Abstract
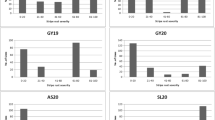
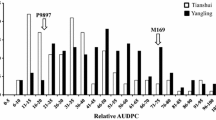
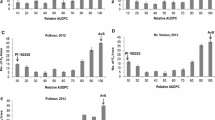
High-temperature adult-plant (HTAP) resistance to stripe rust (caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) is a durable type of resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). This study identified quantitative trait loci (QTL) conferring HTAP resistance to stripe rust in a population consisting of 169 F8:10 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from a cross between a susceptible cultivar Rio Blanco and a resistant germplasm IDO444. HTAP resistance was evaluated for both disease severity and infection type under natural infection over two years at two locations. The genetic linkage maps had an average density of 6.7 cM per marker across the genome and were constructed using 484 markers including 96 wheat microsatellite (SSR), 632 Diversity Arrays Technology (DArT) polymorphisms, two sequence-tagged-site (STS) from semi-dwarf genes Rht1 and Rht2, and two markers for low molecular-weight glutenin gene subunits. QTL analysis detected a total of eight QTL significantly associated with HTAP resistance to stripe rust with two on chromosome 2B, two on 3B and one on each of 1A, 4A, 4B and 5B. QTL on chromosomes 2B and 4A were the major loci derived from IDO444 and explained up to 47 and 42% of the phenotypic variation for disease severity and infection type, respectively. The remaining five QTL accounted for 7–10% of the trait variation. Of these minor QTL, the resistant alleles at the two QTL QYrrb.ui-3B.1 and QYrrb.ui-4B derived from Rio Blanco and reduced infection type only, while the resistant alleles at the other three QTL, QYrid.ui-1A, QYrid.ui-3B.2 and QYrid.ui-5B, all derived from IDO444 and reduced either infection type or disease severity. Markers linked to 2B and 4A QTL should be useful for selection of HTAP resistance to stripe rust.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari M, Wenzl P, Caig V, Carling J, Xia L, Yang S, Uszynski G, Mohler V, Lehmensiek A, Kuchel H, Hayden MJ, Howes N, Sharp PJ, Vaughan P, Rathmell B, Huttner E, Kilian A (2006) Diversity array technology (DArT) for high-throughput profiling of the hexaploid wheat genome. Theor Appl Genet 113:1409–1420
Carter AH, Chen XM, Garland-Campbell K, Kidwell KK (2009) Identifying QTL for high-temperature adult-plant resistance to stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) in the spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivar ‘Louise’. Theor Appl Genet 119:1119–1128
Carver BF, Krenzer EG, Klatt AR, Guenzi AC, Martin BC, Bai G-H (2003) Registration of ‘Intrada’ wheat. Crop Sci 43:1135–1136
Chen XM (2005) Epidemiology and control of stripe rust on wheat. Can J Plant Pathol 27:314–337
Chen XM, Moore M, Milus EA, Long DL, Line RF, Marshall D, Jackson L (2002) Wheat stripe rust epidemics and races of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in the United States in 2000. Plant Dis 86:39–46
Chen XM, Penman L, Wan AM, Cheng P (2010) Virulence races of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in 2006 and 2007 and development of wheat stripe rust and distributions, dynamics, and evolutionary relationships of races from 2000 to 2007 in the United States. Can J Plant Pathol (in press)
Chu CG, Xu SS, Friesen TL, Faris JD (2008) Whole genome mapping in a wheat doubled haploid population using SSRs and TRAPs and the identification of QTL for agronomic traits. Mol Breed 22:251–266
Doerge RW, Churchill GA (1996) Permutation tests for multiple loci affecting a quantitative character. Genetics 142:285–294
Ganal MW, Röder MS (2007) Microsatelite and SNP markers in wheat breeding. In: Varshney RK, Tuberosa R (eds) Genomics-assisted crop improvement, vol 2, genomics applications in crops. Springer, New York, pp 1–24
Guo Q, Zhang ZJ, Xu YB, Li GH, Feng J, Zhou Y (2008) Quantitative trait loci for high-temperature adult-plant and slow-rusting resistance to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici in wheat cultivars. Phytopathology 98:803–809
