Abstract
Based on the similarity in gene structure between rice and wheat, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based landmark unique gene (PLUG) system enabled us to design primer sets that amplify wheat genic sequences including introns. From the previously reported wheat PLUG markers, we chose 144 markers that are distributed on different chromosomes and in known chromosomal regions (bins) to obtain rye-specific PCR-based markers. We conducted PCR with the 144 primer sets and the template of the Imperial rye genomic DNA and found that 131 (91.0 %) primer sets successfully amplified PCR products. Of the 131 PLUG markers, 110 (76.4 %) markers showed rye-specific PCR amplification with or without restriction enzyme digestion. We assigned 79 of the 110 markers to seven rye chromosomes (1R to 7R) using seven wheat–rye (cv. Imperial) chromosome addition and substitution lines: 12 to 1R, 8 to 2R, 11 to 3R, 8 to 4R, 16 to 5R, 12 to 6R, and 12 to 7R. Furthermore, we located their positions on the short or long (L) chromosome arm, using 13 Imperial rye telosomic lines of common wheat (except for 3RL). Referring to the chromosome bin locations of the 79 PLUG markers in wheat, we deduced the syntenic relationships between rye and wheat chromosomes. We also discussed chromosomal rearrangements in the rye genome with reference to the cytologically visible chromosomal gaps.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFLP:
-
Amplified fragment length polymorphism
- CTAB:
-
Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tag
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- GISH:
-
Genomic in situ hybridization
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PLUG:
-
PCR-based landmark unique gene
- RAPD:
-
Random amplified polymorphic DNA
- RFLP:
-
Restriction fragment length polymorphism
- SCAR:
-
Sequence-characterized amplified region
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- STS:
-
Sequence-tagged site
References
Alkhimova A, Heslop-harrison J, Shchapova A, Vershinin AV (1999) Rye chromosome variability in wheat-rye addition and substitution lines. Chromosome Res 7:205–212
Bartoš J, Paux E, Kofler R, Havránková M, Kopecký D, Suchánková P, Šafář J, Šimková H, Town CD, Lelley T, Feuillet C, Doležel J (2008) A first survey of the rye (Secale cereale) genome composition through BAC end sequencing of the short arm of chromosome 1R. BMC Plant Biol 8:95–106
Baum M, Appels R (1991) The cytogenetic and molecular architecture of chromosome 1R-one of the most widely utilized sources of alien chromatin in wheat varieties. Chromosoma 101:1–10
Bednarek PT, Masojć P, Lewandowska R, Myśków B (2003) Saturating rye genetic map with amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. J Appl Genet 44:21–33
Bolibok H, Gruszczyńska A, Hromada-Judycka A, Rakoczy-Trojanowska M (2007) The identification of QTLs associated with the in vitro response of rye (Secale cereale L.). Cell Mol Biol Lett 12:523–535
Brunell MS, Lukaszewski AJ, Whitkus R (1999) Development of arm specific RAPD markers for rye chromosome 2R in wheat. Crop Sci 39:1702–1706
Cox DR, Lehrach H (1991) Genome mapping: PCR based meiotic and somatic cell hybrid analysis. BioEssays 13:193–198
Devos KM, Atkinson MD, Chinoy CN, Francis HA, Harcourt RL, Koebner RMD, Liu CJ, Masojć P, Xie DX, Gale MD (1993) Chromosomal rearrangements in the rye genome relative to that of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 85:673–680
Endo TR (2011) Cytological dissection of the Triticeae chromosomes by the gametocidal system. In: Birchler JA (ed) Plant chromosome engineering. Springer, New York, pp 247–258
