Abstract
Background and Aims
Salt stress negatively affects alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) production and biological nitrogen fixation. We investigated whether rhizobium symbiosis has an effect on host plant tolerance to salt stress.
Methods
We determined the survival rate, oxidative damage level, activities of antioxidant enzymes, and contents of osmotic solutes in the leaf and root of 4-month-old alfalfa with active nodules, inactive nodules or without nodules, and under short-term salt stress.
Results
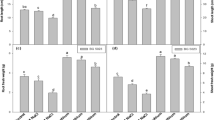
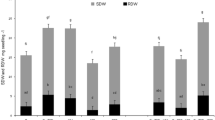
Alfalfa with active nodules showed higher survival rate. Higher survival rate was associated with reduced lipid peroxidation, higher activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX) as well as higher concentrations of reduced glutathione (GSH) and soluble sugar, especially in roots under salt stress. Variance analysis indicated nodulation affected the activities of SOD, CAT, POD, and APX along with concentrations of GSH, soluble sugar, and soluble protein. Inoculation also resulted in higher basal levels of superoxide anion radical (O2 −·) without salt stress.
Conclusions
Rhizobium symbiosis had a positive effect on alfalfa salt tolerance by improving the activity of antioxidant enzymes and osmotic adjustment capacity.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- O2 −·:
-
Superoxide anion radical
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- AN:
-
Alfalfa with active nodules
- IN:
-
Alfalfa with inactive nodules
- NN:
-
Alfalfa with no nodules
References
Aranjuelo I, Molero G, Erice G, Aldasoro J, Arrese-Igor C, Nogués S (2015) Effect of shoot removal on remobilization of carbon and nitrogen during regrowth of nitrogen-fixing alfalfa. Physiol Plant 153:91–104
Ashraf M, Harris PJC (2004) Potential biochemical indicators of salinity tolerance in plants. Plant Sci 166:3–16
Ashraf M, O'Leary JW (1999) Changes in soluble proteins in spring wheat stressed with sodium chloride. Biol Plant 42:113–117
Ashrafi E, Razmjoo J, Zahedi M, Pessarakli M (2015) Screening alfalfa for salt tolerance based on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes. Agron J 107:167–173
Azevedo Neto AD, Prisco JT, Gomes Filho E (2009) Changes in soluble amino-N, soluble proteins and free amino acids in leaves and roots of salt-stressed maize genotypes. J Plant Interact 4:137–144
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Becana M, Dalton DA, Moran JF, Iturbe‐Ormaetxe I, Matamoros MA, Rubio CM (2000) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in legume nodules. Physiol Plant 109:372–381
Berendsen RL, Pieterse CM, Bakker PA (2012) The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci 17:478–486
Bohnert HJ, Nelson DE, Jensen RG (1995) Adaptations to environmental stresses. Plant Cell 7:1099
Bolanos L, Martín M, El-Hamdaoui A, Rivilla R, Bonilla I (2006) Nitrogenase inhibition in nodules from pea plants grown under salt stress occurs at the physiological level and can be alleviated by B and Ca. Plant Soil 280:135–142
Bouhmouch I, Souad-Mouhsine B, Brhada F, Aurag J (2005) Influence of host cultivars and Rhizobium species on the growth and symbiotic performance of Phaseolus vulgaris under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 162:1103–1113
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Caverzan A, Passaia G, Rosa SB, Ribeiro CW, Lazzarotto F, Margis-Pinheiro M (2012) Plant responses to stresses: role of ascorbate peroxidase in the antioxidant protection. Genet Mol Biol 35:1011–1019
Chance B, Maehly AC (1955) Assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Enzymol 2:764–775
Chaudhuri K, Chouchuri M (1993) Effects of short-term NaCl salinity stress on free radical mediated membrane damage in two jute species. Indian J Exp Biol 31:327–331
Chinnusamy V, Jagendorf A, Zhu J-K (2005) Understanding and improving salt tolerance in plants. Crop Sci 45:437–448
Cordovilla MDP, Ligero F, Lluch C (1999) Effects of NaCl on growth and nitrogen fixation and assimilation of inoculated and KNO3 fertilized Vicia faba L. and Pisum sativum L. plants. Plant Sci 140:127–136
Dakora FD (2003) Defining new roles for plant and rhizobial molecules in sole and mixed plant cultures involving symbiotic legumes. New Phytol 158:39–49
Deakin WJ, Broughton WJ (2009) Symbiotic use of pathogenic strategies: rhizobial protein secretion systems. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:312–320
Dreywood R (1946) Qualitative test for carbohydrate material. Ind Eng Chem, Anal Ed 18:499–499
