Abstract
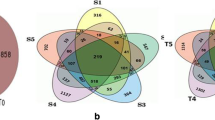
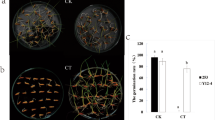
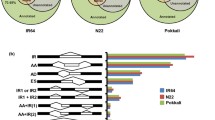
Abiotic stresses such as salinity, iron toxicity, and low temperatures are the main limiting factors of rice (Oryza sativa L.) yield. The elucidation of the genes involved in responses to these stresses is extremely important to understand the mechanisms that confer tolerance, as well as for the development of cultivars adapted to these conditions. In this study, the RNA-seq technique was used to compare the transcriptional profile of rice leaves (cv. BRS Querência) in stage V3, exposed to cold, iron, and salt stresses for 24 h. A range of 41 to 51 million reads was aligned, in which a total range of 88.47 to 89.21 % was mapped in the reference genome. For cold stress, 7905 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were observed, 2092 for salt and 681 for iron stress; 370 of these were common to the three DEG stresses. Functional annotation by software MapMan demonstrated that cold stress usually promoted the greatest changes in the overall metabolism, and an enrichment analysis of overrepresented gene ontology (GO) terms showed that most of them are contained in plastids, ribosome, and chloroplasts. Saline stress induced a more complex interaction network of upregulated overrepresented GO terms with a relatively low number of genes compared with cold stress. Our study demonstrated a high number of differentially expressed genes under cold stress and a greater relationship between salt and iron stress levels. The physiological process most affected at the molecular level by the three stresses seems to be photosynthesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral MN, Arge LWP, Benitez LC, Danielowski R, Silveira SFS, Farias DR, Deuner S, Oliveira AC, Braga EJB, Maia LC (2016) Differential expression of photosynthesis-related genes and quantification of gas exchange in rice plants under abiotic stress. Acta Physiol Plant 38:1–11
Anders S, Pyl PT, Huber W (2015) HTSeq-a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31:166–169
Asch F, Becker M, Kpongor DS (2005) A quick and efficient screen for resistance to iron toxicity in lowland rice. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 168:764–773
Barkla BJ, Vera-Estrella R, Pantoja O (2013) Progress and challenges for abiotic stress proteomics of crop plants. Proteomics 13:1801–1815
Becker M, Asch F (2005) Iron toxicity in rice—conditions and management concepts. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 168:558–573
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Briat JF, Ravet K, Arnaud N, Duc C, Boucherez J, Touraine B, Cellier F, Gaymard F (2010) New insights into ferritin synthesis and function highlight a link between iron homeostasis and oxidative stress in plants. Ann Bot 105:811–822
Chen C, Tao C, Peng H, Ding Y (2007) Genetic analysis of salt stress responses in asparagus bean (Vigna unguiculata (L.) ssp. sesquipedalis verdc.). J Hered 98:655–665
Cheng NH, Pittman JK, Zhu JK, Hirschi KD (2004) The protein kinase SOS2 activates the Arabidopsis H+/Ca2+ antiporter CAX1 to integrate calcium transport and salt tolerance. J Biol Chem 279:2922–2926
Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu JK (2007) Cold stress regulation of gene expression in plants. Trends Plant Sci 12:444–451
Chopra R, Burow G, Hayes C, Emendack Y, Xin Z, Burke J (2015) Transcriptome profiling and validation of gene based single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in sorghum genotypes with contrasting responses to cold stress. BMC Genomics 16:1–11
Conesa A, Götz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Talon M, Robles M (2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 21:3674–3676
Cramer GR, Urano K, Delrot S, Pezzoti M, Shinozaki K (2011) Effect of abiotic stress on plants: a systems biology perspective. BMC Plant Biol 11:163
Cui S, Huang F, Wang J, Ma X, Cheng Y, Liu J (2005) A proteomic analysis of cold stress responses in rice seedlings. Proteomics 5:3162–7312
Deng D, Wu SC, Wu FY, Deng H, Wong MH (2010) Effects of root anatomy and Fe plaque on arsenic uptake by rice seedlings grown in solution culture. Environ Pollut 158:2589–2595
Dubouzet JG, Sakuma Y, Ito Y, Kasuga M, Dubouzet EG, Miura S, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L., encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J 33:751–763
