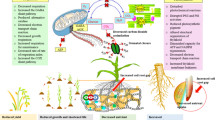
Abstract
Salinity is one of the most significant environmental factors limiting legumes development and productivity. Salt stress disturbs all developmental stages of legumes and affects their hormonal regulation, photosynthesis and biological nitrogen fixation, causing nutritional imbalance, plant growth inhibition and yield losses. At the molecular level, salt stress exposure involves large number of factors that are implicated in stress perception, transduction, and regulation of salt responsive genes’ expression through the intervention of transcription factors. Along with the complex gene network, epigenetic regulation mediated by non-coding RNAs, and DNA methylation events are also involved in legumes’ response to salinity. Different alleviation strategies can increase salt tolerance in legume plants. The most promising ones are Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobia, Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi, seed and plant’s priming. Genetic manipulation offers an effective approach for improving salt tolerance. In this review, we present a detailed overview of the adverse effect of salt stress on legumes and their molecular responses. We also provide an overview of various ameliorative strategies that have been implemented to mitigate/overcome the harmful effects of salt stress on legumes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no data sets were generated or analyzed during the present study.
References
Abd El-Ghany M, Attia M (2020) Effect of exopolysaccharide-producing bacteria and melatonin on faba bean production in saline and non-saline soil. Agronomy 10:316. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10030316
Abd-Alla M, Nafady N, Bashandy S, Hassan A (2019) Mitigation of effect of salt stress on the nodulation, nitrogen fixation and growth of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) by triple microbial inoculation. Rhizosphere 10:100148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2019.100148
Abdel Latef AAH, Tahjib-Ul-Arif M, Rhaman MS (2021) Exogenous auxin-mediated salt stress alleviation in Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.). Agronomy 11:547. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030547
Abdel-Baki G, Shaddad MAK, Mostafa D, Rafat A-S (2018) The effect of seed presoaking with KNO3 on seed germination, proline, protein pattern, ß-amylase and mineral composition of two faba bean cultivars treated with NaCl. Egypt J Bot 58:445–461. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejbo.2018.3423.1166
Abdelhamid M, Mervat ShS, Urs S, Abdel-Kareem ME (2013) Interactive effects of salinity stress and nicotinamide on physiological and biochemical parameters of faba bean plant. Acta Biol Colomb 18:499–510
Abeer H, Abd Allah E, Alqarawi A et al (2014) Alleviation of adverse impact of salinity on Faba bean (Vicia faba L.) by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Pak J Bot 46:2003–2013
Abeer H, Abd Allah E, Alqarawi A, Egamberdieva D (2015) Induction of salt stress tolerance in cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Legume Res Int J 38:579–588
Abid G, Muhovski Y, Mingeot D et al (2017) Identification and characterization of two faba bean (Vicia faba L.) WRKY transcription factors and their expression analysis during salt and drought stress. J Agric Sci 155:791–803
Acosta-Jurado S, Fuentes-Romero F, Ruiz-Sainz J-E et al (2021) Rhizobial exopolysaccharides: genetic regulation of their synthesis and relevance in symbiosis with legumes. Int J Mol Sci 22:6233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126233
Ahmad P, Rasool S (2014) Emerging technologies and management of crop stress tolerance: volume 1-biological techniques, Academic Press, Cambridge
Ahmad F, Singh A, Kamal A (2017) Ameliorative effect of salicylic acid in salinity stressed Pisum sativum by improving growth parameters, activating photosynthesis and enhancing antioxidant defense system. Biosci Biotech Res Comm 10:481–489
Ahmad M, Zahir ZA, Asghar HN, Asghar M (2011) Inducing salt tolerance in mung bean through coinoculation with rhizobia and plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. Can J Microbiol 57:578–589
Ahmad P, Alyemeni MN, Ahanger MA et al (2018) Salicylic acid (SA) induced alterations in growth, biochemical attributes and antioxidant enzyme activity in Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) seedlings under NaCl toxicity. Russ J Plant Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443718010132
Ahmadvand G, Soleimani F, Saadatian B, Pouya M (2012) Effects of seed priming on germination and emergence traits of two soybean cultivars under salinity stress. J Basic Appl Sci Res 3:234–241
Al-Farsi SM, Nawaz A, Nadaf SK et al (2020) Effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of salt stress in lucerne (Medicago sativa). Crop Pasture Sci 71:411–428
Al-Karaki GN, Hammad R, Rusan M (2001) Response of two tomato cultivars differing in salt tolerance to inoculation with mycorrhizal fungi under salt stress. Mycorrhiza 11:43–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720100098
Al-Lawati A, Al-Bahry S, Victor R et al (2016) Salt stress alters DNA methylation levels in alfalfa (Medicago spp.). Genet Mol Res 15:15018299
Alsaeedi AH, El-Ramady H, Alshaal T et al (2017) Engineered silica nanoparticles alleviate the detrimental effects of Na+ stress on germination and growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:21917–21928
Alqarawi A, Hashem A, Abd_Allah E et al (2014) Effect of salinity on moisture content, pigment system, and lipid composition in Ephedra alata Decne. Acta Biol Hung 65:61–71
Alzahrani SM, Alaraidh IA, Khan MA et al (2019a) Identification and characterization of salt-responsive microRNAs in Vicia faba by high-throughput sequencing. Genes 10:303
Alzahrani SM, Alaraidh IA, Migdadi H et al (2019b) Physiological, biochemical, and antioxidant properties of two genotypes of Vicia faba grown under salinity stress. Pak J Bot. https://doi.org/10.30848/PJB2019-3(3)
Anaya F, Fghire R, Wahbi S, Loutfi K (2018) Influence of salicylic acid on seed germination of Vicia faba L. under salt stress. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 17:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2015.10.002
Andersen S, Rozhon W, Šamaj J et al (2007) A plastid-localized glycogen synthase kinase 3 modulates stress tolerance and carbohydrate metabolism. Plant J 49:1076–1090. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.03025.x
Anwar A, Kim J-K (2020) Transgenic breeding approaches for improving abiotic stress tolerance: recent progress and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 21:2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082695
Aranega-Bou P, de la Leyva MO, Finiti I et al (2014) Priming of plant resistance by natural compounds. Hexanoic acid as a model. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00488
Arriagada O, Cacciuttolo F, Cabeza RA et al (2022) A comprehensive review on chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) breeding for abiotic stress tolerance and climate change resilience. Int J Mol Sci 23:6794
Asensio AC, Gil-Monreal M, Pires L et al (2012) Two Fe-superoxide dismutase families respond differently to stress and senescence in legumes. J Plant Physiol 169:1253–1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.04.019
Ashraf M, Akram N (2009) Improving salinity tolerance of plants through conventional breeding and genetic engineering: an analytical comparison. Biotechnol Adv 27:744–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2009.05.026
Ashrafi E, Zahedi M, Razmjoo J (2014) Co-inoculations of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia under salinity in alfalfa. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 60:619–629. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2014.936037
Ashraf M, Akbar A, Askari S et al (2018) Recent advances in abiotic stress tolerance of plants through chemical priming: an overview. In: Rakshit A, Singh H (eds) Advances in seed priming. Springer, Singapore, pp 51–79
Assaha D, Ueda A, Saneoka H et al (2017) The role of Na+ and K+ transporters in salt stress adaptation in glycophytes. Front Physiol 8:509. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00509
Atieno J, Li Y, Langridge P et al (2017) Exploring genetic variation for salinity tolerance in chickpea using image-based phenotyping. Sci Rep 7:1300. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01211-7
Atieno J, Colmer TD, Taylor J et al (2021) Novel salinity tolerance loci in chickpea identified in glasshouse and field environments. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.667910
Awana M, Yadav K, Rani K et al (2019) Insights into salt stress-induced biochemical, molecular and epigenetic regulation of spatial responses in Pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L.). J Plant Growth Regul 38:1545–1561
Ayra L, Ramírez M, Íñiguez LP et al (2018) The common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) Basic Leucine Zipper (bZIP) transcription factor family: response to salinity stress in fertilized and symbiotic N2-fixing plants. Agriculture 8:160
Azad M, Alam M, Hamid M (2013) Modification of salt tolerance level in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) through induced mutation. Legume Res Int J 36:224–233
Azooz M (2009) Salt stress mitigation by seed priming with salicylic acid in two faba bean genotypes differing in salt tolerance. Int J Agric Biol 11:343–350
