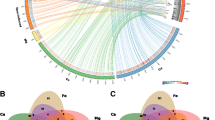
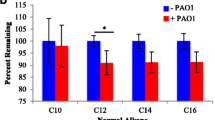
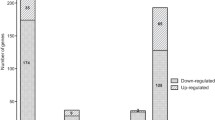
Abstract
The integration of transcriptomics and metabolomics can provide precise information on gene-to-metabolite networks for identifying the function of novel genes. The goal of this study was to identify novel gene functions involved in 2,3-butanediol (2,3-BDO) biosynthesis by a comprehensive analysis of the transcriptome and metabolome of five mutated Klebsiella pneumonia strains (∆wabG = SGSB100, ∆wabG∆budA = SGSB106, ∆wabG∆budB = SGSB107, ∆wabG∆budC = SGSB108, ∆wabG∆budABC = SGSB109). First, the transcriptomes of all five mutants were analyzed and the genes exhibiting reproducible changes in expression were determined. The transcriptome was well conserved among the five strains, and differences in gene expression occurred mainly in genes coding for 2,3-BDO biosynthesis (budA, budB, and budC) and the genes involved in the degradation of reactive oxygen, biosynthesis and transport of arginine, cysteine biosynthesis, sulfur metabolism, oxidoreductase reaction, and formate dehydrogenase reaction. Second, differences in the metabolome (estimated by carbon distribution, CO2 emission, and redox balance) among the five mutant strains due to gene alteration of the 2,3-BDO operon were detected. The functional genomics approach integrating metabolomics and transcriptomics in K. Pneumonia presented here provides an innovative means of identifying novel gene functions involved in 2,3-BDO biosynthesis metabolism and whole cell metabolism.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Köpke M, Mihalcea C, Liew F, Tizard JH, Ali MS, Conolly JJ et al (2011) 2,3-Butanediol production by acetogenic bacteria, an alternative route to chemical synthesis, using industrial waste gas. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:5467–5475
Syu MJ (2001) Biological production of 2,3-butanediol. a review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:358–363
Ji XJ, Huang H, Li S, Du J, Lian M (2008) Enhanced 2,3-butanediol production by altering the mixed acid fermentation pathway in Klebsiella oxytoca. Biotechnol Lett 30:731–734
Xuewu G, Chunhong C, Yazhou W, Chaoqun L, Mingyue W et al (2014) Effect of the inactivation of lactate dehydrogenase, ethanol dehydrogenase, and phosphotransacetylase on 2,3-butanediol production in Klebsiella pneumonia strain. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:44
Ji XJ, Huang H, Ouyang PK (2011) Microbial 2,3-butanediol production: a state-of-the-art review. Biotechnol Adv 29:351–364
Kim DK, Rathnasingh C, Song H, Lee HJ, Seung D et al (2013) Metabolic engineering of a novel Klebsiella oxytoca strain for enhanced 2,3-butanediol production. J Biosci Bioeng 116:186–192
Zhang L, Yang Y, Sun J, Shen Y, Wei D et al (2010) Microbial production of 2,3-butanediol by a mutagenized strain of Serratia marcescens H30. Bioresour Technol 101:1961–1967
Jung MY, Ng CY, Song H, Lee J, Oh MK (2012) Deletion of lactate dehydrogenase in Enterobacter aerogenes to enhance 2,3-butanediol production. Microb Biotechnol 95:461–469
Zhang YP, Li Y, Du CY, Liu M, Cao ZA (2006) Inactivation of aldehyde dehydrogenase: a key factor for engineering 1, 3-propanediol production by Klebsiella pneumonia. Metab Eng 8:578–586
Cheng KK, Liu HJ, Liu DH (2005) Multiple growth inhibition of Klebsiella pneumonia in 1, 3-propanediol fermentation. Biotechnol Lett 27:19–22
Xu YZ, Guo NN, Zheng ZM, Ou XJ, Liu HJ et al (2009) Metabolism in 1,3-propanediol fed-batch fermentation by a D-lactate deficient mutant of Klebsiella pneumonia. Biotechnol Bioeng 104:965–972
Zheng Y, Zhang HY, Zhao L, Wei LJ, Ma XY et al (2008) One-step production of 2,3-butanediol from starch by secretory over-expression of amylase in Klebsiella pneumonia. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83:1409–1412
Zeng AP, Ross A, Biebl H, Tag C, Günzel B et al (1994) Multiple product inhibition and growth modeling of Clostridium butyricum and Klebsiella pneumonia in glycerol fermentation. Biotechnol Bioeng 44:902–911
Lu M, Park C, Lee S, Kim B, Oh MK et al (2013) The regulation of 2,3-butanediol synthesis in Klebsiella pneumonia as revealed by gene over-expressions and metabolic flux analysis. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37:343–353
Converti A, Perego P, Del Borghi M (2003) Effect of specific oxygen uptake rate on Enterobacter aerogenes energetics: carbon and reduction degree balances in batch cultivations. Biotechnol Bioeng 82:370–377
Ji XJ, Haung H, Zhu JG, Ren LJ, Nie ZK et al (2010) Engineering Klebsiella oxytoca for efficient 2, 3-butanediol production through insertional inactivation of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1751–1758
Wood BE, Yomano LP, York SW, Ingram LO (2005) Development of industrial medium required elimination of the 2,3-butanediol fermentation pathway to maintain ethanol yield in an ethanologenic strain of Klebsiella oxytoca. Biotechnol Prog 21:1366–1372
