Abstract
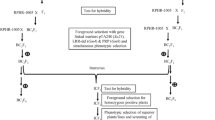
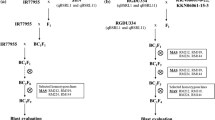
Four genes of rice,Oryza sativa L., conditioning resistance to the bacterial blight pathogenXanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae (X. o. pv.oryzae), were tagged by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. No recombinants were observed betweenxa-5 and RFLP marker lociRZ390, RG556 orRG207 on chromosome 5.Xa-3 andXa-4 were linked to RFLP locusXNpb181 at the top of chromosome 11, at distances of 2.3 cM and 1.7 cM, respectively. The nearest marker toXa-10, also located on chromosome 11, was the RAPD locusO07 2000 at a distance of 5.3 cM. From this study, the conventional map [19, 28] and two RFLP linkage maps of chromosome 11 [14, 26] were partially integrated. Using the RFLP and RAPD markers linked to the resistance genes, we selected rice lines homozygous for pairs of resistance genes,Xa-4 +xa-5 andXa-4 +Xa-10. Lines carryingXa-4 +xa-5 andXa-4 +Xa-10 were evaluated for reaction to eight strains of the bacterial blight pathogen, representing eight pathotypes and three genetic lineages. As expected, the lines carrying pairs of genes were resistant to more of the isolates than their single-gene parental lines. Lines carryingXa-4 +xa-5 were more resistant to isolates of race 4 than were either of the parental lines (‘quantitative complementation’). No such effects were seen forXa-4 +Xa-10. Thus, combinations of resistance genes provide broader spectra of resistance through both ordinary gene action expected and quantitative complementation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard RW: Formulas and tables to facilitate the calculation of recombination values in heredity. Hilgardia 24: 235–278 (1956).
Causse MA, Fulton TM, Cho YG, Ahn SN, Chunwongse J, Wu K, Xiao J, Yu Z, Ronald PC, Harrington SB, Second GA, McCouch SR, Tanksley SD: Satulated molecular map of the rice genome based on an interspecific backcross population. Genetics 138: 1251–1274 (1995).
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB: A plant DNA minipreparation: Version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1: 19–21 (1983).
Ezuka A, Sakaguchi S: Host-parasite relationship in bacterial leaf blight of rice caused byXanthomonas oryzae. Rev Plant Prot Res 11: 93–118 (1978).
Giovannini JJ, Wing RA, Ganal MW, Tanksley SD: Isolation of molecular markers from specific chromosomal intervals using DNA pools from existing mapping populations. Nucl Acids Res 19: 6553–6558 (1991).
Ikeda R, Tabien RE, Khush GS: Chromosomal location ofXa-21. Rice Genet Newsl 8: 102–103 (1992).
Jennings PR: Concluding remarks. In: Proceedings of the Rice Blast Workshop, pp. 217–222. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines (1979).
Kauffman HE, Reddy APK, Hsieh SPY, Merca SD: An improved technique for evaluating resistance of rice varieties toXanthomonas oryzae. Plant Dis Rep 57: 537–541 (1973).
Khush GS, Mackill DJ, Sidhu GS: Breeding rice for resistance to bacterial blight. In: Bacterial Blight of Rice, pp. 207–217. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines (1989).
Kinoshita T: Report of the committee on gene symbolization, nomenclature and linkage groups. Rice Genet Newsl 8: 2–37 (1992).
Kosambi DD: The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugenet 12: 172–175 (1944).
Martin GB, Williams JGK, Tanksley SD: Rapid identification of markers linked to aPseudomonas resistance gene in tomato by using random primers and near-isogenic lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 2336–2340 (1991).
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD: Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76: 815–829 (1988).
McCouch SR, Tanksley SD: Development and use of restriction fragment length polymorphism in rice breeding and genetics. In: Rice Biotechnology, pp. 109–133. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines (1991).
McCouch SR, Abenes ML, Angeles R, Klush GS, Tanksley SD: Molecular tagging of a recessive gene,xa-5, for resistance to bacterial blight of rice. Rice Genet Newsl 8: 143–145 (1992).
Mew TW, Vera Cruz CM, Medalla ES: Changes in race frequency ofXanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae in responce to the planting of rice cultivars in the Phillipines. Plant Dis 76: 1029–1032 (1992).
Nagamura Y, Yamamoto K, Harushima Y, Wu J, Antonio BA, Sue N, Shomura A, Lin SY, Miyamoto Y, Toyama T, Kirihara T, Shimizu T, Wang ZX, Tamura Y, Ashikawa I, Yano M, Kurata N: A high-density STS and EST linkage map of rice. Rice Genome 2: 3 (1993).