Azooz M, Alzahrani A, Youssef M (2013) The potential role of seed priming with ascorbic acid and nicotinamide and their interactions to enhance salt tolerance in broad bean (Vicia faba L.). Aust J Crop Sci 7:2091–2100
Bano DA, Singh R, Waza SA, Singh N (2015) Effect of cowpea Bradyrhizobium (RA-5) and Burkholderia cepacia (RRE-5) on growth parameters of pigeonpea under salt stress conditions. J Pure Appl Microbiol 9:2539–2546
Bano DA, Singh RK, Waza SA, Singh NP (2020) Effect of cowpea bradyrhizobium (RA-5) and Burkholderia cepacia (RRE-5) on growth parameters of pigeonpea under salt stress conditions. In: J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. https://microbiologyjournal.org/effect-of-cowpea-bradyrhizobium-ra-5-and-burkholderia-cepacia-rre-5-on-growth-parameters-of-pigeonpea-under-salt-stress-conditions/. Accessed 29 Aug 2021
Bao A-K, Wang S-M, Wu G-Q et al (2009) Overexpression of the Arabidopsis H+-PPase enhanced resistance to salt and drought stress in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Sci 176:232–240
Bao A, Du B, Touil L et al (2016) Co-expression of tonoplast Cation/H+ antiporter and H+-pyrophosphatase from xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum improves alfalfa plant growth under salinity, drought and field conditions. Plant Biotechnol J 14:964–975
Barnawal D, Bharti N, Maji D et al (2014) ACC deaminase-containing Arthrobacter protophormiae induces NaCl stress tolerance through reduced ACC oxidase activity and ethylene production resulting in improved nodulation and mycorrhization in Pisum sativum. J Plant Physiol 171:884–894
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bassil E, Blumwald E (2014) The ins and outs of intracellular ion homeostasis: NHX-type cation/H+ transporters. Curr Opin Plant Biol 22:1–6
Battaglia M, Covarrubias AA (2013) Late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) proteins in legumes. Front Plant Sci 4:190
Benidire L, Lahrouni M, El Khalloufi F et al (2017) Effects of Rhizobium leguminosarum inoculation on growth, nitrogen uptake and mineral assimilation in Vicia faba plants under salinity stress. J Agric Sci Technol 19:889–901
Benidire L, El Khalloufi F, Oufdou K et al (2020) Phytobeneficial bacteria improve saline stress tolerance in Vicia faba and modulate microbial interaction network. Sci Total Environ 729:139020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139020
Bernard SM, Habash DZ (2009) The importance of cytosolic glutamine synthetase in nitrogen assimilation and recycling. New Phytol 182:608–620
Betti M, García-Calderón M, Pérez-Delgado CM et al (2012) Glutamine synthetase in legumes: recent advances in enzyme structure and functional genomics. Int J Mol Sci 13:7994–8024
Bhagat N, Raghav M, Dubey S, Bedi N (2021) Bacterial exopolysaccharides: insight into their role in plant abiotic stress tolerance. J Microbiol Biotechnol 31:1045–1059. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.2105.05009
Bicakci T, Aksu E, Arslan M (2018) Effect of seed coating on germination, emergence and early seedling growth in Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) under salinity conditions. Fresenius Env Bull 27:6978–6984
Blumwald E, Aharon GS, Apse MP (2000) Sodium transport in plant cells. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA-Biomembr 1465:140–151
Bojović B, Đelić G, Topuzović M, Stanković M (2010) Effects of NaCl on seed germination in some species from families Brassicaceae and Solanaceae. Kragujev J Sci 32:83–87
Boncompagni E, Østerås M, Poggi M, le Rudulier D (1999) Occurrence of choline and glycine betaine uptake and metabolism in the family rhizobiaceae and their roles in osmoprotection. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2072–2077
Bouallègue A, Souissi F, Nouairi I et al (2017) Salicylic acid and hydrogen peroxide pretreatments alleviate salt stress in faba bean (Vicia faba) seeds during germination. Seed Sci Technol 45:675–690
Breria CM, Hsieh C-H, Yen T-B et al (2020) A SNP-based genome-wide association study to mine genetic loci associated to salinity tolerance in mungbean (Vigna radiata L.). Genes 11:759. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11070759
Brígido C, Nascimento FX, Duan J et al (2013) Expression of an exogenous 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase gene in Mesorhizobium spp. reduces the negative effects of salt stress in chickpea. FEMS Microbiol Lett 349:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6968.12294
Bruning B, Rozema J (2013) Symbiotic nitrogen fixation in legumes: perspectives for saline agriculture. Environ Exp Bot 92:134–143
Büyük İ, Inal B, Ilhan E et al (2016) Genome-wide identification of salinity responsive HSP70 s in common bean. Mol Biol Rep 43:1251–1266
Castiglioni P, Bell E, Lund A et al (2018) Identification of GB1, a gene whose constitutive overexpression increases glycinebetaine content in maize and soybean. Plant Direct 2:e00040. https://doi.org/10.1002/pld3.40
Chang C, Wang B, Shi L et al (2010) Alleviation of salt stress-induced inhibition of seed germination in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) by ethylene and glutamate. J Plant Physiol 167:1152–1156
Chang W, Sui X, Fan X et al (2018) Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis modulates antioxidant response and ion distribution in salt-stressed Elaeagnus angustifolia seedlings. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00652
Chao Y, Kang J, Sun Y et al (2009) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel gene encoding zinc finger protein from Medicago sativa L. Mol Biol Rep 36:2315
Chen J, Zhang H, Zhang X, Tang M (2017) Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis alleviates salt stress in black locust through improved photosynthesis, water status, and K+/Na+ homeostasis. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01739
Chen R, Li M, Zhang H et al (2019) Continuous salt stress-induced long non-coding RNAs and DNA methylation patterns in soybean roots. BMC Genom 20:1–12
Chen S, Zhang N, Zhou G et al (2021) Knockout of the entire family of AITR genes in Arabidopsis leads to enhanced drought and salinity tolerance without fitness costs. BMC Plant Biol 21:1–15
Coba de la Pena T, Redondo FJ, Manrique E et al (2010) Nitrogen fixation persists under conditions of salt stress in transgenic Medicago truncatula plants expressing a cyanobacterial flavodoxin. Plant Biotechnol J 8:954–965
Compant S, Reiter B, Sessitsch A et al (2005) Endophytic colonization of Vitis vinifera L. by plant growth-promoting bacterium Burkholderia sp. strain PsJN. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1685–1693. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.4.1685-1693.2005
Conforte VP, Echeverria M, Sánchez C et al (2010) Engineered ACC deaminase-expressing free-living cells of Mesorhizobium loti show increased nodulation efficiency and competitiveness on Lotus spp. J Gen Appl Microbiol 56:331–338. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.56.331
Cordovilla MP, Ligero F, Lluch C (1994) The effect of salinity on N fixation and assimilation in Vicia faba. J Exp Bot 45:1483–1488. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/45.10.1483
Cordovilla M, Ocaña A, Ligero F, Lluch C (1995) Growth stage response to salinity in simbiosis Vicia faba-Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae. Life Sci Adv 14:105–111
Cordovilla MDP, Ligero F, Lluch C (1999) Effect of salinity on growth, nodulation and nitrogen assimilation in nodules of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Appl Soil Ecol 11:1–7
Costa A, Navazio L, Szabo I (2018) The contribution of organelles to plant intracellular Calcium signalling. J Exp Bot. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery185
Dawood M, El-Awadi M (2015) Alleviation of salinity stress on Vicia faba L. plants via seed priming with metatonin. Acta Biológica Colomb 20:223–235. https://doi.org/10.15446/abc.v20n2.43291
De Rossi S, Di Marco G, Bruno L et al (2021) Investigating the drought and salinity effect on the redox components of Sulla Coronaria (L.) Medik. Antioxidants 10:1048
del Pilar CM, Ligero F, Lluch C (1995) Influence of host genotypes on growth, symbiotic performance and nitrogen assimilation in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) under salt stress. Plant Soil 172:289–297
Dell’Aversana E, Cirillo V, Van Oosten MJ et al (2021) Ascophyllum nodosum based extracts counteract salinity stress in tomato by remodeling leaf nitrogen metabolism. Plants 10:1044
Demidchik V, Maathuis FJM (2007) Physiological roles of nonselective cation channels in plants: from salt stress to signalling and development. New Phytol 175:387–404
Desheva G, Desheva GN, Stamatov SK (2020) Germination and early seedling growth characteristics of Arachis hypogaea L. under salinity (NaCl) stress. Agric Conspec Sci 85:113–121
Dissanayake R, Cogan NOI, Smith KF, Kaur S (2021) Application of genomics to understand salt tolerance in lentil. Genes 12:332. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12030332
Dodd I, Pérez-Alfocea F (2012) Microbial amelioration of crop salinity stress. J Exp Bot 63:3415–3428. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers033
Dong W, Song Y, Zhao Z et al (2017) The Medicago truncatula R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene MtMYBS1 enhances salinity tolerance when constitutively expressed in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 490:225–230
Dong W, Liu X, Li D et al (2018) Transcriptional profiling reveals that a MYB transcription factor MsMYB4 contributes to the salinity stress response of alfalfa. PLoS ONE 13:e0204033
