Abstract
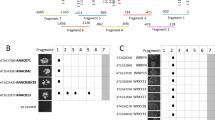
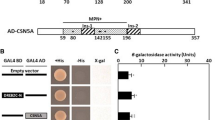
Microsomal oleic acid desaturase (FAD2) catalyzes the first extra-plastidial desaturation in plants, converting oleic acid to linoleic acid, which is a major constituent in all cellular membranes as well as in seed storage oils. Seed-specific FAD2 (SeFAD2) produced 40% of linoleic acids in the total fatty acids of sesame (Sesamum indicum) seeds. The expression of SeFAD2 transcripts was spatially and temporally controlled during seed development. To investigate the regulatory mechanism controlling seed-specific SeFAD2 expression, we isolated a well-matched sequence homologous to the basic region/helix-loop-helix proteins by yeast one-hybrid screening and named it SebHLH. SebHLH transcripts were expressed in developing seeds and roots of sesame. SebHLH:GFP fusion protein localized in the nucleus. Recombinant SebHLH protein bound E-box (CANNTG) and G-box (CACGTG) elements in the region from −179 to −53 of the SeFAD2 gene promoter, and the external C and G nucleotides in the E- and G-box motifs were essential for SebHLH protein binding. The SebHLH gene, under the CaMV35S promoter, and the GUS reporter gene driven by E- and G-box motifs were co-expressed in developing sesame seeds and Arabidopsis transgenic leaves. This co-expression demonstrated that SebHLH protein mediates transactivation of the SeFAD2 gene promoter through binding to E- and G-box elements. E- or G-box elements frequently occur in the 5′-flanking region of genes that are involved in triacylglycerol biosynthesis and that exhibit seed-specific expression in Arabidopsis and other plants, suggesting that bHLH transcription factors play a key role in the transcriptional regulation of genes related to storage lipid biosynthesis and accumulation during seed development.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Urao T, Iwasaki T, Hosokawa D, Shinozaki K (1997) Role of Arabidopsis MYC and MYB homologs in drought- and abscisic acid-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 9:1859–1868
Abe H, Urao T, Ito T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 15:63–78
An G (1987) Binary Ti vectors for plant transformation and promoter analysis. Methods Enzymol 153:292–305
Atchley WR, Terhalle W, Dress A (1999) Positional dependence, cliques, and predictive motifs in the bHLH protein domain. J Mol Evol 48:501–516
Bao X, Katz S, Pollard M, Ohlrogge JB (2002) Carboxylic fatty acids in plants: biochemical and molecular genetic characterization of cyclopropane fatty acid synthesis of Sterculia foetida. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7172–7177
Beisson F, Koo AJ, Ruuska S, Schwender J, Pollard M, Thelen JJ, Paddock T, Salas JJ, Savage L, Milcamps A, Mhaske VB, Cho Y, Ohlrogge JB (2003) Arabidopsis genes involved in acyl lipid metabolism. A 2003 census of the candidates, a study of the distribution of expressed sequence tags in organs, and a web-based database. Plant Physiol 132:681–697
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantization of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Breeden L, Nasmyth K (1985) Regulation of the yeast HO gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 50:643–650
Cahoon EB, Shanklin J, Ohlrogge JB (1992) Expression of a coriander desaturase results in petroselinic acid production in transgenic tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:11184–11188
Cahoon EB, Ripp KG, Hall SE, McGonigle B (2002) Transgenic production of epoxy fatty acids by expression of a cytochrome P450 enzyme from Euphorbia lagascae seed. Plant Physiol 128:615–624
Chinnusamy V, Ohta M, Kanrar S, Lee BH, Hong X, Agarwal M, Zhu JK (2003) ICE1: a regulator of cold-induced transcriptome and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 17:1043–1054
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Crowe AJ, Abenes M, Plant A, Moloney MM (2000) The seed-specific transactivator, ABI3, induces oleosin gene expression. Plant Sci 151:171–181
Davis SJ, Vierstra RD (1998) Soluble, highly fluorescent variants of green fluorescent protein (GFP) for use in higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 36:521–528
