Abstract
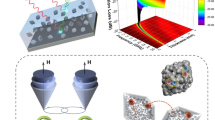
The escalating electromagnetic (EM) pollution issues and the demand to elevate military stealth technology make it imperative to develop cost-effective and high-performance electromagnetic wave (EMW) absorbing materials. In this paper, the flower-like CuS/γ-Fe2O3 van der Waals (vdW) heterostructures have been synthesized via a facile two-step solvothermal approach. The flower-like CuS skeleton increases the attenuation path of EMW while reducing the material density. Different contents of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles anchor between the flower-like CuS nanosheets to constitute a heterogeneous structure, which enables dielectric and magnetic loss synergistically to optimize impedance matching and remarkably improve the EMW absorption performance. The minimum reflection loss (RLmin) is −49.36 dB with a thickness of only 1.6 mm and the effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) reaches 4.64 GHz (13.36–18 GHz). By adjusting the thickness of the absorber, the EAB can cover 96% of the GHz band. Notably, the superior absorption of −61.53 dB at middle frequency band can be obtained by adjusting the amount of Fe2O3 addition. In this study, the adjustment of EM parameters and the optimization of impedance matching have been achieved by constructing a novel vdW heterogeneous structure, which provides fresh ideas and references for the design of high-performance EMW absorbing materials.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma, Z. L.; Kang, S. L.; Ma, J. Z.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y. L.; Liu, C.; Wei, A. J.; Xiang, X. L.; Wei, L. F.; Gu, J. W. Ultraflexible and mechanically strong double-layered aramid nanofiber-Ti3C2Tx MXene/silver nanowire nanocomposite papers for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8368–8382.
Cao, M. S.; Wang, X. X.; Zhang, M.; Cao, W. Q.; Fang, X. Y.; Yuan, J. Variable-temperature electron transport and dipole polarization turning flexible multifunctional microsensor beyond electrical and optical energy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907156.
Guo, Y. Y.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, T. T.; Xie, Y. X.; Zhao, L. B.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, W. X.; Yuan, L. Y.; Meng, A. L.; Zhang, J. et al. Enhancing electromagnetic wave absorption in carbon fiber using FeS2 nanoparticles. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 9591–9601.
Xu, J.; Ma, W. J.; He, P.; Zhou, Y. K.; Liu, X. Y.; Chen, Y.; Zuo, P. Y.; Zhuang, Q. X. A water-induced self-assembly approach to 3D hierarchical magnetic MXene networks for enhanced microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 330–340.
Gu, H. L.; Huang, J.; Li, N.; Yang, H.; Chen, G.; Dong, C. J.; Gong, C. H.; Guan, H. T. Reactive MnO2 template-assisted synthesis of double-shelled PPy hollow nanotubes to boost microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 146, 145–153.
Cheng, J.; Cai, L.; Shi, Y. Y.; Pan, F.; Dong, Y. Y.; Zhu, X. J.; Jiang, H. J.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, Z.; Lu, W. Polarization loss-enhanced honeycomb-like MoS2 nanoflowers/undaria pinnatifida-derived porous carbon composites with high-efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134284.
Bao, S. S.; Zhang, M. X.; Bu, X. J.; Zhang, W. B.; Jiang, Z. Y.; Xie, Z. X. Combinatorial structural engineering of multichannel hierarchical hollow microspheres assembled from centripetal Fe/C nanosheets to achieve effective integration of sound absorption and microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 13565–13575.
Li, Z. J.; Lin, H.; Wu, S. Y.; Su, X. Y.; Wang, T.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, Y. J.; Ling, H. L.; Meng, A. L.; Zhang, M. Rice husk derived porous carbon embedded with Co3Fe7 nanoparticles towards microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 229, 109673.
Liu, Y. L.; Tian, C. H.; Wang, F. Y.; Hu, B.; Xu, P.; Han, X. J.; Du, Y. C. Dual-pathway optimization on microwave absorption characteristics of core–shell Fe3O4@C microcapsules: Composition regulation on magnetic core and MoS2 nanosheets growth on carbon shell. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 141867.
Tian, S. Z.; Li, X. W.; Jiang, J.; Tang, L.; Zhang, H. Q.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z. W. Highly sensitive detection of rabbit IgG by electron spin resonance using CuS nanoparticles as probe. Sensor. Actuat. B Chem. 2021, 338, 129835.
Lv, H.; Kong, Y. F.; Gong, Z. Y.; Zheng, J. Z.; Liu, Y. M.; Wang, G. K. Engineering multifunctional carbon black interface over Mn0.5Cd0.5S nanoparticles/CuS nanotubes heterojunction for boosting photocatalytic hydrogen generation activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 604, 154513.