Dubova L, Šenberga A, Alsiņa I (2015) The effect of double inoculation on the broad bean (Vicia faba L.) yield quality. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/THE-EFFECT-OF-DOUBLE-INOCULATION-ON-THE-BROAD-BEANS-Dubova-%C5%A0enberga/f44c75d49a5b09d4c3b86b2e7c90a7eeb88336f7. Accessed 4 Jul 2021
Duc G, Agrama H, Bao S et al (2015) Breeding annual grain legumes for sustainable agriculture: new methods to approach complex traits and target new cultivar ideotypes. Crit Rev Plant Sci 34:381–411. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2014.898469
Dutta P, Bera A (2014) Effect of NaCl salinity on seed germination and seedling growth of mungbean cultivars. Legume Res Int J 37:161–164
Egamberdieva D, Shurigin V, Gopalakrishnan S, Sharma R (2014) Growth and symbiotic performance of chickpea (Cicer arietinum) cultivars under saline soil conditions. J Biol Chem Res 2014:1–10
Egamberdieva D, Wirth S, Jabborova D et al (2017) Coordination between Bradyrhizobium and Pseudomonas alleviates salt stress in soybean through altering root system architecture. J Plant Interact 12:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2017.1294212
El-Awadi M, Sadak M, Dawood MG et al (2017) Amelioration the adverse effects of salinity stress by using γ-radiation in faba bean plants. Bull NRC 41:293–310
El-Bastawisy ZM, El-Katony TM, Abd El-Fatah SN (2018) Genotypic variability in salt tolerance of Vicia faba during germination and early seedling growth. J King Saud Univ Sci 30:270–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2017.04.004
El-Esawi MA, Al-Ghamdi AA, Ali HM, Alayafi AA (2019) Azospirillum lipoferum FK1 confers improved salt tolerance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) by modulating osmolytes, antioxidant machinery and stress-related genes expression. Environ Exp Bot. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.12.001
El-Serafy RS, El-Sheshtawy A-NA, Atteya AK et al (2021) Seed priming with silicon as a potential to increase salt stress tolerance in Lathyrus odoratus. Plants 10:2140
Etesami H, Beattie G (2018) Mining halophytes for plant growth-promoting halotolerant bacteria to enhance the salinity tolerance of non-halophytic crops. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00148
Evelin H, Devi T, Gupta S, Kapoor R (2019) Mitigation of salinity stress in plants by arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis: current understanding and new challenges. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00470
Fahmi AI, Nagaty HH, Eissa RA, Hassan MM (2011) Effects of salt stress on some nitrogen fixation parameters in faba bean. Pak J Biol Sci PJBS 14:385–391
Farissi M, Bouizgaren A, Faghire M et al (2011) Agro-physiological responses of Moroccan alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) populations to salt stress during germination and early seedling stages. Seed Sci Technol 39:389–401
Farooq M, Hussain M, Wakeel A, Siddique KHM (2015) Salt stress in maize: effects, resistance mechanisms, and management A Review. Agron Sustain Dev 35:461–481
Farooq M, Gogoi N, Hussain M et al (2017) Effects, tolerance mechanisms and management of salt stress in grain legumes. Plant Physiol Biochem 118:199–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.06.020
Fatnassi IC, Chiboub M, Saadani O et al (2015) Impact of dual inoculation with Rhizobium and PGPR on growth and antioxidant status of Vicia faba L. under copper stress. C R Biol 338:241–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2015.02.001
Fernández-Pascual M, De Lorenzo C, De Felipe M et al (1996) Possible reasons for relative salt stress tolerance in nodules of white lupin cv. Multolupa. J Exp Bot 47:1709–1716
Flowers T, Gaur P, Gowda C et al (2010) Salt sensitivity in chickpea. Plant Cell Environ 33:490–509. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02051.x
Forni C, Duca D, Glick BR (2017) Mechanisms of plant response to salt and drought stress and their alteration by rhizobacteria. Plant Soil 410:335–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-3007-x
Fotopoulos V, Christou A, Antoniou C, Manganaris GA (2015) REVIEW ARTICLE Hydrogen sulphide: a versatile tool for the regulation of growth and defence responses in horticultural crops. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 90:227–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2015.11513176
Gamalero E, Glick BR (2015) Bacterial modulation of plant ethylene levels. Plant Physiol 169:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00284
Gao S-Q, Chen M, Xu Z-S et al (2011) The soybean GmbZIP1 transcription factor enhances multiple abiotic stress tolerances in transgenic plants. Plant Mol Biol 75:537–553
Garg N, Manchanda G (2008) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation on salt-induced nodule senescence in Cajanus cajan (pigeonpea). J Plant Growth Regul 27:115–124
Garg N, Pandey R (2015) Effectiveness of native and exotic arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on nutrient uptake and ion homeostasis in salt-stressed Cajanus cajan L. (Millsp.) genotypes. Mycorrhiza 25:165–180
Garg N, Singla R (2004) Growth, photosynthesis, nodule nitrogen and carbon fixation in the chickpea cultivars under salt stress. Braz J Plant Physiol 16:137–146
Geilfus C-M (2018) Chloride: from nutrient to toxicant. Plant Cell Physiol 59:877–886
Geilfus CM, Niehaus K, Gödde V et al (2015) Fast responses of metabolites in Vicia faba L. to moderate NaCl stress. Plant Physiol Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.04.008
Ghanbari M, Mokhtassi-Bidgoli A, Mansour Ghanaei-Pashaki K, Karamniya S (2020) Germination characteristics and enzyme activity of mung bean (Vigna radiata) in response to methyl jasmonate and salinity treatments. Iran J Seed Res 7:83–97
Glick B (2012) Plant growth-promoting bacteria: mechanisms and applications. Scientifica 2012:e963401. https://doi.org/10.6064/2012/963401
Glick BR, Todorovic B, Czarny J et al (2007) Promotion of plant growth by bacterial ACC deaminase. Crit Rev Plant Sci 26:227–242. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680701572966
Gnanasambandam A, Paull J, Torres A et al (2012) Impact of molecular technologies on faba bean (Vicia faba L.) breeding strategies. Agronomy 2:132–166. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy2030132
Guan H, Liu X, Niu F et al (2019) OoNAC72, a NAC-type Oxytropis ochrocephala transcription factor, conferring enhanced drought and salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 10:890
Hajri R, Ouhibi C, Mechri M et al (2018) Salinity and water deficit effects on seed germination and recovery of lotus populations from northern Tunisia. Pak J Bot 50:2085–2090
Hanafy M, El-Banna A, Schumacher H et al (2013) Enhanced tolerance to drought and salt stresses in transgenic faba bean (Vicia faba L.) plants by heterologous expression of the PR10a gene from potato. Plant Cell Rep 32:663–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-013-1401-x
Hanin M, Ebel C, Ngom M et al (2016) New insights on plant salt tolerance mechanisms and their potential use for breeding. Front Plant Sci 7:1787. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01787
HanumanthaRao B, Nair RM, Nayyar H (2016) Salinity and high temperature tolerance in mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] from a physiological perspective. Front Plant Sci 7:957
Hasanuzzaman M, Araújo S, Gill SS (2020) The plant family fabaceae. Springer, Berlin
Hashem A, Abd Allah E, Alqarawi A et al (2014) Alleviation of adverse impact of salinity on faba bean (Vicia faba L.) by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Pak J Bot 46:2003–2013
Hashiguchi A, Komatsu S (2016) Impact of post-translational modifications of crop proteins under abiotic stress. Proteomes 4:42
Hassan MA, Pacurar A, López-Gresa MP et al (2016) Effects of salt stress on three ecologically distinct plantago species. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160236
Hassanein R, El-Kazzaz A, Hashem H et al (2019) Transformation with the sodium/proton antiporter’AtNHX1’enhances salt tolerance in faba bean (’Vicia faba’ L.). Plant Omics 12:48
Ha-Tran DM, Nguyen TTM, Hung S-H et al (2021) Roles of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) in stimulating salinity stress defense in plants: a review. Int J Mol Sci 22:3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063154
He Y, Fu J, Yu C et al (2015) Increasing cyclic electron flow is related to Na+ sequestration into vacuoles for salt tolerance in soybean. J Exp Bot 66:6877–6889
Hellal FA, Abdelhameid M, Abo-Basha DM, Zewainy RM (2012) Alleviation of the adverse effects of soil salinity stress by foliar application of silicon on Faba bean (Vica faba L.). J Appl Sci Res 2012:4428–4433
Hernández-Lucero E, Rodríguez-Hernández AA, Ortega-Amaro MA, Jiménez-Bremont JF (2014) Differential expression of genes for tolerance to salt stress in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Mol Biol Report 32:318–327
Hiz MC, Canher B, Niron H, Turet M (2014) Transcriptome analysis of salt tolerant common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) under saline conditions. PLoS ONE 9:e92598
Hniličková H, Hnilička F, Orsák M, Hejnák V (2019) Effect of salt stress on growth, electrolyte leakage, Na+ and K+ content in selected plant species. Plant Soil Environ 65:90–96
Hoang XLT, Chuong NN, Hoa TTK et al (2021) The drought-mediated soybean GmNAC085 functions as a positive regulator of plant response to salinity. Int J Mol Sci 22:8986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22168986
