Abstract
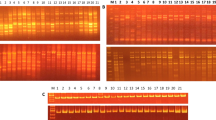
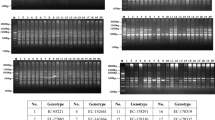
Limited availability of validated, polymorphic microsatellite markers in mung bean (Vigna radiata), an important food legume of India, has been a major hurdle towards its improvement and higher yield. The present study was undertaken in order to develop a new set of microsatellite markers and utilize them for the analysis of genetic diversity within mung bean accessions from India. A GA/CT enriched library was constructed from V. radiata which resulted in 1,250 putative recombinant clones of which 850 were sequenced. SSR motifs were identified and their flanking sequences were utilized to design 328 SSR primer pairs. Of these, 48 SSR markers were employed for assessing genetic diversity among 76 mung bean accessions from various geographical locations in India. Two hundred and thirty four alleles with an average of 4.85 alleles per locus were detected at 48 loci. The polymorphic information content (PIC) per locus varied from 0.1 to 0.88 (average: 0.49 per locus). The observed and expected heterozygosities ranged from 0.40 to 0.95 and 0.40 to 0.81 respectively. Based on Jaccard’s similarity matrix, a dendrogram was constructed using the unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic averages (UPGMA) analysis which revealed that one accession from Bundi, Rajasthan was clustered out separately while remaining accessions were grouped into two major clusters. The markers generated in this study will help in expanding the repertoire of the available SSR markers thereby facilitating analysis of genetic diversity, molecular mapping and ultimately broadening the scope for genetic improvement of this legume.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parida A, Raina SN, Narayan RKJ (1990) Quantitative DNA variation between and within chromosome complements of Vigna species (Fabaceae). Genetica 82(2):125–133
Guo X, Li T, Tang K, Liu RH (2012) Effect of germination on phytochemical profiles and antioxidant activity of mung bean sprouts (Vigna radiata). J Agric Food Chem 60(44):11050–11055
Ramesh CK, Rehman A, Prabhakar BT, Vijay ABR, Aditya RSJ (2011) Antioxidant potentials in sprouts vs. seeds of Vigna radiata and Macrotyloma uniflorum. J Appl Pharm Sci 1(7):99–110
Lavanya RG, Srivastava J, Ranade SA (2008) Molecular assessment of genetic diversity in mung bean germplasm. J Genet 87(1):65–74
Somta P, Seehalak W, Srinives P (2009) Molecular diversity assessment of AVRDC—World vegetable center elite-parental mungbeans. Breed Sci 59:149–157
Raturi A, Singh SK, Sharma V, Pathak R (2012) Stability and environmental indices analyses for yield attributing traits in Indian Vigna radiata genotypes under arid conditions. Asian J Agric Sci 4:126–133
Ali M, Gupta S (2012) Carrying capacity of Indian agriculture: pulse crops. Curr Sci 102(6):874–881
Arora RK, Nayar ER (1984) Wild relatives of crop plants in India. NBPGR Scientific monograph No. 7. National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources, New Delhi
Bisht IS, Bhatl KV, Lakhanpaul S, Latha M, Jayan PK, Biswas BK, Singh AK (2005) Diversity and genetic resources of wild Vigna species in India. Genet Res Crop Evol 52:53–68
Chen NC, Parrot JF, Jacobs T, Baker LR, Carlson PS (1977) Interspecific hybridization of food legumes by unconventional methods of plant breeding. In: Proceedings first international mungbean symposium: Asian Vegetable Research and Development Centre. Shanhnua, pp 247–252
Chowdhury RK, Chowdhury JB (1977) Intergeneric hybridization between Vigna mungo L. Hepper and Phaseolus calcaratus RoxB. Indian J Agric Sci 47:117–121
