Abstract
Main conclusion
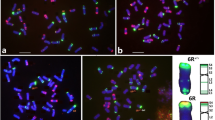
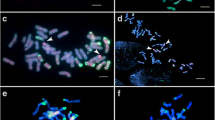
New wheat- Secale africanum chromosome 5R a substitution and translocation lines were developed and identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization and molecular markers, and chromosome 5R a specific genes responsible for grain hardness were isolated.
The wild species, Secale africanum Stapf. (genome RaRa), serves as a valuable germplasm resource for increasing the diversity of cultivated rye (S. cereale L., genome RR) and providing novel genes for wheat improvement. In the current study, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and molecular markers were applied to characterize new wheat–S. africanum chromosome 5Ra derivatives. Labeled rye genomic DNA (GISH) and the Oligo-probes pSc119.2 and pTa535 (FISH) were used to study a wheat–S. africanum amphiploid and a disomic 5Ra (5D) substitution, and to identify a T5DL.5RaS translocation line and 5RaS and 5RaL isotelosome lines. Twenty-one molecular markers were mapped to chromosome 5Ra arms which will facilitate future rapid identification of 5Ra introgressions in wheat backgrounds. Comparative analysis of the molecular markers mapped on 5Ra with homoeologous regions in wheat confirmed a deletion on the chromosome T5DL.5RaS, which suggests that the wheat–S. africanum Robertsonian translocation involving homologous group 5 may not be fully compensating. Complete coding sequences at the paralogous puroindoline-a (Pina) and grain softness protein gene (Gsp-1) loci from S. africanum were cloned and localized onto the short arm of chromosome 5Ra. The S. africanum chromosome 5Ra substitution and translocation lines showed a reduction in the hardness index, which may be associated with the S. africanum- specific Pina and Gsp-1 gene sequences. The present study reports the production of novel wheat–S. africanum chromosome 5Ra stripe rust resistant derivatives and new rye-specific molecular markers, which may find application in future use of wild Secale genome resources for grain quality studies and disease resistance breeding.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bariana HS, McIntosh RA (1993) Cytogenetic studies in wheat. XV. Location of rust resistance genes in VPM1 and their genetic linkage with other disease resistance genes in chromosome 2A. Genome 36:476–482
Bartos B (1993) Chromosome 1R of rye in wheat breeding. Plant Breed Abstr 63:1203–1211
Bhave M, Morris CF (2008a) Molecular genetics of puroindolines and related genes: allelic diversity in wheat and other grasses. Plant Mol Biol 66:205–219
Bhave M, Morris CF (2008b) Molecular genetics of puroindolines and related genes: regulation of expression, membrane binding properties and applications. Plant Mol Biol 66:221–231
Cuacos M, González-García M, González-Sánchez M, Puertas MJ, Vega JM (2011) Activation of rye 5RL neocentromere by an organophosphate pesticide. Cytogenet Genome Res 134(2):151–162
Cuadrado A, Jouve N (2002) Evolutionary trends of different repetitive DNA sequences during speciation in the genus Secale. J Hered 93:339–345
Devos KM, Atkinson MD, Chinoy CN, Francis HA, Harcourt RL, Koebner RMD, Liu CJ, Masojc P, Xie DX, Gale MD (1993) Chromosomal rearrangements in the rye genome relative to that of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 85:673–680
Escobar JS, Scornavacca C, Cenci A, Guilhaumon C, Santoni S, Douzery EJ, Ranwez V, Glémin S, David J (2011) Multigenic phylogeny and analysis of tree incongruences in Triticeae (Poaceae). BMC Evol Biol 11:181
Fu S, Chen L, Wang Y, Li M, Yang Z, Qiu L, Yan B, Ren Z, Tang Z (2015) Oligonucleotide probes for ND-FISH analysis to identify rye and wheat chromosomes. Sci Rep 5:10552
