Abstract
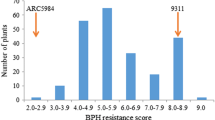
Brown planthopper (BPH) is a destructive insect pest of rice in Asia. Identification and the incorporation of new BPH resistance genes into modern rice cultivars are important breeding strategies to control the damage caused by new biotypes of BPH. In this study, a major resistance gene, Bph18(t), has been identified in an introgression line (IR65482-7-216-1-2) that has inherited the gene from the wild species Oryza australiensis. Genetic analysis revealed the dominant nature of the Bph18(t) gene and identified it as non-allelic to another gene, Bph10 that was earlier introgressed from O. australiensis. After linkage analysis using MapMaker followed by single-locus ANOVA on quantitatively expressed resistance levels of the progenies from an F2 mapping population identified with marker allele types, the Bph18(t) gene was initially located on the subterminal region of the long arm of chromosome 12 flanked by the SSR marker RM463 and the STS marker S15552. The corresponding physical region was identified in the Nipponbare genome pseudomolecule 3 through electronic chromosome landing (e-landing), in which 15 BAC clones covered 1.612 Mb. Eleven DNA markers tagging the BAC clones were used to construct a high-resolution genetic map of the target region. The Bph18(t) locus was further localized within a 0.843-Mb physical interval that includes three BAC clones between the markers R10289S and RM6869 by means of single-locus ANOVA of resistance levels of mapping population and marker-gene association analysis on 86 susceptible F2 progenies based on six time-point phenotyping. Using gene annotation information of TIGR, a putative resistance gene was identified in the BAC clone OSJNBa0028L05 and the sequence information was used to generate STS marker 7312.T4A. The marker allele of 1,078 bp completely co-segregated with the BPH resistance phenotype. STS marker 7312.T4A was validated using BC2F2 progenies derived from two temperate japonica backgrounds. Some 97 resistant BC2F2 individuals out of 433 screened completely co-segregated with the resistance-specific marker allele (1,078 bp) in either homozygous or heterozygous state. This further confirmed a major gene-controlled resistance to the BPH biotype of Korea. Identification of Bph18(t) enlarges the BPH resistance gene pool to help develop improved rice cultivars, and the PCR marker (7312.T4A) for the Bph18(t) gene should be readily applicable for marker-assisted selection (MAS).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam SN, Cohen MB (1998) Detection and analysis of QTLs for resistance to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, in a doubled-haploid rice population. Theor Appl Genet 97:1370–1379
Brar DS, Khush GS (1997) Alien introgression in rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:35–47
Choi SY, Heu MH, Lee JO (1979) Varietal resistance to brown planthopper in Korea: In: Brown planthopper: threat to rice production in Asia. IRRI, Los Baños, pp 219–232
Haldane JBS (1919) The combination of linkage values and the calculation of distances between the loci of linked factors. J Genet 8:299–309
Heinrichs EA (1986) Perspectives and directions for the continued development of insect resistant rice varieties. Agric Ecosyst Environ 18: 9–36
Hirabayashi H, Kaji R, Angeles ER, Ogawa T, Brar DS, Khush GS (1999) RFLP analysis of a new gene for resistance to brown planthopper derived from O. officinalis on rice chromosome 4 (abstract in Japanese). Breed Res 1(Suppl 1):48
Ishii T, Brar DS, Multani DS, Khush GS (1994) Molecular tagging of genes for brown planthopper resistance and earliness introgressed from Oryza australiensis into cultivated rice, Oryza sativa. Genome 37:217–221
Jena KK, Multani DS, Khush GS (1991) Monosomic alien addition lines of Oryza australiensis and alien gene transfer. Rice Genet II:728
Jena KK, Moon HP, Mackill DJ (2003a) Marker-assisted selection: a new paradigm in plant breeding. Korean J Breed 35:133–140
Jena KK, Pasalu IC, Rao YK, Varalaxmi Y, Krishnaiah K, Khush GS, Kochert G (2003b) Molecular tagging of a gene for resistance to brown planthopper in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 129:81–88
Jeon YH, Ahn SN, Choi HC, Hahn TR, Moon HP (1999) Identification of a RAPD marker linked to a brown planthopper resistance gene. Euphytica 107:23–28
