Abstract
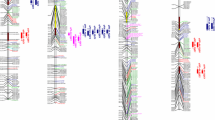
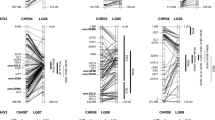
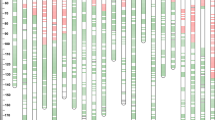
A population of 96 doubled haploid lines (DHLs) was prepared from F1 plants of the hexaploid wheat cross Chinese Spring × SQ1 (a high abscisic acid-expressing breeding line) and was mapped with 567 RFLP, AFLP, SSR, morphological and biochemical markers covering all 21 chromosomes, with a total map length of 3,522 cM. Although the map lengths for each genome were very similar, the D genome had only half the markers of the other two genomes. The map was used to identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for yield and yield components from a combination of 24 site × treatment × year combinations, including nutrient stress, drought stress and salt stress treatments. Although yield QTLs were widely distributed around the genome, 17 clusters of yield QTLs from five or more trials were identified: two on group 1 chromosomes, one each on group 2 and group 3, five on group 4, four on group 5, one on group 6 and three on group 7. The strongest yield QTL effects were on chromosomes 7AL and 7BL, due mainly to variation in grain numbers per ear. Three of the yield QTL clusters were largely site-specific, while four clusters were largely associated with one or other of the stress treatments. Three of the yield QTL clusters were coincident with the dwarfing gene Rht-B1 on 4BS and with the vernalisation genes Vrn-A1 on 5AL and Vrn-D1 on 5DL. Yields of each DHL were calculated for trial mean yields of 6 g plant−1 and 2 g plant−1 (equivalent to about 8 t ha−1 and 2.5 t ha−1, respectively), representing optimum and moderately stressed conditions. Analyses of these yield estimates using interval mapping confirmed the group-7 effects on yield and, at 2 g plant−1, identified two additional major yield QTLs on chromosomes 1D and 5A. Many of the yield QTL clusters corresponded with QTLs already reported in wheat and, on the basis of comparative genetics, also in rice. The implications of these results for improving wheat yield stability are discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammiraju JSS, Dholakia BB, Santra DK, Singh H, Lagu MD, Tamhankar SA, Dhaliwal HS, Rao VS, Gupta VS, Ranjekar PK (2001) Identification of inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers associated with seed size in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 102:726–732
Ayala L, Henry M, van Ginkel M, Singh R, Keller B, Khairallah M (2002) Identification of QTLs for BYDV tolerance in bread wheat. Euphytica 128:249–259
Basten CJ, Zeng Z-B, Weir BS (1996) qtlcartographer: a suite of programs for mapping quantitative trait loci. Abstracts to Plant Genome IV. Academic Press, San Diego, p 108
Bennett MD, Smith JB, Heslop-Harrison JS (1982) Nuclear DNA amounts in angiosperms. Proc R Soc London Ser B 216:179–199
Blanco A, Bellomo MP, Cenci A, De Giovanni C, D’Ovidio R, Iacono E, Laddomada B, Pagnotta MA, Porceddu E, Sciancalepore A, Simeone R, Tanzarella OA (1998) A genetic linkage map of durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 97:721–728
Blanco A, Pasqualone A, Troccoli A, Di Fonzo N, Simeone R (2002) Detection of grain protein content QTLs across environments in tetraploid wheats. Plant Mol Biol 48:615–623
Börner A, Schumann E, Furste A, Coster H, Leithold B, Röder MS, Weber WE (2002) Mapping of quantitative trait loci determining agronomic important characters in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 105:921–936
Bryan GJ, Collins AJ, Stephenson P, Orry A, Smith JB, Gale MD (1997) Isolation and characterisation of microsatellites from hexaploid bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 96:557–563
Butterworth KJ (2000) Flowering time genes of wheat and their influence on environmental adaptability. PhD thesis, University of East Anglia
Byrne PF, Butler JD, Anderson GR, Haley SD (2002) QTL’s for agronomic and morphological traits in a spring wheat population derived from a cross of heat tolerant and heat sensitive lines (poster). In: Plant, Animal and Microbe Genomes X Conf. San Diego, Calif.