Ahn CS, Hartmann RW (1977) Interspecific hybridization among four species of the genus Vigna. In: Proceedings of first international mungbean symposium. Asian vegetable Research and Development Centre, Shanhua, pp 240–246
Gosal SS, Bajaj YPS (1983) Interspecific hybridization between Vigna mungo and Vigna radiata through embryo culture. Euphytica 32:129–137
Bharathi A, VijaySelvaraj KS, Veerabadhiran P, Subba Lakshmi B (2006) Advances in winter pulse pathology research in Australia. Australas Plant Pathol 1(2):120–124
Salam MU, Davidson JA, Thomas GJ, Ford R, Jones RAC, Lindbeck KD, MacLeod WJ, Kimber RBE, Galloway J, Mantri N, Leur JAG, Coutts BA, Freeman AJ, Richardson H, Aftab M, Moore KJ, Knights EJ, Nash P, Verrell A (2011) Advances in winter pulse pathology research in Australia. Australas Plant Pathol 40(6):549–567
Mantri N, Pang E, Ford R (2010) Molecular biology for stress management. In: Yadav SS, McNeil DN, Weeden N, Patil SS (eds) Climate change and management of cool season grain legume crops. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 377–408
Santalla M, Power JB, Davery MR (1998) Genetic diversity in mungbean germplasm revealed by RAPD markers. Plant Breed 117(5):473–478
Lakhanpaul S, Chadha S, Bhat KV (2000) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis in Indian mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek) cultivars. Genetica 109(3):227–234
Bhat KV, Lakhanpaul S, Chadha S (2005) Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) analysis of genetic diversity in Indian mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek) cultivars. Indian J Biotech 4:56–64
Lambridges CL, Lawn RL (2000) Two genetic linkage maps of mungbean using RFLP and RAPD markers. Aust J Agric Res 51(4):415–425
Humphry ME, Konduri V, Lambrides CJ, Magner T, McIntyre CL, Aitken EAB, Liu CJ (2002) Development of a mungbean (Vigna radiata) RFLP linkage map and its comparison with lablab (Lablab purpureus) reveals a high level of colinearity between the two genomes. Theor Appl Genet 105(1):160–166
Eujayl I, Sledge MK, Wang L, May GD, Chekhovskiy K, Zwonitzer JC, Mian MAR (2004) Medicago truncatula EST-SSRs reveal cross species genetic markers for Medicago spp. Theor Appl Genet 108(3):414–422
Gautami B, Ravi K, Narasu ML, Hoisington DA, Varshney RK (2009) Novel set of groundnut SSR markers for germplasm analysis and interspecific transferability. Int J Integr Biol (IJIB) 7(2):100–106
Burstin J, Deniot G, Potier J, Weinachter C, Aubert G, Baranger A (2001) Microsatellite polymorphism in Pisum sativum. Plant Breed 120(4):311–317
Koebner RMD, Donini R, Reeves JC, Cooke RJ, Law JR (2003) Temporal flux in the morphological and molecular diversity of UK barley. Theor Appl Genet 106(3):550–558
Taller JM, Bernardo R (2004) Diverse adapted populations for improving northern maize inbreds. Crop Sci 44(4):1444–1449
Wang L, Guan Y, Guan R, Li Y, Ma Y, Dong Z, Liu X, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Chang R, Xu H, Li L, Lin F, Luan W, Yan Z, Ning X, Zhu L, Cui Y, Piao R, Liu Y, Chen P, Qiu L (2006) Establishment of Chinese soybean Glycine max core collections with agronomic traits and SSR markers. Euphytica 151(2):215–223
Cao QJ, Lu BR, Xia H, Rong J, Sala F, Spada A, Grassi F (2006) Genetic diversity and origin of weedy rice (Oryza sativa f. spontanea) populations found in North-eastern China revealed by simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Ann Bot 98(6):1241–1252
Blair MW, Giraldo MC, Buendia HFE, Duque MC, Beebe SE (2006) Microsatellite marker diversity in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 113(1):100–109
Gimenes MA, Hoshino AA, Barbosa AV, Palmieri DA, Lopes CR (2007) Characterization and transferability of microsatellite markers of the cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Plant Biol 7:9