Wang, Y. C.; Chao, D. L.; Wang, Z. Z.; Ni, J. F.; Li, L. An energetic CuS-Cu battery system based on CuS nanosheet arrays. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5420–5427.
Sun, Y. Y.; Li, Y.; Sheng, L. M.; Lv, T. L.; Guo, R.; Yang, T. R.; Zhang, Q. S.; Xie, J. Y. Universal synthesis of free-standing metal-sulfides@metal@multi-walled carbon nanotube anode for high-performance sodium ion battery. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128732.
Curcio, A.; De Walle, A. V.; Benassai, E.; Serrano, A.; Luciani, N.; Menguy, N.; Manshian, B. B.; Sargsian, A.; Soenen, S.; Espinosa, A. et al. Massive intracellular remodeling of CuS nanomaterials produces nontoxic bioengineered structures with preserved photothermal potential. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 9782–9795.
Liu, P. B.; Gao, S.; Liu, X. D.; Huang, Y.; He, W. J.; Li, Y. T. Rational construction of hierarchical hollow CuS@CoS2 nanoboxes with heterogeneous interfaces for high-efficiency microwave absorption materials. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 192, 107992.
Wang, X. Y.; Wei, S. C.; Yuan, Y.; Li, R. B.; Wang, Y. J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, B.; Dong, C. F. Effect of copper sulfide nanosphere shell on microstructure and microwave absorption properties of cobalt ferrite/carbon nanotube composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 909, 164676.
Wang, F. Y.; Li, X. Z.; Chen, Z. H.; Yu, W.; Loh, K. P.; Zhong, B.; Shi, Y. M.; Xu, Q. H. Efficient low-frequency microwave absorption and solar evaporation properties of γ-Fe2O3 nanocube//graphene composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126676.
Wang, S. S.; Jiao, Q. Z.; Shi, Q.; Zhu, H. H.; Feng, T. Y.; Lu, Q. L.; Feng, C. H.; Li, H. S.; Shi, D. X.; Zhao, Y. Synthesis of porous nitrogen-doped graphene decorated by γ-Fe2O3 nanorings for enhancing microwave absorbing performance. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 1002–1010.
Kou, X.; Zhao, Y. P.; Xu, L. J.; Kang, Z. L.; Wang, Y. C.; Zou, Z. Y.; Huang, P.; Wang, Q. F.; Su, G. H.; Yang, Y. et al. Controlled fabrication of core-shell γ-Fe2O3@C-reduced graphene oxide composites with tunable interfacial structure for highly efficient microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 615, 685–696.
Deng, H.; Li, X. L.; Peng, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, J. P.; Li, Y. D. Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 2842–2845.
Lin, J. D.; Tao, F. F.; Wang, L. X.; Chen, L. Z.; Ying, Y. Q.; Zhang, L. Q.; Liu, H. L.; Xia, M. Y. Solvothermal synthesis of sphere-like CuS microcrystals and improvement as nonenzymatic glucose sensor. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 5509–5516.
Liu, J. L.; Liang, H. S.; Wu, H. J. Hierarchical flower-like Fe3O4/MoS2 composites for selective broadband electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 130, 105760.
Xing, L. S.; Li, X.; Wu, Z. C.; Yu, X. F.; Liu, J. W.; Wang, L.; Cai, C. Y.; You, W. B.; Chen, G. Y.; Ding, J. J. et al. 3D hierarchical local heterojunction of MoS2/FeS2 for enhanced microwave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122241.
Wang, P. Q.; Jia, C. C.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X. F. Van der waals heterostructures by design: From 1D and 2D to 3D. Matter 2021, 4, 552–581.
Xiao, Z. R.; Ji, S.; Li, Y. T.; Hou, F.; Zhang, H. C.; Zhang, X. W.; Wang, L.; Li, G. Z. Tuning oxygen vacancies on mesoporous ceria nanorods by metal doping: Controllable magnetic property. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 1037–1044.
Yuan, M. W.; Sun, Z. M.; Yang, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, Q. M.; Nan, C. Y.; Li, H. F.; Sun, G. B.; Chen, S. W. Self-catalyzed rechargeable lithium-air battery by in situ metal ion doping of discharge products: A combined theoretical and experimental study. Energy Environ. Mater. 2023, 6, e12258.
Ding, S. Q.; Liu, S.; Li, J. J.; Wu, L.; Ma, Z. F.; Yuan, X. X. Multifunctional catalyst CuS for nonaqueous rechargeable lithium-oxygen batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 50065–50075.