Kawaguchi M, Murata K, Ishii T, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C (2001) Assignment of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal) resistance gene bph4 to rice chromosome 6. Breed Sci 51:13–18
Khush GS, Brar DS (2001) Rice genetics from Mendel to functional genomics. Rice Genet IV:3–25
Khush GS, Brar DS (1991) Genetics of resistance to insects in crop plants. Adv Agron 45:223–274
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander ES (1992) Constructing genetic maps with MAPMAKER/EXP 3.0, 3rd edn. Whitehead Institute Technical Report, Cambridge
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu YB, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu BY, Maghirang R, Li ZK, Xing YZ, Zhang QF, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstom R, Declerck G, Scheider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.) DNA Res 9:199–207
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Pathak MD, Cheng CH, Fortuno ME (1969) Resistance to Nephotettix impictiveps and Nilaparvata lugens in varieties of rice. Nature 223:502–504
Ren X, Weng QM, ZhuLL, He GC (2004) Dynamic mapping of quantitative trait loci for resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Cereal Res Commun 32:31–38
Renganayaki K, Friz AK, Sadasivam S, Pammi S, Harrington SE, McCouch SR, Kumar SM, Reddy AS (2002) Mapping and progress toward map-based cloning of brown planthopper biotype-4 resistance gene introgressed from Oryza officinalis into cultivated rice, O. sativa Crop Sci 42:2112–2117
Ronald PC (1998) Resistance gene evolution. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:294–298
SAS Institute (2000) SAS language and procedure: Usage, Release & 01. SAS Inst., Cary
Sasaki T (2005) The completion of the rice genome sequence by IRGSP. Plant Animal Genome XIII:73
Sharma PN, Ketipearachchi Y, Murata K, Torii A, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C (2003) RFLP/AFLP mapping of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stal) resistance gene Bph1 in rice. Euphytica 129(1):109–117
Soundararajan RP, Kadirvel P, Gunathilagraj K, Maheswara M (2004) Mapping of quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to brown planthopper in rice by means of a doubled haploid population. Crop Sci 44:2214–2220
Vos P, Simmon G, Jesse T, Wijbrandi J, Heinen L, Hogers R, Frijters A, Groenendijk J, Diergaarde P, Reijans M, Fierens-Onstenk J, Both MD, Peleman J, Liharska T, Hontelez J, Zabeau M (1998) The tomato Mi-1 gene confers resistance to both root-knot nematodes and potato aphids. Nat Biotech 16:1365–1369
Ware DH, Jaiswal P, Ni J, Yap IV, Pan X, Clark KY, Teytelman L, Schmidt SC, Zhao W, Chang K, Cartinhour S, Stein LD, McCouch SR (2002) Gramene, a tool for grass genomics. Plant Physiol 130:1606–1613
Wing R (2005) Development of BAC fingerprint/sequence-tagged–connector based physical maps to understand and sequence plant genomes. Plant Animal Genome XIII:51
Xu XF, Mei HW, Luo LJ, Cheng XN, Li ZK (2002) RFLP-facilitated investigation of the quantitative resistance of rice to brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens). Theor Appl Genet 104:248–253
Yang HY, You AQ, Yang ZF, Zhang F, He RF, Zhu LL, He GG (2004) High resolution genetic mapping at the Bph15 locus for brown planthopper resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:182–191
Yeo US, Jin YD, Kim HY, Park NB, Lim SJ, Hwang HG, Kim SC, Shon JK (1998) Linkage between shikimic dehydrogenase isomerase and a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens) resistance gene in a japonica rice Milyang 4. Korean J. Breed 30:162–167
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Rural Development Administration (RDA), Suwon, Korea, for financial support of this study. We are thankful to Bill Hardy, IRRI editor, for editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Q. Zhang
K. K. Jena and J. U. Jeung contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jena, K.K., Jeung, J.U., Lee, J.H. et al. High-resolution mapping of a new brown planthopper (BPH) resistance gene, Bph18(t), and marker-assisted selection for BPH resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 112, 288–297 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0127-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0127-8