Abstract
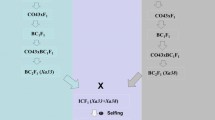
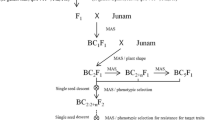
Rice bacterial leaf blight (BB) caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and bacterial leaf streak (BLS) caused by X. oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc) are two important diseases of rice that often outbreak simultaneously and constrain rice production in much of Asia and parts of Africa. Developing resistant cultivars has been the most effective approach to control BB, however, most single resistance genes have limited value in breeding programs because of their narrow-spectrum of resistance to the races of the pathogen. By contrast, there is little progress in breeding varieties resistant to Xoc since BLS resistance in rice was a quantitative trait and so far only a few quantitative resistance loci have been identified. We reported here the development of a high yield elite line, Lu-You-Zhan highly resistant to both BB and BLS by pyramiding Xa23 with a wide-spectrum resistance to BB derived from wild rice and a non-host maize resistance gene, Rxo1, using both marker assisted selection (MAS) and genetic engineering. Our study has provided strong evidence that non-host R genes could be a valuable source of resistance in combating those plant diseases where no single R gene controlling high level of resistance exists and demonstrated that MAS combined with transgenic technologies are an effective strategy to achieve high level of resistance against multiple plant diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari TB, Vera Cruz CM, Zhang Q, Nelson RJ, Skinner DZ, Mew TW, Leach JE (1995) Genetic diversity of Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae in Asia. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:966–971
Chen CH, Zhang W, Huang XM, Lin XH (2006) Major QTL conferring resistance to rice bacterial leaf streak. Agric Sci China 5(3):216–220. doi:10.1016/S1671-2927(06)60041-2
David O, NiÑe L, Pamiela CR, Adam JB (2006) Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars:model pathogens of a model crop. Mol Plant Pathol 7(5):303–324. doi:10.1111/j.1364-3703.2006.00344.x
Fang ZD, Xu ZG, Guo CJ, Yin SZ, Wu SZ, Xu XM, Zhang Q (1990) Studies on pathotypes of Xanthomonas campestris pv. oryzae in China (in Chinese with English abstract). Acta Phytopathol Sin 20(2):81–88
Heath MC (1987) Evolution of plant resistance and susceptibility to fungal invaders. Can J Plant Pathol 9:389–397
Heath MC (2000) Nonhost resistance and nonspecific plant defenses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:315–319. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00087-X
IRRI (1996) Standard evaluation system for rice. IRRI, Manila
Kang L, Li J, Zhao T, Xiao F, Tang X, Thilmony R, He S, Zhou J-M (2003) Interplay of the Arabidopsis nonhost resistance gene NHO1 with bacterial virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:3519–3524. doi:10.1073/pnas.0637377100
Kauffman HE, Reddy APK, Hsieh SPY, Merca SD (1973) A improved technique for evaluation of resistance of rice varieties to Xanthomonas oryzea. Plant Dis Rep 57:537–541
Khush GS, Bacalangco E, Ogawa T (1990) A new gene for resistance to bacterial blight from O.longistamina. Rice Genet Newsl 7:121–122
Lee SW, Choi SH, Han SS, Lee DG, Lee BY (1999) Distribution of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae strains virulent to Xa21 in Korea. Phytopathology 89:928–933. doi:10.1094/PHYTO.1999.89.10.928
Li ZK (2001) QTL mapping in rice: a few critical considerations. Rice Genetics VI. Proceedings of the fourth international rice genetics symposium, 22–27 Oct., 2000. Science Publishers, Inc./International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos (Philippines), pp 153–171
Li ZK, Arif M, Zhong DB, Fu BY, Xu JL, Domingo-Rey J, Ali J, Vijayakumar CHM, Maghirang R, Yu SB, Khush GS (2006) Complex genetic networks underlying the defensive system of rice (Oryza sativa L.) to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:7994–7999. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507492103
Lu HL, Zhou XR, Gong ZX, Upadhyaya MN (2001) Generation of selectable marker-free transgenic rice using double right border (DRB) binary vectors. Aust J Plant Physiol 28:241–248
Marella LS, George MLC, Vera CM, Bernardo MA, Nelson RJ, Leung H (2001) Identification of resistance genes effective against rice bacterial blight pathogen in eastern India. Plant Dis 85(5):506–512. doi:10.1094/PDIS.2001.85.5.506
McDonald BA, Linde C (2002) Pathogen population genetics, evolutionary potential, and durable resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:349–379. doi:10.1146/annurev.phyto.40.120501.101443
Mew TW, Vera Cruz CM, Medalla ES (1992) Changes in the race frequency of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in response to rice cultivars planted in the Philippines. Plant Dis 76:1029–1032