Gupta PK, Balyan HS, Edwards KJ, Isaac P, Korzun V, Röder MS, Gautier MF, Joudrier P, Schlatter AR, Dubcovsky J, De la Pena RC, Khairallah M, Penner G, Hayden MJ, Sharp P, Keller B, Wang RCC, Hardouin JP, Jack P, Leroy P (2002) Genetic mapping of 66 new microsatellite (SSR) loci in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 105:413–422
Guyomarc’h H, Sourdille P, Charmet G, Edwards KJ, Bernard M (2002) Characterization of polymorphic microsatellite markers from Aegilops tauschii and transferability to the D-genome of bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:1164–1172
Haley SD, Quick JS, Stromberger JA, Clayshulter SR, CliVord BL, Johnson JJ (2003) Registration of ‘Avalanche’ wheat. Crop Sci 43:432
Johnson R (1992) Reflection of a plant pathologist on breeding for disease resistance, with emphasis on yellow rust and eyespot of wheat. Plant Pathol 41:239–254
Khlestkina EK, Röder MS, Unger O, Meinel A, Börner A (2007) More precise map position and origin of a durable non-specific adult plant disease resistance against stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis) in wheat. Euphytica 153:1–10
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg I (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Lillemo M, Asalf B, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, Chen XM, He ZH, Bjørnstad Å (2008) The adult plant rust resistance loci Lr34/Yr18 and Lr46/Yr29 are important determinants of partial resistance to powdery mildew in bread wheat line Saar. Theor Appl Genet 116:1155–1166
Lin F, Chen XM (2007) Genetics and molecular mapping of genes for race-specific all-stage resistance and non-race-specific high-temperature adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in spring wheat cultivar Alpowa. Theor Appl Genet 114:1277–1287
Lin F, Chen XM (2009) Quantitative trait loci for non-race specific, high-temperature adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in wheat cultivar Express. Theor Appl Genet 118:631–642
Line RF (2002) Stripe rust of wheat and barley in North America: A retrospective historical review. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:75–118
Line RF, Chen XM (1995) Successes in breeding for and managing durable resistance to wheat rusts. Plant Dis 79:1254–1255
Line RF, Qayoum A (1992) Virulence, aggressiveness, evolution, and distribution of races of Puccinia striiformis (the cause of stripe rust of wheat) in North America, 1968–87. U. S. Department of Agriculture Technical Bulletin No. 1788, p 44
Lu Y, Lan C, Liang S, Zhou X, Liu D, Zhou G, Lu Q, Jing J, Wang M, Xia X, He Z (2009) QTL mapping for adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in Italian common wheat cultivars Libellula and Strampelli. Theor Appl Genet 119:1349–1359
Manly KF, Cudmore RH Jr, Meer JM (2001) Map Manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mammal Genome 12:930–932
Martin TJ, Scifers DL, Harvey TL (2001) Registration of Trego wheat. Crop Sci 41:929–930
Milus EA, Line RF (1986a) Number of genes controlling high temperature, adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in wheat. Phytopathology 76:93–96
Milus EA, Line RF (1986b) Gene action for inheritance of durable, high-temperature, adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in wheat. Phytopathology 76:435–441
Milus EA, Kristensen K, Hovmoller MS (2009) Evidence for increased aggressiveness in a recent widespread strain of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici causing stripe rust of wheat. Phytopathology 99:89–94
Nelson JC (1997) Qgene: software for maker-based genomic analysis and breeding. Mol Breed 3:239–245
Pallotta MA, Warner P, Fox RL, Kuchel H, Jefferies SP, Langridge P (2003) Marker assisted wheat breeding in the southern region of Australia. In: Pogna NE (eds) Proceedings of 10th international wheat genet symposium, Paestum, Italy, vol 2, pp 789–791
Qayoum A, Line RF (1985) High-temperature, adult-plant resistance to stripe rust of wheat. Phytopathology 75:1121–1125