Shi, G. D.; Fan, Z. X.; Du, L. L.; Fu, X. L.; Dong, C. M.; Xie, W.; Zhao, D. B.; Wang, M.; Yuan, M. J. In situ construction of graphdiyne/CuS heterostructures for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 821–828.
Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y. B.; Wang, J.; Pan, F. S. Low-temperatures synthesis of CuS nanospheres as cathode material for magnesium second batteries. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 192–200.
Liu, H. Q.; He, Y. N.; Zhang, H.; Cao, K. Z.; Wang, S. D.; Jiang, Y.; Jing, Q. S.; Jiao, L. F. Lowering the voltage-hysteresis of CuS anode for Li-ion batteries via constructing heterostructure. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 130548.
Li, J. E.; Luo, S.; Zhang, B.; Lu, J. L.; Liu, W. L.; Zeng, Q. X.; Wan, J.; Han, X. Y.; Hu, C. G. High-performance asymmetric Mn(OH)2//Fe2O3 supercapacitor achieved by enhancing and matching respective properties of cathode and anode materials. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105410.
Xu, J. S.; Lu, N.; Yuan, M. W.; Sun, G. B. Rational design of hollow rice-grained α-Fe2O3/carbon nanofibers with optimized impedance matching for electromagnetic wave absorption enhanced. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 5676–5684.
Ye, K. H.; Li, K. S.; Lu, Y. R.; Guo, Z. J.; Ni, N.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y. C.; Ji, H. B.; Wang, P. S. An overview of advanced methods for the characterization of oxygen vacancies in materials. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 116, 102–108.
Wang, Z. Y.; Miao, J. Y.; Zhang, H. X.; Wang, D.; Sun, J. B. Hollow cubic ZnSnO3 with abundant oxygen vacancies for H2S gas sensing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122226.
Liu, S. Q.; Wen, H. R.; Ying, G.; Zhu, Y. W.; Fu, X. Z.; Sun, R.; Wong, C. P. Amorphous Ni(OH)2 encounter with crystalline CuS in hollow spheres: A mesoporous nano-shelled heterostructure for hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 7–14.
Li, M. C.; Qian, Y. T.; Du, J. M.; Wu, H. R.; Zhang, L. Y.; Li, G.; Li, K. D.; Wang, W. M.; Kang, D. J. CuS nanosheets decorated with CoS2 nanoparticles as an efficient electrocatalyst for enhanced hydrogen evolution at all pH values. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 14016–14022.
Xu, X.; Guo, Y.; Bloom, B. P.; Wei, J. J.; Li, H. Y.; Li, H. L.; Du, Y. K.; Zeng, Z.; Li, L. Q.; Waldeck, D. H. Elemental core level shift in high entropy alloy nanoparticles via X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis and first-principles calculation. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 17704–17712.
Xie, Y. X.; Guo, Y. Y.; Cheng, T. T.; Zhao, L. B.; Wang, T.; Meng, A. L.; Zhang, M.; Li, Z. J. Efficient electromagnetic wave absorption performances dominated by exchanged resonance of lightweight PC/Fe3O4@PDA hybrid nanocomposite. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141205.
Zhao, B.; Shao, G.; Fan, B. B.; Zhao, W. Y.; Xie, Y. J.; Zhang, R. Synthesis of flower-like CuS hollow microspheres based on nanoflakes self-assembly and their microwave absorption properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 10345–10352.
Guo, C. Y.; Xia, F. Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xi, L.; Zuo, Y. L. Flowerlike iron oxide nanostructures and their application in microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 631, 183–191.
Cui, G. Z.; Wang, L. B.; Li, L.; Xie, W.; Gu, G. X. Synthesis of CuS nanoparticles decorated Ti3C2Tx MXene with enhanced microwave absorption performance. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2020, 30, 343–351.
Zhang, Y.; Dai, F.; Mouldi, A.; Bouallegue, B.; Akhtar, M. N. Tunable microwave absorption features in bi-layer absorber based on mesoporous CuS micro-particle with 3D hierarchical structure and nanosphere like NiCo2O4. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 9146–9156.
Zhang, B.; Lin, S. F.; Zhang, J. J.; Li, X. P.; Sun, X. D. Facile synthesis of sandwich-like rGO/CuS/polypyrrole nanoarchitectures for efficient electromagnetic absorption. Materials 2020, 13, 446.
Ji, S. N.; Li, C. P.; Zhang, Z. M.; Jiang, X. H.; Yu, L. M. Hollow γ-Fe2O3@Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) versus γ-Fe2O3@SiO2@Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) core–shell structures for highly effective microwave absorption. Synth. Met. 2018, 239, 59–65.