Horie T, Hauser F, Schroeder JI (2009) HKT transporter-mediated salinity resistance mechanisms in Arabidopsis and monocot crop plants. Trends Plant Sci 14:660–668
Hossain MR, Pritchard J, Ford-Lloyd BV (2016) Qualitative and quantitative variation in the mechanisms of salinity tolerance determined by multivariate assessment of diverse rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. Plant Genet Resour 14:91
Ighodaro OM, Akinloye OA (2018) First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex J Med 54:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajme.2017.09.001
Ilangumaran G, Schwinghamer TD, Smith DL (2021) Rhizobacteria from root nodules of an indigenous legume enhance salinity stress tolerance in soybean. Front Sustain Food Syst 4:308. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2020.617978
Irshad A, Rehman RNU, Abrar MM et al (2021) Contribution of rhizobium-legume symbiosis in salt stress tolerance in medicago truncatula evaluated through photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes, and compatible solutes accumulation. Sustainability 13:3369. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063369
Isayenkov SV, Maathuis FJM (2019) Plant salinity stress: many unanswered questions remain. Front Plant Sci 10:80
Islam MM, Haque MS, Sarwar AG (2019) Salt tolerance of cowpea genotypes during seed germination and seedling growth. J Bangl Agric Univ 17:39–44
Ivanchenko MG, Napsucialy-Mendivil S, Dubrovsky JG (2010) Auxin-induced inhibition of lateral root initiation contributes to root system shaping in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 64:740–752. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04365.x
Jaarsma R, Vries R, Boer A (2013) Effect of salt stress on growth, Na+ accumulation and proline metabolism in potato (Solanum tuberosum) Cultivars. PLoS ONE 8:e60183. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060183
Janczarek M, Skorupska A (2007) The Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii RosR: transcriptional regulator involved in exopolysaccharide production. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact MPMI 20:867–881. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-20-7-0867
Janczarek M, Kutkowska J, Piersiak T, Skorupska A (2010) Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii rosR is required for interaction with clover, biofilm formation and adaptation to the environment. BMC Microbiol 10:284. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-10-284
Jatan R, Chauhan PS, Lata C (2019) Pseudomonas putida modulates the expression of miRNAs and their target genes in response to drought and salt stresses in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Genomics 111:509–519
Jha B, Mishra A, Jha A, Joshi M (2013) Developing transgenic Jatropha using the SbNHX1 gene from an extreme halophyte for cultivation in saline wasteland. PLoS ONE 8:e71136
Jha UC, Bohra A, Jha R, Parida SK (2019) Salinity stress response and ‘omics’ approaches for improving salinity stress tolerance in major grain legumes. Plant Cell Rep 38:255–277
Ji H, Pardo JM, Batelli G et al (2013) The Salt Overly Sensitive (SOS) pathway: established and emerging roles. Mol Plant 6:275–286
Kaashyap M, Ford R, Kudapa H et al (2018) Differential regulation of genes involved in root morphogenesis and cell wall modification is associated with salinity tolerance in chickpea. Sci Rep 8:1–19
Kader MA, Lindberg S (2005) Uptake of sodium in protoplasts of salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant cultivars of rice, Oryza sativa L. determined by the fluorescent dye SBFI. J Exp Bot 56:3149–3158
Kadian N, Yadav K, Badda N, Aggarwal A (2013) AM fungi ameliorates growth, yield and nutrient uptake in Cicer arietinum L. under salt stress. Russ Agric Sci 39:321–329
Kang S, Waqas M, Khan A, Lee I (2014a) Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria: potential candidates for gibberellins production and crop growth promotion. Use of microbes for the alleviation of soil stresses, vol 1. Springer, New York, pp 1–19
Kang S-M, Radhakrishnan R, Khan AL et al (2014b) Gibberellin secreting rhizobacterium, Pseudomonas putida H-2-3 modulates the hormonal and stress physiology of soybean to improve the plant growth under saline and drought conditions. Plant Physiol Biochem 84:115–124
Katerji N, van Hoorn JW, Hamdy A, Mastrorilli M (2003) Salinity effect on crop development and yield, analysis of salt tolerance according to several classification methods. Agric Water Manag 62:37–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3774(03)00005-2
Kaushal M, Wani SP (2016) Rhizobacterial-plant interactions: strategies ensuring plant growth promotion under drought and salinity stress. Agric Ecosyst Environ 231:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.06.031
Kaundal R, Duhan N, Acharya BR et al (2021) Transcriptional profiling of two contrasting genotypes uncovers molecular mechanisms underlying salt tolerance in alfalfa. Sci Rep 11:5210. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84461-w
Keshavarzi MHB (2011) Effect of salt stress on germination and early seedling growth of savory (Satureja hortensis). Aust J Basic Appl Sci 5:3274–3279
Ketehouli T, Idrice Carther KF, Noman M et al (2019) Adaptation of plants to salt stress: characterization of Na+ and K+ transporters and role of CBL gene family in regulating salt stress response. Agronomy 9:687
Khalil SK, Mexal JG, Murray LW (2001) Germination of soybean seed primed in aerated solution of polyethylene glycol 8000. OnLine J Biol Sci 1:105–107
Khan HA, Siddique KHM, Colmer TD (2017) Vegetative and reproductive growth of salt-stressed chickpea are carbon-limited: sucrose infusion at the reproductive stage improves salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 68:2001–2011
Khan AL, Hamayun M, Kim Y-H et al (2011) Ameliorative symbiosis of endophyte (Penicillium funiculosum LHL06) under salt stress elevated plant growth of Glycine max L. Plant Physiol Biochem 49:852–861
Khan MA, Asaf S, Khan AL et al (2019) Halotolerant rhizobacterial strains mitigate the adverse effects of NaCl stress in soybean seedlings. BioMed Res Int 2019:e9530963. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9530963
Khandal H, Parween S, Roy R et al (2017) MicroRNA profiling provides insights into post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in chickpea root apex under salinity and water deficiency. Sci Rep 7:1–14
Khazaei H, O’Sullivan D, Stoddard F et al (2020) Recent advances in Faba Bean genetic and genomic tools for crop improvement. Legume Sci. https://doi.org/10.2094/preprints202012.0372.v1
Kheloufi A, Chorfi A, Mansouri L-M (2017) Germination kinetics in two Acacia karroo hayne ecotypes under salinity conditions. Open Access Libr J 4:1–11
Kim JH, Kim WT, Kang BG (2001) IAA and N6-benzyladenine inhibit ethylene-regulated expression of ACC oxidase and ACC synthase genes in mungbean hypocotyls. Plant Cell Physiol 42:1056–1061. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pce133
Kim S, Kang J, Cho D et al (2004) ABF2, an ABRE-binding bZIP factor, is an essential component of glucose signaling and its overexpression affects multiple stress tolerance. Plant J 40:75–87
Kloepper JW, Rodríguez-Kábana R, Zehnder GW et al (1999) Plant root-bacterial interactions in biological control of soilborne diseases and potential extension to systemic and foliar diseases. Australas Plant Pathol 28:21. https://doi.org/10.1071/AP99003
Kohli D, Joshi G, Deokar AA et al (2014) Identification and characterization of wilt and salt stress-responsive microRNAs in chickpea through high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 9:e108851
Kołodziejek J (2018) Seed germination responses to some environmental factors in the red feather (Trifolium rubens). Pak J Bot 50:59–65
Kong Z, Glick BR, Duan J et al (2015) Effects of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase-overproducing Sinorhizobium meliloti on plant growth and copper tolerance of Medicago lupulina. Plant Soil 391:383–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2434-4
Korver RA, Koevoets IT, Testerink C (2018) Out of shape during stress: a key role for auxin. Trends Plant Sci 23:783–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2018.05.011
Koskey G, Mburu SW, Kimiti JM et al (2018) Genetic characterization and diversity of rhizobium isolated from root nodules of mid-altitude climbing bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) varieties. Front Microbiol 9:968. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00968
Kronzucker HJ, Britto DT (2011) Sodium transport in plants: a critical review. New Phytol 189:54–81
Kumar A (2017) Germination behaviour of soybean varieties under different salinity stress. Int J Appl Agric Res 12:69–76
Kumar A, Verma J (2018) Does plant–microbe interaction confer stress tolerance in plants: a review? Microbiol Res 207:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2017.11.004
Kumar S, Kalita A, Srivastava R, Sahoo L (2017) Co-expression of Arabidopsis NHX1 and bar improves the tolerance to salinity, oxidative stress, and herbicide in transgenic mungbean. Front Plant Sci 8:1896. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01896
Kumar N, Bharadwaj C, Sahu S et al (2021) Genome-wide identification and functional prediction of salt-stress related long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Physiol Mol Biol Plants 27:2605–2619