Gale MD, Devos KM (1998) Comparative genetics in the grasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1971–1974
Gustafson JP, Ma XF, Korzun V, Snape JW (2009) A consensus map of rye integrating mapping data from five mapping populations. Theor Appl Genet 118:793–800
Gyawali YP, Nasuda S, Endo TR (2009) Cytological dissection and molecular characterization of chromosome 1R derived from ‘Burgas 2’ common wheat. Genes Genet Syst 84:407–416
Gyawali YP, Nasuda S, Endo TR (2010) A cytological map of the short arm of rye chromosome 1R constructed with 1R dissection stocks of common wheat and PCR-based markers. Cytogenet Genome Res 129:224–233
Hackauf B, Rudd S, van der Voort JR, Miedaner T, Wehling P (2009) Comparative mapping of DNA sequences in rye (Secale cereale L.) in relation to the rice genome. Theor Appl Genet 118:371–384
Haseneyer G, Schmutzer T, Seidel M, Zhou R, Mascher M, Schön CC, Taudien S, Scholz U, Stein N, Mayer KF, Bauer E (2011) From RNA-seq to large-scale genotyping-genomics resources for rye (Secale cereale L.). BMC Plant Biol 11:131
International Barley Genome Sequencing Consortium, Mayer KF, Waugh R, Brown JW, Schulman A, Langridge P, Platzer M, Fincher GB, Muehlbauer GJ, Sato K, Close TJ, Wise RP, Stein N (2012) A physical, genetic and functional sequence assembly of the barley genome. Nature 491:711–716
Ishikawa G, Yonemaru J, Saito M, Nakamura T (2007) PCR-based landmark unique gene (PLUG) markers effectively assign homoeologous wheat genes to A, B and D genomes. BMC Genomics 8:135
Ishikawa G, Nakamura T, Ashida T, Saito M, Nasuda S, Endo TR, Wu J, Matsumoto T (2009) Localization of anchor loci representing five hundred annotated rice genes to wheat chromosomes using PLUG markers. Theor Appl Genet 118:499–514
Isik Z, Parmaksiz I, Coruh C, Geylan-Su YS, Cebeci O, Beecher B, Budak H (2007) Organellar genome analysis of rye (Secale cereale) representing diverse geographic regions. Genome 50:724–734
Koebner RMD (1995) Generation of PCR-based markers for the detection of rye chromatin in a wheat background. Theor Appl Genet 90:740–745
Kofler R, Bartos J, Gong L, Stift G, Suchankova P, Simkova H, Berenyi M, Burg K, Dolezel J, Lelley T (2008) Development of microsatellite markers specific for the short arm of rye (Secale cereale L.) chromosome 1. Theor Appl Genet 117:915–926
Konieczny A, Ausubel FM (1993) A procedure for mapping Arabidopsis mutations using co-dominant ecotype-specific PCR-based markers. Plant J 4:403–410
Korzun V, Malyshev S, Kartel N, Westermann T, Weber WE, Börner A (1998) A genetic linkage map of rye (Secale cereale L.). Theor Appl Genet 96:203–208
Korzun V, Malyshev S, Voylokov AV, Börner A (2001) A genetic map of rye (Secale cereale L.) combining RFLP, isozyme, protein, microsatellite and gene loci. Theor Appl Genet 102:709–717
Krattinger S, Wicker T, Keller B (2009) Map-based cloning of genes in Triticeae (wheat and barley). In: Feuillet C, Muehlbauer GJ (eds) Plant genetics and genomics. Springer, New York, pp 337–358
Lee TG, Hong MJ, Johnson JW, Bland DE, Kim DY, Seo YW (2009) Development and functional assessment of EST-derived 2RL-specific markers for 2BS.2RL translocations. Theor Appl Genet 119:663–673
Li Y, Böck A, Haseneyer G, Korzun V, Wilde P, Schön CC, Ankerst DP, Bauer E (2011) Association analysis of frost tolerance in rye using candidate genes and phenotypic data from controlled, semi-controlled, and field phenotyping platforms. BMC Plant Biol 27:146
Loarce Y, Hueros G, Ferrer E (1996) A molecular linkage map of rye. Theor Appl Genet 93:1112–1118