El-Akhal M, Rincón A, Coba de la Peña T, Lucas MM, El Mourabit N, Barrijal S, Pueyo JJ (2013) Effects of salt stress and rhizobial inoculation on growth and nitrogen fixation of three peanut cultivars. Plant Biol 15:415–421
El Msehli S et al (2011) Crucial role of (homo) glutathione in nitrogen fixation in Medicago truncatula nodules. New Phytol 192:496–506
Elstner EF, Heupel A (1976) Inhibition of nitrite formation from hydroxylammoniumchloride: a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Anal Biochem 70:616
Ertani A, Schiavon M, Muscolo A, Nardi S (2013) Alfalfa plant-derived biostimulant stimulate short-term growth of salt stressed Zea mays L. plants. Plant Soil 364:145–158
Evelin H, Kapoor R, Giri B (2009) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in alleviation of salt stress: a review. Ann Bot 104:1263–1280
Feng G, Zhang F, Li X, Tian C, Tang C, Rengel Z (2002) Improved tolerance of maize plants to salt stress by arbuscular mycorrhiza is related to higher accumulation of soluble sugars in roots. Mycorrhiza 12:185–190
Frendo P, Harrison J, Norman C, Jiménez MJH, Van de Sype G, Gilabert A, Puppo A (2005) Glutathione and homoglutathione play a critical role in the nodulation process of Medicago truncatula. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 18:254–259
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutases I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930
Gossett DR, Millhollon EP, Lucas M (1994) Antioxidant response to NaCl stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive cultivars of cotton. Crop Sci 34:706–714
Groten K et al (2006) Redox regulation of peroxiredoxin and proteinases by ascorbate and thiols during pea root nodule senescence. FEBS Lett 580:1269–1276
Grover M, Ali SZ, Sandhya V, Rasul A, Venkateswarlu B (2011) Role of microorganisms in adaptation of agriculture crops to abiotic stresses. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:1231–1240
Harrison J, Jamet A, Muglia CI, Van de Sype G, Aguilar OM, Puppo A, Frendo P (2005) Glutathione plays a fundamental role in growth and symbiotic capacity of Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 187:168–174
Hernandez J, Olmos E, Corpas F, Sevilla F, Del Rio L (1995) Salt-induced oxidative stress in chloroplasts of pea plants. Plant Sci 105:151–167
Hissin PJ, Hilf R (1976) A fluorometric method for determination of oxidized and reduced glutathione in tissues. Anal Biochem 74:214–226
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Stn, Circ 347
Hoffman BM, Lukoyanov D, Yang ZY, Dean DR, Seefeldt LC (2014) Mechanism of nitrogen fixation by nitrogenase: the next stage. Chem Rev 114:4041–4062
Hurkman WJ, Fornari CS, Tanaka CK (1989) A comparison of the effect of salt on polypeptides and translatable mRNAs in roots of a salt-tolerant and a salt-sensitive cultivar of barley. Plant Physiol 90:1444–1456
Kaschuk G, Kuyper TW, Leffelaar PA, Hungria M, Giller KE (2009) Are the rates of photosynthesis stimulated by the carbon sink strength of rhizobial and arbuscular mycorrhizal symbioses? Soil Biol Biochem 41:1233–1244
Khadri M, Tejera NA, Lluch C (2006) Alleviation of salt stress in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) by exogenous abscisic acid supply. J Plant Growth Regul 25:110–119
Kiers ET, Rousseau RA, West SA, Denison RF (2003) Host sanctions and the legume-rhizobium mutualism. Nature 425:78–81
Lauter D, Munns D, Clarkin K (1981) Salt response of chickpea as influenced by N supply. Agron J 73:961–966
Lutts S, Kinet J, Bouharmont J (1996) Effects of salt stress on growth, mineral nutrition and proline accumulation in relation to osmotic adjustment in rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity resistance. Plant Growth Regul 19:207–218
Mittova V, Volokita M, Guy M (2015) Antioxidative systems and stress tolerance: insight from wild and cultivated tomato species. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species signaling and communication in plants. Springer, In, pp 89–131
Morant-Manceau A, Pradier E, Tremblin G (2004) Osmotic adjustment, gas exchanges and chlorophyll fluorescence of a hexaploid triticale and its parental species under salt stress. J Plant Physiol 161:25–33
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Palma F, Tejera NA, Lluch C (2013) Nodule carbohydrate metabolism and polyols involvement in the response of Medicago sativa to salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 85:43–49
Pauly N et al (2006) Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species and glutathione: key players in the legume–Rhizobium symbiosis. J Exp Bot 57:1769–1776