Parida SK, Kalia SK, Kaul S, Dalal V, Hemaprabha G, Selvi A, Pandit A, Singh A, Gaikwad K, Sharma TR, Srivastava PS, Singh NK, Mohapatra T (2009) Informative genomic microsatellite markers for efficient genotyping applications in sugarcane. Theor Appl Genet 118(2):327–338
Sethy NK, Shokeen B, Edwards KJ, Bhatia S (2006) Development of microsatellite markers and analysis of intra-specific genetic variability in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Theor Appl Genet 112(8):1416–1428
Gaur R, Sethy NK, Choudhary S, Shokeen B, Gupta V, Bhatia S (2011) Advancing the STMS genomic resources for defining new locations on the intraspecific genetic linkage map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). BMC Genomics 12:117
Choudhary S, Gaur R, Gupta S, Bhatia S (2012) EST-derived genic molecular markers: development and utilization for generating an advanced transcript map of chickpea. Theor Appl Genet 124(8):1449–1462
Mastan SG, Sudheer PDVN, Rahman H, Ghosh A, Rathore MS, Prakash CR, Chikara J (2012) Molecular characterization of intra-population variability of Jatropha curcas L. using DNA based molecular markers. Mol Biol Rep 39(4):4383–4390
Baldwin S, Pither-Joyce M, Wright K, Chen L, McCallum J (2012) Development of robust genomic simple sequence repeat markers for estimation of genetic diversity within and among bulb onion (Allium cepa L.) populations. Mol Breed 30(3):1401–1411
Rai MK, Phulwaria M, Shekhawat NS (2013) Transferability of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers developed in guava (Psidium guajava L.) to four Myrtaceae species. Mol Biol Rep 40(8):5067–5071
Bali S, Raina SN, Bhat V, Aggarwal RK, Goel S (2013) Development of a set of genomic microsatellite markers in tea (Camellia L.) (Camelliaceae). Mol Breed 32(3):735–741
Varshney RK, Kudapa H, Roorkiwal M, Thudi M, Pandey MK, Saxena RK, Chamarthi SK, Mohan SM, Mallikarjuna N, Upadhyaya H, Gaur PM, Krishnamurthy L, Saxena KB, Nigam SN, Pande S (2012) Advances in genetics and molecular breeding of three legume crops of semi-arid tropics using next-generation sequencing and high-throughput genotyping technologies. J Biosci 37(5):811–820
Kumar SV, Tan SG, Quah SC, Yusoff K (2002) Isolation of microsatellite markers in mungbean, Vigna radiata. Mol Ecol Notes 2(2):96–98
Kumar SV, Tan SG, Quah SC, Yusoff K (2002) Isolation and characterization of seven tetranucleotide microsatellite loci in mung bean, Vigna radiata. Mol Ecol Notes 2:293–295
Miyagi M, Humphry M, Ma ZY, Lambrides CJ, Bateson M, Liu CJ (2004) Construction of bacterial artificial chromosome libraries and their application in developing PCR-based markers closely linked to a major locus conditioning bruchid resistance in mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). Theor Appl Genet 110(1):151–156
Gwag JG, Chung WK, Chung HK, Lee JH, Ma KH, Dixit A, Park YJ, Cho EG, Kim TS, Lee SH (2006) Characterization of new microsatellite markers in mungbean, Vigna radiata (L.). Mol Ecol Notes 6(4):1132–1134
Seehalak W, Somta P, Sommanas W, Srinives P (2009) Microsatellite markers for mungbean developed from sequence database. Mol Ecol Res 9(3):862–864
Tangphatsornruang S, Somta P, Uthaipaisanwong P, Chanprasert J, Sangsrakru D, Seehalak W, Sommanas W, Tragoonrung S, Srinives P (2009) Characterization of microsatellites and gene contents from genome shotgun sequences of mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.)Wilczek). BMC Plant Biol 9:137
Somta P, Seehalak W, Srinives P (2009) Development, characterization and cross-species amplification of mungbean (Vigna radiata) genic microsatellite markers. Conserv Genet 10(6):1939–1943