Elec V, Quimio CA, Mendoza R, Sajise AGC, Beebout SEJ, Gregorio GB, Singh RK (2013) Maintaining elevated Fe2+ concentration in solution culture for the development of a rapid and repeatable screening technique for iron toxicity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Soil 372:253–264
Fang WC, Kao CH (2000) Enhanced peroxidase activity in rice leaves in response to excess iron, copper and zinc. Plant Sci 158:71–76
FAO (2008) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/ag/agl/agll/spush. Accessed 15 January 2016
Finatto T, Oliveira AC, Chaparro C, Maia LC, Farias DR, Woyann LG, Mistura CC, Soares-Bresolin AP, Llauro C, Panaud O, Picault N (2015) Abiotic stress and genome dynamics: specific genes and transposable elements response to iron excess in rice. Rice 8:13
Fowler S, Thomashow MF (2002) Arabidopsis transcriptome profiling indicates that multiple regulatory pathways are activated during cold acclimation in addition to the CBF cold response pathway. Plant Cell 14:1675–1690
Fracasso A, Trindade LM, Amaducci S (2016) Drought stress tolerance strategies revealed by RNA-Seq in two sorghum genotypes with contrasting WUE. BMC Plant Biol 16:115
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J, Hornik K, Hothorn T, Huber W, Iacus S, Irizarry R, Leisch F, Li C, Maechler M, Rossini AJ, Sawitzki G, Smith C, Smyth G, Tierney L, Yang JYH, Zhang J (2004) Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5:R80
Goulas E, Schubert M, Kieselbach T, Kleczkowski LA, Gardeström P, Schröder W, Hurry V (2006) The chloroplast lumen and stromal proteomes of Arabidopsis thaliana show differential sensitivity to short- and long-term exposure to low temperature. Plant J 47:720–734
Hannah MA, Wiese D, Freund S, Fiehn O, Heyer AG, Hincha DK (2006) Natural genetic variation of freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 142:98–112
Hirschi KD (1999) Expression of Arabidopsis CAX1 in tobacco: altered calcium homeostasis and increased stress sensitivity. Plant Cell 11:2113–2122
Huner PA, Öquist G, Sarhan F (1998) Energy balance and acclimation to light and cold. Trends Plant Sci 3:224–230
Hussain K, Nisar MF, Majeed A, Nawaz K, Bhatti KH, Afghan S, Shahazad A, Zia-Ul-Hussnian S (2010) What molecular mechanism is adapted by plants during salt stress tolerance? Afr J Biotechnol 9:416–422
Kapoor K, Srivastava A (2010) Assessment of salinity tolerance of Vinga mungo var. Pu-19 using ex vitro and in vitro methods. Asian J Biotechnol 2:73–85
Kawasaki S, Borchert C, Deyholos M, Wang H, Brazille S, Kawai K, Galbraith D, Bohnert HJ (2001) Gene expression profiles during the initial phase of salt stress in rice. Plant Cell 13:889–905
Kirk GJD (2004) The biogeochemistry of submerged soils, 1st edn. Wiley, Chichester
Kreps JA, Wu Y, Chang HS, Zhu T, Wang X, Harper JF (2002) Transcriptome changes for Arabidopsis in response to salt, osmotic, and cold stress. Plant Physiol 130:2129–2141
Kumari S, Sabharwal VP, Kushwaha HR, Sopory SK, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2009) Transcriptome map for seedling stage specific salinity stress response indicates a specific set of genes as candidate for saline tolerance in Oryza sativa L. Funct Integr Genomics 9:109–123
Langmead B, Salzberg S (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359
Lee S, Jeon J, An G (2012) Iron homeostasis and fortification in rice. J Plant Biol 55:261–267
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lou Q, Chen L, Sun Z, Xing Y, Li J, Xu X, Mei H, Luo L (2007) A major QTL associated with cold tolerance at seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 158:87–94
Majerus V, Bertin P, Lutts S (2007) Effects of iron toxicity on osmotic potential, osmolytes and polyamines concentrations in the African rice (Oryza glaberrima Steud.). Plant Sci 173:96–105
Misra AN, Latowski D, Strzalka K (2006) The xanthophyll cycle activity in kidney bean and cabbage leaves under salinity stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 53:102–109
Mizuno H, Kawahara Y, Sakai H, Kanamori H, Wakimoto H, Yamagata H, Oono Y, Wu YJ, Ikawa H, Itoh Y, Matsumoto T (2010) Massive parallel sequencing of mRNA in identification of unannotated salinity stress-inducible transcripts in rice (Oryza sativa L.). BMC Genomics 11:683
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Munro HN (1990) Iron regulation of ferritin gene expression. J Cell Biochem 44:107–15. doi:10.1002/jcb.240440205
