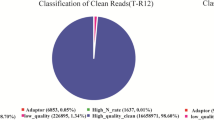
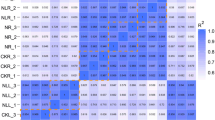
Abstract
Citrus, as one of the most economically important fruits worldwide, is adversely affected by salinity stress. However, its molecular mechanisms underlying salinity tolerance are still not clear. In this study, next-generation RNA-seq technology was applied to analyze the gene expression profiling of citrus roots at 3 time points over a 24-h period of salt treatment. A total of 1831 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified. Among them, 1195 and 1090 DEGs were found at 4 and 24 h, of which 454 were overlapped. Based on functional annotation, the salt overly sensitive (SOS) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) signaling pathways were found to be involved. Meanwhile, we found that hormone metabolism and signaling played important roles in salt stress. In addition, a multitude of transcription factors (TFs) including WRKY, NAC, MYB, AP2/ERF, bZIP, GATA, bHLH, ZFP, SPL, CBF, and CAMTA were identified. The genes related to cell wall loosening and stiffening (xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolases, peroxidases) were also involved in salt stress. Our data not only provided a genetic resource for discovering salt tolerance-related genes, but also furthered our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying salt tolerance in citrus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akpinar BA, Kantar M, Budak H (2015) Root precursors of microRNAs in wild emmer and modern wheats show major differences in response to drought stress. Funct Integr Genomics 15(5):587–598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-015-0453-0
Alvarez I, Tomaro ML, Benavides MP (2003) Changes in polyamines, proline and ethylene in sunflower calluses treated with NaCl. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 74(1):51–59. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023302012208
Audic S, Claverie JM (1997) The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res 7(10):986–995. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.7.10.986
Balal RM, Khan MM, Shahid MA, Mattson NS, Abbas T, Ashfaq M, Garcia-Sanchez F, Ghazanfer U, Gimeno V, Iqbal Z (2012) Comparative studies on the physiobiochemical, enzymatic, and ionic modifications in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive citrus rootstocks under NaCl stress. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 137:86–95
Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D (2001) The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann Stat 29:1165–1188
Brumós J, Colmenero-Flores JM, Conesa A, Izquierdo P, Sánchez G, Iglesias DJ, López-Climent MF, Gómez-Cadenas A, Talón M (2009) Membrane transporters and carbon metabolism implicated in chloride homeostasis differentiate salt stress responses in tolerant and sensitive Citrus rootstocks. Funct Integr Genomics 9(3):293–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-008-0107-6
Cao WH, Liu J, He XJ, Mu RL, Zhou HL, Chen SY, Zhang JS (2007) Modulation of ethylene responses affects plant salt-stress responses. Plant Physiol 143(2):707–719. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.094292
Che J, Yamaji N, Shen RF, Ma JF (2006) An Al-inducible expansin gene, OsEXPA10 is involved in root cell elongation of rice. Plant J 88(1):132–142. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13237
Cicero LL, Madesis P, Tsaftaris A, Lo Piero AR (2015) Tobacco plants over-expressing the sweet orange tau glutathione transferases (CsGSTUs) acquire tolerance to the diphenyl ether herbicide fluorodifen and to salt and drought stresses. Phytochemistry 116:69-77
Cramer G, Schimdt C, Bidart C (2001) Analysis of cell wall hardening and cell wall enzymes of salt-stressed maize (Zea mays) leaves. Funct Plant Biol 28(2):101–109. https://doi.org/10.1071/PP00101
Cui C, Cai J, Zhang S (2013) Allelopathic effects of walnut (Juglans regia L.) rhizospheric soil extracts on germination and seedling growth of turnip (Brassica rapa L.) Allelopathy J 32:37–48
De Oliveira TM, Cidade LC, Gesteira AS, Coelho FMA, Filho WSS, Costa MGC (2011) Analysis of the NAC transcription factor gene family in citrus reveals a novel member involved in multiple abiotic stress responses. Tree Genet Genomes 7(6):1123–1134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-011-0400-8
Deinlein U, Stephan AB, Horie T, Luo W, Xu G, Schroeder JI (2014) Plant salt-tolerance mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci 19(6):371–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.02.001
Ding HD, Zhang XH, Xu SC, Sun LL, Jiang MY, Zhang A, Jin YG (2009) Induction of protection against paraquat-induced oxidative damage by abscisic acid in maize leaves is mediated through mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Integr Plant Biol 51(10):961–972. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2009.00868.x
