Abstract
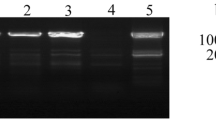
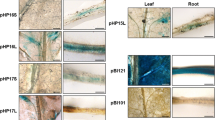
LEA1 gene from Glycine max can be expressed in late-embryo stage of plants, and respond to salinity and dehydration stress. To elucidate the mechanism for stress tolerance and high expression in seeds, we isolated and characterized the promoter of LEA1 gene (EQ, 1997 bp) starting the 5′LEA1 coding region. A deletion mutant of EQ promoter (ED) and the full length promoter (EQ) were fused to GUS reporter gene and transformed into the tobacco leaf discs. The results indicated that expression of the reporter gene (GUS) could be regulated by EQ promoter, and was stronger than the mutant under the stress conditions. Also, the expression level of GUS gene driven by EQ promoter in transgenic tobacco seeds was significantly higher than that by the mutant promoter, which meant that it had a better tissue-specificity. Therefore, the active domain for the promoter was located between −1997 and −1000 bp. Additionally, the activity of EQ promoter was 2.1-, 3.3- and 0.4- times stronger than the activity of promoter CaMV35S under salt (24 h), drought (10 h) or ABA (24 h), respectively. Meanwhile, the GUS activity of EQ promoter in seeds was 1.8-fold stronger compared to the promoter CaMV35S. In summary, the new promoter (EQ) is bi-functional, stress-inducible and seed-specific. These findings provide a further understanding for the regulation of LEA1gene expression, and suggest a new way for improving seed quality under saline and alkaline land.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya S, Ranjan R, Pattanaik S, Maiti IB, Dey N (2014) Efficient chimeric plant promoters derived from plant infecting viral promoter sequences. Planta 239:381–396. doi:10.1007/s00425-013-1973-2
Amara I, Odena A, Oliveira E, Moreno A, Masmoudi K, Pagès M, Goday A (2012) Insights into maize LEA proteins: from proteomics to functional approaches. Plant Cell Physiol 53:312–329. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcr183
Bai Y, Yang Q, Kang J, Sun Y, Gruber M, Chao Y (2012) Isolation and functional characterization of a Medicago sativa L. gene, MsLEA3-1. Mol Biol Rep 39:2883–2892. doi:10.1007/s11033-011-1048-z
Ditzer A1, Bartels D (2006) Identification of a dehydration and ABA-responsive promoter regulon and isolation ofcorresponding DNA binding proteins forthe group 4 LEA geneCpC2 from C. Plantagineum. Plant Mol Biol 61(4–5):643–663. doi:10.1007/s11103-006-0038-3
Bi H, Luang S, Li Y, Bazanova N, Morran S, Song Z, Perera MA, Hrmova M, Borisjuk N, Lopato S (2016) Identification and characterization of wheat drought-responsive MYB transcription factors involved in the regulation of cuticle biosynthesis. J Exp Bot 67(18):5363–5380. doi:10.1093/jxb/erw298
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Campos F, Cuevas-Velazquez C, Fares MA, Reyes JL, Covarrubias AA (2013) Group 1 LEA proteins, an ancestral plant protein group, are also present in other eukaryotes, and in the archeae and bacteria domains. Mol Genet Genom 288:503–517. doi:10.1007/s00438-013-0768-2
Cao J, Li X (2015) Identification and phylogenetic analysis of late embryogenesis abundant proteins family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Planta 241:757–772. doi:10.1007/s00425-014-2215-y
Checker VG, Chhibbar AK, Khurana P (2012) Stress-inducible expression of barley Hva1 gene in transgenic mulberry displays enhanced tolerance against drought, salinity and cold stress. Transgenic Res 21:939–957. doi:10.1007/s11248-011-9577-8
Chen L, Jiang BJ, Wu CX, Sun S, Hou WS, Han TF (2015) The characterization of GmTIP, a root-specific gene from soybean, and the expression analysis of its promoter. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 121:259–274. doi:10.1007/s11240-014-0682-2
Chen Y, Han Y, Zhang M, Zhou S, Kong X, Wang W (2016) Over expression of the wheat expansin gene TaEXPA2 improved seed production and drought tolerance in transgenic tobacco plants. PloS ONE 11(4):e0153494. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0153494
Décima Oneto C, Otegui ME, Baroli I, Beznec A, Faccio P, Bossio E, Blumwald E, Lewi D (2016) Water deficit stress tolerance in maize conferred by expression of an isopentenyl transferase (IPT) gene driven by a stress- and maturation-induced promoter. J Biol Technol 220:66–77. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.01.014