Ogawa T (1993) Methods and strategy for monitoring race distribution and identification of resistance genes to bacterial leaf blight (Xanthomonas campetris pv. oryzae) in rice. JARQ 27:71–80
Pan HJ, Wang CL, Zhao KJ, Zhang Q, Fan YL, Zhou SC, Zhu LH (2003) Molecular mapping by PCR-based markers and marker-assisted selection of Xa23 a bacterial blight resistance gene in rice. Acta Agronomica Sin 29(4):501–507
Peart JR, Lu R, Sadanandom A, Malcuit I, Moffet P, Brice DC, Schauser L, Jaggard DA, Xiao S, Coleman MJ, Dow M, Jones JD, Shirasu K, Baulcombe DC (2002) Ubiquitin ligase-associated protein SGT1 is required for host and nonhost disease resistance in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:10865–10869. doi:10.1073/pnas.152330599
Song WY, Wang GL, Chen LL (1804–1806) Han-Suk Kim, Pi LY, Holsten T, Gardner J, Wang B, Zhai WX, Zhu LH, Fauquet C, Ronald P (1995) A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science 270:279
Tang DZ, Wu WR, Li WM, Lu H, Worland AJ (2000) Mapping of QTLs conferring resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice. Theor Appl Genet 101:286–291. doi:10.1007/s001220051481
Thorsten N, Volker L (2005) Non-host resistance in plants: new insights into and old phenomenon. Mol Plant Pathol 6(3):335–345. doi:10.1111/j.1364-3703.2005.00279.x
Tu J, Ona I, Zhang Q, Mew TW, Khush GS, Datta SK (1998) Transgenic rice variety “IR72” with Xa21 is resistant to bacterial blight. Theor Appl Genet 97:31–36. doi:10.1007/s001220050863
Vauterin L, Hoste B, Kersters K, Swings J (1995) Reclassification of Xanthomonas. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:472–489
Xu J, Wang H, Lin Y, Xi Y (1997) Studies on the inheritance of the resistance of rice to bacterial leaf streak and bacterial leaf blight. Acta Genet Sin 24:330–335
Xu MR, Xia ZH, Zhai WX, Xu JL, Zhou YL, Li ZK (2008) Construction of double right-border binary vector carrying non-host gene Rxol resistant to rice bacterial leaf streak. Chin J Rice Sci 22(2):208–210
Zeng JM, Lin WX (2003) Research progress on rice bacterial leaf streak and its resistance (in Chinese). Mol Plant Breed 1(2):257–263
Zeng LX, Huang SH, Wu SZ (2002) Resistance of IRBB21 (Xa21) to five races of bacterial blight in Guangdong. J Plant Prot 29(2):97–100
Zhai WX, Li XB, Tian WZ, Zhou YL, Pan XB, Cao SY, Zhao XF, Zhao B, Zhang Q, Zhu LH (2000) Introduction of rice blight resistance gene, Xa21, into five Chinese rice varieties through an Agrobacterim-mediated system. Sci China 43(4):361–368 Series C
Zhai WX, Wang WM, Zhou YL, Li XB, Zheng XW, Zhang Q, Wang GL, Zhu LH (2001) Breeding bacterial blight-resistant hybrid rice with the cloned bacterial blight resistance gene Xa21. Mol Breed 8:285–293. doi:10.1023/A:1015234802902
Zhang Q (1991) Genetic evaluation and utilization of resistance to rice bacterial blight in China (in Chinese with English abstract). Scientia Agric Sin 24(2):26–36
Zhang Q, Lin SC, Zhao BY, Wang CL, Yang WC, Zhou YL, Li DY, Chen CB, Zhu LH (1998) Identification and tagging a new gene for resistance to bacterial blight (Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae) from O. rufipogon. Rice Genet Newsl 15:138–142
Zhang Q, Wang CL, Zhao KJ, Zhou YL, Caslana VC, Zhu XD, Li DY, Jiang QX (2001) The effectiveness of advanced rice lines with new resistance gene Xa23 to rice bacterial blight. Rice Genet Newsl 18:71–72
Zhao BY, Ardales E, Brasset E, Claflin LE, Leach JE, Hulbert SH (2004) The Rxo1/Rba1 locus of maize controls resistance reaction to pathogenic and non-host bacteria. Theor Appl Genet 109:71–79. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1623-y
Zhao BY, Lin XH, Poland J, Trick H, Leach JE, Hulbert SH (2005) A maize resistance gene functions against bacterial streak disease in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(43):15383–15388. doi:10.1073/pnas.0503023102
Zheng JS, Li YZ, Fang XJ (2005) Detection of QTL conferring resistance to bacterial leaf streak in rice chromosome 2 (O. sativa L. spp. indica). Sci Agric Sin 38(9):1923–1925
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30571200) and the Ministry of Agriculture (948 # 2006-G51 for providing the financial support. We acknowledge Prof. SH Hulbert, Kansas State University, USA for providing us with plasmid pCAMBIA1305-1 containing Rxo1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Y-L Zhou and J-L Xu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, YL., Xu, JL., Zhou, SC. et al. Pyramiding Xa23 and Rxo1 for resistance to two bacterial diseases into an elite indica rice variety using molecular approaches. Mol Breeding 23, 279–287 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9232-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9232-0