Muthamilarasan M, Bonthala VS, Mishra AK, Khandelwal R, Khan Y, Roy R, Prasad M (2014) C2H2 type of zinc finger transcription factors in foxtail millet define response to abiotic stresses. Funct Integr Genomics 14:531–543
Nakashima K, Ito Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2009) Transcriptional regulatory networks in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis and grasses. Plant Physiol 149:88–95
Omidbakhshfard MA, Omranian N, Ahmadi FS, Nikoloski Z, Mueller-Roeber B (2012) Effect of salt stress on genes encoding translation-associated proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal Behav 7:1095–1102
Oono Y, Kawahara Y, Kanamori H, Mizuno H, Yamagata H, Yamamoto M, Hosokawa S, Ikawa H, Akahane I, Zhu Z, Wu J, Itoh T, Matsumoto T (2011) mRNA-Seq reveals a comprehensive transcriptome profile of rice under phosphate stress. Rice 4:50–65
Oono Y, Yazawa T, Kawahara Y, Kanamori H, Kobayashi F, Sasaki H, Mori S, Wu J, Handa H, Itoh T, Matsumoto T (2014) Genome-wide transcriptome analysis reveals that cadmium stress signaling controls the expression of genes in drought stress signal pathways in rice. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096946
Quinet M, Vromman D, Clippe A, Bertin P, Lequeux H, Dufey I, Lutts S, Lefèvre I (2012) Combined transcriptomic and physiological approaches reveal strong differences between short- and long-term response of rice (Oryza sativa) to iron toxicity. Plant Cell Environ 35:1837–1859
Rahman H, Jagadeeshselvam N, Valarmathi R, Sachin B, Sasikala R, Senthil N, Sudhakar D, Robin S, Muthurajan R (2014) Transcriptome analysis of salinity responsiveness in contrasting genotypes of finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) through RNA-sequencing. Plant Mol Biol 85:485–503
Rengasamy P (2006) World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J Exp Bot 57:1017–1023
Rensink WA, Iobst S, Hart A, Stegalkina S, Liu J, Buell CR (2005) Gene expression profiling of potato responses to cold, heat and salt stress. Funct Integr Genomics 5:201–207
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2008) edgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26:139–140
Sage RF, Kubien DS (2007) The temperature response of C3 and C4 photosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ 30:1086–1106
Sahrawat KL (2004) Iron toxicity in wetland rice and the role of other nutrients. J Plant Nutr 27:1471–1504
Shabala S, Cuin TA (2008) Potassium transport and plant salt tolerance. Physiol Plant 133:651–669
Shen C, Li D, He R, Fang Z, Xia Y, Gao J, Shen H, Cao M (2014) Comparative transcriptome analysis of RNA-Seq data for cold-tolerant and cold-sensitive rice genotypes under cold stress. J Plant Biol 57:337–348
Singh RK, Redoña E, Refuerzo L (2010) Varietal improvement for abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants: special reference to salinity in rice. In: Pareek A, Spory SK, Bohnert HJ, Govindjee A (eds) Abiotic stress adaptation in plants: physiological, molecular and genomics foundation. Springer Science + Business Media LLC, New York, pp 387–415
Soda N, Kushwaha HR, Soni P, et al (2013) A suite of new genes defining salinity stress tolerance in seedlings of contrasting rice genotypes. Funct Integr Genomics 13:351–365. doi:10.1007/s10142-013-0328-1
Stein RJ, Duarte GL, Spohr MG, Lopes SIG, Fett JP (2009) Distinct physiological responses of two rice cultivars subjected to iron toxicity under field conditions. Ann Appl Biol 154:269–277
Suh HJ, Kim CS, Lee JY, Jung J (2002) Photodynamic effect of iron excess on photosystem II function in pea plants. Photochem Photobiol 75:513–518
Sultana N, Ikeda T, Itoh R (1999) Effect of NaCl salinity on photosynthesis and dry matter accumulation in developing rice grains. Environ Exper Bot 42:211–220
Sun SJ, Guo SQ, Yang X, Bao YM, Tang HJ, Sun H, Huang J, Zhang HS (2010) Functional analysis of a novel Cys2/His2-type zinc finger protein involved in salt tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 6:2807–2818
Supek F, Bošnjak M, Škunca N, Šmuc T (2011) REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of gene ontology terms. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021800
