Abstract
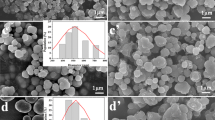
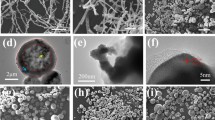
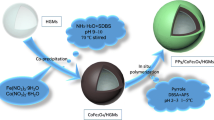
Uniform γ-Fe2O3/microporous SiO2/polypyrrole (Fe/m-SiO2/PPy) microspheres (MSs) with “watermelon-like” structures were successfully fabricated using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) as a pore-directing agent. In the “watermelon-like” microspheres, γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles represented the seeds, m-SiO2 the pulp, and PPy the rind. Through synergistic harnessing of the magnetic loss properties of γ-Fe2O3 and the dielectric loss properties of the m-SiO2/PPy core/shell structure, the Fe/m-SiO2/PPy MSs displayed outstanding excellent electromagnetic wave absorption (EMWA) properties. The maximum reflection loss (RLmax) of Fe/m-SiO2/PPy was − 51.24 dB (7.44 GHz) with a thickness of 4.0 mm, with an effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) (RL < − 10 dB) of 4.16 GHz at a loading of 14.2 wt% in a paraffin wax matrix. These results conclusively demonstrate that Fe/m-SiO2/PPy MSs-containing composites are very efficient EMWA materials and that porous core/shell/shell structures offer a promising approach for the rational design of lightweight high-performance EMW absorbers.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu XF, Hao CC, Jiang H et al (2017) Hierarchical NiCo2O4/Co3O4/NiO porous composite: a lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber with tunable absorbing performance. J Mater Chem C 5(15):3770–3778
Melvin GJH, Ni QQ, Suzuki Y et al (2014) Microwave-absorbing properties of silver nanoparticle/carbon nanotube hybrid nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 49(14):5199–5207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8229-9
Liu PB, Huang Y, Yan J et al (2016) Magnetic graphene@PANI@porous TiO2 ternary composites for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J Mater Chem C 4(26):6362–6370
Sun D, Zou Q, Wang Y et al (2014) Controllable synthesis of porous Fe3O4@ZnO sphere decorated graphene for extraordinary electromagnetic wave absorption. Nanoscale 6(12):6557–6562
Wang Y, Han BQ, Chen N et al (2016) Enhanced microwave absorption properties of MnO2 hollow microspheres consisted of MnO2 nanoribbons synthesized by a facile hydrothermal method. J Alloys Compd 3(676):224–230
Zhang D, Cheng J, Yang X et al (2014) Electromagnetic and microwave absorbing properties of magnetite nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotubes/polyaniline multiphase heterostructures. J Mater Sci 49(20):7221–7230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8429-3
Qiu J, Wang Y, Gu M (2007) Microwave absorption properties of substituted BaFe12O19/TiO2 nanocomposite multilayer film. J Mater Sci 42(1):166–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0919-5
He Q, Yuan T, Zhang X et al (2014) Electromagnetic field absorbing polypropylene nanocomposites with tuned permittivity and permeability by nanoiron and carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem C 118(42):24784–24796
Li XA, Zhang B, Ju CH et al (2011) Morphology-controlled synthesis and electromagnetic properties of porous Fe3O4 nanostructures from iron alkoxide precursors. J Phys Chem C 115(115):12350–12357
Qiao MT, Lei XF, Ma Y et al (2016) Well-defined core-shell Fe3O4@Polypyrrole composite microspheres with tunable shell thickness: synthesis and their superior microwave absorption performance in the Ku band. Ind Eng Chem Res 55(22):6263–6275
Huo J, Wang L, Yu H (2009) Polymeric nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave absorption. J Mater Sci 44(15):3917–3927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3561-1
Liu QT, Liu XF, Feng HB et al (2017) Metal organic framework-derived Fe/carbon porous composite with low Fe content for lightweight and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem Eng J 314:320–327
Liu Q, Cao B, Feng C et al (2012) High permittivity and microwave absorption of porous graphitic carbons encapsulating Fe nanoparticles. Compos Sci Technol 72(13):1632–1636
Zheng YW, Wang XX, Wei S et al (2017) Fabrication of porous graphene-Fe3O4 hybrid composites with outstanding microwave absorption performance. Compos A 95:237–247
Nanni F, Travaglia P, Valentini M (2009) Effect of carbon nanofibres dispersion on the microwave absorbing properties of CNF/epoxy composites. Compos Sci Technol 69(3–4):485–490
Zhang A, Tang M, Cao X et al (2014) The effect of polyethylenimine on the microwave absorbing properties of a hybrid microwave absorber of Fe3O4/MWNTs. J Mater Sci 49(13):4629–4635. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8165-8
Chen YJ, Zhang F, Zhao G (2010) Synthesis, multi-nonlinear dielectric resonance, and excellent electromagnetic absorption characteristics of Fe3O4/ZnO core/shell nanorods. J Phys Chem C 114(20):9239–9244
Wang G, Chang Y, Wang L (2012) Synthesis, characterization and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4/Co core/shell-type nanoparticles. Adv Powder Technol 23(6):861–865
Wu ZC, Tan DG, Tian K et al (2017) Facile preparation of core-shell Fe3O4@Polypyrrole composites with superior electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J Phys Chem C 121(29):15784–15792
Zhao B, Guo XQ, Zhao WY et al (2016) Yolk-shell Ni@SnO2 composites with a designable interspace to improve the electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(42):28917–28925
Lv H, Liang X, Ji G et al (2015) Porous three-dimensional flower-like Co/CoO and its excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(18):9776–9783
