Abstract
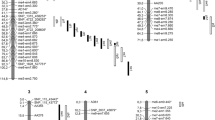
SSR markers are desirable markers in analysis of genetic diversity, quantitative trait loci mapping and gene locating. In this study, SSR markers were developed from two genomic libraries enriched for (GA)n and (CA)n of foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.], a crop of historical importance in China. A total of 100 SSR markers among the 193 primer pairs detected polymorphism between two mapping parents of an F2 population, i.e. “B100” of cultivated S. italica and “A10” of wild S. viridis. Excluding 14 markers with unclear amplifications, and five markers unlinked with any linkage group, a foxtail millet SSR linkage map was constructed by integrating 81 new developed SSR markers with 20 RFLP anchored markers. The 81 SSRs covered nine chromosomes of foxtail millet. The length of the map was 1,654 cM, with an average interval distance between markers of 16.4 cM. The 81 SSR markers were not evenly distributed throughout the nine chromosomes, with Ch.8 harbouring the least (3 markers) and Ch.9 harbouring the most (18 markers). To verify the usefulness of the SSR markers developed, 37 SSR markers were randomly chosen to analyze genetic diversity of 40 foxtail millet accessions. Totally 228 alleles were detected, with an average 6.16 alleles per locus. Polymorphism information content (PIC) value for each locus ranged from 0.413 to 0.847, with an average of 0.697. A positive correlation between PIC and number of alleles and between PIC and number of repeat unit were found [0.802 and 0.429, respectively (P < 0.01)]. UPGMA analysis revealed that the 40 foxtail millet cultivars could be grouped into five clusters in which the landraces’ grouping was largely consistent with ecotypes while the breeding varieties from different provinces in China tended to be grouped together.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JA, Churchill GA, Autrique JE, Tanksley SD, Sorrells ME (1993) Optimizing parental selection for genetic linkage maps. Genome 36:181–186
Bassam BJ, Caetano-Anolles G, Gresshoff PM (1991) Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 196:80–83
Bell CJ, Ecker JR (1994) Assignment of 30 microsatellite loci to the linkage map of Arabidopsis. Genomics 19:137–144
Bhattramakki D, Dong J, Chabra AK, Hart GE (2000) An integrated SSR and RFLP linkage map of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Genome 43:988–1002
Castiglioni P, Ajmone-Marsan P, van Wijk R, Motto M (1999) AFLP markers in a molecular linkage map of maize: codominant scoring and linkage group distribution. Theor Appl Genet 99:425–431
Cregan PB, Mudge J, Fickus EW, Marek LF, Danesh D, Denny R, Mathews BF, Jarvik T, Young ND (1999) Targeted isolation of simple sequence repeat markers through the use of bacterial artificial chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 98:919–928
De Wet JMJ, Oestry-Stidd LL, Cubero JL (1979) Origins and evolution of foxtail millet. J Agric Trop Bot Appl 26:53–63
Devos KM, Wang ZM, Beales CJ, Sasaki T, Gale MD (1998) Comparative genetic maps of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) and rice (Oryza sativa). Theor Appl Genet 96:63–68
Devos KM, Pittaway TS, Reynolds A, Gale MD (2000) Comparative mapping reveals a complex relationship between the pearl millet genome and those of foxtail millet and rice. Theor Appl Genet 100:190–198
Doust AN, Devos KM, Gadberry MD, Gale MD, Kellogg EA (2004) Genetic control of branching in foxtail millet. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9045–9050
Doust AN, Devos KM, Gadberry MD, Gale MD, Kellogg EA (2005) The genetic basis for inflorescence variation between foxtail and green millet (Poaceae). Genetics 169:1659–1672
Edwards KJ, Barker JHA, Daly A, Jones C, Karp A (1996) Microsatellite libraries enriched for several microsatellite sequences in plants. Biotechniques 20:758
Fisher PJ, Gardner RC, Richardson TE (1996) Single locus microsatellites isolated using 5’-anchored PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4369–4371
Fukunaga K, Kato M (2003) Mitochondrial DNA variation in foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. Euphytica 129:7–13
Fukunaga K, Domon E, Kawase M (1997) Ribosomal DNA variation in foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv., and a survey of variation from Europe and Asia. Theor Appl Genet 95:751–756
Fukunaga K, Wang ZM, Kato K, Kawase M (2002) Geographical variation of nuclear genome RFLPs and genetic differentiation in foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. Genet Resour Crop Evol 49:95–101
Hayden MJ, Sharp PJ (2001) Targeted development of informative microsatellite (SSR) markers. Nucleic Acids Res 29(8):e44
Jia XP, Shi YS, Song YC, Wang GY, Wang TY, Li Y (2007) Development of EST-SSR in foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:233–236
Jusuf M, Pernes J (1985) Genetic variability of foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.): Electrophoretic study of five isoenzyme systems. Theor Appl Genet 71:385–391
Kawase K, Sakamoto S (1984) Variation, geographical distribution and genetical analysis of esterase isozymes in foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. Theor Appl Genet 67:529–533
Kawase M, Sakamoto S (1987) Geographical distribution of landrace groups classified by pollen sterility in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L. P. Beauv). Japanese J Breed 37:1–9
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Küster H (1984) Neolithic plant remains from Eberdingenhochdorf, southern Germany. In: Van Zeist WV, Casparoe WA (eds) Plants and ancient man (studies in palaeoethnobotany). A.A. Bakame, Rotterdam, pp 307–311
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Le Thierry d’ Ennequin M, Panaud O, Toupance B, Sarr A (2000) Assessment of relationships between Setaria italica and its wild relative S. viridis using AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 100:1061–1066
Li Y, Wu SZ (1996) Traditional maintenance and multiplication of foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.) landraces in China. Euphytica 87:33–38