Kumari P, Khanna V (2015) (PDF) ACC-deaminase and EPS production by salt tolerant rhizobacteria augment growth in Chickpea under salinity stress. Int J Bio-Resour Stress Manag. https://doi.org/10.5958/0976-4038.2015.00084.6
Lan Y, Cai D, Zheng Y (2005) Expression in Escherichia coli of three different soybean late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) genes to investigate enhanced stress tolerance. J Integr Plant Biol 47:613–621
Lavania D, Siddiqui M, Al-Whaibi M et al (2014) Genetic approaches for breeding heat stress tolerance in faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Acta Physiol Plant 37:1737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-014-1737-z
Lavrenko S, Lavrenko N, Lykhovyd P (2019) Effect of degree of salinity on seed germination and initial growth of chickpea (Cicer arietinum). Biosyst Divers 27:101–105
Lelandais-Brière C, Naya L, Sallet E et al (2009) Genome-wide Medicago truncatula small RNA analysis revealed novel microRNAs and isoforms differentially regulated in roots and nodules. Plant Cell 21:2780–2796
Lemaire B, Dlodlo O, Chimphango S et al (2015) Symbiotic diversity, specificity and distribution of rhizobia in native legumes of the Core Cape Subregion (South Africa). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 91:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiu024
Leonforte A, Sudheesh S, Cogan NO et al (2013) SNP marker discovery, linkage map construction and identification of QTLs for enhanced salinity tolerance in field pea (Pisum sativum L.). BMC Plant Biol 13:161. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-13-161
Li X-P, Tian A-G, Luo G-Z et al (2005) Soybean DRE-binding transcription factors that are responsive to abiotic stresses. Theor Appl Genet 110:1355–1362
Li TY, Zhang Y, Liu H et al (2010) Stable expression of Arabidopsis vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene AtNHX1, and salt tolerance in transgenic soybean for over six generations. Chin Sci Bull 55:1127–1134
Li D, Zhang Y, Hu X et al (2011a) Transcriptional profiling of Medicago truncatula under salt stress identified a novel CBF transcription factor MtCBF4 that plays an important role in abiotic stress responses. BMC Plant Biol 11:1–19
Li W, Wang D, Jin T et al (2011b) The vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene SsNHX1 from the halophyte salsola soda confers salt tolerance in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol Report 29:278–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0224-y
Li Z, Xu J, Gao Y et al (2017) The synergistic priming effect of exogenous salicylic acid and H2O2 on chilling tolerance enhancement during maize (Zea mays L.) seed germination. Front Plant Sci 8:1153. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01153
Li X, Liu Q, Feng H et al (2020) Dehydrin MtCAS31 promotes autophagic degradation under drought stress. Autophagy 16:862–877
Li M, Chen R, Jiang Q et al (2021) GmNAC06, a NAC domain transcription factor enhances salt stress tolerance in soybean. Plant Mol Biol 105:333–345
Liang X, Hou X, Li J et al (2019) High-resolution DNA methylome reveals that demethylation enhances adaptability to continuous cropping comprehensive stress in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 19:1–17
Liao Y, Zou H-F, Wei W et al (2008) Soybean GmbZIP44, GmbZIP62 and GmbZIP78 genes function as negative regulator of ABA signaling and confer salt and freezing tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 228:225–240
Liu H-H, Tian X, Li Y-J et al (2008) Microarray-based analysis of stress-regulated microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA 14:836–843
Liu M, Wang T-Z, Zhang W-H (2015a) Sodium extrusion associated with enhanced expression of SOS1 underlies different salt tolerance between Medicago falcata and Medicago truncatula seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 110:46–55
Liu W, Li R-J, Han T-T et al (2015b) Salt stress reduces root meristem size by nitric oxide-mediated modulation of auxin accumulation and signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 168:343–356. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00030
Liu S, Li M, Su L et al (2016) Negative feedback regulation of ABA biosynthesis in peanut (Arachis hypogaea): a transcription factor complex inhibits AhNCED1 expression during water stress. Sci Rep 6:37943. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37943
Liu J, Liu J, Liu J et al (2019) The potassium transporter SlHAK10 is involved in mycorrhizal potassium uptake1[OPEN]. Plant Physiol 180:465–479. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.01533
Lloret J, Wulff BBH, Rubio JM et al (1998) Exopolysaccharide II production is regulated by salt in the halotolerant strain Rhizobium meliloti EFB1. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1024
Long R, Li M, Kang J et al (2015) Small RNA deep sequencing identifies novel and salt-stress-regulated microRNAs from roots of Medicago sativa and Medicago truncatula. Physiol Plant 154:13–27
López M, Herrera-Cervera JA, Iribarne C et al (2008) Growth and nitrogen fixation in Lotus japonicus and Medicago truncatula under NaCl stress: nodule carbon metabolism. J Plant Physiol 165:641–650
Luo G, Wang Y, Xie Z et al (2006) The putative Ser/Thr protein kinase gene GmAAPK from soybean is regulated by abiotic stress. J Integr Plant Biol 48:327–333
Ma W, Guinel FC, Glick BR (2003) Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase promotes nodulation of pea plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4396–4402. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.8.4396-4402.2003
Ma W, Charles TC, Glick BR (2004) Expression of an exogenous 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase gene in sinorhizobium meliloti increases its ability to nodulate alfalfa. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5891–5897. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.10.5891-5897.2004
Ma H, Zhao D, Ning Q et al (2018) A multi-year beneficial effect of seed priming with gibberellic acid-3 (GA 3) on plant growth and production in a perennial grass, Leymus chinensis. Sci Rep 8:13214. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31471-w
Magwanga RO, Lu P, Kirungu JN et al (2018) Characterization of the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) proteins family and their role in drought stress tolerance in upland cotton. BMC Genet 19:1–31
Manchanda G, Garg N (2008) Salinity and its effects on the functional biology of legumes. Acta Physiol Plant 30:595–618
Manchanda G, Garg N (2011) Alleviation of salt-induced ionic, osmotic and oxidative stresses in Cajanus cajan nodules by AM inoculation. Plant Biosyst 145:88–97
Mansouri L, Heleili N, Boukhatem Z, Kheloufi A (2019) Seed germination and radicle establishment related to type and level of salt in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L. var. djedida). Cercet Agron În Mold Agron Res Mold 52:262–277
Matamoros MA, Dalton DA, Ramos J et al (2003) Biochemistry and molecular biology of antioxidants in the rhizobia-legume symbiosis. Plant Physiol 133:499–509. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.025619
Mbarki S, Skalicky M, Vachova P et al (2020) Comparing salt tolerance at seedling and germination stages in local populations of Medicago ciliaris L. to Medicago intertexta L. and Medicago scutellata L. Plants 9:526
Meng Y, Chen F, Shuai H et al (2016) Karrikins delay soybean seed germination by mediating abscisic acid and gibberellin biogenesis under shaded conditions. Sci Rep 6:1–12
Metwali EMR, Abdelmoneim TS, Bakheit MA, Kadasa NMS (2015) Alleviation of salinity stress in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) plants by inoculation with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). Plant Omics 8:449–460
Miao L, St. Clair DK (2009) Regulation of superoxide dismutase genes: implications in diseases. Free Radic Biol Med 47:344–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.05.018
Miller-Williams M, Loewen PC, Oresnik IJ (2006) Isolation of salt-sensitive mutants of Sinorhizobium meliloti strain Rm1021. Microbiol Read Engl 152:2049–2059. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.28937-0
Mishra S, Behura R, Awasthi JP et al (2014a) Ectopic overexpression of a mungbean vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene (VrNHX1) leads to increased salinity stress tolerance in transgenic Vigna unguiculata L. Walp Mol Breed 34:1345–1359
Mishra S, Panda SK, Sahoo L (2014b) Transgenic Asiatic grain legumes for salt tolerance and functional genomics. Rev Agric Sci 2:21–36
Mishra S, Alavilli H, Lee B et al (2015) Cloning and characterization of a novel vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene (VuNHX1) from drought hardy legume, cowpea for salt tolerance. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult PCTOC 120:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0572-7
Mohammed A (2018) Effectiveness of exopolysaccharides and biofilm forming plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on salinity tolerance of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Afr J Microbiol Res 12:399–404. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR2018.8822
Mokrani S, Nabti E, Cruz C (2020) Current advances in plant growth promoting bacteria alleviating salt stress for sustainable agriculture. Appl Sci 10:7025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207025
Moradi A (2016) Effect of mycorrhizal inoculation on growth, nitrogen fixation and nutrient uptake in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) under salt stress. Cercetări Agronomice în Moldova 1(165):67–80.