Du DL, Zhang QX, Cheng TG, Pan HT, Yang WR, Sun LD (2013) Genome-wide identification and analysis of late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) genes in Prunus mume. Mol Biol Rep 40:1937–1946. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-2250-3
Fujita Y, Fujita M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011) ABA-mediated transcriptional regulation in response to osmotic stress in plants. J Plant Res 124:509–525. doi:10.1007/s10265-011-0412-3
He S, Tan L, Hu Z, Chen G, Wang G, Hu T (2012) Molecular characterization and functional analysis by heterologous expression in E. coli under diverse abiotic stresses for OsLEA5, the atypical hydrophobic LEA protein from Oryza sativa L. Mol Genet Genom 287:39–54. doi:10.1007/s00438-011-0660-x
Hoekema A, Hirsch PR, Hooykaas PJJ, Schilperoort RA (1983) A binary plant vector strategy based on separation of vir- and T-region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti-plasmid. Nature 303:179–180. doi:10.1038/303179a0
Hou JJ, Jiang PP, Qi SM, Zhang K, He QX, Xu CZ, Ding ZH, Zhang KW, Li KP (2016) Isolation and functional validation of salinity and osmotic stress inducible promoter from the maize type-II H+ pyrophosphatase gene by deletion analysis in transgenic tobacco plants. PloS One 11(4):e0154041. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0154041
Hu XW, Liu SX, Guo JC, Li JT, Duan RJ, Fu SP (2009) Embryo and anther regulation of the mabinlin II sweet protein gene in Capparis masaikai Lévl. Funct Integr Genom 9:351–361. doi:10.1007/s10142-009-0117-z
Huang SX, Gao YF, Liu JK, Peng XL, Niu XL, Fei ZJ, Cao SQ, Liu YS (2012) Genome-wide analysis of WRKY transcription factors in Solanum lycopersicum. Mol Genet Genom 287:495–513. doi:10.1007/s00438-012-0696-6
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusion: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3091–3907
Jyothsnakumari G, Thippeswamy M, Veeranagamallaiah G, Sudhakar C (2009) Differential expression of LEA proteins in two genotypes of mulberry under salinity. Biol Plant 53:145–150. doi:10.1007/s10535-009-0022-2
Kim MJ, Kim H, Shin JS, Chung CH, O hlrogge JB, Suh MC (2006) Seed-specific expression of sesame microsomal oleic acid desaturase is controlled by combinatorial properties between negative cis-regulatory elements in the SeFAD2 promoter and enhancers in the 5′-UTR inron. Mol Genet Genom 276:351–368. doi:10.1007/s00438-006-0148-2
Kim MJ, Kim JK, Shin JS, Suh MC (2007) The SebHLH transcription factor mediates trans-activation of the SeFAD2 gene promoter through binding to E- and G-box elements. Plant Mol Biol 64:453–466. doi:10.1007/s11103-007-9165-8
Kumar GM, Mamidala P, Podile AR (2009) Regulation of Polygalacturonase-inhibitory proteins in plants is highly dependent on stress and light responsive elements. Plant Omics 2:238–249. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap
Lan Y, Cai D, Zheng YZ (2005) Expression in Escherichia coli of three different soybean late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) genes to investigate enhanced stress tolerance. J Integr Plant Biol 47:613–621
Li XS, Zhang DY, Li HY, Wang YC, Zhang YM, Wood AY (2014) EsDREB2B, a novel truncated DREB2-type transcription factor in the desert legume Eremosparton songoricum, enhances tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses in yeast and transgenic tobacco. BMC Plant Biol 14:44. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-14-44
Liang Y, Xiong ZY, Zheng JX, Xu DY, Zhu ZY, Xiang J, Gan JP, Raboanatahiry N, Yin YT, Li MT (2016) Genome-wide identification, structural analysis and new insights into late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) gene family formation pattern in Brassica napus. Sci Rep 6:24265. doi:10.1038/srep24265
Ling J, Jiang WJ, Zhang Y, Yu HJ, Mao ZC, Gu XF, Huang SW, Xie BY (2011) Genome-wide analysis of WRKY gene family in Cucumis sativus. BMC Genom 12:471. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-471