Moe KT, Chung J-W, Cho Y-I, Moon J-K, Ku J-H, Jung J-K, Lee J, Park Y-J (2011) Sequence information on simple sequence repeats and single nucleotide polymorphisms through transcriptome analysis of mungbean. J Integr Plant Biol 53(1):63–73
Singh N, Singh H, Nagarajan P (2013) Development of SSR markers in mung bean, Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek using in silico methods. J Crop Weed 9(1):69–74
Gupta SK, Bansal R, Gopalakrishna T (2014) Genome-wide SNP discovery in mungbean by Illumina HiSeq. Theor Appl Genet 195:245–258
Van K, Kang YJ, Han KS, Lee YH, Gwag JG, Moon JK, Lee SH (2013) Genome-wide SNP discovery in mungbean by Illumina HiSeq. Theor Appl Genet 126(8):2017–2027
Hamblin MT, Warburton ML, Buckler ES (2007) Empirical comparison of simple sequence repeats and single nucleotide polymorphisms in assessment of maize diversity and relatedness. PLoS One 2(12):e1367
Yang X, Xu Y, Shah T, Li H, Han Z, Li J, Yan J (2011) Comparison of SSRs and SNPs in assessment of genetic relatedness in maize. Genetica 139(8):1045–1054
Emanuelli F, Lorenzi S, Grzeskowiak L, Catalano V, Stefanini M, Troggio M, Myles S, Martinez-Zapater JM, Zyprian E, Moreira FM, Grando MS (2013) Genetic diversity and population structure assessed by SSR and SNP markers in a large germplasm collection of grape. BMC Plant Biol 13:39
Khanuja SPS, Shasany AK, Darokar MP, Kumar S (1999) Rapid isolation of DNA from dry and fresh samples of plant producing large amounts of secondary metabolites and essential oils. Plant Mol Biol Rep 17(1):74
Malmberg R, Messing J, Sussex I (1985) Molecular biology of plants: a laboratory course manual. Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Kijas JMH, Fowler JCS, Garbett CA, Thomas MR (1994) Enrichment of microsatellites from the citrus genome using biotinylated oligonucleotide sequences bound to streptavidin-coated magnetic particles. Biotechniques 16(4):656–662
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Huang X, Madan A (1999) CAP3: a DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res 9(9):868–877
Castelo AT, Martins W, Gao GR (2002) TROLL-tandem repeat occurrence locator. Bioinformatics 18(4):634–636
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (1997) PRIMER 3. Code available at, http://www.genome.wi.mit.edu/genome_software/other/primer3.html
Choudhary S, Sethy NK, Shokeen B, Bhatia S (2009) Development of chickpea EST-SSR markers and analysis of allelic variation across related species. Theor Appl Genet 118(3):591–608
Yeh FC, Boyle TJB (1997) Population genetic analysis of co-dominant and dominant markers and quantitative traits. Belg J Bot 129:157
Anderson JA, Churchill GA, Autrique JE, Tanksley SD, Sorrells ME (1993) Optimizing parental selection for genetic linkage maps. Genome 36(1):181–186
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale Bulletin de la societe vauodoise des sciences. Naturelles 44:223–270
Rohlf FJ (1998) NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, in: Version 2. 1. Exeter Software, Applied Biostatistics Setauket, NewYork
Yap IV, Nelson RJ (1996) WinBoot: a program for performing bootstrap analysis of binary data to determine the confidence limits of UPGMA-based dendrograms. IRRI, Philippines
Bhattramakki D, Dong J, Chhabra K, Hart GE (2000) An integrated SSR and RFLP linkage map of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Genome 43(6):988–1002
Sharopova N, McMullen MD, Schultz L, Schroeder S, Sanchez-Villeda H, Gardiner J, Bergstrom D, Houchins K, Melia-Hancock S, Musket T, Duru N, Polacco M, Edwards K, Ruff T, Register JC, Brouwer C, Thompson R, Velasco R, Chin E, Lee M, Woodman-Clikeman W, Long MJ, Liscum E, Cone K, Davis G, Coe EH (2002) Development and mapping of SSR markers for maize. Plant Mol Biol 48:463–481