Geng H, Beecher BS, He Z, Kiszonas AM, Morris CF (2012) Prevalence of puroindoline D1 and puroindoline b-2 variants in US Pacific Northwest wheat breeding germplasm pools, and their association with kernel texture. Theor Appl Genet 124:1259–1269
Guzman C, Caballero L, Martin MA, Alvarez JB (2012) Molecular characterization and diversity of the Pina and Pinb genes in cultivated and wild diploid wheat. Mol Breed 30:69–78
Hammer K, Khoshbakht K (2005) Towards a ‘red list’ for crop plant species. Genet Resour Crop Evol 52:249–265
Heslop-Harrison JS, Schwarzacher T (2011) Organization of the plant genome in chromosomes. Plant J 66:18–33
Ishikawa G, Nakamura T, Ashida T, Saito M, Nasuda S, Endo T, Wu J, Matsumoto T (2009) Localization of anchor loci representing five hundred annotated rice genes to wheat chromosomes using PLUG markers. Theor Appl Genet 118:499–514
Jiang HR, Dai DQ, Sun DF (1992) Creation of special germplasm resources in Triticum. J Sichuan Agric Univ 10:255–259 (in Chinese)
Khush GS, Stebbins GL (1961) Cytogenetic and evolutionary studies in Secale, I. Some new data on the ancestry of S. cereale. Am J Bot 48:723–730
Lei MP, Li GR, Zhang SF, Liu C, Yang ZJ (2011) Molecular cytogenetic characterization of a new wheat-Secale africanum 2Ra(2D) substitution line for resistant to stripe rust. J Genet 90:283–287
Lei MP, Li GR, Liu C, Yang ZJ (2012) Characterization of new wheat-Secale africanum derivatives reveals evolutionary aspects of chromosome 1R in rye. Genome 55:765–774
Lesage VS, Merlino M, Chambon C, Bouchet B, Marion D, Branlard G (2012) Proteomes of hard and soft near-isogenic wheat lines reveal that kernel hardness is related to the amplification of a stress response during endosperm development. J Exp Bot 63:1001–1011
Li J, Endo TR, Saito M, Ishikawa G, Nakamura T, Nasuda S (2013) Homoeologous relationship of rye chromosome arms as detected with wheat PLUG markers. Chromosoma 122:555–564
Linkiewicz AM, Qi LL, Gill BS, Ratnasiri A, Echalier B, Chao S, Lazo GR, Hummel DD, Anderson OD, Akhunov ED, Dvorák J, Pathan MS, Nguyen HT, Peng JH, Lapitan NL, Miftahudin Gustafson JP, La Rota CM, Sorrells ME, Hossain KG, Kalavacharla V, Kianian SF, Sandhu D, Bondareva SN, Gill KS, Conley EJ, Anderson JA, Fenton RD, Close TJ, McGuire PE, Qualset CO, Dubcovsky J (2004) A 2500-locus bin map of wheat homoeologous group 5 provides insights on gene distribution and colinearity with rice. Genetics 168:665–676
Liu GT, Peng YL, Chen WQ, Zhang ZY (2010) First detection of virulence in Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in China to resistance genes Yr24 (= Yr26) present in wheat cultivar Chuanmai 42. Plant Dis 94:1163
Lukaszewski AJ, Gustafson JP (1987) Plant Breeding Reviews. In: Janick J (ed) Cytogenetics of triticale, vol 5. AVI Publishing, NewYork, pp 41–93
Manzanero S, Puertas MJ, Jimenez G, Vega JM (2000) Neocentric activity of rye 5RL chromosome in wheat. Chromosom Res 8:543–554
Massa AN, Morris CF (2006) Molecular evolution of the puroindoline-a, puroindoline-b, and grain softness protein-1 genes in the tribe Triticeae. J Mol Evol 63:526–536
Morris CF (2002) Puroindolines: the molecular genetic basis of wheat grain hardness. Plant Mol Biol 48:633–647
Morris CF, Geng H, Beecher BS, Ma D (2013) A review of the occurrence of grain softness protein-1 genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Mol Biol 83:507–521
Pretorius ZA, Singh RP, Wagoire WW, Payne TS (2000) Detection of virulence to wheat stem rust resistance gene Sr31 in Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici in Uganda. Plant Dis 84:203
Qi L, Echalier B, Friebe B, Gill BS (2003) Molecular characterization of a set of wheat deletion stocks for use in chromosome bin mapping of ESTs. Funct Integr Genom 3:39–55
Quraishi UM, Abrouk M, Bolot S, Pont C, Throude M, Guilhot N, Confolent C, Bortolini F, Praud S, Murigneux A, Charmet G, Salse J (2009) Genomics in cereals: from genome-wide conserved orthologous set (COS) sequences to candidate genes for trait dissection. Funct Integr Genom 9:473–484