Chen YT, Liao TL, Wu KM, Lauderdale TL, Yan JJ et al (2009) Genomic diversity of citrate fermentation in Klebsiella pneumonia. BMC Microbiol 9:168
Park J, Song H, Lee HJ, Seung D (2013) Genome-scale reconstruction and in silico analysis of Klebsiella oxytoca for 2,3-butanediol production. Microb Cell Fact 12:20
Shin SH, Kim S, Kim JY, Lee S, Um Y et al (2012) Complete genome sequence of the 2,3-butanediol-producing Klebsiella pneumonia strain KCTC 2242. J Bacteriol 194:2736–2737
Jung SG, Jang JH, Kim AY, Lim MC, Kim B et al (2013) Removal of pathogenic factors from 2,3-butanediol-producing Klebsiella species by inactivating virulence-related wabG gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:1997–2007
Kim B, Lee S, Park J, Lu M, Oh MK et al (2012) Enhanced 2,3-butanediol production in recombinant Klebsiella pneumonia via overexpression of synthesis-related genes. J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:1258–1263
Lee S, Kim B, Jeong D, Oh MK, Um Y et al (2013) Observation of 2,3-butanediol biosynthesis in Lys regulator mutated Klebsiella pneumonia at gene transcription level. J Biotechnol 168:520–526
Gerhard G (1985) Bacterial metabolism. Springer, Berlin
Liao YC, Huang TW, Chen FC, Charusanti P, Hong JSJ et al (2011) An experimentally validated genome-scale metabolic reconstruction of Klebsiella pneumonia MGH 78578, iYL1228. J Bacteriol 193:1710–1717
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods 5:621–628
Cui YL, Zhou JJ, Gao LR, Zhu CQ, Jiang X, Fu SL et al (2014) Utilization of excess NADH in 2,3-butanediol-deficient Klebsiella pneumonia for 1,3-propanediol production. J Appl Microbiol 117:690–698
Obinger C, Regelsberger G, Pircher A, Sevcik-Klöckler A, Strasser G, Peschek GA (1999) Hydrogen peroxide removal in Cyanobacteria: characterization of a catalase-peroxidase from Anacystis nidulans. In: Peschek GA, Löffelhardt W, Schmetterer G (eds) The phototrophic prokaryotes, chap 84. Springer, US, pp 719–731
Wang W, Sun J, Hartlep M, Deckwer YD, Zeng AP (2003) Combined use of proteomic analysis and enzyme activity assays for metabolic pathway analysis of glycerol fermentation by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biotechnol Bioeng 83:525–536
Ji XJ, Xia ZF, Fu NH, Nie ZK, Shen MQ et al (2013) Cofactor engineering through heterologous expression of an NADH oxidase and its impact on metabolic flux redistribution in Klebsiella pneumonia. Biotechnol Biofuels 6:7
Zhao H, Ma K, Lu Y, Zhang C, Wang L et al (2009) Cloning and knockout of formate hydrogen lyase and H2-uptake hydrogenase genes in Enterobacter aerogenes for enhanced hydrogen production. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:186–194
Cunin R, Glansdorff N, Pierard A, Stalon V (1986) Biosynthesis and metabolism of arginine in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 50:314–352
Lu CD (2006) Pathways and regulation of bacterial arginine metabolism and perspectives for obtaining arginine overproducing strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechno 70:261–272
Friedrich B, Magasanik B (1978) Utilization of Arginine by Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol 133:680–685
Brenchley JE, Prival MJ, Magasani B (1973) Regulation of the synthesis of enzymes responsible for glutamate formation in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol 248:6122–6128
Wirtz M, Droux M (2005) Synthesis of the sulfur amino acids: cysteine and methionine. Photosynth Res 86:345–362
Seilflein TA, Lawrence JG (2001) Methionine-to-cysteine recycling in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol 183:336–346
Thomas D, Surdin-Kerjan Y (1997) Metabolism of sulfur amino acids in Saccharomyces c erevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 61:503–532
Zhou D, White RH (1991) Transsulfuration in archaebacteria. J Bacteriol 173:3250–3251
Cheng K-K, Wu J, Wang G-Y, Li W-Y, Feng J, Zhang J-A (2013) Effects of pH and dissolved CO2 level on simultaneous production of 2,3-butanediol and succinic acid using Klebsiella pneumonia. Bioresour Technol 135:500–503
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the R&D Program of MOTIE/KEIT (No. 10035578, Development of 2,3-Butanediol and Derivative Production Technology for C-Zero Bio-Platform Industry). This work was also supported by the Graduate School of Specialization for Biotechnology Program of the Ministry of Knowledge Economy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S. Lee and B. Kim contributed equally to this work.
J. Yang and D. Jeong also contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Kim, B., Yang, J. et al. Comparative whole genome transcriptome and metabolome analyses of five Klebsiella pneumonia strains. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 38, 2201–2219 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1459-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-015-1459-7