Ma XF, Wanous MK, Houchins K, Rodriguez Milla MA, Goicoechea PG, Wang Z, Xie M, Gustafson JP (2001) Molecular linkage mapping in rye (Secale cereale L). Theor Appl Genet 102:517–523
Madej LJ (1996) Worldwide trends in rye growing and breeding. Vortr Pflanzenzuecht 35:1–6
Martis MM, Klemme S, Banaei-Moghaddam AM, Blattner FR, Macas J, Schmutzer T, Scholz U, Gundlach H, Wicker T, Simkova H, Novak P, Neumann P, Kubalakova M, Bauer E, Haseneyer G, Fuchs J, Dolezel J, Stein N, Mayer KFX, Houben A (2012) Selfish supernumerary chromosome reveals its origin as a mosaic of host genome and organellar sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:13343–13346
Masojć P, Myśków B, Milczarski P (2001) Extending a RFLP-based genetic map of rye using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and isozyme markers. Theor Appl Genet 102:1273–1279
Mayer KFX, Martis M, Hedley PE, Simková H, Liu H, Morris JA, Steuernagel B, Taudien S, Roessner S, Gundlach H, Kubaláková M, Suchánková P, Murat F, Felder M, Nussbaumer T, Graner A, Salse J, Endo T, Sakai H, Tanaka T, Itoh T, Sato K, Platzer M, Matsumoto T, Scholz U, Dolezel J, Waugh R, Stein N (2011) Unlocking the barley genome by chromosomal and comparative genomics. Plant Cell 23:1249–1263
McIntosh RA (1988) Catalogue of gene symbols in wheat. In: Miller TE, Koebner RMD (eds) Proc 7th Intl Wheat Genet Symp. IPSR Cambridge Laboratory, Cambridge, pp 1225–1323
Milczarski P, Banek-Tabor A, Lebiecka K, Stojałowski S, Myśków B, Masojć P (2007) New genetic map of rye composed of PCR-based molecular markers and its alignment with the reference map of the DS2 × RXL10 intercross. J Appl Genet 48:11–24
Milczarski P, Bolibok-Bragoszewska H, Myskow B, Stojalowski S, Heller-Uszynska K, Goralska M, Bragoszewski P, Uszynski G, Kilian A, Rakoczy-Trojanowska M (2011) A high density consensus map of rye (Secale cereale L.) based on DArT markers. PLoS One 6:e28495
Mochida K, Yoshida T, Sakurai T, Ogihara Y, Shinozaki K (2009) TriFLDB: a database of clustered full-length coding sequences from Triticeae with applications to comparative grass genomics. Plant Physiol 150:1135–1146
Murat F, Xu JH, Tannier E, Abrouk M, Guilhot N, Pont C, Messing J, Salse J (2010) Ancestral grass karyotype reconstruction unravels new mechanisms of genome shuffling as a source of plant evolution. Genome Res 20:1545–1557
Nagy ED, Lelley T (2003) Genetic and physical mapping of sequence-specific amplified polymorphic (SSAP) markers on the 1RS chromosome arm of rye in a wheat background. Theor Appl Genet 107:1271–1277
Paterson AH, Bowers JE, Chapman BA (2004) Ancient polyploidization predating divergence of the cereals, and its consequences for comparative genomics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9903–9908
Philipp U, Wehling P, Wricke G (1994) A linkage map of rye. Theor Appl Genet 88:243–248
Qi L, Friebe B, Gill BS (2006) Complex genome rearrangements reveal evolutionary dynamics of pericentromeric regions in the Triticeae. Genome 49:1628–1639
Rice Annotation Project (2008) The Rice Annotation Project Database (RAP-DB): 2008 update. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D1028–D1033
Saal B, Wricke G (1999) Development of simple sequence repeat markers in rye (Secale cereale L.). Genome 42:964–972
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Sakai K, Nasuda S, Sato K, Endo TR (2009) Dissection of barley chromosome 3H in common wheat and a comparison of 3H physical and genetic maps. Genes Genet Syst 84:25–34
Schubert I (2007) Chromosome evolution. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:109–115