Rabinovich SV (1998) Importance of wheat–rye translocations for breeding modern cultivars of Triticum aestivum L. Euphytica 100:323–340
Silkova OG, Leononva IN, Krasilova NM, Dubovets NI (2011) Preferential elimination of chromosome 5R of rye in the progeny of 5R5D dimonosomics. Genetika 47:1064–1072
Tang ZX, Ross K, Ren ZL, Yang ZJ, Zhang HY, Chikmawati T, Miftahudin, Gustafson JP (2011) Wild crop relatives: genomic and breeding resources cereals. In: Kole C (ed) Wealth of wild species: role in plant genome elucidation and improvement—Secale. Springer, Newyork, pp 367–395
Tang Z, Yang Z, Fu S (2014) Oligonucleotides replacing the roles of repetitive sequences pAs1, pSc119.2, pTa-535, pTa71, CCS1, and pAWRC.1 for FISH analysis. J Appl Genet 55:313–318
Turnbull KM, Turner M, Mukai Y, Yamamoto M, Morell MK, Appels R, Rahman S (2003) The organization of genes tightly linked to the Ha locus in Aegilops tauschii, the D-genome donor to wheat. Genome 46:330–338
Turner M, Mukai Y, Leroy P, Charef B, Appels R, Rahman S (1999) The Ha locus of wheat: identification of a polymorphic region for tracing grain hardness in crosses. Genome 42:1242–1250
Wilkinson MD, Castells-Brooke N, Shewry PR (2013) Diversity of sequences encoded by the Gsp-1 genes in wheat and other grass species. J Cereal Sci 57:1–9
Xue S, Zhang Z, Lin F, Kong Z, Cao Y, Li C, Yi H, Mei M, Zhu H, Wu J, Xu H, Zhao D, Tian D, Zhang C, Ma Z (2008) A high-density intervarietal map of the wheat genome enriched with markers derived from expressed sequence tags. Theor Appl Genet 117:181–189
Yanaka M, Takata K, Terasawa Y, Ikeda TM (2011) Chromosome 5H of Hordeum species involved in reduction in grain hardness in wheat genetic background. Theor Appl Genet 123:1013–1018
Yang ZJ, Li GR, Ren ZL (2000) Identification of amphiploid between Triticum durum cv. Ailanmai native to Sichuan, China and Secale africanum. Wheat Inf Serv 91:20–24
Yang ZJ, Li GR, Ren ZL (2001) Identification of Triticum durum–Secale africanum amphiploid and its crossability with common wheat. J Genet Breed 55:45–50
Yang ZJ, Li GR, Feng J, Jiang HR, Ren ZL (2005) Molecular cytogenetic characterization and disease resistance observation of wheat-Dasypyrum breviaristatum partial amphiploid and its derivatives. Hereditas 142:80–85
Yang ZJ, Li GR, Jia JQ, Zeng X, Lei MP, Zeng ZX, Zhang T, Ren ZL (2009) Molecular cytogenetic characterization of wheat-Secale africanum amphiploids and derived introgression lines with stripe rust resistance. Euphytica 167:197–202
Zhang RQ, Cao YP, Wang XE, Feng YG, Chen PD (2010) Development and characterization of a Triticum aestivum–H. villosa T5VS·5DL translocation line with soft grain texture. J Cereal Sci 51(2):220–225
Zhang R, Wang X, Chen P (2012) Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of a small alien-segment translocation line carrying the softness genes of Haynaldia villosa. Genome 55:1–8
Zhou JP, Yang ZJ, Li GR, Liu C, Tang ZX, Zhang Y, Ren ZL (2010) Diversified chromosomal distribution of tandemly repeated sequences revealed evolutionary trends in Secale (Poaceae). Plant Syst Evol 287:49–56
Acknowledgments
We particularly thank Dr. I. Dundas at University of Adelaide, Australia, and Dr. Niaz Ali at Hazara University, Pakistan for reviewing the manuscript. We are thankful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31171542, 31101143 and 30871518) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Gao, D., La, S. et al. Characterization of wheat-Secale africanum chromosome 5Ra derivatives carrying Secale specific genes for grain hardness. Planta 243, 1203–1212 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2472-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-016-2472-z