Peleg-Grossman S, Melamed Book N, Levine A (2012) ROS production during symbiotic infection suppresses pathogenesis-related gene expression. Plant Signaling Behav 7:409–415
Peoples MB, Craswell ET (1992) Biological nitrogen fixation: investments, expectations and actual contributions to agriculture. Plant Soil 141:13–39
Polle A (2001) Dissecting the superoxide dismutase-ascorbate-glutathione-pathway in chloroplasts by metabolic modeling. Computer simulations as a step towards flux analysis. Plant Physiol 126:445–462
Porcel R, Aroca R, Ruiz Lozano JM (2012) Salinity stress alleviation using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. A review. Agron Sustainable Dev 32:181–200
Puckette MC, Weng H, Mahalingam R (2007) Physiological and biochemical responses to acute ozone-induced oxidative stress in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:70–79
Rasool S, Ahmad A, Siddiqi T, Ahmad P (2013) Changes in growth, lipid peroxidation and some key antioxidant enzymes in chickpea genotypes under salt stress. Acta Physiol Plant 35:1039–1050
Redondo FJ, de la Pena TC, Lucas MM, Pueyo JJ (2012) Alfalfa nodules elicited by a flavodoxin-overexpressing Ensifer meliloti strain display nitrogen-fixing activity with enhanced tolerance to salinity stress. Planta 236:1687–1700
Ruiz J, Blumwald E (2002) Salinity-induced glutathione synthesis in Brassica napus. Planta 214:965–969
Santos R, Hérouart D, Sigaud S, Touati D, Puppo A (2001) Oxidative burst in Alfalfa-Sinorhizobium meliloti symbiotic interaction. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 14:86–89
Sassi-Aydi S, Aydi S, Abdelly C (2012) Inoculation with the native Rhizobium gallicum 8a3 improves osmotic stress tolerance in common bean drought-sensitive cultivar. Acta Agric Scand, Sect B 62:179–187. doi:10.1080/09064710.2011.597425
Serraj R, Drevon JJ (1998) Effects of salinity and nitrogen source on growth and nitrogen fixation in alfalfa. J Plant Nutr 21:1805–1818
Shao HB, Chu LY, Shao MA, Jaleel CA, Mi HM (2008) Higher plant antioxidants and redox signaling under environmental stresses. C R Biol 331:433–441
Shrivastava P, Kumar R (2015) Soil salinity: a serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J Biol Sci 22:123–131
Siddiqui MH, Khan MN, Mohammad F, Khan MMA (2008) Role of nitrogen and gibberellin (GA3) in the regulation of enzyme activities and in osmoprotectant accumulation in Brassica juncea L. under salt stress. J Agron Crop Sci 194:214–224
Siqueira JO, Nair MG, Hammerschmidt R, Safir GR, Putnam AR (1991) Significance of phenolic compounds in plant‐soil‐microbial systems. Crit Rev Plant Sci 10:63–121
Sreenivasulu N, Ramanjulu S, Ramachandra-Kini K, Prakash HS, Shekar-Shetty H, Savithri HS, Sudhakar C (1999) Total peroxidase activity and peroxidase isoforms as modified by salt stress in two cultivars of fox-tail millet with differential salt tolerance. Plant Sci 141:1–9
Szabados L, Savouré A (2010) Proline: a multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci 15:89
Wang WB, Kim YH, Lee HS, Kim KY, Deng XP, Kwak SS (2009) Analysis of antioxidant enzyme activity during germination of alfalfa under salt and drought stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:570–577
Wu QS, Zou YN, Liu W, Ye XF, Zai HF, Zhao LJ (2010) Alleviation of salt stress in citrus seedlings inoculated with mycorrhiza: changes in leaf antioxidant defense systems. Plant Soil Environ 56:470–475
Yousef A, Sprent J (1983) Effects of NaCl on growth, nitrogen incorporation and chemical composition of inoculated and NH4NO3 fertilized Vicia faba (L.) plants. J Exp Bot 34:941–950
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (31372357, 31272490), the National Key Technology R&D Program in the 12th Five-Year Plan of China (2011BAD17B05), the major project for Tibetan forage industry (Z2014C02N02), and China Agriculture Research System (CARS-35). The authors thank Drs. Yajun Wu and Roger N Gates from South Dakota State University for their advice on statistical analysis and constructive comments to this manuscript, as well as the anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful critique and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Timothy J. Flowers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, P. et al. Rhizobium symbiosis contribution to short-term salt stress tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Soil 402, 247–261 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2792-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2792-6