Gupta P, Varshney R (2000) The development and use of microsatellite markers for genetic analysis and plant breeding with emphasis on bread wheat. Euphytica 113(3):163–185
Zane L, Bargelloni L, Patarnello T (2002) Strategies for microsatellite isolation: a review. Mol Ecol 11(1):1–16
Somta P, Musch W, Kongsamai B, Chanprame S, Nakasathien S, Toojinda T, Sorajjapinun W, Seehalak W, Tragoonrung S, Srinives P (2008) New microsatellite markers isolated from mungbean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek). Mol Ecol Res 8(5):1155–1157
Isemura T, Kaga A, Tabata S, Somta P, Srinives P, Shimizu T, Jo U, Vaughan DA, Tomooka N (2012) Construction of a genetic linkage map and genetic analysis of domestication related traits in mungbean (Vigna radiata). PLoS One 7(8):e41304
Dan Z, Xu-Zhen C, Li-Xia W, Su-Hua W, Yan-Ling M (2010) Construction of mungbean genetic linkage map. Acta Agron Sin 36(6):932–939
Squirrell J, Hollingsworth PM, Woodhead M, Russell J, Lowe AJ, Gibby M, Powell W (2003) How much effort is required to isolate nuclear microsatellites from plants? Mol Ecol 12(6):1339–1348
Pestova F, Ganal MW, Roder MS (2000) Isolation and mapping of microstallite markers specific for the D-genome of bread wheat. Genome 43(4):689–697
Jones ES, Dupal MP, Kolliker R, Drayton MC, Forster JW (2001) Development and characterization of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers for perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Theor Appl Genet 102:405–415
Hirata M, Cai HW, Inoue M, Yuyama N, Miura Y, Komatsu T, Takamizo T, Fujimori M (2006) Development of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers and construction of an SSR based linkage map in Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.). Theor Appl Genet 113(2):270–279
Tsuruta SI, Hashiguchi M, Ebina M, Matsuo T, Yamamoto T, Kobayashi M, Takahara M, Nakagawa H, Akashi R (2005) Development and characterization of simple sequence repeat markers in Zoysia japonica Steud. Grassl Sci 51(3):249–257
Saha MC, Cooper JD, Rouf Mian MA, Chekhovskiy K, May GD (2006) Tall fescue genomic SSR markers: development and transferability across multiple grass species. Theor Appl Genet 113(8):1449–1458
Jia X, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Zhang C, Shi Y, Song Y, Wang T, Li Y (2009) Development and genetic mapping of SSR markers in foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.]. Theor Appl Genet 118(4):821–829
Wang YW, Samuels TD, Wu YQ (2011) Development of 1,030 genomic SSR markers in switchgrass. Theor Appl Genet 122(4):677–686
Toth G, Gaspari Z, Jurka J (2000) Microsatellites in different eukaryotic genomes survey and analysis. Genome Res 10(7):967–981
Cardle L, Ramsay L, Milbourne D, Macaulay M, Marshall D, Waugh R (2000) Computational and experimental characterization of physically clustered simple sequence repeats in plants. Genetics 156:847–854
Powell W, Machray GC, Provan J (1996) Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats. Trends Plant Sci 1(7):215–222
Varshney RK, Kumar A, Balyan HS, Roy JK, Prasad M, Gupta PK (2000) Characterization of microsatellites and development of chromosome specific STMS markers in bread wheat. Plant Mol Biol Rep 18(1):5–16
Rajendrakumar P, Biswal AK, Balachandran SM, Srinivasarao K, Sundaram RM (2007) Simple sequence repeats in organellar genomes of rice: frequency and distribution in genic and intercoding regions. Bioinformatics 23(1):1–4
Hamwieh A, Udupa SM, Sarker A, Jung C, Baum M (2009) Development of new microsatellite markers and their application in the analysis of genetic diversity in lentils. Breed Sci 59:77–86
Shokeen B, Choudhary S, Sethy NK, Bhatia S (2011) Development of SSR and gene-targeted markers for construction of a framework linkage map of Catharanthus roseus. Ann Bot (Lond) 108(2):321–336
