Abstract
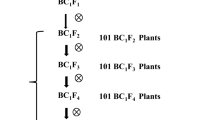
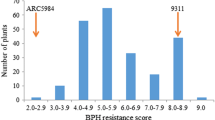
Resistance to the brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens Stål, a devastating sucking insect pest of rice, is an important breeding objective in rice improvement programs. Bph15, one of the 17 major BPH resistance genes so far identified in both cultivated and wild rice, has been identified in an introgression line, B5, and mapped on chromosome 4 flanked by restriction fragment length polymorphism markers C820 and S11182. In order to pave the way for positional cloning of this gene, we have developed a high-resolution genetic map of Bph15 by positioning 21 DNA markers in the target chromosomal region. Mapping was based on a PCR-based screening of 9,472 F2 individuals derived from a cross between RI93, a selected recombinant inbred line of B5 bearing the resistance gene Bph15, and a susceptible variety, Taichung Native 1, in order to identify recombinant plants within the Bph15 region. Recombinant F2 individuals with the Bph15 genotype were determined by phenotype evaluation. Analysis of recombination events in the Bph15 region delimited the gene locus to an interval between markers RG1 and RG2 that co-segregated with the M1 marker. A genomic library of B5 was screened using these markers, and bacterial artificial chromosome clones spanning the Bph15 chromosome region were obtained. An assay of the recombinants using the sub-clones of these clones in combination with sequence analysis delimited the Bph15 gene to a genomic segment of approximately 47 kb. This result should serve as the basis for eventual isolation of the Bph15 resistance gene.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson LK, Doyle GC, Brigham B, Carter J, Hooker KD, Lai A, Rice M, Stack SM (2003) High-resolution crossover maps for each bivalent of Zea mays using recombination nodules. Genetics 165:849–865
Chen M, Presting G, Barbazuk W, Goicoechea J, Blackmon B, Fang G, Kim H, Frisch D, Yu Y, Sun S, Higingbottom S, Phimphilai J, Phimphilai D, Thurmond S, Gaudette B, Li P, Liu J, Hatfield J, Main D, Farrar K, Henderson C, Barnett L, Costa R, Williams B, Walser S, Atkins M, Hall C, Budiman M, Tomkins J, Luo M, Bancroft I, Salse J, Regad F, Mohapatra T, Singh N, Tyagi A, Soderlund C, Dean R, Wing R (2002) An integrated physical and genetic map of the rice genome. Plant Cell 14:537–545
Copenhaver GP, Browne WE, Preuss D (1998) Assaying genome-wide recombination and centromere functions with Arabidopsis tetrads. Genetics 95:247–252
Dussle C, Quint M, Melchinger A, Xu M, Lübberstedt T (2003) Saturation of two chromosome regions conferring resistance to SCMV with SSR and AFLP markers by targeted BSA. Theor Appl Genet 106:485–493
Feng Q, Zhang YJ, Hao P, Wang SG, Fu G, Huang YC, Li Y, Zhu JJ, Liu YL, Hu X, Jia PX, Zhang Y, Zhao Q, Ying K, Yu SL, Tang YS, Weng QJ, Zhang L, Lu Y, Mu J, Lu Q, Zhang LS, Yu Z, Fan DL, Liu XH, Lu TT, Li C, Wu YR, Sun TG, Lei HY, Li T, Hu H, Guan JP, Wu M, Zhang RQ, Zhou B, Chen ZH, Chen L, Jin ZQ, Wang R, Yin HF, Cai Z, Ren SG, Lv G, Gu WY, Zhu GF, Tu YF, Jia J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Kang H, Chen XY, Shao CY, Sun Y, Hu QP, Zhang XL, Zhang W, Wang LJ, Ding CW, Sheng HH, Gu JL, Chen ST, Ni L, Zhu FH, Chen W, Lan LF, Lai Y, Cheng ZK, Gu MH, Jiang JM, Li JY, Hong GF, Xue YB, Han B (2002) Sequence and analysis rice chromosome 4. Nature 420:316–320
Frohman LA, Mizobuchi M (1992) A rapid and simple method for labeling short DNA fragments using Taq polymerase. Biotechniques 12:350–354
Fu Q, Chen W, Zhang ZT (1994) Evaluation for resistance of the interspecific somatic rice hybrids to Nilaparvata lugens. Chin J Rice Sci 8:247–249
Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G., Wang R, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H et al (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Science 296:92–100
Heinrichs EA (1979) Control of leafhopper and planthopper vectors of rice viruses. In: Moramorosch K, Arris KF (eds) Leafhopper vectors and planthopper disease agents. Academic Press, New York, pp 529–558
Hirabayashi H, Ogawa T (1995) RFLP mapping of Bph-1 (the brown planthopper resistance gene) in rice. Jpn J Breed 45:369–371
Hirabayashi H, Angeles ER, Kaji R, Ogawa T, Brar DS, Khush GS (1998) Identification of the brown planthopper resistance gene derived from O. officinalis using molecular markers in rice (abstract in Japanese). Breed Sci 48[Suppl1]:82
Huang Z, He GC, Shu LH, Li XH, Zhang QF (2001) Identification and mapping of two brown planthopper resistance genes in rice. Theor Appl Genet 102:929–934
Ikeda R (1985) Studies on the inheritance of resistance to the rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) and the breeding of resistant rice cultivars. Bull Nat Agric Res Cent 3:51–54
IRRI (1988) Standard evaluation system for rice. International Rice Research Institute, Manila
Ishii T, Brar DS, Multani DS, Khush GS (1994) Molecular tagging of genes for brown planthopper resistance and earliness introgressed from Oryza australiensis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Genome 37:217–221
Kawaguchi M, Murata K, Ishii T, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C (2001) Assignment of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph4 to the rice chromosome 6. Breed Sci 51:13–18