Moustafa-Farag M, Elkelish A, Dafea M et al (2020) Role of melatonin in plant tolerance to soil stressors: salinity, pH and heavy metals. Mol Basel Switz 25:E5359. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225359
Muchate N, Rajurkar N, Suprasanna P, Nikam T (2019) NaCl induced salt adaptive changes and enhanced accumulation of 20-hydroxyecdysone in the in vitro shoot cultures of Spinacia oleracea (L.). Sci Rep 9:12522. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48737-6
Muscolo A, Panuccio MR, Zhair Z et al (2019) Use of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria to ameliorate the performance of lentil under salinity: rhizobium and lentil under salinity. J Appl Bot Food Qual 92:179–186. https://doi.org/10.5073/JABFQ.2019.092.024
Mutch L, Young J (2004) Diversity and specificity of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae on wild and cultivated legumes. Mol Ecol 13:2435–2444. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2004.02259.x
Nadeem S, Ahmad M, Zahir Z et al (2014) The role of mycorrhizae and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) in improving crop productivity under stressful environments. Biotechnol Adv 32:429–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.12.005
Nadeem M, Li J, Yahya M et al (2019) Grain legumes and fear of salt stress: focus on mechanisms and management strategies. Int J Mol Sci 20:799
Najar R, Aydi S, Sassi-Aydi S et al (2019) Effect of salt stress on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence in Medicago truncatula. Plant Biosyst Int J Deal Asp Plant Biol 153:88–97
Nascimento FX, Rossi MJ, Soares CRFS et al (2014) New insights into 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase phylogeny, evolution and ecological significance. PLoS ONE 9:e99168. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099168
Nascimento FX, Rossi MJ, Glick BR (2016) Role of ACC deaminase in stress control of leguminous plants. In: Subramaniam G, Arumugam S, Rajendran V (eds) Plant growth promoting actinobacteria: a new avenue for enhancing the productivity and soil fertility of grain legumes. Springer, Singapore, pp 179–192
Naz R, Bano A (2015) Molecular and physiological responses of sunflower (Helianthus Annuus L.) to pgpr and sa under salt stress. Pak J Bot 47:35–42
Nguyen NT, Vu HT, Nguyen TT et al (2019a) Co-expression of Arabidopsis AtAVP1 and AtNHX1 to improve salt tolerance in soybean. Crop Sci 59:1133–1143
Nguyen Q, Vu L, Nguyen L et al (2019b) Overexpression of the GmDREB6 gene enhances proline accumulation and salt tolerance in genetically modified soybean plants. Sci Rep 9:19663. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55895-0
Ning L, Kan G, Shao H, Yu D (2018) Physiological and transcriptional responses to salt stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.) seedlings. Land Degrad Dev 29:2707–2719
Noori F, Etesami H, Najafi Zarini H et al (2018) Mining alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) nodules for salinity tolerant non-rhizobial bacteria to improve growth of alfalfa under salinity stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 162:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.092
Numan M, Bashir S, Khan Y et al (2018) Plant growth promoting bacteria as an alternative strategy for salt tolerance in plants: a review. Microbiol Res 209:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2018.02.003
Nyaga JW, Njeru EM (2020) Potential of native rhizobia to improve cowpea growth and production in semiarid regions of Kenya. Front Agron 2:28. https://doi.org/10.3389/fagro.2020.606293
Okazaki S, Nukui N, Sugawara M, Minamisawa K (2004) Rhizobial strategies to enhance symbiotic interactions: rhizobitoxine and 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. Microb Environ 19:99–111. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.19.99
Orabi S, Abdelhamid M (2016) Protective role of α-tocopherol on two Vicia faba cultivars against seawater-induced lipid peroxidation by enhancing capacity of anti-oxidative system. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 15:145–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2014.09.001
Orozco-Mosqueda M, Glick B, Santoyo G (2020) ACC deaminase in plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPB): an efficient mechanism to counter salt stress in crops. Microbiol Res 235:126439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2020.126439
Osman ME, Mohsen AA, Nessim AA et al (2019) Evaluation of biochar as a soil amendment for alleviating the harmful effect of salinity on Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. Egypt J Bot 59:617–631
Palma F, López-Gómez M, Tejera NA, Lluch C (2014) Involvement of abscisic acid in the response of Medicago sativa plants in symbiosis with Sinorhizobium meliloti to salinity. Plant Sci Int J Exp Plant Biol 223:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.02.005
Pantola S, Bargali K, Bargali S (2017) Effects of NaCl on germination and seedling growth in macrotyloma uniflorum and Vigna mungo. Curr Agric Res J 5:169
Panwar M, Tewari R, Nayyar H (2016) Native halo-tolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Enterococcus and Pantoea sp. improve seed yield of Mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) under soil salinity by reducing sodium uptake and stress injury. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 22:445–459
Paparella S, Araújo SS, Rossi G et al (2015) Seed priming: state of the art and new perspectives. Plant Cell Rep 34:1281–1293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1784-y
de la Peña TC, Redondo FJ, Manrique E et al (2010) Nitrogen fixation persists under conditions of salt stress in transgenic Medicago truncatula plants expressing a cyanobacterial flavodoxin. Plant Biotechnol J 8:954–965. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00519.x
Pennycooke JC, Cheng H, Stockinger EJ (2008) Comparative genomic sequence and expression analyses of Medicago truncatula and alfalfa subspecies falcata COLD-ACCLIMATION-SPECIFIC genes. Plant Physiol 146:1242–1254
Percey WJ, Shabala L, Breadmore MC et al (2014) Ion transport in broad bean leaf mesophyll under saline conditions. Planta 240:729–743
Phang T, Shao G, Lam H (2008) Salt tolerance in soybean. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1196–1212
Pi E, Xu J, Li H et al (2019) Enhanced salt tolerance of rhizobia-inoculated soybean correlates with decreased phosphorylation of the transcription factor GmMYB183 and altered flavonoid biosynthesis*. Mol Cell Proteom 18:2225–2243. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.RA119.001704
Pitann B, Kranz T, Zörb C et al (2011) Apoplastic pH and growth in expanding leaves of Vicia faba under salinity. Environ Exp Bot 74:31–36
Podder S, Ray J, Das D, Sarker BC (2020) Effect of salinity (NaCl) on germination and seedling growth of mungbean (Vigna radiata L.). J Biosci Agric Res 24:2012–2019
Preston JC, Hileman L (2013) Functional evolution in the plant SQUAMOSA-PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (SPL) gene family. Front Plant Sci 4:80
Qados AMSA (2011) Effect of salt stress on plant growth and metabolism of bean plant Vicia faba (L.). J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 10:7–15
Qados AMSA (2015) Mechanism of nanosilicon-mediated alleviation of salinity stress in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) plants. Am J Exp Agric 7:78–95
Qados A, Moftah A (2015) Influence of silicon and nano-silicon on germination, growth and yield of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) under salt stress conditions. Am J Exp Agric. https://doi.org/10.9734/ajea/2015/14109
Qu L, Huang Y, Zhu C et al (2016) Rhizobia-inoculation enhances the soybean’s tolerance to salt stress. Plant Soil 400:209–222
Quan W, Liu X, Wang H, Chan Z (2016) Physiological and transcriptional responses of contrasting alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) varieties to salt stress. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-0981-x
Rabie GH, Almadini AM (2005) Role of bioinoculants in development of salt-tolerance of Vicia faba plants under salinity stress. Afr J Biotechnol 4:210–222. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2005.000-3041
Rabiei Z, Hosseini SJ, Pirdashti H, Hazrati S (2020) Physiological and biochemical traits in coriander affected by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria under salt stress. Heliyon 6:e05321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05321
Rahman M, Bhuiyan M, Ali M et al (2017) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the tolerance to sodium chloride levels, and on growth and yield of lentil (Lens culinaris). Agricult 15:156–169
Razzaq MK, Akhter M, Ahmad RM et al (2022) CRISPR-Cas9 based stress tolerance: new hope for abiotic stress tolerance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum). Mol Biol Rep 49:8977–8985
Rohman MM, Molla MR, Akhi AH et al (2020) Use of osmolytes for improving abiotic stress tolerance in Fabaceae plants. The plant family Fabaceae. Springer, Berlin, pp 181–222
Russo DM, Williams A, Edwards A et al (2006) Proteins exported via the PrsD-PrsE type I secretion system and the acidic exopolysaccharide are involved in biofilm formation by Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Bacteriol 188:4474–4486. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00246-06
Sagervanshi A, Naeem A, Geilfus C-M et al (2021) One-time abscisic acid priming induces long-term salinity resistance in Vicia faba: Changes in key transcripts, metabolites, and ionic relations. Physiol Plant 172:146–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13315
Saghari M, Khoshrou V, Alahmadi MJ, Foroughifar H (2020) The effect of salinity stress on germination and growth characteristics of haloxylon aphyllum and halothamnus subaphyllus. Plant Arch 20:3664–3668
Saha P, Chatterjee P, Biswas AK (2010) NaCl pretreatment alleviates salt stress by enhancement of antioxidant defense system and osmolyte accumulation in mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek). Indian J Exp Bio 48:593–600