do Amaral MN, Arge LWP, Benitez LC, Danielowski R, da Silveira Silveira SF, da Rosa Farias D, de Oliveira AC, da Maia LC, Braga EJB (2016) Comparative transcriptomics of rice plants under cold, iron, and salt stresses. Funct Integr Genomics 16(5):567–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-016-0507-y
Droillard MJ, Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Laurière C (2002) Different protein kinase families are activated by osmotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspensions: involvement of the MAP kinases AtMPK3 and AtMPK6. FEBS Lett 527(1-3):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03162-9
Droillard MJ, Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Laurière C (2004) Involvement of MPK4 in osmotic stress response pathways in cell suspensions and plantlets of Arabidopsis thaliana: activation by hypoosmolarity and negative role in hyperosmolarity tolerance. FEBS Lett 574(1-3):42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2004.08.001
Fry SC, Willis SC, Paterson AE (2000) Intraprotoplasmic and wall-localised formation of arabinoxylan-bound diferulates and larger ferulate coupling-products in maize cell-suspension cultures. Planta 211(5):679–692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250000330
Ganie SA, Dey N, Mondal TK (2016) Promoter methylation regulates the abundance of osa-miR393a in contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress. Funct Integr Genomics 16(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-015-0460-1
Golldack D, Li C, Mohan H, Probst N (2014) Tolerance to drought and salt stress in plants: unraveling the signaling networks. Front Plant Sci 5:151
Gómez-Cadenas A, Arbona V, Jacas J, Primo-Millo E, Talon M (2002) Abscisic Acid Reduces Leaf Abscission and Increases Salt Tolerance in Citrus Plants. J Plant Growth Reg 21(3):234-240
Guo J, Shi G, Guo X, Zhang L, Xu W, Wang YS, Zhen S, Hua J (2015) Transcriptome analysis reveals that distinct metabolic pathways operate in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive upland cotton varieties subjected to salinity stress. Plant Sci 238:33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.05.013
Hasegawa PM (2013) Sodium (Na+) homeostasis and salt tolerance of plants. Environ Exper Botany 92:19-31
Hill CB, Cassin A, Keeble-GagnWère G, Doblin MS, Bacic A, Roessner U (2016) De novo transcriptome assembly and analysis of differentially expressed genes of two barley genotypes reveal root-zone-specific responses to salt exposure. Sci Rep 6:31588
Hu LX, Huang ZH, Liu SQ, Fu JM (2012) Growth response and gene expression in antioxidant-related enzymes in two bermudagrass genotypes differing in salt tolerance. J Am Soc Horticul Sci 137:134–143
Hu L, Li H, Chen L, Lou Y, Amombo E, Fu J (2015a) RNA-seq for gene identification and transcript profiling in relation to root growth of bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) under salinity stress. BMC Genomics 16(1):575. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1799-3
Hu W, Yan Y, Hou X, He Y, Wei Y, Yang G, He G, Peng M (2015b) TaPP2C1, a group F2 protein phosphatase 2C gene, confers resistance to salt stress in transgenic tobacco. PLoS One 10(6):e0129589. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129589
Huang Q, Wang Y, Li B, Chang J, Chen M, Li K, Yang G, He G (2015) TaNAC29, a NAC transcription factor from wheat, enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 15(1):268. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0644-9
Jiang K, Moe-Lange J, Hennet L, Feldman LJ (2016) Salt stresses affects the redox status of Arabidopsis root meristems. Front Plant Sci 7:81
Jin LF, Liu YZ, Du W, Fu LN, Hussain SB, Peng SA (2017) Physiological and transcriptional analysis reveals pathways involved in iron deficiency chlorosis in fragrant citrus. Tree Genet Genomes 13(3):51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-017-1136-x
Jung J-H, Park C-M (2014) Auxin modulation of salt stress signaling in Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant Sign Behav 6(8):1198-1200
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Okuno Y, Hattori M (2004) The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res 32:277–280
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M, Hirakawa M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Kawashima S, Okuda S, Tokimatsu T, Yamanishi Y (2008) KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res 36:480–484
Kawaura K, Mochida K, Yamazaki Y, Ogihara Y (2006) Transcriptome analysis of salinity stress responses in common wheat using a 22k oligo-DNA microarray. Funct Integr Genomics 6(2):132–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-005-0010-3
Kim MC, Chung WS, Yun D-J, Cho MJ (2009) Calcium and Calmodulin-Mediated Regulation of Gene Expression in Plants. Mol Plant 2(1):13-21
