14–24
Renganayaki K, Fritz AK, Sadasivam S, Pammi S, Harrington SE, McCouch SR, Kumar SM, Reddy AS (2002) Mapping and progress toward map-based cloning of brown planthopper biotype-4 resistance gene introgressed from Oryza officinalis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Crop Sci 42:2112–2117
Sun LH, Su CC, Wang CM, Zhai HQ, Wan JM (2005) Mapping of a major resistance gene to the brown planthopper in the rice cultivar Rathu Heenati. Breed Sci 55(4):391–396
Tanaka K, Endo S, Kazana H (2000) Toxicity of insecticides to predators of rice planthoppers: spiders, the mirid bug and the dryinid wasp. Appl Entomol Zool 35:177–187
Van Ooijen JW (2004) MapQTL 5, software for the mapping of quantitative trait loci in experimental populations. Kyazma BV, The Netherlands Plant Research International, Wageningen
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap 3.0, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Kyazma BV, The Netherlands Plant Research International, Wageningen
Wang GL, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, McCouch SR, Champoux MC, Nelson RJ (1994) RFLP mapping of genes conferring complete and partial resistance to blast in a durably resistant rice cultivar. Genetics 136:1421–1434
Watanabe T, Kitagawa H (2000) Photosynthesis and translocation of assimilates in rice plants following phloem feeding by planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Homoptera: Delphacidae). J Ecol Entomol 93:1192–1198
Will T, Tjallingii WF, Thönnessen A, Bel A (2007) Molecular sabotage of plant defense by aphid saliva. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:10536–10541
Yang HY, Ren X, Weng QM, Zhu LL, He GC (2002) Molecular mapping and genetic analysis of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene. Hereditas 136(1):39–43
Yang HY, You AQ, Yang ZF, Zhang FT, He RF, Zhu LL, He GC (2004) High-resolution genetic mapping at the Bph15 locus for brown planthopper resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 10:182–191
Yue B, Xue WY, Luo LJ, Xing YZ (2006) QTL analysis for flag leaf characteristics and their relationships with yield and yield traits in rice. J Genet Genomics 33:824–832
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 30671287), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (grant no. 2006AA10Z144) and the Special Fund for Public Industry from the Ministry of Agriculture of China (grant no. 200803003) and the National Major Project of Breeding for New Transgenic Organisms (grant no. 2009ZX08009-047B).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Y. Xu.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Figure S1.
Overview of the host choice test of the BPH. (a) Overview of the host choice test before the BPH treatment. (b) Observation of the BPH location in NIL-9311 and 9311 plants at 120 h in the host choice test. The labels with ‘NIL’ and ‘AA11-6-1’ denote NIL-9311 plants; the labels with ‘9311’ and ‘P15’ denote 9311 plants (TIFF 8100 kb)
Supplemental Figure S2.
High-resolution genetic map of the Bph6 gene on rice chromosome 4 and the molecular marker genotypes and phenotypes of part recombinants. (a) High-resolution genetic linkage map. The numbers below the linkage map show the genetic distances (in cM). (b) Molecular marker genotypes and phenotypes of the recombinants. The black, white and gray bars denote the marker genotypes of Swarnalata homozygotes, 9311 homozygotes and heterozygotes, respectively. C1, control 1, homozygous for Swarnalata in the target region; C2, control 2, homozygous for 9311 in the target region; 9311, the susceptible parent; Swa, the resistant parent Swarnalata. a) BPH resistance score (mean ± SD, n = 7 replicates) (TIFF 5855 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, Y., Guo, J., Jing, S. et al. High-resolution mapping of the brown planthopper resistance gene Bph6 in rice and characterizing its resistance in the 9311 and Nipponbare near isogenic backgrounds. Theor Appl Genet 121, 1601–1611 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1413-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1413-7