Li, C. P.; Ji, S. N.; Jiang, X. H.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Zhang, Z. M.; Yu, L. M. Microwave absorption by watermelon-like microspheres composed of γ-Fe2O3, microporous silica and polypyrrole. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 9635–9649.
Ma, W. J.; Tang, C. H.; He, P.; Wu, X. H.; Cui, Z. K.; Lin, S. L.; Liu, X. Y.; Zhuang, Q. X. Morphology-controlled fabrication strategy of hollow mesoporous carbon spheres@f-Fe2O3 for microwave absorption and infrared stealth. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 34985–34996.
Zhang, N.; Huang, Y.; Wang, M. Y. Synthesis of graphene/thorns-like polyaniline/α-Fe2O3@SiO2 nanocomposites for lightweight and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 212–222.
Liu, Y.; Fu, Y. W.; Liu, L.; Li, W.; Guan, J. G.; Tong, G. X. Low-cost carbothermal reduction preparation of monodisperse Fe3O4/C core–shell nanosheets for improved microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16511–16520.
Tayebi Pak, A.; Masoudpanah, S. M.; Adeli, M.; Jazirehpour, M. Hierarchical porous Fe3O4/RGO nanocomposite powders as high performance microwave absorbers. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 548–560.
Zeng, X. J.; Cheng, X. Y.; Yu, R. H.; Stucky, G. D. Electromagnetic microwave absorption theory and recent achievements in microwave absorbers. Carbon 2020, 168, 606–623.
Ren, S. N.; Yu, H. J.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z. K.; Lin, T. F.; Huang, Y. D.; Yang, J.; Hong, Y. C.; Liu, J. Y. State of the art and prospects in metal-organic framework-derived microwave absorption materials. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 68.
Qin, M.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. Dielectric loss mechanism in electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105553.
Cheng, J.; Jiang, H. J.; Cai, L.; Pan, F.; Shi, Y. Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Lu, S. D.; Yang, Y.; Li, L. X. et al. Porous N-doped C/VB-group VS2 composites derived from perishable garbage to synergistically solve the environmental and electromagnetic pollution. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141208.
Xiong, J.; Xiang, Z.; Deng, B. W.; Wu, M. C.; Yu, L. Z.; Liu, Z. C.; Cui, E. B.; Pan, F.; Liu, R.; Lu, W. Engineering compositions and hierarchical yolk-shell structures of NiCo/GC/NPC nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 513, 145778.
Quan, B.; Liang, X. H.; Ji, G. B.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Ma, J. N.; Zhang, Y. N.; Li, D. R.; Xu, G. Y. Dielectric polarization in electromagnetic wave absorption: Review and perspective. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 728, 1065–1075.
Zheng, T. T.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Z. R.; Zhu, J. H.; Wu, G. L.; Yin, P. F. Customized dielectric-magnetic balance enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance in CuxS/CoFe2O4 composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 140876.
Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Tan, S. J.; Peymanfar, R.; Aslibeiki, B.; Ji, G. B. Ultrabroad microwave absorption ability and infrared stealth property of nano-micro CuS@rGO lightweight aerogels. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 171.
Sun, G. B.; Dong, B. X.; Cao, M. H.; Wei, B. Q.; Hu, C. W. Hierarchical dendrite-like magnetic materials of Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3, and Fe with high performance of microwave absorption. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 1587–1593.
Wu, N. N.; Liu, C.; Xu, D. M.; Liu, J. R.; Liu, W.; Shao, Q.; Guo, Z. H. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of three-dimensional porous Fe3O4/C composite flowers. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12471–12480.
Sun, Y. C.; Cui, W. Y.; Li, J. L.; Wu, J. Z. In-situ growth strategy to fabrication of MWCNTs/Fe3O4 with controllable interface polarization intensity and wide band electromagnetic absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 770, 67–75.
Shu, R. W.; Li, X. H.; Tian, K. H.; Shi, J. J. Fabrication of bimetallic metal-organic frameworks derived Fe3O4/C decorated graphene composites as high-efficiency and broadband microwave absorbers. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2022, 228, 109423.
Chen, J. B.; Zheng, J.; Huang, Q. Q.; Wang, F.; Ji, G. B. Enhanced microwave absorbing ability of carbon fibers with embedded FeCo/CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 36182–36189.
Shu, R. W.; Li, X. H.; Shi, J. J. Construction of porous carbon-based magnetic composites derived from iron zinc bimetallic metal-organic framework as broadband and high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 633, 43–52.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22271018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, N., Xu, J., Yuan, M. et al. Flower-like CuS/γ-Fe2O3 van der Waals heterostructures with high-efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Nano Res. 17, 3324–3333 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6058-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6058-3