Abstract
A multi-scale simulation of the tip test, developed to determine the tribological characteristics of the back-extrusion process, was conducted on an AA 3003 alloy. A microstructure-level simulation, coupled with crystal plasticity finite element (CPFE) analysis, was utilized to characterize the macro-mechanical properties of the AA 3003. Owing to the limited size of the material provided, we performed CPFE analyses rather than multiple mechanical tests to determine the plastic anisotropy characteristics of the AA 3003 alloy. A three-dimensional finite element (FE) model of the tip test was developed using two different yield functions, namely the generalized von Mises yield function and Hill’s (1948) yield function, with material parameters identified from the CPFE analyses. The results revealed the following: 1. The directionality observed during the tip test is governed by the plastic anisotropy, rather than the frictional conditions. 2. The plastic anisotropy results in different Coulomb friction values. Therefore, the anisotropy should be carefully addressed in the tip test.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The material investigated in this study, rolled AA 3003, was an example of this limitation. Indeed, AA 3003 showed pronounced earing behavior following the tip test; however, the amount of material available limited its use for multiple mechanical tests.
The main purpose of the current study is to focus on the effect of plastic anisotropy during the tip test. The effect of temperature in the experiment was ignored for the sake of simplicity.
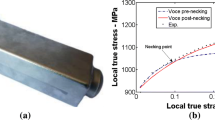
Although there is a discrepancy with regard to the small strain region between the experimental results and the H/V fits, the flow stress under this small strain range is not of significant importance considering the large amount of deformation that occurs during the tip test.
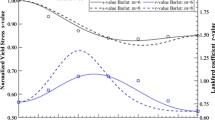
To estimate the number of FEs (or Euler angles) required to accurately represent the macroscopic behavior of Al 3003, CPFE simulations with various number of FEs, such as 126, 225, 343, 512, 1000, 3375, 8000, and 27000, were conducted to predict r-value in uniaxial tension along the RD. The results revealed that the relative error of the predicted r-value becomes less than 2 pct when over 1000 FEs were used. Therefore, we decided to use the FE model with 1000 FEs (or 1000 Euler angles) for subsequent CPFE simulations.
The force ratio of 1/2 was imposed for the plane-strain tension along the TD.
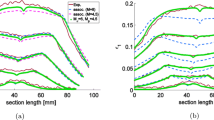
To compensate for test-to-test scattering caused by machining errors and the thickness of the paint (in the case of the DIC measurement), the tip height value at the origin was brought to the same value in representative tests.
The methodology used to measure the radial tip distance is detailed elsewhere.[11]
Although the radial tip distance also showed directionality, the average value of the measured radial tip distances at four different points was used for simplicity. This is a reasonable assumption considering the conclusion in Section VI–B, in which the friction does not influence the directionality of the radial tip distance but only changes the overall value.
It should be noted that the earing in the tip test should be distinguished from the earing in the sheet metal forming, in particular, the earing in the cup drawing of sheet metals. The earing in the cup drawing is mostly induced by the planar anisotropy under uniaxial tensile stress state in the flange region. In contrast, the material undergoes compression (States Ι and ΙΙ) and plane-strain tension (State ΙΙΙ) modes in the tip test. Therefore, unlike the cup drawing case, the earing in the tip test is not solely dependent on the planar anisotropy.
References
H. Kudo: Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1960, vol. 2, pp. 102-27.
J. B. Hawkyard and W. Johnson: Int. J. Mech. Sci., 1967, vol. 9, pp. 163-82.
T. Robinson, H. Ou, and C. G. Armstrong: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2004, vol. 153–154, pp. 54-59.
S. J. Mirahmadi, M. Hamedi, and M. Cheraghzadeh: Tribol. Trans., 2015, vol. 58, pp. 778-85.
M. Dehghan, F. Qods, M. Gerdooei, and J. Doai: Appl. Mech. Mater., 2012, vol. 249–250, pp. 663-66.
Y. T. Im, O. Vardan, G. Shen, and T. Altan: CIRP Ann. - Manuf. Technol., 1988, vol. 37, 225-30.
T. Nakamura, N. Bay, and Z.-L. Zhang: J. Tribol., 1997, vol. 119, pp. 501-06.
T. Nakamura, N. Bay, and Z.-L. Zhang: J. Tribol., 1998, vol. 120, pp. 716-23.
A. Buschhausen, K. Weinmann, J. Y. Lee, and T. Altan: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1992, vol. 33, pp. 95-108.
T. Nishimura, T. Sato, and Y. Tada, J: Mater. Process. Technol., 1995, vol. 53, pp. 726-35.
Y.-T. Im, J.-S. Cheon, and S.-H. Kang: J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 2002, vol. 124, pp. 409-15.
