Abstract
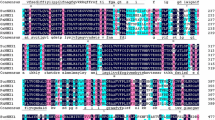
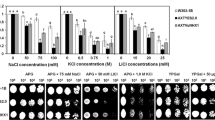
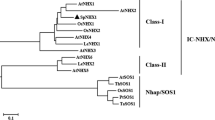
A putative vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene (SsNHX1) was isolated from the halophyte Salsola soda using the rapid amplification of cDNA ends method. Highly conserved regions of plant vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter, including amiloride-binding domain, NHE (Na+/H+ exchange) domain, and 12 transmembrane segments, were found in the deduced amino acid sequence of SsNHX1. Multiple alignments of vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporters showed that SsNHX1 shared high identity with other plant vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporters. Phylogenetic relationship analysis indicated that SsNHX1 was clustered into the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter group. Taken together, these results suggest that SsNHX1 is a new member of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter family. The effective expression of SsNHX1 in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) enhanced the salt tolerance of transgenic alfalfa which could grow in high concentrations of NaCl (up to 400 mM) over 50 days. This was the highest level of salt tolerance reported in transgenic plants. A further analysis of the physiological characteristics of transgenic and wild-type plants, including the Na+ and K+ contents, superoxide dismutase activity, the rate of electrolyte leakage, and the proline content, showed that large amounts of Na+ in the cytoplasm of leaves were transported into vacuoles by the exogenous Na+/H+ antiporter, which averted the toxic effects of Na+ to the cell of transgenic alfalfa.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RACE:
-
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- WT:
-
Wild type
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- REL:
-
Rate of electrolyte leakage
- EC:
-
Electrical conductivity
References
Aharonovitz O, Grinstein S (1999) Na+/H+ exchangers: structure, function and regulation. Drugs News Perspect 12:105–109
Antúnez I, Retamosa EC, Villar R (2001) Relative growth rate in phylogenetically related deciduous and evergreen woody species. Oecologia 128:172–180. doi:10.1007/s004420100645
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258. doi:10.1126/science.285.5431.1256
Ballesteros E, Blumwald E, Donaire JP, Belver A (2006) Na+/H+ antiporter activity in tonoplast vesicles isolated from sunflower roots induced by NaCl stress. Physiol Plant 99:328–334. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1997.tb05420.x
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207. doi:10.1007/BF00018060
Bellucci M, De Marchis F, Mannucci R, Arcioni S (2003) Jellyfish green fluorescent protein as a useful reporter for transient expression and stable transformation in Medicago sativa L. Plant Cell Rep 22:328–337. doi:10.1007/s00299-003-0693-7
Blumwald E (2000) Sodium transport and salt tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:431–434. doi:10.1016/S0955-0674(00)00112-5
Chen H, An R, Tang JH, Cui XH, Hao FSH, Chen J, Wang XCH (2007) Over-expression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in an upland rice. Mol breeding 19:215–225. doi:10.1007/s11032-006-9048-8
Chen LH, Zhang B, Xu ZQ (2008) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of Arabidopsis vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene AtNHX1 in common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum). Transgenic Res 17:121–132. doi:10.1007/s11248-007-9085-z
Counillon L, Franchi A, Pouysségur J (1993) A point mutation of the Na+/H+ exchanger gene (NHE1) and amplification of the mutated allele confer amiloride resistance upon chronic acidosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:4508–4512
Flowers TJ, Troke PF, Yeo AR (1997) The mechanism of salt tolerance in halophytes. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 28:89–121. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.28.060177.000513
Fridovich I (1986) Superoxide dismutases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 58:61–79
Fukuda A, Chiba K, Maeda M, Nakamura A, Maeshima M, Tanaka Y (2004a) Effect of salt and osmotic stresses on the expression of genes for the vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase, H+-ATPase subunit A, and Na+/H+ antiporter from barley. J Exp Bot 55:585–594. doi:10.1093/jxb/erh070
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Tagiri A, Tanaka H, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Tanaka Y (2004b) Function, intracellular localization and the importance in salt tolerance of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from rice. Plant Cell Physiol 45:146–159. doi:org/10.1093/pcp/pch014
Giannopolitis CN, Ries SK (1977) Superoxide dismutase: I. Occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314. doi:10.1104/pp.59.2.309
Greenway H, Munns R (1980) Mechanisms of salt tolerance in nonhalophytes. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 31:149–190. doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.31.060180.001053
Hamada A, Shono M, Xia T, Ohta M, Hayashi Y, Tanaka A, Hayakawa T (2001) Isolation and characterization of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from the halophyte Atriplex gmelini. Plant Mol Biol 46:35–42. doi:10.1023/A:1010603222673
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.51.1.463
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffmann NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227:1229–1231. doi:10.1126/science.227.4691.1229
Kasuga M, Liu Q, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1999) Improving plant drought, salt, and freezing tolerance by gene transfer of a single stress-inducible transcription factor. Nat Biotechnol 17:287–291. doi:10.1038/7036
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163. doi:10.1093/bib/5.2.150
Lutts S, Kinet JM, Bouharmont J (1996) NaCl-induced senescence in leaves of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars differing in salinity resistance. Ann Bot 78:389–398. doi:10.1006/anbo.1996.0134