Zhou L, Gao C, Xu WJ et al (2010) Robust Fe3O4/SiO2-Pt/Au/Pd magnetic nanocatalysts with multifunctional hyperbranched polyglycerol amplifiers. Langmuir 26(13):11217–11225
Guo XH, Deng YH, Gu D et al (2009) Synthesis and microwave absorption of uniform hematite nanoparticle and their core-shell mesoporous silica nanocomposites. J Mater Chem 19(37):6706–6712
Qiang R, Du YC, Wang Y et al (2016) Rational design of yolk-shell C@C Microspheres for the effective enhancement in microwave absorption. Carbon 98:599–606
Micheli D, Apollo C, Pastore R et al (2010) X-Band microwave characterization of carbon-based nanocomposite material, absorption capability comparison and RAS design simulation. Compos Sci Technol 70(2):400–409
Ji SN, Zhang ZM, Ji XH et al (2017) Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of γ-Fe2O3-SiO2-poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) core-shell-shell nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 52(20):12358–12369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1337-6
Zhang ZM, Li Q, Yu LM et al (2011) Highly conductive polypyrrole/γ-Fe2O3 nanospheres with good magnetic properties obtained through an improved chemical one-step method. Macromolecules 44(12):4610–4615
Zhang L, Liu TQ, Chen Y et al (2016) Magnetic conducting polymer/mesoporous SiO2 yolk/shell nanomaterials: multifunctional nanocarriers for controlled release of doxorubicin. RSC Adv 6(11):8572–8579
Liang CY, Gou YJ, Wu LN et al (2016) Nature of electromagnetic-transparent SiO2 shell in hybrid nanostructure enhancing electromagnetic attenuation. J Phys Chem C 120(24):12967–12973
Zhang J, Wang XW (2018) Microwave absorbing property and preparation of CoNi@SiO2@PPy composite in X-band. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29(2):1592–1599
Tian C, Du Y, Xu P et al (2015) Constructing uniform core-shell PPy@PANI composites with tunable shell thickness toward enhancement in microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(36):20090–20099
Li WZ, Qiu T, Wang LL et al (2013) Preparation and electromagnetic properties of core/shell Polystyrene@Polypyrrole@Nickel composite microspheres. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(3):883–891
Yin YC, Liu XF, Wei XJ et al (2016) Porous CNTs/Co composite derived from zeolitic imidazolate framework: a lightweight, ultrathin, and highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(50):34686–34698
Zhou H, Wang JC, Zhuang JD et al (2013) A covalent route for efficient surface modification of ordered mesoporous carbon as high performance microwave absorbers. Nanoscale 5(24):12502–12511
Jiang LW, Wang ZH, Geng DY et al (2016) Carbon-encapsulated Fe nanoparticles embedded in organic polypyrrole polymer as a high performance microwave absorber. J Phys Chem C 120(49):28320–28329
Li YN, Zhao Y, Lu XY et al (2016) Self-healing superhydrophobic polyvinylidene fluoride/Fe3O4@polypyrrole fiber with core-sheath structures for superior microwave absorption. Nano Res 9(7):2034–2045
Wang G, Gao Z, Tang S et al (2012) Microwave absorption properties of carbon nanocoils coated with highly controlled magnetic materials by atomic layer deposition. ACS Nano 6(12):11009–11017
Feng JT, Wang YC, Hou YH et al (2017) Tunable design of yolk-shell ZnFe2O4@RGO@TiO2 microspheres for enhanced high-frequency microwave absorption. Inorg Chem Front 4:935–945
Jiang JJ, Li D, Geng DY et al (2014) Microwave absorption properties of core double-shell FeCo/C/BaTiO3 nanocomposites. Nanoscale 6(8):3967–3971
Lv H, Ji GB, Zhang HQ et al (2015) CoxFey@C composites with tunable atomic ratios for excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. Sci Rep 5:18249–18259
Sun Y, Xu JL, Qiao W et al (2016) Constructing two-, zero-, and one-dimensional integrated nanostructures: an effective strategy for high microwave absorption performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(46):31878–31886
Zhang Z, Deng J, Shen J et al (2007) Chemical one step method to prepare polyaniline nanofibers with electromagnetic function. Macromol Rapid Commun 28(5):585–590
Nanni F, Travaglia P, Valentini M (2009) Effect of carbon nanofibres dispersion on the microwave absorbing properties of CNF/epoxy composites. Compos Sci Technol 69(3–4):485–490
Wu F, Xie A, Sun M et al (2015) Reduced graphene oxide (RGO) modified spongelike polypyrrole (PPy) aerogel for excellent electromagnetic absorption. J Mater Chem A 3(27):14358–14369
Wang YF, Chen DL, Yin X et al (2015) Hybrid of MoS2 and reduced graphene oxide: a lightweight and broadband electromagnetic wave absorber. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(47):26226–26234
Yang H, Cao W, Zhang D et al (2015) NiO hierarchical nanorings on SiC: enhancing relaxation to tune microwave absorption at elevated temperature. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(13):7073–7077
Zhang ZL, Ji ZJ, Duan YP et al (2013) The superior electromagnetic properties of carbonyl-iron/Fe91.2Si3.1P2.9Sb2.8 composites powder and impedance match mechanism. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 24(3):968–973
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41476059) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016M600557).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Ji, S., Jiang, X. et al. Microwave absorption by watermelon-like microspheres composed of γ-Fe2O3, microporous silica and polypyrrole. J Mater Sci 53, 9635–9649 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2262-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2262-z