Stojałowski S, Mysków B, Milczarski P, Masojć P (2009) A consensus map of chromosome 6R in rye (Secale cereale L.). Cell Mol Biol Lett 14:190–198
Tenhola-Roininen T, Kalendar R, Schulman AH, Tanhuanpää P (2011) A doubled haploid rye linkage map with a QTL affecting alpha-amylase activity. J Appl Genet 52:299–304
Tsuchida M, Fukushima T, Nasuda S, Masoudi-Nejad A, Ishikawa G, Nakamura T, Endo TR (2008) Dissection of rye chromosome 1R in common wheat. Genes Genet Syst 83:43–53
Tyrka M, Bednarek PT, Kilian A, Wędzony M, Hura T, Bauer E (2011) Genetic map of triticale compiling DArT, SSR, and AFLP markers. Genome 54:391–401
Varshney RK, Sigmund R, Borner A, Korzun V, Stein N, Sorrells ME, Langridge P, Graner A (2005) Interspecific transferability and comparative mapping of barley EST-SSR markers in wheat, rye and rice. Plant Sci 168:195–202
Vershinin AV, Schwarzacher T, Heslop-Harrison JS (1995) The large-scale genomic organization of repetitive DNA families at the telomeres of rye chromosomes. Plant Cell 7:1823–1833
Vershinin AV, Alkhimova EG, Heslop-Harrison JS (1996) Molecular diversification of tandemly organized DNA sequences and heterochromatic chromosome regions in some Triticeae species. Chromosome Res 4:517–525
Wang CM, Li LH, Zhang XT, Gao Q, Wang RF, An DG (2009) Development and application of EST-STS markers specific to chromosome 1RS of Secale cereal. Cereal Res Commun 37:13–21
Wanous MK, Gustafson JP (1995) A genetic map of rye chromosome 1R integrating RFLP and cytogenetic loci. Theor Appl Genet 91:720–726
Wicker T, Mayer KF, Gundlach H, Martis M, Steuernagel B, Scholz U, Simková H, Kubaláková M, Choulet F, Taudien S, Platzer M, Feuillet C, Fahima T, Budak H, Dolezel J, Keller B, Stein N (2011) Frequent gene movement and pseudogene evolution is common to the large and complex genomes of wheat, barley, and their relatives. Plant Cell 23:1706–1718
Xu H, Yin D, Li L, Wang Q, Li X, Yang X, Liu W, An D (2012) Development and application of EST-based markers specific for chromosome arms of rye (Secale cereale L.). Cytogenet Genome Res 136:220–228
Zhou YH, Hu ZM, Dang BY, Wang HA, Deng XD, Wang LL, Chen ZH (1999) Microdissection and microcloning of rye (Secale cereale L.) chromosome 1R. Chromosoma 108:250–255
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Adam J. Lukaszewski, University of California, USA, and to John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK, for providing us the wheat–rye addition and substitution lines used in this study. This is a contribution (no. 6XX) from the Laboratory of Plant Genetics, Graduate School of Agriculture, Kyoto University, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
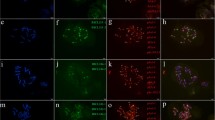
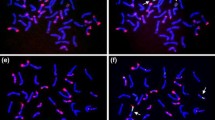
FISH (green)/GISH (pink) photomicrographs of the mitotic metaphase cells of the wheat-rye addition and substitution (for 3R) lines. FISH probe: pSc200, GISH probe: rye total genomic DNA. Bar = 10 μm (JPEG 233 kb)
Fig. S2
Gel images of the PCR products of the 84 PLUG markers assigned to respective rye chromosomes and chromosome arms. Note that PCR products and restriction enzyme-digested PCR products were separated on 1 % and 4 % agarose gels, respectively (JPEG 2053 kb)
Table S1
(XLS 18 kb)
Table S2
(XLS 52 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Endo, T.R., Saito, M. et al. Homoeologous relationship of rye chromosome arms as detected with wheat PLUG markers. Chromosoma 122, 555–564 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-013-0428-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-013-0428-7