Li HW, Li CH, Pao WK (1945) Cytological and genetic studies of interspecific cross of the cultivated foxtail millet, Setaria italica P. Beauv. and the green foxtail millet, S. viridis L. J Am Soc Agron 37:32–54
Li Y, Cao YS, Wu SZ, Zhang XZ (1995) A diversity analysis of foxtail millet (Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.) landraces of Chinese origin. Genet Resour Crop Evol 43:377–384
Li Y, Jia J, Wang Y, Wu S (1998) Intraspecific and interspecific variation in Setaria revealed by RAPD analysis. Genet Resour Crop Evol 45:279–285
Maguire TL, Edwards KJ, Saenger P, Henry R (2000) Characterisation and analysis of microsatellite loci in a mangrove species, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. (Avicenniaceae). Theor Appl Genet 101:279–285
Marinoni D, Akkak A, Bounous G, Edwards KJ, Botta R (2003) Development and characterization of microsatellite markers in Castanea sativa (Mill.). Mol Breed 11:127–136
Matsuoka YS, Mitchell E, Kresovich S, Goodman M, Doebley J (2002) Microsatellites in Zea—variability, patterns of mutations, and use for evolutionary studies. Theor Appl Genet 104:436–450
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Kono I, Yano M, Fjellstrom R, DeClerck G, Schneider D, Cartinhour S, Ware D, Stein L (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 9:199–207
Merdinoglu DG, Butterlin L, Bevilacqua V, Chiquet AF (2005) Development and characterization of a large set of microsatellite markers in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) suitable for multiplex PCR. Mol Breed 15:349–366
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76:5269–5273
Panaud O, Chen SR, McCouch R (1996) Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet 252:597–607
Pandey M, Gailing O, Fischer D, Hattemer HH, Finkeldey R (2004) Characterization of microsatellite markers in sycamore (Acer pseudoplatanus L.). Mol Ecol Notes 4:253–255
Pejic I, Ajmone-Marsan P, Morgante M, Kozumplick V (1998) Comparative analysis of genetic similarity among maize inbred lines detected by RFLPs, RAPDs, SSRs, and AFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 97:1248–1255
Powel W, Morgante M, Andre C, Hanafey M, Vogel J (1996) The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breed 2:225–238
Prasad M, Varshney RK, Royj K (2000) The use of microsatellites for detecting DNA polymorphism, genotype identification and genetic diversity in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 100:584–592
Rohlf JF (1995) NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, Version 2.11. Exeter Software, Setauket
Russell JR, Fuller JD, Macaulay M (1997) Direct evaluation of levels of genetic variation among barley accessions detected by RFLPs, AFLPs, SSRs and RAPDs. Theor Appl Genet 93:714–723
Sargent DJ, Hadonou AM, Simpson DW (2003) Development and characterization of polymorphic microsatellite markers from Fragaria viridis, a wild diploid strawberry. Mol Ecol Notes 3:550–552
Schmidt T, Jung C, Metzla M (1991) Distribution and evolution of two satellite DNAs in the genus Beta. Theor Appl Genet 82:793–799
Schontz D, Rether B (1998) Genetic variability in foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv. using a heterologous rDNA probe. Plant Breed 117:231–234
Schontz D, Rether B (1999) Genetic variability in foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.: identification and classification of lines with RAPD markers. Plant Breed 118:190–192
Sivaraman L, Ranjekar PK (1984) Novel molecular features of millet genomes. Indian J Biochem Biophys 21:299–303
Smulders MJM, Bredemeijer G, Rus-Kortekaas W, Arens P, Vosman B (1997) Use of short microsatellites from database sequence to generate polymorphism among Lycopersicon esculentum cultivars and accessions of other Lycopersicon species. Theor Appl Genet 97:264–272
Tautz D, Renz M (1984) Simple sequences are ubiquitous components of eukaryotic genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 12:4127–4138
Thomas MR, Scott NS (1993) Microsatellite repeats in grapevine reveal DNA polymorphisms when analysed as sequence tagged sites (STSs). Theor Appl Genet 86:985–990
Toth G, Gaspari Z, Jurka J (2000) Microsatellites in different eukaryotic genome, survey and analysis. Genome Res 10:1967–1981
Ueno S, Tsumura Y, Washitani I (2003) Development of microsatellite markers in Primula sieboldii E. Morren, a threatened Japanese perennial herb. Conserv Genet 4:809–811
Viruel MA, Hormaza JI (2004) Development, characterization and variability analysis of microsatellites in lychee (Litchi chinensis Sonn., Sapindaceae). Theor Appl Genet 108:896–902
Wang ZM, Devos KM, Liu CJ, Wang RQ, Gale MD (1998) Construction of RFLP-based maps of foxtail millet. Theor Appl Genet 96:31–36
Xu Y, Zhu L, Xiao J (1997) Chromosomal regions associated with segregation distortion of molecular markers in F2, backcross, doubled haploid, and recombinant inbred populations in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Genet Genomics 253:535–545
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr M. Gale of John Innes Center for providing seeds of the mapping population, Dr K. Devos of the University of Georgia at Athens for providing RFLP data and advice, and Prof. Ping Lu for providing seeds of foxtail millet accessions. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for valuable suggestions and careful corrections. This research was supported by the Basic Research Program (grant no. 2005CCA02500) and National Research Program for Public Will (grant no. 2005DIA4J019) of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, and National Natural Science Foundation (grant no. 30571168).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by A. Schulman.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, X., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y. et al. Development and genetic mapping of SSR markers in foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.]. Theor Appl Genet 118, 821–829 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0942-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0942-9