Drysdale CM, Dueñas E, Jackson BM, Reusser U, Braus GH, Hinnebusch AG (1995) The transcriptional activator GCN4 contains multiple activation domains that are critically dependent on hydrophobic amino acids. Mol Cell Biol 15:1220–1233
Ellenberger T, Fass D, Arnaud M, Harrison SC (1994) Crystal structure of transcription factor E47: E-box recognition by a basic region helix-loop helix dimer. Genes Dev 8:970–980
Ferre-D’Amare AR, Pognonec P, Roeder RG, Burley SK (1994) Structure and function of the b/HLH/Z domain of USF. EMBO J 13:180–189
Fuji Y, Shimizu T, Toda T, Yaganida M, Hakoshima T (2000) Structural basis for the diversity of DNA recognition by bZip transcription factors. Nat Struct Biol 7:889–893
Goodrich J, Carpenter R, Coen ES (1992) A common gene regulates pigmentation pattern in diverse plant species. Cell 68:955–964
Heppard EP, Kinney AJ, Stecca KL, Miao GH (1996) Developmental and growth temperature regulation of two different microsomal ω-6 desaturase genes in soybeans. Plant Physiol 110:311–319
Jans DA (1995) The regulation of protein transport to the nucleus by phosphorylation. Biochem J 311:705–716
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusion: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Jin UH, Lee JW, Chung YS, Lee JH, Yi YB, Kim YK, Hyung NI, Pyee JH, Chung CH (2001) Characterization and temporal expression of a ω-6 fatty acid desaturase cDNA from sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) seeds. Plant Sci 161:935–941
Kawagoe Y, Murai N (1996) A novel basic region/helix-loop-helix protein binds to a G-box motif CACGTG of the bean storage protein b-phaseolin gene. Plant Sci 116:47–57
Kim MJ, Shin JS, Kim JK, Suh MC (2005) Genomic structures and characterization of the 5′-flanking regions of acyl carrier protein and Δ4-palmitoyl-ACP desaturase genes from Coriandrum sativum. Biochim Biophys Acta 1730:235–244
Kim MJ, Kim HJ, Shin JS, Chung CH, Ohlrogge JB, Suh MC (2006) Seed-specific expression of sesame microsomal oleic acid desaturase is controlled by combinatorial properties between negative cis-regulatory elements in the SeFAD2 promoter and enhancers in the 5′UTR intron. Mol Genet Genomics 276:351–368
Kinney AJ (1994) Genetic modification of the storage lipids of plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol 5:144–151
Kinney AJ (1996) Development of genetically engineered soybeans for food applications. J Food Lipids 3:273–292
Kinney AJ, Cahoon EB, Hitz WD (2002) Manipulating desaturase activities in transgenic crop plants. Biochem Soc Trans 30:1099–1103
Klein TM, Fromm M, Weissinger A, Tomas D, Schaaf S, Sletten K, Sanford JC (1988) Transfer of foreign genes into intact maize cells with high-velocity microprojectiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4305–4309
Ledent V, Vervoort M (2001) The basic helix-loop-helix protein family: comparative genomics and phylogenetic analysis. Genome Res 11:754–770
Li X, Duan X, Jiang H, Sun Y, Tang Y, Yuan Z, Guo J, Liang W, Chen L, Yin J, Ma H, Wang J, Zhang D (2006) Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 141:1167–1184
Littlewood TD, Evan GI (1998) Basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Liu Q, Singh S, Green A (2000) Genetic modification of cotton seed oil using inverted-repeat gene-silencing techniques. Biochem Soc Trans 28:927–929
Ludwig SR, Habera LF, Dellaporta SL, Wessler SR (1989) Lc, a member of the maize R gene family responsible for tissue-specific anthocyanin production, encodes a protein similar to transcriptional activators and contains the myc homology region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7092–7096
Ma PCM, Rould MA, Weintraub H, Pabo CO (1994) Crystal structure MyoD bHLH domain-DNA complex: perspectives on DNA recognition and implications for transcriptional activation. Cell 77:451–450
Maruyama I, Rakow TL, Maruyama HI (1995) cRACE: a simple method for identification of the 5′-end of mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 23:3796–3797
Massari ME, Murre C (2000) Helix-loop-helix proteins: regulators of transcription in eukaryotic organisms. Mol Cell Biol 20:429–440