Khush GS (1979) Genetics of and breeding for resistance to brown planthopper. Threat to rice production in Asia. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander ES (1992) Constructing genetic maps with mapmaker/exp 3.0, 3rd edn. Whitehead Institute Technical Report, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Liu GY, Yan HH, Fu Q, Qian Q, Zhang ZT, Zhai WX, Zhu LH (2001) Mapping of a new gene for brown planthopper resistance in cultivated rice introgressed from Oryza eichingeri. Chin Sci Bull 46:1459–1462
Liu KD, Wang J, Li HB, Xu CG, Liu AM, Li XH, Zhang Q (1997) A genome-wide analysis of wide compatibility in rice and the precise location of the S5 locus in the molecular map. Theor Appl Genet 95:809–814
Liu Y, Whittier R (1995) Thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR: Automatable amplification and sequencing of insert end fragments from P1 and YAC clones for chromosome walking. Genomics 25:674–681
Murai H, Hashimoto Z, Sharma PN, Shimizu T, Murata K, Takumi S, Mori N, Kawasaki S, Nakamura C (2001) Construction of a high-resolution linkage map of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph2. Theor Appl Genet 103:526–532
Murata K, Fujiwara M, Kaneda C, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C (1998) RFLP mapping of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene bph2 of indica rice introgressed into a japonica breeding line “Norin-PL4”. Genes Genet Syst 73:359–364
Murata K, Fujiwara M, Murai H, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C (2001) Mapping of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene Bph9 on the long arm of rice chromosome 12. Cereal Res Commun 29: 245-250
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch SR (1996) Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet 252:597–607
Ren X, Weng QM, Zhu LL, He GC (2004) Dynamic mapping of quantitative trait loci for resistance to brown planthopper in rice. Cereal Res Commun 32:31–38
Renganayaki K, Fritz AK, Sadasivam S, Pammi S, Harrington SE, McCouch SR, Kumar SM, Reddy AS (2002) Mapping and progress toward map-based cloning of brown planthopper biotype-4 resistance gene introgressed from Oryza officinalis into cultivated rice, O. sativa. Crop Sci 42:2112–2117
Sharma PN, Ketipearachchi Y, Murata K, Torii A, Takumi S, Mori N, Nakamura C (2003) RFLP/AFLP mapping of a brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene Bph1 in rice. Euphytica 129(1):109–117
Shi Z, Ren X, Weng Q, Li X, He GC (2003) Construction of a genomic library from a brown planthopper-resistant rice line using a transformation-competent vector and identification of clones spanning the Qbp1 locus. Plant Sci 165:879–885
Sogawa K, Liu GJ, Shen JH (2003) A review on the hyper-susceptibility of Chinese hybrid rice to insect pests. Chin J Rice Sci 17:23–30
Takahashi Y, Shomura A, Sasaki T, Yano M (2001) Hd6, a rice quantitative trait locus involved in photoperiod sensitivity, encodes the α subunit of protein kinase CK2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:7922–7927
Takita T (1996) A new dominant gene for brown planthopper resistance found in an improved Japanese rice strain (abstract in Japanese). Breed Sci 46 [Suppl 1]:211
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Martin GB (1995) Chromosome landing: a paradigm for map-based gene cloning in plants with large genomes. Trends Genet 11:64–68
Temnykh S, Declerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Van De Lee T, Hornes M, Fritjers A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wu J, Yamagata H, Hayashi-Tsugane M, Hijishita S, Fujisawa M, Shibata M, Iton Y, Nakamura M, Sakaguchi M, Yoshihara R, Kobayashi H, Ito K, Karasawa W, Yamamoto M, Saji S, Katagiri S, Kanamori H, Namiki N, Katayose Y, Matsumoto T, Sasaki T (2004) Composition and structure of the centromeric region of rice chromosome 8. Plant Cell 16:967–976
Xu J, Yang D, Domingo J, Ni J, Huang N (1998) Screening for overlapping bacterial artificial chromosome clones by PCR analysis with an arbitrary primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5661–5666
Yang HY, Ren X, Weng QM, Zhu LL, He GC (2002) Molecular mapping and genetic analysis of a rice brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugens Stål) resistance gene. Hereditas 136:39–43
Zhang Y, Huang Y, Zhang L, Li Y, Lu T, Lu Q, Feng Q, Zhao Q, Cheng Z, Xue Y, Wing RA, Han B (2004) Structural features of the rice chromosome 4 centromere. Nucleic Acids Res 32:2023–2033
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Dr. B. Han for sequencing the BAC clones. This research was supported by grants from the National Special Key Project on Functional Genomics and Biochip of China, the National Program of High Technology Development (2001AA227151) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30170085). The work has been carried out in compliance with the current laws governing genetic experimentation in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Q. Zhang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., You, A., Yang, Z. et al. High-resolution genetic mapping at the Bph15 locus for brown planthopper resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 110, 182–191 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1844-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1844-0