Sahoo D, Kumar S, Mishra S et al (2016) Enhanced salinity tolerance in transgenic mungbean overexpressing Arabidopsis antiporter (NHX1) gene. Mol Breed 36:144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0564-x
Saïdi S, Ramírez-Bahena M, Santillana N et al (2014) Rhizobium laguerreae sp. nov. nodulates Vicia faba on several continents. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:242–247. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.052191-0
Sakuma Y, Maruyama K, Osakabe Y et al (2006) Functional analysis of an Arabidopsis transcription factor, DREB2A, involved in drought-responsive gene expression. Plant Cell 18:1292–1309
Salgotra RK, Gupta M (2019) Exploring the role of epigenetics in cereal and leguminous crops exposed to abiotic stress. Epigenetics in plants of agronomic importance: fundamentals and applications. Springer, Cham, pp 149–170
Sallam A, Ul-Allah S (2019) Genomics-aided breeding for climate-smart traits in Faba Bean. In: Kole C (ed) Genomic designing of climate-smart pulse crops. Springer, Cham, pp 359–395
Sanyal D, Bangerth F (1998) Stress induced ethylene evolution and its possible relationship to auxin-transport, cytokinin levels, and flower bud induction in shoots of apple seedlings and bearing apple trees. Plant Growth Regul 24:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005948918382
Sarkar T, Thankappan R, Kumar A et al (2014) Heterologous expression of the AtDREB1A gene in transgenic peanut-conferred tolerance to drought and salinity stresses. PLoS ONE 9:e110507. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110507
Sarker U, Oba S (2020) The response of salinity stress-induced A. tricolor to growth, anatomy, physiology, non-enzymatic and enzymatic antioxidants. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.559876
Segami S, Makino S, Miyake A et al (2014) Dynamics of vacuoles and H+-pyrophosphatase visualized by monomeric green fluorescent protein in Arabidopsis: artifactual bulbs and native intravacuolar spherical structures. Plant Cell 26:3416–3434
Semida WM, Taha RS, Abdelhamid MT, Rady MM (2014) Foliar-applied α-tocopherol enhances salt-tolerance in Vicia faba L. plants grown under saline conditions. South Afr J Bot 95:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2014.08.005
Sevanayak D, Edna A, Koti R et al (2020) Salinity tolerance of forage range legumes during germination and early seedling growth. Progressive Res 12:1357–1360
Sadak M, Abdelhamid M, Schmidhalter U (2015) Effect of foliar application of aminoacids on plant yield and some physiological parameters in bean plants irrigated with seawater. Acta Biológica Colomb 20:141–152. https://doi.org/10.15446/abc.v20n1.42865
Sehrawat N, Yadav M, Sharma AK et al (2019) Salt stress and mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek]: effects, physiological perspective and management practices for alleviating salinity. Arch Agron Soil Sci 65:1287–1301
Shahzad M, Zörb C, Geilfus C, Mühling KH (2013) Apoplastic Na+ in Vicia faba leaves rises after short-term salt stress and is remedied by silicon. J Agron Crop Sci 199:161–170
Sheidaei S, Zahedi M, Meibodo S (2011) Effect of salinity stress on dry matter accumulation and ion distribution pattern in five safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) genotypes. Iran J Field Crop Sci 41:811–819
Shi H, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Zhu J-K (2002) The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 14:465–477
Shrivastava P, Kumar R (2015) Soil salinity: a serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J Biol Sci 22:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2014.12.001
Shu K, Qi Y, Chen F et al (2017) Salt stress represses soybean seed germination by negatively regulating GA biosynthesis while positively mediating ABA biosynthesis. Front Plant Sci 8:1372
Shukla PS, Agarwal PK, Jha B (2012) Improved salinity tolerance of Arachis hypogaea (L.) by the interaction of halotolerant plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. J Plant Growth Regul 31:195–206
Sidari M, Santonoceto C, Anastasi U et al (2008) Variations in four genotypes of lentil under NaCl-salinity stress. Am J Agric Biol Sci 3:410–416
Silva LR, Bento C, Gonçalves AC et al (2017) Legume bioactive compounds: influence of rhizobial inoculation. AIMS Microbiol 3:267–278. https://doi.org/10.3934/microbiol.2017.2.267
Singh R, Shelke G, Kumar A, Jha P (2015) Biochemistry and genetics of ACC deaminase: a weapon to “stress ethylene” produced in plants. Front Microbiol 6:937. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00937
Slama I, Abdelly C, Bouchereau A et al (2015) Diversity, distribution and roles of osmoprotective compounds accumulated in halophytes under abiotic stress. Ann Bot 115:433–447. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcu239
Smýkal P, Coyne C, Ambrose M et al (2015) Legume crops phylogeny and genetic diversity for science and breeding. Crit Rev Plant Sci 34:43–104. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2014.897904
Souana K, Taïbi K, Abderrahim LA et al (2020) Salt-tolerance in Vicia faba L. is mitigated by the capacity of salicylic acid to improve photosynthesis and antioxidant response. Sci Hortic 273:109641
Stoddard FL, Balko C, Erskine W et al (2006) Screening techniques and sources of resistance to abiotic stresses in cool-season food legumes. Euphytica 147:167–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-4723-8
Sun Y, Wang D, Bai Y et al (2006) Studies on the overexpression of the soybean GmNHX1 in Lotus corniculatus: the reduced Na+ level is the basis of the increased salt tolerance. Chin Sci Bull 51:1306–1315
Sun Z, Wang Y, Mou F et al (2016) Genome-wide small RNA analysis of soybean reveals auxin-responsive microRNAs that are differentially expressed in response to salt stress in root apex. Front Plant Sci 6:1273
Sun T, Ma N, Wang C et al (2021) A golgi-localized sodium/hydrogen exchanger positively regulates salt tolerance by maintaining higher K+/Na+ ratio in soybean. Front Plant Sci 12:638340
Sunkar R, Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu J-K (2007) Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci 12:301–309
Swaraj K, Bishnoi NR (1999) Effect of salt stress on nodulation and nitrogen fixation in legumes. IJEB 37(09): 843-848
Tajini F, Trabelsi M, Drevon J (2012) Combined inoculation with Glomus intraradices and Rhizobium tropici CIAT899 increases phosphorus use efficiency for symbiotic nitrogen fixation in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Saudi J Biol Sci 19:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2011.11.003
Talukdar D (2011) Isolation and characterization of NaCl-tolerant mutations in two important legumes, Clitoria ternatea L. and Lathyrus sativus L.: induced mutagenesis and selection by salt stress. J Med Plants Res 5:3619–3628
Tang R, Li C, Xu K et al (2010) Isolation, functional characterization, and expression pattern of a Vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter Gene TrNHX1 from Trifolium repens L. Plant Mol Biol Report 28:102–111
Tavakkoli E, Rengasamy P, McDonald G (2010) High concentrations of Na+ and Cl– ions in soil solution have simultaneous detrimental effects on growth of faba bean under salinity stress. J Exp Bot 61:4449–4459. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq251
Tavakkoli E, Paull J, Rengasamy P, McDonald G (2012) Comparing genotypic variation in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) in response to salinity in hydroponic and field experiments. Field Crops Res 127:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2011.10.016
Teakle N, Tyerman S (2010) Mechanisms of Cl- transport contributing to salt tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 33:566–589. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02060.x
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91:503–527
Thompson AJ, Jackson AC, Symonds RC et al (2000) Ectopic expression of a tomato 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene causes over-production of abscisic acid. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 23:363–374. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00789.x
Tian C, Wang E, Wu L et al (2008) Rhizobium fabae sp. nov., a bacterium that nodulates Vicia faba. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2871–2875. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.2008/000703-0
Tian H, Guo F, Zhang Z et al (2020) Discovery, identification, and functional characterization of long noncoding RNAs in Arachis hypogaea L. BMC Plant Biol 20:1–16
Timmusk S, Paalme V, Pavlicek T et al (2011) Bacterial distribution in the rhizosphere of wild barley under contrasting microclimates. PLoS ONE 6:e17968. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017968
Toker C (2014) Mutagenesis for resistance to abiotic stresses: chickpea as model crop. Mutagenesis: exploring novel genes and pathways. Wageningen Academic Publishers, Wageningen, pp 78–81
Tlahig S, Bellani L, Karmous I et al (2021) Response to salinity in legume species: an insight on the effects of salt stress during seed germination and seedling growth. Chem Biodivers 18:e2000917
Tsavkelova E (2011) Bacteria Associated with Orchid Roots. In: Maheshwari DK (ed) Bacteria in agrobiology: plant growth responses. Springer, Berlin, pp 221–258
Uno Y, Furihata T, Abe H et al (2000) Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factors involved in an abscisic acid-dependent signal transduction pathway under drought and high-salinity conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:11632–11637. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.190309197
Van Dam J, Faaij AP, Hilbert J et al (2009) Large-scale bioenergy production from soybeans and switchgrass in Argentina: Part B. Environmental and socio-economic impacts on a regional level. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 13:1679–1709
Vance ME, Kuiken T, Vejerano EP et al (2015) Nanotechnology in the real world: redeveloping the nanomaterial consumer products inventory. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.6.181
