Abstract
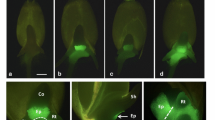
The soybean encounters severe root-related biotic and abiotic stresses causing extensive yield losses annually. The use of a root-specific promoter to confer expression of genes in a targeted manner has the potential to benefit the genetic improvement of the soybean. Several tonoplast intrinsic protein genes (TIPs) in plants like tobacco, strawberry, tomato, maize, pine, have been identified exhibiting root-specific expression. To explore the possibility of root-specific gene and promoter utilizations in soybean, we cloned soybean GmTIP and the upstream promoter sequence from soybean, and examined the expression patterns and promoter activity. Fluorometric GUS assays revealed that the GUS activity was obviously higher in roots than in leaves in transgenic Arabidopsis, regardless of the length of the promoter fragment. Weak GUS expression was found in other organs except root in transgenic Arabidopsis with the GmTIPp-2054 construct. Deletion analysis of the GmTIP promoter displayed that it still keep root-specific expression and can also be induced by various factors, such as methyl jasmonate, salicylic acid, abscisic acid, gibberellins acid, indole-3-acetic acid, NaCl, and PEG6000. This study provides a useful tool for soybean root improvement by genetic engineering.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam I, Sharmin SA, Kim KH, Yang JK, Choi MS, Lee BH (2010) Proteome analysis of soybean roots subjected to short-term drought stress. Plant Soil 333:491–505
Bhullar S, Chakravarthy S, Advani S, Datta S, Pental D, Burma PK (2003) Strategies for development of functionally equivalent promoters with minimum sequence homology for transgene expression in plants: cis-elements in a novel DNA context versus domain swapping. Plant Physiol 132:988–998
Bogusz D, Llewellyn DJ, Craig S, Dennis ES, Appleby CA, Peacock JW (1990) Non legume haemoglobin genes retain organ-specific expression in heterologous transgenic plants. Plant Cell 2:633–641
Boursiac Y, Chen S, Luu DT, Sorieul M, van den Dries N, Maurel C (2005) Early effects of salinity on water transport in Arabidopsis roots. Molecular and cellular features of aquaporin expression. Plant Physiol 139:790–805
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cao D, Hou W, Liu W, Yao W, Wu C, Liu X, Han T (2011) Overexpression of TaNHX2 enhances salt tolerance of ‘composite’ and whole transgenic soybean plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 107:541–552
Charrier B, Scollan C, Ross S, Zubko E, Meyer P (2000) Co-silencing of homologous transgenes in tobacco. Mol Breed 6:407–419
Chaumont F, Barrieu F, Wojcik E, Chrispeels MJ, Jung R (2001) Aquaporins constitute a large and highly divergent protein family in maize. Plant Physiol 125:1206–1215
Chrispeels MJ, Maurel C (1994) Aquaporins: the molecular basis of facilitated water movement through living plant cells. Plant Physiol 105:9–13
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Conkling MA, Cheng CL, Yamamoto YT, Goodman HM (1990) Isolation of transcriptionally regulated root-specific genes from tobacco. Plant Physiol 93:1203–1211
Fang RX, Nagy F, Sivasubramaniam S, Chua NH (1989) Multiple cis-regulatory elements for maximal expression of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter in transgenic plants. Plant Cell 1:141–150
Hartman GL, West ED, Herman TK (2011) Crop that feed the World 2. Soybean—worldwide production, use, and constraints caused by pathogens and pests. Food Secur 3:5–17
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999) Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA element (PLACE) database. Nucleic Acids Res 27:297–300
James C (2013) Status of commercialized biotech/GM crops: 2013. No. 46. ISAAA: Ithaca
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Report 5:387–405
Kaldenhoff R, Fisher M (2006) Functional aquaporin diversity in plants. BBA Biomembranes 1758:1134–1141
Kirch HH, Vera-Estrella R, Golldack D, Quigley F, Michalowski CB, Barka BJ, Bohnert HJ (2000) Expression of water channel proteins in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Plant Physiol 123:111–124
Koenning SR, Wrather JA (2010) Suppression of soybean yield potential in the continental United States from plant diseases estimated from 2006 to 2009. Plant Health Prog. doi:10.1094/PHP-2010-1122-01-RS
