Abstract
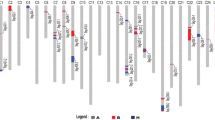
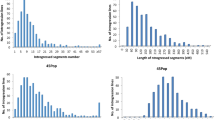
We crossed Luyuan343, containing the Gossypium barbadense (GB) genomic component, with Lumianyan22, a high-yielding Gossypium hirsutum (GH) variety, to evaluate the introgressive exogenous genomic components that contribute to fiber quality in upland cotton. A total of 158 of 334 mapping simple sequence repeats (SSR) loci screened from 18,467 SSR primer pairs were identified as putative GB introgression loci. Twenty-four quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for fiber quality and lint percentage were detected by WinQTLCart 2.5 based on three phenotypic datasets collected over 2 years in two different locations. Of these QTLs, 20 were mapped in the introgression chromosomal regions; the GB alleles contributed to improved fiber quality at eight loci, which were located in the introgression segments of chromosome (Chr.) 3, Chr.7 and Chr.25. A total of eight digenic epistasis and nine significant QTL × environment (QE) interactions were identified by QTLNetwork-2.2. Fiber elongation was found to be most easily influenced by environment since all QTLs for this trait showed significant QE interaction with large effects. Fiber length, fiber strength, and lint percentage were scarcely affected by environment as no or minor QE interaction effects for these traits were detected. Genome-wide identification of the introgressive GB components and mapping of the fiber-related QTLs indentified in this study will be beneficial for the simultaneous marker-assistant selection of improved fiber quality and lint yield in upland cotton breeding.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- QE:
-
QTL × environment
- MAS:
-
Marker-assisted selection
- GB:
-
Gossypium barbadense
- GH:
-
Gossypium hirsutum
References
Adams K, Cronn R, Percifield R, Wendel J (2003) Genes duplicated by polyploidy show unequal contributions to the transcriptome and organ-specific reciprocal silencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4649–4654
Barone A, Di Matteo A, Carputo D, Frusciante L (2009) High-throughput genomics enhances tomato breeding efficiency. Curr Genomics 10(1):1–9
Campbell BT, Saha S, Percy R, Frelichowski J, Jenkins JN, Park W, Mayee CD, Gotmare V, Dessauw D, Giband M, Du X, Jia Y, Constable G, Dillon S, Abdurakhmonov IY, Abdukarimov A, Rizaeva SM, Abdullaev A, Barroso PAV, Pádua JG, Hoffmann LV, Podolnaya L (2010) Status of the global cotton germplasm resources. Crop Sci 50(4):1161–1179
Campbell BT, Chee PW, Lubbers E, Bowman DT, Meredith WR, Johnson J, Fraser DE (2011) Genetic improvement of the Pee Dee cotton germplasm collection following seventy years of plant breeding. Crop Sci 51(3):955–968
Chapman NH, Bonnet J, Grivet L, Lynn J, Graham N, Smith R, Sun G, Walley PG, Poole M, Causse M, King GJ, Baxter C, Seymour GB (2012) High-resolution mapping of a fruit firmness-related quantitative trait locus in tomato reveals epistatic interactions associated with a complex combinatorial locus. Plant Physiol 159(4):1644–1657
Chaudhary B, Flagel L, Stupar RM, Udall JA, Verma N, Springer NM, Wendel JF (2009) Reciprocal silencing, transcriptional bias and functional divergence of homeologs in polyploid cotton (Gossypium). Genetics 182(2):503–517
Chee P, Draye X, Jiang CX, Decanini L, Delmonte TA, Bredhauer R, Smith CW, Paterson AH (2005) Molecular dissection of interspecific variation between Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense (cotton) by a backcross-self approach: I. Fiber elongation. Theor Appl Genet 111(4):757–763
Chen H, Qian N, Guo W, Song Q, Li B, Deng F, Dong C, Zhang T (2009) Using three overlapped RILs to dissect genetically clustered QTL for fiber strength on Chro.D8 in Upland cotton. Theor Appl Genet 119(4):605–612
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138(3):963–971
Draye X, Chee P, Jiang CX, Decanini L, Delmonte TA, Bredhauer R, Smith CW, Paterson AH (2005) Molecular dissection of interspecific variation between Gossypium hirsutum and G. barbadense (cotton) by a backcross-self approach: II. Fiber fineness. Theor Appl Genet 111(4):764–771
Fernie AR, Tadmor Y, Zamir D (2006) Natural genetic variation for improving crop quality. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9(2):196–202
Flagel L, Wendel J (2010) Evolutionary rate variation, genomic dominance and duplicate gene expression evolution during allotetraploid cotton speciation. New Phytol 186:184–193