P. Chauviere, K. H. Jung, D. K. Kim, H. C. Lee, S. H. Kang, and Y. T. Im: J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 2008, vol. 22, pp. 924-30.
Y.-T. Im, S.-H. Kang, and J.-S. Cheon: J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 2003, vol. 125, pp. 378-83.
S.-H. Kang, J.-H. Lee, J.-S. Cheon, and Y.-T. Im: Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2004, vol. 46, pp. 855-69.
H. J. Bong, D. Leem, J. H. Kim, Y. T. Im: and M. G. Lee, Met. Mater. Int. 2016, vol. 22, pp. 356-63.
K. H. Jung, H. C. Lee, D. K. Kim, S. H. Kang, and Y. T. Im: Wear, 2012, vol. 286–287, pp. 19-26.
K.-H. Jung, H.-C. Lee, J. S. Ajiboye, S.-H. Kang, and Y.-T. Im: J. Tribol., 2009, vol. 132, pp. 11601.
K. H. Jung, H. C. Lee, J. S. Ajiboye, and Y. T. Im: Tribol. Lett., 2009, vol. 37, 353-59.
F. Barlat and H. Bong: in 60 Excell. Invent. Met. Form. SE - 7, A.E. Tekkaya, W. Homberg, and A. Brosius, eds., Springer, Berlin, 2015, pp. 43–48.
H. J. Bong, F. Barlat, D. C. Ahn, H.-Y. Kim: and M.-G. Lee, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2013, vol. 75, 94-109.
H. J. Bong, F. Barlat, M.-G. Lee, and D. C. Ahn: Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2012, vol. 64, 1-10.
M. G. Lee, J. W. Lee, J. J. Gracio, G. Vincze, E. F. Rauch, and F. Barlat: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2013, vol. 79, 570-83.
M. Liu, K.A. Tieu, K. Zhou, C.-T. Peng: Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 2016, vol. 47 pp. 2717–25.
J.-H. Jung, Y.-S. Na, K.-M. Cho, D.M. Dimiduk, Y.S. Choi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, vol. 46, 4834–40.
S. F. Choudhury, L. Ladani: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 46A, pp. 1108-18.
K. Zhang and B. Holmedal and O. S. Hopperstad and S. Dumoulin: Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2014, vol. 22, pp. 75015.
R. K. Verma, P. Biswas, T. Kuwabara, and K. Chung: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, vol. 604, pp. 98-102.
K. Inal, R. K. Mishra, and O. Cazacu: Int. J. Solids Struct., 2010, vol. 47, pp. 2223-33.
H. Lim, R. Dingreville, L. A. Deibler, T. E. Buchheit, and C. C. Battaile: Comput. Mater. Sci. 2016, vol. 117, pp. 437-44.
B. Klusemann, B. Svendsen, and H. Vehoff: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2012, vol. 52, pp. 25-32.
M. Knezevic and S. R. Kalidindi: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2007, vol. 39, pp. 643-48.
H. Lim, J. D. Carroll, C. C. Battaile, T. E. Buchheit, B. L. Boyce, and C. R. Weinberger: Int. J. Plast., 2014, vol. 60, pp. 1-18.
F. Meier, C. Schwarz, and E. Werner: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2014, vol. 94, pp. 122-31.
J. Jung, J. I. Yoon, J. H. Moon, H. K. Park, and H. S. Kim: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2017, vol. 126, pp. 121-31.
A. Khajezade, M.H. Parsa, H. Mirzadeh: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, vol. 47 pp. 941–48.
M.I. Latypov, M.-G. Lee, Y. Beygelzimer, D. Prilepo, Y. Gusar, H.S. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, vol. 47, 1248–60
Y.S. Choi, M.A. Groeber, P.A. Shade, T.J. Turner, J.C. Schuren, D.M. Dimiduk, M.D. Uchic, A.D. Rollett: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 6352–59.
F. Barlat and O. Richmond: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1987, vol. 95, 15-29.
M. Kuroda: in AIP Conf. Proc., 2005, vol. 778, pp. 445–50.
F. Khakbaz and M. Kazeminezhad: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 532, pp. 26-30.
R. Fournier and S. Fournier: Sheet Metal Handbook, HP Books, 1989, p. 143.
S. Lim, H. Huh: Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2017, vol. 18, pp. 719-27.
J. H. Sung, J. H. Kim, and R. H. Wagoner: Int. J. Plast., 2010, vol. 26, pp. 1746-71.
A. Smith, Z. Chen, J. J. Y. Lee, M. G. Lee, and R. Wagoner, Int. J. Plast. 2014, vol. 58, pp. 100-19
W.F. Hosford and R.M. Caddel: Metal Forming: Mechanics and Metallurgy, Cambridge University Press, 1983.
