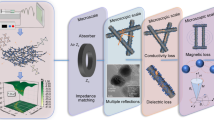
Abstract
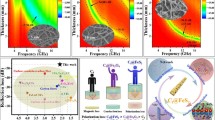
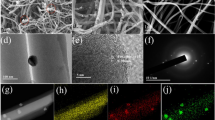
Electromagnetic wave absorption materials are widely used in electronic equipment and military fields. However, high cost and complex preparation processes become a major obstacle in promoting popularization in the civil field. To solve the problems above, researchers have made great efforts to develop Fe-based carbon composites. However, most of the typical composites require a high filling ratio while achieving excellent properties. Therefore, in this study, carbon nanofibers (CNFs) combined with the hollow rice-grained α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles were prepared by the in-situ transformation method. The rational microstructure design provided a solution for reducing the filling ratio, optimizing impedance matching, and improving electromagnetic wave absorption performance. The strong reflection loss value (−38.1 dB) and broad effective absorption bandwidth (4.6 GHz) for Fe2O3/CNFs composites were achieved with a low filling ratio (20 wt.%), and the analysis of electromagnetic parameters validated that the microstructure of Fe2O3/CNFs plays a crucial role in the performance improvement. With the optimized impedance matching and simple preparation method, Fe2O3/CNFs have broad application prospects in electromagnetic wave absorption.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts, S.; Vermeeren, G.; Van Den Bossche, M.; Aminzadeh, R.; Verloock, L.; Thielens, A.; Leroux, P.; Bergs, J.; Braem, B.; Philippron, A. et al. Lessons learned from a distributed RF-EMF sensor network. Sensors 2022, 22, 1715.
Romeo, S.; Zeni, O.; Scarfi, M. R.; Poeta, L.; Lioi, M. B.; Sannino, A. Radiofrequency electromagnetic field exposure and apoptosis: A scoping review of in vitro studies on mammalian cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2322.
Yang, H. H.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Wu, X. W.; Gan, P.; Luo, X. L.; Zhong, S. X.; Zuo, W. Q. Effects of acute exposure to 3500 MHz (5G) radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation on anxiety-like behavior and the auditory cortex in guinea pigs. Bioelectromagnetics 2022, 43, 106–118.
Cao, M. S.; Han, C.; Wang, X. X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y. L.; Shu, J. C.; Yang, H. J.; Fang, X. Y.; Yuan, J. Graphene nanohybrids: Excellent electromagnetic properties for the absorbing and shielding of electromagnetic waves. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 4586–4602.
Song, Q.; Ye, F.; Kong, L.; Shen, Q. L.; Han, L. Y.; Feng, L.; Yu, G. J.; Pan, Y. A.; Li, H. J. Graphene and MXene nanomaterials: Toward high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption in gigahertz band range. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000475.
Wang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Fang, C. Q.; Hou, X. L.; Xie, L. Recent advances in MXenes composites for electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 136, 105956.
Zhang, Z. W.; Cai, Z. H.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y. L.; Wang, Z. Y.; Xia, L.; Ma, S. P.; Yin, Z. Z.; Wang, R. F.; Cao, Y. S. et al. The recent progress of MXene-based microwave absorption materials. Carbon 2021, 174, 484–499.
Cheng, J.; Cai, L.; Shi, Y. Y.; Pan, F.; Dong, Y. Y.; Zhu, X. J.; Jiang, H. J.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, Z.; Lu, W. Polarization loss-enhanced honeycomb-like MoS2 nanoflowers/undaria pinnatifida-derived porous carbon composites with high-efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134284.
Jin, C.; Chen, J. H.; Zhang, B. C.; Kong, L. W.; An, S. N.; He, Z. S.; Liu, J. L. Low-cost mmwave metallic waveguide based on multilayer integrated vertical-EBG structure and its application to slot array antenna design. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 2205–2213.
Li, W.; Chen, X. Q.; Zhang, Z. L.; Wu, Z.; Yang, L.; Zou, Y. H. Ultralight and low-cost structural absorbers with enhanced microwave absorption performance based on sustainable waste biomass. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2022, 70, 401–409.
Liu, Q. C.; Zi, Z. F.; Zhang, M.; Pang, A. B.; Dai, J. M.; Sun, Y. P. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of urchin-like Fe/α-Fe2O3 composite synthesized by a simple thermal oxidation. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2014, 152, 137–143.
Xie, G. X.; Cheng, G. T.; Lv, T. Y.; Ma, J. Q.; Zhang, T. T.; Zhang, Y. R.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, L. L.; Wang, X. X.; Long, Y. Z. Electromagnetic properties and microwave absorption of electrospun Fe2O3-carbon composite nanofibers with particle-nanorod structure. Nano 2021, 16, 2150143.
Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Kong, X. Constructing holey γ-Fe2O3 nanosheets with enhanced capability for microwave absorption. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 23, 100690.
Cheng, Y.; Chen, P.; Dong, S. T.; Zhang, Z. Y.; Guo, Y. H. Development of a porous iron-based magnetic absorber with enhanced electromagnetic absorption performance. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 6799–6809.
Fang, Y.; Wang, W. J.; Wang, S.; Hou, X. W.; Xue, W. D.; Zhao, R. A quantitative permittivity model for designing electromagnetic wave absorption materials with conduction loss: A case study with microwave-reduced graphene oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135672.
Li, S. S.; Tang, X. W.; Zhang, Y. W.; Lan, Q. Q.; Hu, Z. W.; Li, L.; Zhang, N.; Ma, P. M.; Dong, W. F.; Tjiu, W. et al. Corrosion-resistant graphene-based magnetic composite foams for efficient electromagnetic absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 8297–8310.
Tian, K. H.; Huang, Y. N.; Zhang, C.; Shu, R. W.; Zhu, J. B.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z. H.; Li, C.; Liu, X. W. In-situ synthesis of graphite carbon nitride nanotubes/cobalt@carbon with castor-fruit-like structure as high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorbers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 620, 454–464.
Zhang, X. C.; Liu, M. J.; Xu, J.; Ouyang, Q. Y.; Zhu, C. L.; Zhang, X. L.; Zhang, X. T.; Chen, Y. J. Flexible and waterproof nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays on cotton-derived carbon fiber for electromagnetic wave absorption and electric-thermal conversion. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133794.
Liu, X. D.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X. X.; Yan, J.; Zong, M. Flexible N-doped carbon fibers decorated with Cu/Cu2O particles for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interf Sci. 2022, 616, 347–359.
Ma, M. L.; Liao, Z. J.; Su, X. W.; Zheng, Q. X.; Liu, Y. Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wan, F. Magnetic CoNi alloy particles embedded N-doped carbon fibers with polypyrrole for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 2203–2212.
Zhao, K.; Ye, F.; Cheng, L. F.; Liu, R. Z.; Liang, J.; Li, X. Synthesis of embedded ZrC-SiC-C microspheres via carbothermal reduction for thermal stability and electromagnetic wave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 591, 153105.
Wang, R.; Sun, Q. L.; Gu, H.; Ye, W.; Yuan, G. Q.; Yang, Z. T.; Long, X. Y. Preparation and electromagnetic-wave-absorption properties of a nitrogen-doped carbon-supported iron(II, III) oxide composite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 1383–1394.
Shu, Y.; Zhao, T. K.; Li, X. H.; Yang, L.; Cao, S. Q.; Ahmad, A.; Jiang, T.; Luo, H. J.; Jing, Z. M.; Ui Ain, N. Surface plasmon resonance-enhanced dielectric polarization endows coral-like Co@CoO nanostructures with good electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 585, 152704.
Guo, R.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, L. J.; Fan, Y. C.; Jiang, W. Porous N-doped Ni@SiO2/graphene network: Three-dimensional hierarchical architecture for strong and broad electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 106, 108–117.
Li, N.; Cao, M. H.; Hu, C. W. A simple approach to spherical nickel-carbon monoliths as light-weight microwave absorbers. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 18426–18432.
Li, N.; Hu, C. W.; Cao, M. H. Enhanced microwave absorbing performance of CoNi alloy nanoparticles anchored on a spherical carbon monolith. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 7685–7689.
Kong, B.; Liu, R.; Guo, J. H.; Lu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, Y. J. Tailoring micro/nano-fibers for biomedical applications. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 19, 328–347.
Al-Dhahebi, A. M.; Ling, J.; Krishnan, S. G.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Elumalai, N. K.; Saheed, M. S. M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Jose, R. Electrospinning research and products: The road and the way forward. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022, 9, 011319.
Luo, H. L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z. W.; Xiong, G. Y.; Wan, Y. Z. Constructing superior carbon-nanofiber-based composite microwave absorbers by engineering dispersion and loading of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on three-dimensional carbon nanofibers derived from bacterial cellulose. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 201, 130–138.
Liu, H.; Li, Y. J.; Yuan, M. W.; Sun, G. B.; Liao, Q. L.; Zhang, Y. Solid and macroporous Fe3C/N-C nanofibers with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorbability. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16832.
Li, Y. J.; Yuan, M. W.; Liu, H. H.; Sun, G. B. In situ synthesis of CoFe2O4 nanocrystals decorated in mesoporous carbon nanofibers with enhanced electromagnetic performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 826, 154147.