Nelson RJ, Baraoidan MR, Vera Cruz CM, Yap IV, Leach JE, Mew TW, Leung H: Relationship between phylogeny and pathotype for the bacterial blight pathogen of rice. Appl Envir Microbiol 60: 3275–3283 (1994).
Ogawa T, Tabien RE, Busto GA, Khush GS, Mew TW: The relationship betweenXa-3, Xa-4 andXa-4 b for resistance to rice bacterial blight. Rice Genet Newsl 3: 83–84 (1986).
Ogawa T, Yamamoto T, Khush GS, Mew TW, Kaku H: Near-isogenic lines as international differentials for resistance to bacterial blight of rice. Rice Genet Newsl 5: 106–107 (1988).
Ogawa T, Khush GS: Bacterial Blight of Rice, pp. 177–192. International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines (1989).
Ogawa T, Yamamoto T, Khush GS, Mew TW: Breeding of near-isogenic lines of rice with single genes for resistance to bacterial blight pathogen (Xanthomonas campestris pv.oryzae). Japan J Breed 41: 523–529 (1991).
Ou SH: Rice Diseases. Commonwealth Mycology Institute, Kew, England, p. 368 (1972).
Penner GA, Chong J, Levesque-Lemay M, Molnar SJ, Fedak G: Identification of a RAPD marker linked to the oat stem rust genePg3. Theor Appl Genet 85: 702–705 (1993).
Ronald PC, Albano B, Tabien R, Abenes L, Wu K, McCouch S, Tanksley SD: Genetic and physical analysis of the rice bacterial blight disease resistance locus,Xa-21. Mol Gen Genet 236: 113–120 (1992).
Saito A, Yano M, Kishimoto N, Nakagahra M, Yoshimura A, Saito K, Kuhara S, Ukai Y, Kawase M, Nagamine T, Yoshimura S, Ideta O, Ohsawa R, Hayano Y, Iwata N, Sugiura M: Linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphism loci in rice. Japan J Breed 41: 665–670 (1991).
Swings J, Mooter MVD, Vauterin L, Hoste B, Gillis M, Mew TW, Kersters K: Reclassification of the causal agents of bacterial blight (Xanthomonas campestris pv.oryzae) and bacterial leaf streak (Xanthomonas campestris pv.oryzicola) of rice as pathovars ofXanthomonas oryzae (ex Ishiyama 1922) sp. nov., nom. rev. Int J Syst Bact 40: 309–311 (1990).
Yoshimura A, Mew TW, Khush GS, Omura T: Inheritance of resistance to bacterial blight in rice cultivar Cas 209. Phytopathology 73: 1409–1412 (1983).
Yoshimura A, Mew TW, Khush GS, Omura T: Genetics of bacterial blight resistance in a breeding line of rice. Phytopathology 74: 773–777 (1984).
Yoshimura S, Yoshimura A, Saito A, Kishimoto N, Kawase M, Yano M, Nakagahra M, Ogawa T, Iwata N: RFLP analysis of introgressed chromosomal segments in three near-isogenic lines of rice for bacterial blight resistance genes,Xa-1, Xa-3 andXa-4. Jpn J Genet 67: 29–37 (1992).
Yoshimura S, Yoshimura A, Nelson RJ, Mew TW, Iwata N: TaggingXa-1, the bacterial blight resistance gene in rice, by using RAPD markers. Breed Sci 45: 81–85 (1995).
Young ND, Zamir D, Ganal MW, Tanksley SD: Use of isogenic lines and simultaneous probing to identify DNA markers tightly linked to theTm-2a gene in tomato. Genetics 120: 579–585 (1988).
Young ND, Tanksley SD: Restriction fragment length polymorphism maps and the concept of graphical genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 77: 95–101 (1989).
Yu ZH, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, Tanksley SD: Tagging genes for blast resistance in rice via linkage to RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 81: 471–476 (1991).
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV: DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl Acids Res 18: 6531–6535 (1990).
Williamson VM, Ho JY, Wu FF, Miller N, Kaloshian I: A PCR-based marker tightly linked to a nematode resistance gene,Mi, in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 87: 757–763 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshimura, S., Yoshimura, A., Iwata, N. et al. Tagging and combining bacterial blight resistance genes in rice using RAPD and RFLP markers. Mol Breeding 1, 375–387 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01248415
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01248415