Fonceka D, Tossim H-A, Rivallan R, Vignes H, Faye I, Ndoye O, Moretzsohn M, Bertioli D, Glaszmann J-C, Courtois B, Rami J-F (2012) Fostered and left behind alleles in peanut: interspecific QTL mapping reveals footprints of domestication and useful natural variation for breeding. BMC Plant Biol 12(1):26
Guo W, Cai C, Wang C, Han Z, Song X, Wang K, Niu X, Lu K, Shi B (2007) A microsatellite-based, gene-rich linkage map reveals genome structure, function and evolution in Gossypium. Genetics 176(1):527–541
Kloth R (1998) Analysis of commonality for traits of cotton fiber. J Cotton Sci 2:17–22
Korff M, Wang H, Léon J, Pillen K (2006) AB-QTL analysis in spring barley: II. Detection of favourable exotic alleles for agronomic traits introgressed from wild barley (H. vulgare ssp. spontaneum). Theor Appl Genet 112(7):1221–1231
Korff M, Wang H, Léon J, Pillen K (2008) AB-QTL analysis in spring barley: III. Identification of exotic alleles for the improvement of malting quality in spring barley (H. vulgare ssp. spontaneum). Mol Breed 21(1):81–93
Lacape JM, Nguyen TB, Thibivilliers S, Bojinov B, Courtois B, Cantrell RG, Burr B, Hau B (2003) A combined RFLP-SSR-AFLP map of tetraploid cotton based on a Gossypium hirsutum x Gossypium barbadense backcross population. Genome 46(4):612–626
Lacape JM, Llewellyn D, Jacobs J, Arioli T, Becker D, Calhoun S, Al-Ghazi Y, Liu S, Palaï O, Georges S (2010) Meta-analysis of cotton fiber quality QTLs across diverse environments in a Gossypium hirsutum x G. barbadense RIL population. BMC Plant Biol 10(1):132
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newberg LA (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1(2):174–181
Lin Z, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Guo X (2009) A high-density integrative linkage map for Gossypium hirsutum. Euphytica 166(1):35–45
May OL (1999) Genetic variation in fiber quality. Cotton fibers, developmental biology, quality improvement, and textile processing. Food Products Press, New York, pp 183–229
McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997) Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14:111–131
Mehboob-ur-Rahman M-u-R, Shaheen T, Tabbasam N, Iqbal M, Ashraf M, Zafar Y, Paterson A (2012) Cotton genetic resources. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 32(2):419–432
Meredith WR (2005) Minimum number of genes controlling cotton fiber strength in a backcross population. Crop Sci 45(3):1114–1119
Montalvo JG Jr (2005) Relationships between micronaire, fineness, and maturity. Part I. Fundamentals. J Cotton Sci 9:81–88
Paterson AH, Brubaker CL, Wendel JF (1993) A rapid method for extraction of cotton (Gossypium spp.) genomic DNA suitable for RFLP or PCR analysis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 11(2):122–127
Paterson AH, Saranga Y, Menz M, Jiang CX, Wright RJ (2003) QTL analysis of genotype x environment interactions affecting cotton fiber quality. Theor Appl Genet 106(3):384–396
Pestsova EG, Borner A, Roder MS (2006) Development and QTL assessment of Triticum aestivum-Aegilops tauschii introgression lines. Theor Appl Genet 112(4):634–647
Reinisch AJ, Dong JM, Brubaker CL, Stelly DM, Wendel JF, Paterson AH (1994) A detailed RFLP map of cotton, Gossypium hirsutum x Gossypium barbadense: chromosome organization and evolution in a disomic polyploid genome. Genetics 138(3):829–847
Rong J, Abbey C, Bowers JE, Brubaker CL, Chang C, Chee PW, Delmonte TA, Ding X, Garza JJ, Marler BS, Park C-H, Pierce GJ, Rainey KM, Rastogi VK, Schulze SR, Trolinder NL, Wendel JF, Wilkins TA, Williams-Coplin TD, Wing RA, Wright RJ, Zhao X, Zhu L, Paterson AH (2004) A 3347-locus genetic recombination map of sequence-tagged sites reveals features of genome organization, transmission and evolution of cotton (Gossypium). Genetics 166(1):389–417
Rong J, Feltus F, Waghmare V, Pierce G, Chee P, Draye X, Saranga Y, Wright R, Wilkins T, May O, Smith C, Gannaway J, Wendel J, Paterson A (2007) Meta-analysis of polyploid cotton QTL shows unequal contributions of subgenomes to a complex network of genes and gene clusters implicated in lint fiber development. Genetics 176:2577–2588
Shen X, Guo W, Lu Q, Zhu X, Yuan Y, Zhang T (2007) Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci for fiber quality and yield trait by RIL approach in Upland cotton. Euphytica 155(3):371–380
Steele KA, Price AH, Shashidhar HE, Witcombe JR (2006) Marker-assisted selection to introgress rice QTLs controlling root traits into an Indian upland rice variety. Theor Appl Genet 112(2):208–221
Stelly DM (1993) Interfacing cytogenetics with the cotton genome mapping effort. Pro Beltwide Cotton Conf 3:1545–1550
Su X, Gao G, Shi X, Zhu D (2000) Breeding of a terrestrial long-staple cotton—Luyuan 343. Acta Agric Nucleatae Sinica 14(3):180–183