Basavaraja, S.; Vijayanand, H.; Venkataraman, A.; Deshpande, U. P.; Shripathi, T. Characterization of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles synthesized through self-propagating combustion route. Synth. React. Inorg. Metal-Org. Nano-Metal Chem. 2007, 37, 409–412.
Jia, C. J.; Sun, L. D.; Luo, F.; Han, X. D.; Heyderman, L. J.; Yan, Z. G.; Yan, C. H.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, Z.; Takano, M. et al. Large-scale synthesis of single-crystalline iron oxide magnetic nanorings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16968–16977.
Zhang, S. S.; Deng, P.; Yu, L. L.; Ni, Y.; Ling, C.; Zhu, Z. Y.; Liu, R. J. Fabrication and formation mechanism of hollow-structure supermagnetic α-Fe2O3/Fe3O4 heterogeneous nanospindles. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 2492–2501.
Uhm, Y. R.; Kim, W. W.; Rhee, C. K. A study of synthesis and phase transition of nanofibrous Fe2O3 derived from hydrolysis of Fe nanopowders. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 561–564.
Liu, H. H.; Li, Y. J.; Yuan, M. W.; Sun, G. B.; Li, H. F.; Ma, S. L.; Liao, Q. L.; Zhang, Y. In situ preparation of cobalt nanoparticles decorated in N-doped carbon nanofibers as excellent electromagnetic wave absorbers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22591–22601.
Min, W. X.; Xu, D. W.; Chen, P.; Chen, G. Z.; Yu, Q.; Qiu, H. F.; Zhu, X. Y. Synthesis of novel hierarchical CoNi@NC hollow microspheres with enhanced microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 8000–8016.
Xu, C.; Jin, D. Discussion on heat treatment of FeOOH. Inf. Rec. Mater. 1987, 3, 10–13,17.
Han, Y. H.; Yuan, J.; Zhu, Y. H.; Wang, Q. Q.; Li, L.; Cao, M. S. Implantation of WSe2 nanosheets into multi-walled carbon nanotubes for enhanced microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 609, 746–754.
Ji, J. D.; Huang, Y.; Yin, J. H.; Zhao, X. C.; Cheng, X. W.; He, S. L.; Li, X.; He, J.; Liu, J. P. Synthesis and electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of monodispersive Fe3O4/α-Fe2O3 composites. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 3935–3944.
Wang, X. Y.; Huang, J. G.; Feng, H.; Li, J. F.; Pu, Z. D.; Yin, X. C. Facile preparation of the dendritic Fe3O4 with a core—shell microstructure in SiO2-B2O3-Al2O3-CaO-Fe2O3 glass-ceramic system for enhanced microwave absorbing performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 877, 160147.
Zhang, H.; Xie, A. J.; Wang, C. P.; Wang, H. S.; Shen, Y. H.; Tian, X. Y. Novel rGO/α-Fe2O3 composite hydrogel: Synthesis, characterization and high performance of electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8547–8552.
Guo, C. Y.; Xia, F. Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xi, L.; Zuo, Y. L. Flowerlike iron oxide nanostructures and their application in microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 631, 183–191.
Quan, B.; Xu, G. Y.; Li, D. R.; Liu, W.; Ji, G. B.; Du, Y. W. Incorporation of dielectric constituents to construct ternary heterojunction structures for high-efficiency electromagnetic response. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 498, 161–169.
Ma, W. J.; Tang, C. H.; He, P.; Wu, X. H.; Cui, Z. K.; Lin, S.; Liu, X. Y.; Zhuang, Q. X. Morphology-controlled fabrication strategy of hollow mesoporous carbon spheres@f-Fe2O3 for microwave absorption and infrared stealth. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 34985–34996.
Lv, H. L.; Liang, X. H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H. Q.; Tang, D. M.; Zhang, B. S.; Ji, G. B.; Du, Y. W. Coin-like α-Fe2O3@CoFe2O4 core-shell composites with excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4744–4750.
Hu, H. H.; Zheng, Y.; Ren, K.; Wang, J. Y.; Zhang, Y. H.; Zhang, X. F.; Che, R. C.; Qin, G. W.; Jiang, Y. Position selective dielectric polarization enhancement in CNT based heterostructures for highly efficient microwave absorption. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 2324–2332.
Jia, Z. R.; Wang, B. B.; Feng, A. L.; Liu, J. J.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z. Y.; Wu, G. L. Development of spindle-cone shaped of Fe/α-Fe2O3 hybrids and their superior wideband electromagnetic absorption performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 799, 216–223.