Kim HS, Park S, Ji CY, Park S, Jeong JC, Lee H, Kwak S (2016) Molecular characterization of biotic and abiotic stress-responsive MAP kinase genes, IbMPK3 and IbMPK6, in sweetpotato. Plant Physiol Biochem 108:37–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.06.036
Kumari S, Sabharwal VP, Kushwaha HR, Sopory SK, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2009) Transcriptome map for seedling stage specific salinity stress response indicates a specific set of genes as candidate for saline tolerance in Oryza sativa L. Funct Integr Genomics 9(1):109–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-008-0088-5
Kumari S, Joshi R, Singh K, Roy S, Tripathi AK, Singh P, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2015) Expression of a cyclophilin OsCyp2-P isolated from a salt-tolerant landrace of rice in tobacco alleviates stress via ion homeostasis and limiting ROS accumulation. Funct Integr Genomics 15(4):395–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-014-0429-5
Kurusu T, Kuchisu K, Tada Y (2015) Plant signaling networks involving Ca(2+) and Rboh/Nox-mediated ROS production under salinity stress. Front Plant Sci 6:427
Kwon T, Sparks JA, Nakashima J, Allen SA, Tang Y, Blancaflor EB (2015) Transcriptional response of Arabidopsis seedlings during spaceflight reveals peroxidase and cell wall remodeling genes associated with root hair development. Am J Bot 102(1):21–35. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1400458
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9(4):357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Lavenus J, Goh T, Roberts I, Guyomarch S, Lucas M, Smet ID, Fukaki H, Beekman T, Bennett M, Llaplaze L (2013) Lateral root development in Arabidopsis: fifty shades of auxin. Trends Plant Sci 18(8):450–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2013.04.006
Li S, Fan C, Li Y, Zhang J, Sun J, Chen Y, Tian C, Su X, Lu M, Liang C, Hu Z (2016) Effects of drought and salt-stresses on gene expression in Caragana korshinskii seedings revealed by RNA-seq. BMC Genomics 17(1):200. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2562-0
Liu H, Zhou X, Dong N, Liu X, Zhang H, Zhang Z (2011) Expression of a wheat MYB gene in transgenic tobacco enhances resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum, and to drought and salt stresses. Funct Integr Genomics 11(3):431–443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-011-0228-1
Ludwig AA, Romeis T, Jones JD (2004) CDPK-mediated signaling pathways: specificity and cross-talk. J Exp Bot 55(395):181–188. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh008
Ma N, Wang Y, Qiu S, Kang Z, Che S, Wang G, Huang J (2013) Overexpression of OsEXPA8, a root-specific gene, improves rice growth and root system architecture by facilitating cell extension. PLoS One 8(10):e75997. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075997
Magdalena MJ, Testerink C (2015) Tuning plant signaling and growth to survive salt. Trends Plant Sci 20:586–594
María FL, Vicent A, Rosa MP, Aurelio G (2007) Relationship between salt tolerance and photosynthetic machinery performance in citrus. Environ Exp Bot 62:176–184
Miller G, Shulaev V, Mittler R (2008) Reactive oxygen signaling and abiotic stress. Physiol Plantarum 133(3):481–489. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2008.01090.x
Narusaka Y, Nakashima K, Shinwari ZK, Sakuma Y, Furihata T, Abe H, Narusaka M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Interaction between two cis-acting elements, ABRE and DRE, in ABA-dependent expression of Arabidopsis rd29A gene in response to dehydration and high-salinity stresses. Plant J 34(2):137–148. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01708.x
Neumann PM, Azaizeh H, Leon D (1994) Hardening of root cell walls: a growth inhibitory response to salinity stress. Plant Cell Environ 17(3):303–309. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.1994.tb00296.x
Ouyang B, Yang T, Li H, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Fei Z, Ye Z (2007) Identification of early salt stress response genes in tomato root by suppression subtractive hybridization and microarray analysis. J Exp Bot 58(3):507–520. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erl258
Pedranzani H, Racagni G, Alemano S, Miersch O, Ramírez I, Peña-Cortés H, Taleisnic E, Machado-Domenech E, Abdala G (2003) Salt tolerant tomato plants show increased levels of jasmonic acid. Plant Growth Regu 4:149–158
Pereira SS, Guimarã FCM, Carvalho JFC, Stolf-Moreira R, Oliveira MCN, Rolla AAP, Farias JRB, Neumaier N, Nepomuceno AL (2011) Transcription factors expressed in soybean roots under drought stress. Genet Mol Res 10(4):3689–3701. https://doi.org/10.4238/2011.October.21.5
Pessarakli M, Touchane H (2006) Growth responses of bermudagrass and seashore paspalum under various levels of sodium chloride stress. J Food Agr Enviro 4:240–243