Sun FD, Zhang JH, Wang SF, Gong WK, Shi YZ, Liu AY, Li JW, Gong JW, Shang HH, Yuan YL (2011) QTL mapping for fiber quality traits across multiple generations and environments in upland cotton. Mol Breed 30(1):1–14
Tang QY, Feng MG (2007) DPS data processing system: experimental design, statistical analysis, and data mining. Science Press, Beijing
Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1997) Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277(5329):1063–1066
Voorrips R (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93(1):77–78
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2006) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5 Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh. Available at: http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Wang F, Gong Y, Zhang C, Liu G, Wang L, Xu Z, Zhang J (2011) Genetic effects of introgression genomic components from Sea Island cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.) on fiber related traits in upland cotton (G. hirsutum L.). Euphytica 181(1):41–53
Wendel JF, Brubaker CL, Seelanan T (2010) The origin and evolution of Gossypium. In: Stewart JM, Oosterhuis DM, Heitholt JJ, Mauney JR (eds) Physiology of cotton. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 1–18
Xu P, Zhu J, Zhang X, Ni W, Xu Y, Shen X (2012a) Molecular mapping and identification of QTLs for fiber micronaire on chromosome 7 from Gossypium klotzschianum. Acta Agron Sin 38(03):447–453
Xu X, Liu X, Ge S, Jensen JD, Hu F, Li X, Dong Y, Gutenkunst RN, Fang L, Huang L, Li J, He W, Zhang G, Zheng X, Zhang F, Li Y, Yu C, Kristiansen K, Zhang X, Wang J, Wright M, McCouch S, Nielsen R, Wang J, Wang W (2012b) Resequencing 50 accessions of cultivated and wild rice yields markers for identifying agronomically important genes. Nat Biotech 30(1):105–111
Yang J, Hu C, Hu H, Yu R, Xia Z, Ye X, Zhu J (2008) QTLNetwork: mapping and visualizing genetic architecture of complex traits in experimental populations. Bioinformatics 24(5):721–723
Yu J, Herrmann M (2006) Inheritance and mapping of a powdery mildew resistance gene introgressed from Avena macrostachya in cultivated oat. Theor Appl Genet 113(3):429–437
Yu JZ, Kohel RJ, Fang DD, Cho J, Van Deynze A, Ulloa M, Hoffman SM, Pepper AE, Stelly DM, Jenkins JN, Saha S, Kumpatla SP, Shah MR, Hugie WV, Percy RG (2012) A high-density simple sequence repeat and single nucleotide polymorphism genetic map of the tetraploid cotton genome. G3 Genes Genomes Genet 2(1):43–58
Zamir D (2001) Improving plant breeding with exotic genetic libraries. Nat Rev Genet 2(12):983–989
Zamir D (2008) Plant breeders go back to nature. Nat Genet 40(3):269–270
Zhang J, Guo W, Zhang T (2002) Molecular linkage map of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. × Gossypium barbadense L.) with a haploid population. Theor Appl Genet 105(8):1166–1174
Zhang ZS, Hu MC, Zhang J, Liu DJ, Zheng J, Zhang K, Wang W, Wan Q (2009) Construction of a comprehensive PCR-based marker linkage map and QTL mapping for fiber quality traits in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Mol Breed 24(1):49–61
Zhang Z, Rong J, Waghmare V, Chee P, May OL, Wright R, Gannaway J, Paterson A (2011) QTL alleles for improved fiber quality from a wild Hawaiian cotton. Gossypium tomentosum. Theor Appl Genet 123(7):1075–1088
Zhang K, Zhang J, Ma J, Tang S, Liu D, Teng Z, Liu D, Zhang Z (2012) Genetic mapping and quantitative trait locus analysis of fiber quality traits using a three-parent composite population in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Mol Breed 29(2):335–348
Zheng P (2008) A phenylalanine in DGAT is a key determinant of oil content and composition in maize. Nat Genet 40:367–372
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported in part by grants from the National Science Foundation in China (31171598), National Major Project on Transgenic Breeding in China (2013ZX08005-003), The National High-tech Program of China (2012AA101108-04-02), and Agro-Bio Resources Innovation and Utilization Project of Seed-Industrialized Development Program in Shandong Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Furong Wang and Zhenzhen Xu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Xu, Z., Sun, R. et al. Genetic dissection of the introgressive genomic components from Gossypium barbadense L. that contribute to improved fiber quality in Gossypium hirsutum L.. Mol Breeding 32, 547–562 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9888-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9888-y