Liu GB, Xu H, Zhang L, Zheng YZ (2011) Fe binding properties of two soybean (Glycine max L.) LEA4 proteins associated with antioxidant activity. Plant Cell Physiol 52:994–1002. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcr052
Liu Y, Wang L, Xing X, Sun L, Pan J, Kong X, Zhang M, Li D (2013) ZmLEA3, a multifunctional Group 3 LEA protein from maize (Zea mays L.), is involved in biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Physiol 54:944–959. doi:10.1093/pcp/pct047
Liu AL, Yu Y, Li RT, Duan XB, Zhu D, Sun XL, Duanmu HZ, Zhu YM (2015) A novel hybrid proline-rich type gene GsEARLI17 from Glycine soja participated in leaf cuticle synthesis and plant tolerance to salt and alkali stresses. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 121:633–646. doi:10.1007/s11240-015-0734-2
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408 doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Luo K, Zhang GF, Deng W, Luo FT, Qiu K, Pei Y (2008) Functional characterization of a cotton late embryogenesis-abundant D113 gene promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Rep 27:707–717. doi:10.1007/s00299-007-0482-9
Ma J, Li MY, Wang F, Tang J, Xiong AS (2015) Genome-wide analysis of Dof family transcription Factors and their responses to abiotic stresses in Chinese cabbage. BMC Genom 16:33. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-47
Maiti S, Patro S, Pal A, Dey N (2015) Identification of a novel salicylic acid inducible endogenous plant promoter regulating expression of CYR1, a CC-NB-LRR type candidate disease resistance gene in Vigna mungo. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 120:489–505. doi:10.1007/s11240-014-0616-z
Pan Y, Ma X, Liang H, Zhao Q, Zhu D, Yu J (2015) Spatial and temporal activity of the foxtail millet (Setaria italica) seed-specific promoter pF128. Planta 241:57–67. doi:10.1007/s00425-014-2164-5
Pedrosa AM, Martins CdeP, Gonçalves LP, Costa MG (2015) Late embryogenesis abundant (lea) constitutes a large and diverse family ofproteinsinvolved in development and abiotic stress responses in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis L. Osb.). PLoS ONE 10(12):e0145785. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0145785
Phan TT, Sun B, Niu JQ, Tan QL, Li J, Yang LT, Li YR (2016) Over expression of sugarcane gene SoSnRK2.1 confers drought tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Rep 35:1891–1905. doi:10.1007/s00299-016-2004-0
Reddy PS, Reddy GM, Pandey P, Chandrasekhar K, Reddy MK (2012) Cloning and molecular characterization of a gene encoding late embryogenesis abundant protein from Pennisetum glaucum: protection against abiotic stresses. Mol Biol Rep 39:7163–7174. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-1548-5
Sahoo DK, Sarkar S, Raha S, Maiti IB, Dey N (2014) Comparative analysis of synthetic DNA promoters for high-level gene expression in plants. Planta 240:855–875. doi:10.1007/s00425-014-2135-x
Shih MD, Hsieh TY, Jian WT, Wu MT, Yang SJ, Hoekstra FA, Hsing YI (2012) Functional studies of soybean (Glycine max L.) seed LEA proteins GmPM6, GmPM11, and GmPM30 by CD and FTIR spectroscopy. Plant Sci 196:152–159. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.07.012
Shinde S, Shinde R, Downey F, Ng CK (2013) Abiotic stress-induced oscillations in steady-state transcript levels of Group 3 LEA protein genes in the moss, Physcomitrella patens. Plant Signal Behav 8:e22535. doi:10.4161/psb.22535
Su L, Zhao CZ, Bi YP, Wan SB, Xia H, Wang XJ (2011) Isolation and expression analysis of LEA genes in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). J Biosci 36:223–228. doi:10.1007/s12038-011-9058-5
Sunkara S, Bhatnagar-Mathur P, Sharma KK (2014) Isolation and functional characterization of a novel seed-specific promoter region from peanut. App Biochem Biotechnol 172:325–339. doi:10.1007/s12010-013-0482-x
Swire-Clark GA, Marcotte WR Jr (1999) The wheat LEA protein Em functions as an osmo protective molecule in Saccahromyces cerevisiae. Plant Mol Biol 39:117–128. doi:10.1023/A:1006106906345
Tanaka S, Ikeda K, Miyasaka H (2004) Isolation of a new member of group 3 late embryogenesis abundant protein gene from a halo tolerant green alga by a functional expression screening with cyanobacterial cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett 236:41–45. doi:10.1016/j.femsle