Wahab AMA, Zahran HH (1981) Effects of salt stress on nitrogenase activity and growth of four legumes. Biol Plant 23:16. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02909205
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1105-5
Wang S-M, Zhang J-L, Flowers TJ (2007) Low-affinity Na+ uptake in the halophyte Suaeda maritima. Plant Physiol 145:559–571
Wang T-Z, Liu M, Zhao M-G et al (2015a) Identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs involved in osmotic and salt stress in Medicago truncatula using genome-wide high-throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol 15:1–13
Wang Y, Chai C, Valliyodan B et al (2015b) Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of the PIN auxin transporter gene family in soybean (Glycine max). BMC Genom 16:951. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-2149-1
Wang Z, Cheng K, Wan L et al (2015c) Genome-wide analysis of the basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor gene family in six legume genomes. BMC Genom 16:1–15
Wang W, Xia MX, Chen J et al (2016a) Gene expression characteristics and regulation mechanisms of superoxide dismutase and its physiological roles in plants under stress. Biochem Mosc 81:465–480. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297916050047
Wang Y, Zhang Z, Zhang P et al (2016b) Rhizobium symbiosis contribution to short-term salt stress tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Soil 402:247–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2792-6
Wang J, Meng X, Dobrovolskaya OB et al (2017) Non-coding RNAs and their roles in stress response in plants. GenomicsProteom Bioinform 15:301–312
Wang Y, Jiang L, Chen J et al (2018a) Overexpression of the alfalfa WRKY11 gene enhances salt tolerance in soybean. PLoS ONE 13:e0192382
Wang Z, Yang Q, Shao Y et al (2018b) GmLEA2-1, a late embryogenesis abundant protein gene isolated from soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.), confers tolerance to abiotic stress. Acta Biol Hung 69:270–282
Wang H, Liang L, Liu B et al (2020) Arbuscular mycorrhizas regulate photosynthetic capacity and antioxidant defense systems to mediate salt tolerance in maize. Plants 9:1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111430
Wang T, Xun H, Wang W et al (2021) Mutation of GmAITR genes by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing results in enhanced salinity stress tolerance in soybean. Front Plant Sci 2752
Welgama A, Florentine S, Marchante H et al (2019) The germination success of Acacia longifolia subsp. longifolia (Fabaceae): a comparison between its native and exotic ranges. Aust J Bot 67:414–424
Williams L, Grigg SP, Xie M et al (2005) Regulation of Arabidopsis shoot apical meristem and lateral organ formation by microRNA miR166g and its AtHD-ZIP target genes. 132(16):3657–3668
Windels D, Dang TT, Chen Z, Verdier J (2021) Snapshot of epigenetic regulation in legumes. Legume Sci 3:e60
Winicov I, Bastola D (1999) Transgenic overexpression of the transcription factor Alfin1 enhances expression of the endogenous MsPRP2 gene in alfalfa and improves salinity tolerance of the plants. Plant Physiol 120:473–480
Wu H, Li Z (2019) The importance of Cl− exclusion and vacuolar Cl− sequestration: revisiting the role of Cl− transport in plant salt tolerance. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01418
Xavier LJC, Germida JJ (2002) Response of lentil under controlled conditions to co-inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia varying in efficacy. Soil Biol Biochem 34:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00165-1
Xu J, Xue C, Xue D et al (2013) Overexpression of GmHsp90s, a heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) gene family cloning from soybean, decrease damage of abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 8:e69810
Yan F, Zhu Y, Zhao Y et al (2020) De novo transcriptome sequencing and analysis of salt-, alkali-, and drought-responsive genes in Sophora alopecuroides. BMC Genom 21:423. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-06823-4
Yang Q, Wu M, Wang P et al (2005) Cloning and expression analysis of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Alfalfa. DNA Seq 16:352–357. https://doi.org/10.1080/10425170500272742
Yang S, Zhang Z, Xue Y et al (2014) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi increase salt tolerance of apple seedlings. Bot Stud 55:70. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40529-014-0070-6
Yang Y, Yu T-F, Ma J et al (2020) The soybean bZIP transcription factor gene GmbZIP2 confers drought and salt resistances in transgenic plants. Int J Mol Sci 21:670
Yasin NA, Khan WU, Ahmad SR et al (2018) Imperative roles of halotolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and kinetin in improving salt tolerance and growth of black gram (Phaseolus mungo). Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:4491–4505
Yasir TA, Khan A, Skalicky M et al (2021) Exogenous sodium nitroprusside mitigates salt stress in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) by affecting the growth, yield, and biochemical properties. Molecules 26:2576
Yinsuo J, Gray V, Straker C (2004) The influence of Rhizobium and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on nitrogen and phosphorus accumulation by Vicia faba. Ann Bot 94:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mch135
Yoo S-J, Weon H-Y, Sang J, Sang MK (2019) Induced tolerance to salinity stress by halotolerant bacteria Bacillus aryabhattai H19-1 and B mesonae H20-5 in tomato plants. J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:1124–1136. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1904.04026
Younesi O, Baghbani A, Namdari A (2013) The effects of Pseudomonas fluorescence and Rhizobium meliloti co-inoculation on nodulation and mineral nutrient contents in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) under salinity stress. Int J Agric Crop Sci IJACS 5:1500–1507
Yousef A, Sprent J (1983) Effects of NaCl on growth, nitrogen incorporation and chemical composition of inoculated and NH4NO3 fertilized Vicia faba (L.) plants. J Exp Bot 34:941–950
Yousef F, Shafique F, Ali Q, Malik A (2020) Effects of salt stress on the growth traits of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) and pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedlings. Biol Clin Sci Res J 2020:1
Yu X, Liu Y, Wang S et al (2016) CarNAC4, a NAC-type chickpea transcription factor conferring enhanced drought and salt stress tolerances in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 35:613–627
Yu S, Yu L, Hou Y et al (2019) Contrasting effects of NaCl and NaHCO3 stresses on seed germination, seedling growth, photosynthesis, and osmoregulators of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Agronomy 9:409
Yuan C, Li C, Lu X et al (2020) Comprehensive genomic characterization of NAC transcription factor family and their response to salt and drought stress in peanut. BMC Plant Biol 20:1–21
Yung W, Li M, Sze C et al (2021) Histone modifications and chromatin remodelling in plants in response to salt stress. Physiol Plant 173:1495–1513
Zahaf O, Blanchet S, de Zélicourt A et al (2012) Comparative transcriptomic analysis of salt adaptation in roots of contrasting medicago truncatula genotypes. Mol Plant 5:1068–1081. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sss009
Zahran HH, Marín-Manzano MC, Sánchez-Raya AJ et al (2007) Effect of salt stress on the expression of NHX-type ion transporters in Medicago intertexta and Melilotus indicus plants. Physiol Plant 131:122–130
Zahran HH, Sprent JI (1986) Effects of sodium chloride and polyethylene glycol on root-hair infection and nodulation of Vicia faba L. plants by Rhizobium leguminosarum. Planta 167:303–309
Zhang X, Harper R, Karsisto M, Lindström K (1991) Diversity of rhizobium bacteria isolated from the root nodules of leguminous trees. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 41:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-41-1-104
Zhang W-H, Skerrett M, Walker NA et al (2002) Nonselective currents and channels in plasma membranes of protoplasts from coats of developing seeds of bean. Plant Physiol 128:388–399
Zhang W, Walker NA, Patrick JW, Tyerman SD (2004) Calcium-dependent K current in plasma membranes of dermal cells of developing bean cotyledons. Plant Cell Environ 27:251–262
Zhang Y, Zheng W, Everall I et al (2015) Rhizobium anhuiense sp. nov., isolated from effective nodules of Vicia faba and Pisum sativum. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:2960–2967. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.000365
Zhang H, Yasmin F, Song BH (2019) Neglected treasures in the wild—legume wild relatives in food security and human health. Curr Opin Plant Biol 49:17–20
Zhang W, Wang N, Yang J et al (2020) The salt-induced transcription factor GmMYB84 confers salinity tolerance in soybean. Plant Sci 291:110326
Zhao Q, Bao Y (2015) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and two phenolic acids of Medicago sativa under various mixed salt-alkaline stresses. Acta Bot Boreali-Occident Sin 35:1829–1836
Zhou Q, Tian A, Zou H et al (2008) Soybean WRKY-type transcription factor genes, GmWRKY13, GmWRKY21, and GmWRKY54, confer differential tolerance to abiotic stresses in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Biotechnol J 6:486–503
Zhou SJ, Jing Z, Shi JL (2013) Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of the MLO gene family in Cucumis sativus. Genet Mol Res 12:6565–6578
Funding
This article is being produced in the framework of the PRIMA DIVICIA project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing-Original draft preparation, SB and FH; Writing-Review and editing, MF and AS; Supervision, MF and AS. All authors have read and agreed the proof version to be published.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bouzroud, S., Henkrar, F., Fahr, M. et al. Salt stress responses and alleviation strategies in legumes: a review of the current knowledge. 3 Biotech 13, 287 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03643-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03643-7