Moon H, Smith MA, Kunst L (2001) A condensing enzyme from the seeds of Lesquerella fendleri that specifically elongates hydroxy fatty acids. Plant Physiol 127:1635–1643
Murre C, McCaw PS, Baltimore D (1989) A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell 56:777–783
Nair SK, Burley SK (2000) Functional genomics: recognizing DNA in the library. Nature 404:715–718
Okuley J, Lightner J, Feldmann K, Yadav N, Lark E, Browse J (1994) Arabidopsis FAD2 gene encodes the enzyme that is essential for polyunsaturated lipid synthesis. Plant Cell 6:147–158
Pirtle IL, Kongcharoensuntorn W, Nampaisansuk M, Knesek JD, Chapman KD, Pirtle RM (2001) Molecular cloning and functional expression of the gene for a cotton Δ-12 fatty acid desaturase (FAD2). Biochim Biophys Acta 1522:122–129
Radicella JP, Turks D, Chandler VL (1991) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA encoding B-Peru, a regulatory protein of the anthocyanin pathway in maize. Plant Mol Biol 17:127–130
Regier JL, Shen F, Triezenberg SJ (1993) Pattern of aromatic and hydrophobic amino acids critical for one of two subdomains of the VP16 transcriptional activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:883–887
Rossak M, Smith M, Kunst L (2001) Expression of the FAE1 gene and FAE1 promoter activity in developing seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 46:717–725
Shanklin J, Cahoon EB (1998) Desaturation and related modifications of fatty acids. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:611–641
Shimizu T, Toumoto A, Ihara K, Shimizu M, Kyogoku Y, Ogawa N, Oshima Y, Hakoshima T (1997) Crystal structure of PHO4 bHLH domain-DNA complex: flanking base recognition. EMBO J 16:4689–4697
Slocombe SP, Cummins I, Paul Jarvis R, Murphy DJ (1992) Nucleotide sequence and temporal regulation of a seed-specific Brassica napus cDNA encoding a stearoyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) desaturase. Plant Mol Biol 20:151–155
Somerville C, Browse J, Jaworski JG, Ohlrogge J (2000) Lipids. In: Buchanan B, Gruissem W, Jones R (eds) Biochemistry & molecular biology of plants. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockville, pp 456–527
Suh MC, Schultz DJ, Ohlrogge JB (1999) Isoforms of acyl carrier protein involved in seed-specific fatty acid synthesis. Plant J 17:679–688
Suh MC, Kim MJ, Hur C-G, Bae JM, Park YI, Kang C-W, Ohlrogge JB (2003) Comparative analysis of expressed sequence tags from Sesamum indicum and Arabidopsis thaliana developing seeds. Plant Mol Biol 52:1107–1123
Tang GQ, Novitzky WP, Carol Griffin H, Huber SC, Dewey RE (2005) Oleate desaturase enzymes of soybean: evidence of regulation through differential stability and phosphorylation. Plant J 44:433–446
Toledo-Ortiz G, Huq E, Quail PH (2003) The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 15:1749–1770
Triezenberg SJ (1995) Structure and function of transcriptional activation domains. Curr Opin Genetics Dev 5:190–196
Urao T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Urao S, Shinozaki K (1993) An Arabidopsis myb homolog is induced by dehydration stress and its gene product binds to the conserved MYB recognition sequence. Plant Cell 5:1529–1539
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Kyung Hee Paek for providing the pCAMBIA 1305.1 vector containing the minimal CaMV35S promoter and the NOS terminator and Sung Han Ok for helpful discussion about yeast one-hybrid screening. This work was supported by grants from the Agricultural Plant Stress Research Center (R11-2001-0920301-0) and the Interdisciplinary Research Program (R01-2006-000-11056-0) of the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence of the SebHLH cDNA from Sesamum indicum reported here has been registered in the GenBankTM/EBI Data Bank under accession number EF397568.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.J., Kim, JK., Shin, J.S. et al. The SebHLH transcription factor mediates trans-activation of the SeFAD2 gene promoter through binding to E- and G-box elements. Plant Mol Biol 64, 453–466 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9165-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9165-8