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio-assays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Ohta M, Hayashi Y, Nakashima A, Hamada A, Tanaka A, Nakamura T, Hayakawa T (2002) Introduction of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Atriplex gmelini confers salt tolerance to rice. FEBS Lett 532:279–282. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03679-7
Orlowski J, Grinstein S (1997) Na+/H+ exchangers of mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 272:22373–22376. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.36.22373
Putney LK, Denker SP, Barber DL (2002) The changing face of the Na+/H+ exchanger, NHE1: structure, regulation, and cellular actions. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 42:527–552. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.42.092001.143801
Raychaudhuri SS, Deng XW (2000) The role of superoxide dimutase in combating oxidative stress in higher plants. Bot Rev 66:89–98
Shi H, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of expression of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene AtNHX1 by salt stress and abscisic acid. Plant Mol Biol 50:543–550. doi:10.1023/A:1019859319617
Shi H, Ishitani M, Kim C, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97:6896–6901. doi:10.1073/pnas.120170197
Shi H, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Zhu JK (2002) The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell 14:465–477. doi:10.1105/tpc.010371
Somers DA, Samac DA, Olhoft PM (2003) Recent advances in legume transformation. Plant Physiol 131:892–899. doi:1104/pp.102.017681
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882. doi:10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
Uchimiya H, Murashige T (1974) Evaluation of parameters in the isolation of viable protoplasts from cultured tobacco cells. Plant Physiol 54:936–944. doi:10.1104/pp.54.6.936
Wang J, Zuo K, Wu W, Song J, Sun X, Lin J, Li X, Tang K (2003) Molecular cloning and characterization of a new Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Brassica napus. DNA Seq 14:351–358. doi:10.1080/10855660310001596211
Winicov I (2000) Alfin1 transcription factor overexpression enhances plant root growth under normal and saline conditions and improves salt tolerance in alfalfa. Planta 210:416–422. doi:10.1007/PL00008150
Winicov I, Bastola DR (1999) Transgenic overexpression of the transcription factor Alfin1 enhances expression of the endogenous MsPRP2 gene in alfalfa and improves salinity tolerance of the plants. Plant Physiol 120:473–480. doi:10.1104/pp.120.2.473
Wu CA, Yang GD, Meng QW, Zheng CC (2004) The cotton GhNHX1 gene encoding a novel putative tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter plays an important role in salt stress. Plant Cell Physiol 45:600–607. doi:10.1093/pcp/pch071
Wu YY, Chen QJ, Chen M, Chen J, Wang XC (2005) Salt-tolerant transgenic perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) obtained by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene. Plant Sci 169:65–73. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.02.030
Wu CX, Gao XH, Kong XQ, Zhao YX, Zhang H (2009) Molecular cloning and functional analysis of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene ThNHX1 from a halophytic plant Thellungiella halophila. Plant Mol Biol Rep 27:1–12. doi:10.1007/s11105-008-0048-1
Xia T, Apse MP, Aharon GS, Blumwald E (2002) Identification and characterization of a NaCl-inducible vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter in Beta vulgaris. Physiol Plant 116:206–212. doi:10.1034/j.1399-3054.2002.1160210.x
Xiong LM, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell 14:165–183. doi:10.1105/tpc.000596
Xue ZY, Zhi DY, Xue GP, Zhang H, Zhao YX, Xia GM (2004) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) expressing a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene with improved grain yields in saline soils in the field and a reduced level of leaf Na+. Plant Sci 167:849–859. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.05.034
Yamaguchi T, Blumwald E (2005) Developing salt-tolerant crop plants: challenges and opportunities. Trends Plant Sci 10:615–620. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2005.10.002
Yang Q, Wu M, Wang P, Kang J, Zhou X (2005) Cloning and expression analysis of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from alfalfa. DNA Seq 16:352–357. doi:10.1080/10425170500272742
Yu Q, Rengel Z (1999) Drought and salinity differentially influence activities of superoxide dismutases in narrow-leafed lupins. Plant Sci 142:1–11. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(98)00246-5
Zhang HX, Blumwald E (2001) Transgenic salt-tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in foliage but not in fruit. Nat Biotechnol 19:765–768. doi:10.1038/90824
Zhang HX, Hodson JN, Williams JP, Blumwald E (2001) Engineering salt-tolerant Brassica plants: characterization of yield and seed oil quality in transgenic plants with increased vacuolar sodium accumulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:12832–12836. doi:10.1073/pnas.231476498
Zhao JS, Zhi DY, Xue ZY, Liu H, Xia GM (2007) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic progeny of tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea) expressing a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 164:1377–1383. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2007.04.001
Zhu JK (2000) Genetic analysis of plant salt tolerance using Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 124:941–948. doi:10.1104/pp.124.3.941
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Project of Scientific and Technical Supporting Programs Funded by Ministry of Science & Technology of China (2008BADB3B09), the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (B07017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Wang, D., Jin, T. et al. The Vacuolar Na+/H+ Antiporter Gene SsNHX1 from the Halophyte Salsola soda Confers Salt Tolerance in Transgenic Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 29, 278–290 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0224-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-010-0224-y