Wang, L.; Yu, X. F.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Che, R. C. Conductive-network enhanced microwave absorption performance from carbon coated defect-rich Fe2O3 anchored on multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2019, 155, 298–308.
Chen, W. J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, B. B.; Jiang, Q. R.; Bao, S. S.; Jiang, Z. Y. Rational construction and microwave absorption properties of porous FeOx/Fe/C composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 829, 154519.
Zhou, J. H.; He, J. P.; Wang, T.; Li, G. X.; Guo, Y. X.; Zhao, J. Q.; Ma, Y. O. Design of mesostructured gamma-Fe2O3/carbon nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave absorption applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 8211–8214.
Fu, H. H.; Guo, Y.; Yu, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xie, Y.; Ling, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Li, S. Q.; Zhang, W. Tuning the shell thickness of core—shell α-Fe2O3@SiO2 nanoparticles to promote microwave absorption. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 957–962.
Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Che, R. C. Hollow porous Fe2O3 microspheres wrapped by reduced graphene oxides with high-performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 11167–11176.
Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Mao, X.; Zhuang, Q.; Xie, Z.; Han, Z. γ-Fe2O3-MWNT/poly(p-phenylenebenzobisoxazole) composites with excellent microwave absorption performance and thermal stability. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 6440–6447.
Saeed, M. S.; Seyed-Yazdi, J.; Hekmatara, H. Fe2O3/Fe3O4/PANI/MWCNT nanocomposite with the optimum amount and uniform orientation of Fe2O3/Fe3O4 NPs in polyaniline for high microwave absorbing performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 843, 156052.
Zhong, B.; Wang, C. J.; Yu, Y. L.; Xia, L.; Wen, G. W. Facile fabrication of carbon microspheres decorated with B(OH)3 and α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: Superior microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 402–409.
Zhong, B.; Wang, C. J.; Wen, G. W.; Yu, Y. L.; Xia, L. Facile fabrication of boron and nitrogen co-doped carbon@Fe2O3/Fe3C/Fe nanoparticle decorated carbon nanotubes three-dimensional structure with excellent microwave absorption properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 132, 141–150.
Kou, X.; Zhao, Y. P.; Xu, L. J.; Kang, Z. L.; Wang, Y. C.; Zou, Z. Y.; Huang, P.; Wang, Q. F.; Su, G. H.; Yang, Y. et al. Controlled fabrication of core—shell γ-Fe2O3@C-reduced graphene oxide composites with tunable interfacial structure for highly efficient microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 615, 685–696.
Wang, S.; Jiao, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Shi, Q.; Yue, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Feng, C.; Shi, D. Controllable synthesis of γ-Fe2O3 nanotube/porous rGO composites and their enhanced microwave absorption properties. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019 7, 7004–7013.
Yu, X. F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xing, L. S.; You, W. B.; Liu, J. W.; Chen, G. Y.; Ding, G. Z.; Ding, J. Z.; Liu, X. H. et al. Improved microwave absorption performance of a multi-dimensional Fe2O3/CNTCM@CN assembly achieved by enhanced dielectric relaxation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 5715–5726.
Qiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D. M.; Kong, L. X.; Lv, L. F.; Yang, F.; Wang, F. L.; Liu, W.; Liu, J. R. Design and synthesis of TiO2/Co/carbon nanofibers with tunable and efficient electromagnetic absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122591.
Qin, M.; Zhang, L. M.; Wu, H. J. Dielectric loss mechanism in electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105553.
Sun, X. X.; Li, Y. B.; Huang, Y. X.; Cheng, Y. J.; Wang, S. S.; Yin, W. L. Achieving super broadband electromagnetic absorption by optimizing impedance match of rGO sponge metamaterials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2107508.
Wang, Y. Q.; Zhao, H. B.; Cheng, J. B.; Liu, B. W.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Y. Z. Hierarchical Ti3C2Tx@ZnO hollow spheres with excellent microwave absorption inspired by the visual phenomenon of eyeless urchins. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 76.
Wang, Y. Q.; Wang, H. G.; Ye, J. H.; Shi, L. Y.; Feng, X. Magnetic CoFe alloy@C nanocomposites derived from ZnCo-MOF for electromagnetic wave absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123096.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (No. 21771024 and 22271018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2022_5178_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Rational design of hollow rice-grained α-Fe2O3/carbon nanofibers with optimized impedance matching for electromagnetic wave absorption enhanced
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Lu, N., Yuan, M. et al. Rational design of hollow rice-grained α-Fe2O3/carbon nanofibers with optimized impedance matching for electromagnetic wave absorption enhanced. Nano Res. 16, 5676–5684 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5178-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-022-5178-5