Quarrie SA, Steed A, Calestani C, Semikhodskii A et al (2005) A high-density genetic map of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) from the cross Chinese Spring × SQ1 and its use to compare QTLs for grain yield across a range of environments. Theor Appl Genet 110:865–880
Ramburan VP, Pretorius ZA, Louw JH, Boyd LA, Smith PH, Boshoff WHP, Prins R (2004) A genetic analysis of adult plant resistance to stripe rust in the wheat cultivar Kariega. Theor Appl Genet 108:1426–1433
Röder MS, Plaschke J, König SU, Börner A, Sorrells ME, Tanksley SD, Ganal MW (1995) Abundance, variability and chromosome location of microsatellites in wheat. Mol Gen Genet 246:327–333
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier MH, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:207–333
Santra DK, Chen XM, Santra M, Campbell KG, Kidwell KK (2008) Identification and mapping QTL for high-temperature adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivar Stephens. Theor Appl Genet 117:793–802
Semagn K, Bjørnstad Å, Ndjiondjop MN (2006) An overview of molecular marker methods for plants. Afr J Biotech 5:2540–2568
Somers DJ, Isaac P, Edwards K (2004) A high-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 109:1105–1114
Song QJ, Shi JR, Singh S, Fickus EW, Costa JM, Lewis J, Gill BS, Ward R, Cregan PB (2005) Development and mapping of microsatellite (SSR) markers in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 110:550–560
Sourdille P, Cadalen T, Guyomarc’h H, Snape JW, Perretant MR, Charmet G, Boeuf C, Bernard S, Bernard M (2003) An update of the Courtot × Chinese Spring intervarietal molecular marker linkage map for the QTL detection of agronomic traits in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 106:530–538
Sourdille P, Singh S, Cadalen T, Brown-Guedira GL, Gay G, Qi L, Gill BS, Dufour P, Murigneux A, Bernard M (2004) Microsatellite-based deletion bin system for the establishment of genetic-physical map relationships in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Funct Integr Genomics 4:12–25
Stubbs RW (1985) Stripe rust. In: Roelfs AP, Bushnell WR (eds) The cereal rusts, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 61–101
Wenzl P, Kudrna D, Jaccoud D, Huttner E, Kleinhofs A, Kilian A (2004) Diversity arrays technology (DArT) for whole genome profiling of barley. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(26):9915–9920
Windes JM, Souza E, Sunderman DW, Goates B (1995) Registration of four dwarf bunt resistant wheat germplasm: Idaho 352, Idaho 364, Idaho 443, and Idaho 444. Crop Sci 35:1239–1240
Wu J, Carver BF (1999) Sprout damage and preharvest sprout resistance in hard white winter wheat. Crop Sci 39:41–447
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the National Research Initiative Competitive Grants 2006-55606-16629, the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture Triticeae-CAP 2011-68002-30029, and the Idaho Wheat Commission Grant. The authors sincerely thank Dr. Deven R. See, Dr. Paul St Amand, Dr. Gina Brown-Guediera, Dr. Daryl Klindworth, Mr. Weidong Zhao, Mrs. Karen Peterson and Mr. Junli Zhang for technical assistance in genotyping SSR markers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11032_2011_9590_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Fig. 1 S1 Genetic linkage maps constructed for the Rio Blanco × IDO444 RIL population. The positions of marker loci are shown to the right of the linkage groups and the centiMorgan (cM) distances between loci are shown along the left. LMW: low-molecular-weight glutenin gene subunit; Rht: reduced height genes (PDF 220 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Chu, C., Souza, E.J. et al. Genome-wide identification of QTL conferring high-temperature adult-plant (HTAP) resistance to stripe rust (Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici) in wheat. Mol Breeding 29, 791–800 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9590-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9590-x