Lescot M, De′hais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouz P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327
Li DD, Tai FJ, Zhan ZT, Li Y, Zheng Y, Wu YF, Li XB (2009) A cotton gene encodes a tonoplast aquaporin that is involved in cell tolerance to cold stress. Gene 438:26–32
Li Y, Sun Y, Yang Q, Kang J, Zhang T, Gruber MY, Fang F (2012) Cloning and function analysis of an alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) zinc finger protein promoter MsZPP. Mol Biol Rep 39:8559–8569
Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AKM (2003) Root-specific expression of a western white pine PR10 gene is mediated by different promoter region in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 52:102–120
Liu S, Kandoth PK, Warren SD, Yeckel G, Heinz R, Alden J, Yang C, Jamai A, EI-Mellouki T, Juvale PS, Hill J, Baum TJ, Cianzio S, Whitham SA, Korkin D, Mitchum MG, Meksem K (2012) A soybean cyst nematode resistance gene points to a new mechanism of plant resistance to pathogens. Nature 492:256–260
Lopez F, Bousser A, Sissoëff I, Hoarau J, Mahé A (2004) Characterization in maize of ZmTIP2-3, a root-specific tonoplast intrinsic protein exhibiting aquaporin activity. J Exp Bot 55:539–541
Mahajan S, Tuteja N (2005) Cold, salinity and drought stresses: an overview. Arch Biochem Biophys 444:139–158
Martínez-Ballesta MC, Diaz R, Martínez V, Carvajal M (2003) Different blocking effects of HgCl2 and NaCl on aquaporins of pepper plants. J Plant Physiol 160:1487–1492
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:493–497
Nan L, Lin H, Guan Y, Chen F (2002) Functional analysis of cis-acting sequences regulating root-specific expression in transgenic tobacco. Chin Sci Bull 47:1441–1445
Powles S (2010) Gene amplification delivers glyphosate-resistant weed evolution. PNAS 107:955–956
Sarda X, Tousch D, Ferrare K, Cellier F, Alcon C, Dupuis JM, Casse F, Lamaze T (1999) Characterization of closely related delta-TIP genes encoding aquaporins which are differentially expressed in sunflower roots upon water deprivation through exposure to air. Plant Mol Biol 40:179–191
Schäffner AR (1998) Aquaporin function, structure, and expression: are there more surprises to surface in water relation? Planta 204:131–139
Vaughan SP, James DJ, Lindesy K, Massiah AJ (2006) Characterization of FaRB7, a near root-specific gene from strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) and promoter activity analysis in homologous and heterologous hosts. J Exp Bot 57:3901–3910
Wang Z, Huang B (2004) Physiological recovery of Kentucky bluegrass from simultaneous drought and heat stress. Crop Sci 44:1729–1736
Wang X, Eggenberger AL, Nutter FW Jr, Hill JH (2001) Pathogen-derived transgenic resistance to soybean mosaic virus in soybean. Mol Breed 8:119–127
Wang X, Li Y, Ji W, Bai X, Cai H, Zhu D, Sun XL, Chen LJ, Zhu YM (2011) A novel Glycine soja tonoplast intrinsic protein gene responds to abiotic stress and depresses salt and dehydration tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Physiol 168:1241–1248
Xu L, Ye RJ, Zheng YS, Wang ZK, Zhou P, Lin YJ, Li DD (2010a) Isolation of the endosperm-specific LPAAT gene promoter from coconut (Cocosnucifera L.) and its functional analysis in transgenic rice plants. Plant Cell Rep 29:1061–1068
Xu XB, Guo S, Chen K, Song HM, Liu JJ, Guo LB, Qian Q, Wang HZ (2010b) A 796 bp PsPR10 gene promoter fragment increased root-specific expression of the GUS reporter gene under the abiotic stresses and signal molecules in tobacco. Biotechnol Lett 32:1533–1539
Yamamoto YT, Cheng CL, Conkling MA (1990) Root-specific genes from tobacco and Arabidopsis homologous to an evolutionarily conserved gene family of membrane channel proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 18:7449
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our thanks to Professor Pedro S.C.F. Rocha for his gift of the pC13P1 and pC13(Delt)GUS vectors. This project was supported by the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-04), the Major Science and Technology Projects of China (2013ZX08010-004), and the CAAS Innovation Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Jiang, B., Wu, C. et al. The characterization of GmTIP, a root-specific gene from soybean, and the expression analysis of its promoter. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 121, 259–274 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0682-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0682-2