Cadalen T, Boeuf C, Bernard S, Bernard M (1997) An intervarietal molecular marker map in Triticum aestivum L. Em. Thell. and comparison with a map from a wide cross. Theor Appl Genet 94:367–377
Cattivelli L, Baldi P, Crosatti C, Di Fonzo N, Faccioli P, Grossi M, Mastrangelo AM, Pecchioni N, Stanca AM (2002) Chromosome regions and stress-related sequences involved in resistance to abiotic stress in Triticeae. Plant Mol Biol 48:649–665
Chalmers KJ, Campbell AW, Kretschmer J, Karakousis A, Henschke PH, Pierens S, Harker N, Pallotta M, Cornish GB, Shariflou MR, Rampling LR, McLauchlan A, Daggard G, Sharp PJ, Holton TA, Sutherland MW, Appels R, Langridge P (2001) Construction of three linkage maps in bread wheat, Triticum aestivum. Aust J Agric Res 52:1089–1119
Chao S, Sharp PJ, Worland AJ, Warham EJ, Koebner RMD, Gale MD (1989) RFLP-based genetic maps of wheat homoeologous group 7 chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 78:495–504
Devos KM, Dubcovsky J, Dvorak J, Chinoy CN, Gale MD (1995) Structural evolution of wheat chromosomes 4A, 5A, and 7B and its impact on recombination. Theor Appl Genet 91:282–288
Eujayl I, Sorrells ME, Baum M, Wolters P, Powell W (2002) Isolation of EST-derived microsatellite markers for genotyping the A and B genomes of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:399–407
Finlay KW, Wilkinson GN (1963) The analysis of adaptation in a plant-breeding programme. Aust J Agric Res 14:342–354
Forster BP, Miller TE, Law CN (1988) Salt tolerance of two wheat- Agropyron junceum disomic addition lines. Genome 30:559–564
Franckowiak J (1997) Revised linkage maps for morphological markers in barley, Hordeum vulgare. Barley Genet Newsl 26:9–21
Gale MD, Youssefian S (1985) Dwarfing genes in wheat. In: Russell GE (ed) Progress in plant breeding. J Butterworth and Co, London, pp 1–35
Gale MD, Atkinson MD, Chinoy CN, Harcourt RL, Jia J, Li QY, Devos KM (1995) Genetic maps of hexaploid wheat. In: Li ZS, Xin ZY (eds) Proc 8th Int Wheat Genetics Symp. Agric Scientech Press, Beijing, pp 29–40/Genome 37:871–875
Groos C, Robert N, Bervas E, Charmet G (2003) Genetic analysis of grain protein-content, grain yield and thousand-kernel weight in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 106:1032–1040
Hart GE (2001) Molecular-marker maps of the cultivated wheats and other Triticum species. In: Phillips RL, Vasil IK (eds) DNA-based markers in plants. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 421–441
Huang S, Sirikhachornkit A, Su X, Faris J, Gill B, Haselkorn R, Gornicki P (2002) Genes encoding plastid acetyl-CoA carboxylase and 3-phosphoglycerate kinase of the Triticum/Aegilops complex and the evolutionary history of polyploid wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8133–8138
Isla R, Royo A, Aragues R (1997) Field screening of barley cultivars to soil salinity using a sprinkler and a drip irrigation system. Plant Soil 197:105–117
Khavkin E, Coe E (1997) Mapped genomic locations for developmental functions and QTLs reflect concerted groups in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 95:343–352
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) mapmaker: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Langridge P, Lagudah ES, Holton TA, Appels R, Sharp PJ, Chalmers KJ (2001) Trends in genetic and genome analysis in wheat: a review. Aust J Agric Res 52:1043–1077
Laurie DA, Reymondie S (1991) High frequencies of fertilization and haploid seedling production in crosses between commercial hexaploid wheat varieties and maize. Plant Breed 106:182–189
Li WL, Nelson JC, Chu CY, Shi LH, Huang SH, Liu DJ (2002) Chromosomal locations and genetic relationships of tiller and spike characters in wheat. Euphytica 125:357–366