Tiwari V, Chaturvedi AK, Mishra A, Jha B (2014) The transcriptional regulatory mechanism of the peroxisomal ascorbate peroxidase (pAPX) gene cloned from an extreme halophyte, Salicornia brachiata. Plant Cell Physiol 55:201–217. doi:10.1093/pcp/pct172
Wang YW, Wang WC, Jin SH, Wang J, Wang B, Hou BK (2012) Over-expression of a putative poplar glycosyltransferase gene, PtGT1, in tobacco increases lignin content and causes early flowering. J Exp Bot 63(7):2799–2808. doi:10.1093/jxb/ers001
Wei ZG, Qu ZS, Zhang LJ, Zhao SJ, Bi ZH, Ji XH, Wang XW, Wei HR (2015) Over expression of poplar xylem sucrose synthase in tobacco leads to a thickened cell wall and increased height. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0120669. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0120669
Xie CJ, Zhang BB, Wang D, Kou F, Zhao X, Yang X (2011) Molecular cloning and characterization of an achene-seed-specific promoter from motherwort (Leonurus japonicus Houtt). Biotechnol Lett 33:167–172. doi:10.1007/s10529-010-0392-8
Xu MY, You JF, Hou NN, Zhang HM, Chen G, Yang ZM (2010) Mitochondrial enzymes and citrate transporter contribute to the aluminium-induced citrate secretion from soybean (Glycine max) roots. Funct Plant Biol 37:285–295. doi:10.1071/FP09223
Yin G, Xu H, Liu J, Gao C, Sun J, Yan Y, Hu Y (2014) Screening and identification of soybean seed-specific genes by using integrated bioinformatics of digital differential display, microarray, and RNA-seq data. Gene 546:177–186. doi:10.1016/j.gene
Zavallo D, Lopez Bilbao M, Hopp HE, Heinz R (2010) Isolation and functional Characterization of two novel seed-specific promoters from sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Plant Cell Rep 29:239–248. doi:10.1007/s00299-010-0816-x
Zhai Y, Shao SL, Sha W, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Ren WW, Zhang C (2017) Over expression o soybean GmERF9 enhances the tolerance to drought and cold in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 128:607–618. doi:10.1007/s11240-016-1137-8
Zhang J, Martin JM, Beecher B, Morris CF, Hannah LC, Giroux MJ (2009) Seed-specific expression of the wheat puroindoline genes improves maize wet milling yields. Plant Biotechnol J 7(8):733–743. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7652.2009
Zhao P, Liu F, Ma M, Gong J, Wang Q, Jia P, Zheng G, Liu H (2011) Over expression of AtLEA3-3 confers resistance to cold stress in Escherichia coli and provides enhanced osmotic stress tolerance and ABA sensitivity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Biol (Mosk) 45:851–862. doi:10.1134/S0026893311050165
Zhao Y, Shao SL, Li XW, Zhai Y, Zhang QL, Qian DD, Wang QY (2012) Isolation and activity analysis of a seed-abundant soyAP1 gene promoter from soybean. Plant Mol Biol Report 30:1400–1407. doi:10.1007/s11105-012-0441-7
Zheng TC, Li S, Zang LN, Dai LJ, Yang CP, Qu GZ (2014) Over expression of Two PsnAP1 Genes from Populus simonii × P. nigra causes early flowering in transgenic tobacco and Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 9(10):e111725. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111725
Zou YD, Hong R, He S, Liu GB, Huang ZB, Zheng YZ (2011) Polyproline II structure is critical forthe enzyme protective function of soybean Em (LEA1) conserved domains. Biotechnol Lett 33:1667–1673. doi:10.1007/s10529-011-0602-z
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang province (C201458), Government talent training program (UNPYSCT-2016090), National Nature Science Foundation (31570207), Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang province (ZD201408) and National Nature Science Foundation (31301335).
Author contributions
Conceived and designed the overall study -YZ, WS, YW; performed experiments -YZ, YW, LQ, YZ, YZ, MJZ; analyzed the data -YZ, WS, YZ; wrote the manuscript -YZ, WS, LQ, YZ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Sergio J Ochatt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, Q. et al. Cloning of a new LEA1 gene promoter from soybean and functional analysis in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 130, 379–391 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1234-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1234-3