Thimm O, Bläsing O, Gibon Y, Nagel A, Meyer S, Krüger P, Selbig J, Müller LA, Rhee SY, Stitt M (2004) MAPMAN: a user-driven tool to display genomics data sets onto diagrams of metabolic pathways and other biological processes. Plant J 37:914–939
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25:1105–1111
Usadel B, Blasing OE, Gibon Y, Retzlaff K, Hoehne M, Gunther M, Stitt M (2008) Multilevel genomic analysis of the response of transcripts, enzyme activities and metabolites in Arabidopsis rosettes to a progressive decrease of temperature in the non-freezing range. Plant Cell Environ 31:518–547
Wakasa Y, Oono Y, Yazawa T, Hayashi S, Ozawa K, Handa H, Matsumoto T, Takaiwa F (2014) RNA sequencing-mediated transcriptome analysis of rice plants in endoplasmic reticulum stress conditions. BMC Plant Biol 14:101
Walia H, Wilson C, Condamine P, Liu X, Ismail AM, Zeng L, Wanamaker SI, Mandal J, Xu J, Cui X (2005) Comparative transcriptional profiling of two contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress during the vegetative growth stage. Plant Physiol 139:822–835
Walia H, Wilson C, Zeng L, Ismail AM, Condamine P, Close TJ (2007) Genome-wide transcriptional analysis of salinity stressed japonica and indica rice genotypes during panicle initiation stage. Plant Mol Biol 63:609–623
Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2010) Exploring plant transcriptomes using ultra high-throughput sequencing. Brief Funct Genomics 9:118–128
Wang B, Zheng J, Liu Y, Wang J, Wang G (2012) Cloning and characterization of the stress-induced bZIP gene ZmbZIP60 from maize. Mol Biol Rep 39:6319–6327
Wu ZJ, Li XH, Liu ZW, Li H, Wang YX, Zhuang J (2015) Transcriptome-based discovery of AP2/ERF transcription factors related to temperature stress in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Funct Integr Genomics 15:741–752
Yadav SK (2010) Cold stress tolerance mechanisms in plants. a review. Agron Sustain Dev 30:515–527
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Yan SP, Zhang QY, Tang ZC, Su WA, Sun WN (2006) Comparative proteomic analysis provides new insights into chilling stress responses in rice. Mol Cell Proteomics 5:484–496
Yoshida S, Forno DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA (1976) Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice, 3rd edn. The Philippines, International Rice Research Institute (IRRI)
Zhang Y, Xu YH, Yi HY, Gong JM (2012) Vacuolar membrane transporters OsVIT1 and OsVIT2 modulate iron translocation between flag leaves and seeds in rice. Plant J 72:400–410
Zhu JK (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:441–445
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Brazilian research funding agencies: Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists that would prejudice the impartiality of this scientific work.
Funding source
None.
Additional information
Marcelo Nogueira do Amaral and Luis Willian Pacheco Arge contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Phenotypic characterization of rice plants of cv. “BRS Querência” under a cold stress, b iron stress, and c salt stress (PDF 126 kb)
Supplementary Material 2
PCA cluster analysis of the different RNA-seq libraries based on Log2FC (PDF 10 kb)
Supplementary Material 3
List of primers used in RT-qPCR reactions (XLSX 10 kb)
Supplementary Material 4
Transcriptional profiles of rice plants (cv. BRS Querência) under cold, iron, and salt stress and their relations (PDF 259 kb)
Supplementary Material 5
List of differentially expressed genes identified by RNA-seq (FDR <0.01) in rice plants subjected to stress by cold, iron, and salt (XLS 2254 kb)
Supplementary Material 6
REViGO graphical representation of upregulated overrepresented GO terms under each stress. Graphical representation of interactions of GO terms with upregulated biological processes. a Cold stress, b Iron stress, c Salt stress (PDF 81 kb)
Supplementary Material 7
REViGO graphical representation of upregulated overrepresented GO terms under each stress. Graphical representation of interactions of GO terms with downregulated biological processes. a Cold stress, b Iron stress, c Salt stress. (PDF 36 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
do Amaral, M.N., Arge, L.W.P., Benitez, L.C. et al. Comparative transcriptomics of rice plants under cold, iron, and salt stresses. Funct Integr Genomics 16, 567–579 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-016-0507-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-016-0507-y