Li Z-K, Luo LJ, Mei HW, Wang DL, Shu QY, Tabien R, Zhong DB, Ying CS, Stansel JW, Khush GS, Paterson AH (2001) Overdominant epistatic loci are the primary genetic basis of inbreeding depression and heterosis in rice. I. Biomass and grain yield. Genetics 158:1737–1753
Liu Y-G, Tsunewaki K (1991) Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis in wheat. II. Linkage maps of the RFLP sites in common wheat. Jpn J Genet 66:617–633
Mahmood A, Quarrie SA (1993) Effects of salinity on growth, ionic relations and physiological traits of wheat, disomic addition lines from Thinopyrum bessarabicum and two amphiploids. Plant Breed 110:265–276
Mano Y, Takeda K (1997) Mapping quantitative trait loci for salt tolerance at germination and the seedling stage in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Euphytica 94:263–272
Manyowa NM, Miller TE (1991) The genetics of tolerance to high mineral concentrations in the tribe Triticeae—a review and update. Euphytica 57:175–185
Marino CL, Nelson JC, Lu YH, Sorrells ME, Leroy P, Tuleen NA, Lopes CR, Hart GE (1996) Molecular genetic maps of the group 6 chromosomes of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em. Thell). Genome 39:359–366
Messmer MM, Keller M, Zanetti S, Keller B (1999) Genetic linkage map of a wheat × spelt cross. Theor Appl Genet 98:1163–1170
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) The isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nelson JC, Sorrells ME, Van Deynze AE, Lu YH, Atkinson M, Bernard M, Leroy P, Faris JD, Anderson JA (1995a) Molecular mapping of wheat—major genes and rearrangements in homoeologous groups 4, 5, and 7. Genetics 141:721–731
Nelson JC, Van Deynze AE, Autrique E, Sorrells ME, Lu YH, Merlino M, Atkinson M, Leroy P (1995b) Molecular mapping of wheat. Homoeologous group 2. Genome 38:516–524
Nelson JC, Van Deynze AE, Autrique E, Sorrells ME, Lu YH, Negre S, Bernard M, Leroy P (1995c) Molecular mapping of wheat. Homoeologous group 3. Genome 38:525–533
Paillard S, Schnurbusch T, Winzeler M, Messmer M, Sourdille P, Abderhalden O, Keller B, Schachermayr G (2003) An integrative genetic linkage map of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 107:1235–1242
Pakniyat H, Handley LL, Thomas WTB, Connolly T, Macaulay M, Caligari PDS, B.P. Forster BP (1997) Comparison of shoot dry weight, Na+ content and δ13 C values of ari-e and other semi-dwarf barley mutants under salt-stress. Euphytica 94:7–14
Peng J, Richards DE, Hartley NM, Murphy GP, Devos KM, Flintham JE, Beales J, Fish LJ, Worland AL, Pelica F, Sudhakar D, Christou P, Snape JW, Gale MD, Harberd NP (1999) ’Green revolution’ genes encode mutant gibberellin response modulators. Nature 400:256–261
Peng J, Korol AB, Fahima T, Röder MS, Ronin YI, Li YC, Nevo E (2000) Molecular genetic maps in wild Emmer wheat, Triticum dicoccoides: genome-wide coverage, massive negative interference, and putative quasi-linkage. Genome Res 10:1509–1531
Quarrie SA (1981) Genetic variability and heritability of drought-induced abscisic acid accumulation in spring wheat. Plant Cell Environ 4:147–151
Quarrie SA (1987a) Evaluation of the influence of a metabolic character on drought resistance exemplified by studies on abscisic acid in wheat and maize. In: Monti L, Porceddu E (eds) Drought resistance in plants: physiological and genetic aspects. Commission of the European Communities, Luxembourg, pp 111–129
Quarrie SA (1987b) Use of genotypes differing in endogenous abscisic acid levels in studies on physiology and development. In: Hoad GV, Lenton JR, Jackson MB, Atkin RK (eds) Hormone action in plant development: a critical appraisal. Butterworths, London, pp 89–105