Reinhardt DH, Rost TL (1995) Primary and lateral root development of dark- and light-grown cotton seedlings under salinity stress. Bat Acta 108(5):457–465. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.1995.tb00521.x
Ren H, Fan Y, Gao Z, Wei K, Li G, Liu J, Chen L, Li B, Hu J, Jia W (2007) Roles of a sustained activation of NCED3 and the synergistic regulation of ABA biosynthesis and catabolism in ABA signal production in Arabidopsis. Chinese Sci Bull 52(4):484–491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0072-9
Richards DE, King KE, Ait-ali T, Harberd NP (2001) How gibberellin regulates plant growth and development: a molecular genetic analysis of gibberellins signaling. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52(1):67–88. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.52.1.67
Saab IN, Sharp RE, Pritchard J, Voetberg GS (1990) Increased endogenous abscisic acid maintains primary root growth and inhibits shoot growth of maize seedling at low water potentials. Plant Physiol 93(4):1329–1336. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.93.4.1329
Sahi C, Singh A, Kumar K, Blumwald E, Grover A (2006) Salt stress response in rice: genetics, molecular biology, and comparative genomics. Funct Integr Genomics 6(4):263–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-006-0032-5
Sathee L, Sairam RK, Chinnusamy V, Jha SK (2015) Differential transcript abundance of salt overly sensitive (SOS) pathway genes is a determinant of salinity stress tolerance of wheat. Acta Physiol Plant 37(8):169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1910-z
Schopfer P, Liszkay A, Bechtold M, Frahry G, Wagner A (2002) Evidence that hydroxyl radicals mediate auxin-induced extension growth. Planta 214:821–828
Sharma N, Abrams SR, Waterer DR (2005) Uptake, movement, activity, and persistence of an abscisic acid analog (80 acetylene ABA methyl ester) in marigold and tomato. J Plant Growth Regul 24(1):28–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-004-0438-z
Shen X, Wang Z, Song X, Xu J, Jiang C, Zhao Y, Ma C, Zhang H (2014) Transcriptomic profiling revealed an important role of cell wall remodeling and ethylene signaling pathway during salt acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 86(3):303–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-014-0230-9
Sripinyowanich S, Klomsakul P, Boonburapong B, Bangyeekhun T, Asami T, Gu H, Buaboocha T, Chadchawan S (2013) Exogenous ABA induces salt tolerance in indica rice (Oryza sativa L.): the role of OsP5CS1 and OsP5CR gene expression during salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 86:94–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.01.009
Srivastava A, Rai A, Patade V, Suprasanna P (2013) Calcium signaling and its significance in alleviating salt stress in plants. In: Ahmad P, Azooz MM, Prasad MNV (eds) Salt stress in plants. Springer, New York, pp 197–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6108-1_9
Sun X, Xu L, Wang Y, Yu R, Zhu X, Luo X, Gong Y, Wang R, Limera C, Zhang K, Liu L (2015) Identification of novel and salt-responsive miRNAs to explore miRNA-mediated regulatory network of salt stress response in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). BMC Genom 16(1)
Sun X, Xu L, Wang Y, Lou X, Zhu X, Kinuthia KB, Nie S, Feng H, Li C, Liu L (2016) Transcriptome-based gene expression profiling identifies differentially expressed genes critical for salt stress response in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) Plant Cell Rep 35(2):329–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1887-5
Syvertsen JP, Garcia-Sanchez F (2014) Multiple abiotic stresses occurring with salinity stress in citrus. Environ Exp Bot 103:128–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.09.015
Tani T, Sobajima H, Okada K, Chujo T, Arimura S, Tsutsumi N, Nishimura M, Seto H, Nojiri H, Yamane H (2008) Identification of the OsOPR7 gene encoding 12-oxophytodienoate reductase involved in the biosynthesis of jasmonic acid in rice. Planta 227(3):517–526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0635-7
Tanou G, Ziogas V, Belghazi M, Christou A, Filippou P, Job D, Fotopoulos V, Molassiotis A (2014) Polyamines reprogram oxidative and nitrosative status and the proteome of citrus plants exposed to salinity stress. Plant Cell Environ 37(4):864–885. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12204
Tattersall EAR, Grimplet J, Deluc L, Wheatley MD, Vincent D, Osborne C, Ergül A, Lomen E, Blank RR, Schlauch KA, Cushman JC, Cramer GR (2007) Transcript abundance profiles reveal larger and more complex responses of grapevine to chilling compared to osmotic and salinity stress. Funct Integr Genomics 7(4):317–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-007-0051-x