Cuc LM, Mace ES, Crouch JH, Quang VD, Long TD, Varshney RK (2008) Isolation and characterization of novel microsatellite markers and their application for diversity assessment in cultivated groundnut (Arachis hypogaea). BMC Plant Biol 8:55
Jena SN, Srivastava A, Rai KM, Ranjan A, Singh SK, Nisar T, Srivastava M, Bag SK, Mantri S, Asif MH, Yadav HK, Tuli R, Sawant SV (2012) Development and characterization of genomic and expressed SSRs for levant cotton (Gossypium herbaceum L.). Theor Appl Genet 124(3):565–576
Shokeen B, Sethy NK, Kumar S, Bhatia S (2007) Isolation and characterization of microsatellite markers for analysis of molecular variation in the medicinal plant Madagascar periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don). Plant Sci 172(3):441–451
Gupta S, Kumari K, Sahu PP, Vidapu S, Prasad M (2012) Sequence-based novel genomic microsatellite markers for robust genotyping purposes in foxtail millet [Setaria italic L.) P. Beauv.]. Plant Cell Rep 31(2):323–337
Pejic I, Ajmone-Marsan P, Morgante M, Kozumplick V, Castiglioni P, Taramino G, Motto M (1998) Comparative analysis of genetic similarity among maize inbred lines detected by RFLPs, RAPDs, SSRs, and AFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 97:1248–1255
Prasad M, Varshney RK, Roy JK, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2000) The use of microsatellites for detecting DNA polymorphism, genotype identification and genetic diversity in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 100:584–592
Morgante M, Olivieri AM (1993) PCR amplified microsatellites as markers in plant genetics. Plant J 3(1):175–182
Lagercrantz U, Ellegren H, Andersson L (1993) The abundance of various polymorphic microsatellite motifs differs between plants and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res 21(5):1111–1115
Wright S (1978) Evolution and the genetics of populations. Variability within and among natural populations, vol 4. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Smartt J (1990) Grain legumes: evolution and genetic resources. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Tomooka N, Lairungreang C, Nakeeraks P, Egawa Y, Thavarasook C (1991) Center of genetic diversity, dissemination pathways and landrace differentiation in mung bean. In: Thavasarook C (ed) Proceedings of mung bean meeting 90, Tropical agricultural Research Center, Japan, Thailand office, Bangkok, pp 47–71
Sangiri C, Kaga A, Tomooka N, Vaughan D, Srinives P (2007) Genetic diversity of the mungbean (Vigna radiata, Leguminosae) genepool on the basis of microsatellite analysis. Aust J Bot 55:837–847
Acknowledgments
This research work was supported by the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), New Delhi, India. Financial assistance provided by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), India through the Project Grant (DBT-PDF Program, IISc, Bangalore) to DS is thankfully acknowledged. We are thankful to Dr. Arjun Lal (NBPGR, New Delhi) and Dr. Rakesh Aggarwal (CAZRI, Jodhpur) for providing the accessions of V. radiata for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11033_2014_3436_MOESM1_ESM.doc
List of 328 V. radiata SSR primer pairs developed in this study. Their sequences, repeat motifs, annealing temperature (Tm), amplification product size (bp) and Genbank accession numbers are mentioned
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shrivastava, D., Verma, P. & Bhatia, S. Expanding the repertoire of microsatellite markers for polymorphism studies in Indian accessions of mung bean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). Mol Biol Rep 41, 5669–5680 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3436-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3436-7