R. Hielscher and H. Schaeben: J. Appl. Crystallogr., 2008, vol. 41, pp. 1024-37.
H. Huh, C.G. Park, C.S. Lee, and Y.T. Keum: in Proc. 9th AEPA 2008 (World Scientific, Daejeon, Korea, 2009), pp. 527–28.
S. Akramove, M. G. Lee, I. Kim, D. Y. Sung, B. H. Park, and I. Kim, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2005, vol. 495–497, pp. 803-8.
R. J. Asaro and J. R. Rice: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1977, vol. 25, pp. 309-38.
E. H. Lee: J. Appl. Mech., 1969, vol. 36, pp. 1-6.
R. Hill and J. R. Rice: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1972, vol. 20, pp. 401-13.
D. Peirce, R. J. Asaro, and A. Needleman: Acta Metall., 1982, vol. 30, pp. 1087-1119.
M. G. Lee, H. Lim, B. L. Adams, J. P. Hirth, and R. H. Wagoner: Int. J. Plast., 2010, vol. 26, pp. 925-38.
J. R. Rice: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1971, vol. 19, pp. 433-55.
J.W. Hutchinson: in Proc. R. Soc. Lond., 1976 vol. A 348, pp. 101–27.
C. A. Bronkhorst, S. R. Kalidindi, and L. Anand: The Royal Society, 1992, vol. 341, pp. 443–477.
S. R. Kalidindi, C. A. Bronkhorst, and L. Anand: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1992, vol. 40, pp. 537-69.
J. Gubicza, N. Q. Chinh, J. L. Lábár, S. Dobatkin, Z. Hegedűs, and T. G. Langdon, J. Alloys Compd, 2009, vol. 483, pp. 271-74.
H. Wiedersich, JOM, 1964, vol. 16(5), pp. 425-30.
G. Schoeck and R. Frydman, Phys. Status Solidi, 1972, vol. 53, pp. 661-73.
M. Kassner, J. Mater. Sci, 1990, vol. 25(4), pp. 1997-2003.
U.F. Kocks: J. Eng. Mater. Technol. Trans. ASME, 1976, vol. 98 Ser H, pp. 76–85.
S.R. Kalidindi: Ph.D. Thesis, Polycrystal Plasticity: Constitutive Modeling and Deformation Processing, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1992.
R. Hill: Proc. R. Soc. London A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., 1948, vol. 193, pp. 281-97.
K. Zhang, B. Holmedal, O. S. S. Hopperstad, S. Dumoulin, J. Gawad, A. Van Bael, and P. Van Houtte, Int. J. Plast, 2015, vol. 66, pp. 3-30.
Y. Hanabusa, H. Takizawa, and T. Kuwabara, J. Mater. Process. Technol, 2013, vol. 213, pp. 961-70.
F. Barlat, H. Aretz, J. W. Yoon, M. E. Karabin, J. C. Brem, and R. E. Dick, Int. J. Plast. 2005, vol. 21, pp. 1009-39.
J. C. Pierret, A. Rassili, G. Vaneetveld, R. Bigot, and J. Lecomte-Beckers, Int. J. Mater. Form, 2010, vol. 3, 763-66.
T. J. Shin, Y. H. Lee, J. T. Yeom, S. H. Chung, S. S. Hong, I. O. Shim, N. K. Park, C. S. Lee, and S. M. Hwang, Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng, 2005, vol. 194, 3838-69.
H. Bašić, I. Demirdžić, and S. Muzaferija, Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng, 2005, vol. 62, pp. 475-94.
J.-H. Cheng: Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng., 1988, vol. 26, pp. 1-18.
W. K. Liu, T. Belytschko, and H. Chang: Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng., 1986, vol. 58, pp. 227-45.
D. J. Benson: Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1989, vol. 72, pp. 305-50.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge H.G. Kim for the XRD measurement. H.M. Back and Dr. D.K. Kim kindly helped for the tip-test experiments at KAIST. J. Lee appreciates the support by the Fundamental Research Program of the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS). MGL appreciates supports from National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (2017R1A2A2A05069619) and Engineering Research Center (2012R1A5A1051500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 2, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bong, H.J., Leem, D., Lee, J. et al. A Coupled Crystal Plasticity and Anisotropic Yield Function Model to Identify the Anisotropic Plastic Properties and Friction Behavior of an AA 3003 Alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 49, 282–294 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4406-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4406-1