Quarrie SA, Gulli M, Calestani C, Steed A, Marmiroli N (1994) Location of a gene regulating drought-induced abscisic acid production on the long arm of chromosome 5A of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 89:794–800
Quarrie SA, Dodig D, Pekic S, Kirby J, Kobiljski B (2003) Prospects for marker-assisted selection of improved drought responses in wheat. Bulg J Plant Physiol Special Issue 2003, pp 83–95
Reynolds MP, Trethowan R, Crossa J, Vargas M, Sayre KD (2002) Physiological factors associated with genotype by environment interaction in wheat. Field Crops Res 75:139–160
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier M-H, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Semikhodskii AG, Quarrie SA, Snape JW (1997) Mapping quantitative trait loci for salinity responses in wheat. In: Jevtic S, Pekic S (eds) Drought and plant production, vol. 2. Proc Int Symp. Agricultural Research Institute Serbia, Belgrade, pp 83–92
Sharp PJ, Kreis M, Shewry PR, Gale MD (1988) Location of B-amylase sequences in wheat and its relatives. Theor Appl Genet 75:286–290
Singh RP, Huerta-Espino S, Rajaram S, Crossa J (1998) Agronomic effects from chromosome translocations 7DL.7Ag and 1BL.1RS in spring wheat. Crop Sci 38:27–33
Slafer GA (2003) Genetic basis of yield as viewed from a crop physiologist’s perspective. Ann Appl Biol 142:117–128
Snape JW, Sarma R, Quarrie SA, Fish L, Galiba G, Sutka J (2001) Mapping genes for flowering time and frost tolerance in cereals using precise genetic stocks. Euphytica 120:309–315
Sutka J, Snape JW (1989) Location of a gene for frost resistance on chromosome 5A of wheat. Euphytica 42:41–44
Thomas WTB (2003) Prospects for molecular breeding of barley. Ann Appl Biol 142:1–12
Van Deynze AE, Dubcovsky J, Gill KS, Nelson JC, Sorrells ME, Dvorak J, Gill BS, Lagudah ES, McCouch SR, Appels R (1995) Molecular-genetic maps for group 1 chromosomes of Triticeae species and their relation to chromosomes in rice and oat. Genome 38:45–59
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Yan L, Loukoianov A, Tranquilli G, Helguera M, Fahima T, Dubcovsky J (2003) Positional cloning of the wheat vernalization gene VRN1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6263–6268
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the following funding sources that allowed aspects of this research to be carried out: molecular marker work from the BC-MURST (Italy) programme (C. Calestani), EU FP4 Biotechnology programme for the EGRAM project (E. Waterman) and EU FP5 Sustainable agriculture SUSTAIN project no. QLK5-CT-2001-01461 (D. Z. Habash, J. Weyen, J. Schondelmaier); molecular marker work and field trials from the BBSRC RASP (Resource Allocation and Stress in Plants) programme (C. Chinoy, P. Farmer, L. Saker, D.T. Clarkson), EU INTAS programme (A. Abugalieva, M. Yessimbekova, Y. Turuspekov, S. Abugalieva, R. Tuberosa, M.-C. Sanguineti) and EU INCO-DC programme (N. Steele, P. Hollington, R. Aragüés, A. Royo). D. Dodig acknowledges financial support from the Serbian Ministry of Science and Technology. The John Innes Centre is supported by a grant-in-aid from the Biotechnological and Biological Sciences Research Council. The helpful comments on this manuscript of Professor John Snape are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Langridge
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quarrie, S.A., Steed, A., Calestani, C. et al. A high-density genetic map of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) from the cross Chinese Spring × SQ1 and its use to compare QTLs for grain yield across a range of environments. Theor Appl Genet 110, 865–880 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1902-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1902-7