Tatusov RL, Fedorova ND, Jackson JD, Jacobs AR, Kiryutin B, Koonin EV, Krylov DM, Mazumder R, Mekhedov SL, Nikolskaya AN, Rao BS, Smirnov S, Sverdlov AV, Vasudevan S, Wolf Y, Yin JJ, Natale DA (2003) The COG database: an updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinformatics 4(1):41. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-4-41
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-seq. Bioinformatics 25(9):1105–1111. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp120
Tuteja N (2007) Abscisic acid and abiotic stress signaling. Plant Signal Behav 2(3):135–138. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.2.3.4156
Walia H, Wilson C, Wahid A, Condamine P, Cui X, Close TJ (2006) Expression analysis of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) during salinity stress. Funct Integr Genomics 6(2):143–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-005-0013-0
Wang W, Liu J (2015) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the polyamine oxidase gene family in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis). Gene 555(2):421–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.11.042
Wang Y, Mopper S, Hasentein KH (2001) Effects of salinity on endogenous ABA, IAA, JA, and SA in Iris hexagona. J Chem Ecol 27(2):327–342. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005632506230
Wu CH, Apweiler R, Bairoch A, Natale DA, Barker WC, Boeckmann B, Ferro S, Gasteiger E, Huang H, Lopez R, Magrane M, Martin MJ, Mazumder R, Donovan CO, Redaschi N, Suzek B (2006) The universal protein resource (UniProt): an expanding universe of protein information. Nucleic Acids Res 34:187–191
Xian L, Sun P, Hu S, Wu J, Liu J (2014) Molecular cloning and characterization of CrNCED1, a gene encoding 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase in Citrus reshni, with functions in tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses. Planta 1:61–77
Xie R, Li Y, He S, Zheng Y, Yi S, Lv Q, Deng L, Margis R (2014) Genome-Wide Analysis of Citrus R2R3MYB Genes and Their Spatiotemporal Expression under Stresses and Hormone Treatments. PLoS ONE 9(12):e113971
Xu H, Li K, Yang F, Shi Q, Wang X (2010) Overexpression of CsNMAPK in tobacco enhanced seed germination under salt and osmotic stresses. Mol Biol Rep 37(7):3157–3163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9895-6
Yao W, Wang L, Zhou B, Wang S, Li R, Jiang T (2016) Over-expression of poplar transcription factor ERF76 gene confers salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. J Plant Physiol 198:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2016.03.015
Yaxley JR, Ross JJ, Sherriff LJ, Reid JB (2001) Gibberellin biosynthesis mutations and root development in pea. Plant Physiol 125(2):627–633. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.125.2.627
Zhang JL, Shi H (2013) Physiological and molecular mechanisms of plant salt tolerance. Photosynth Res 115(1):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9813-6
Zhang F, Zhu G, Du L, Shang X, Cheng C, Yang B, Hu Y, Cai C, Guo W (2016) Genetic regulation of salt stress tolerance revealed by RNA-Seq in cotton diploid wild species, Gossypium davidsonii. Sci Rep 6(1):20582. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20582
Zhu Z, Zhou M, Shabala L, Shabala S (2016) Physiological and molecular mechanisms mediating xylem Na+ loading in barley in the context of salinity stress tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 40(7):1009–1020. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12727
Zou H, Wenwen Y, Zang G, Kang Z, Zhang Z, Huang J, Wang G (2015) OsEXPB2, a b-expansin gene, is involved in rice root system architecture. Mol Breeding 35:1–14
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2016B022), National Nature Science Foundation of NSFC (31301743), National Science-technology Support Plan Projects (2014BAD16B02), and Key Scientific Research Project of Henan Higher Education (16A210011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
Venn diagrams representing the numbers of transcripts and the overlaps of sets obtained across three comparisons S_0h, S_4 h and S_24 h indicate the libraries from the samples at 0 h, 4 h and 24 h under salt treatment, respectively (JPEG 200 kb)
Fig. S2
Venn diagrams representing the numbers of DEGs and the overlaps of sets obtained across two comparisons S_0h was used as calibrators to normalize the DEGs in other two salt-stressed libraries S_0h, S_4 h and S_24 h indicate the libraries from the samples at 0 h, 4 h and 24 h under salt treatment, respectively (JPEG 80 kb)
Table S1
(DOCX 28 kb)
Table S2
(XLSX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, R., Pan, X., Zhang, J. et al. Effect of salt-stress on gene expression in citrus roots revealed by RNA-seq. Funct Integr Genomics 18, 155–173 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-017-0582-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-017-0582-8