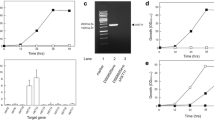
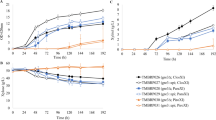
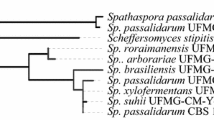
Abstract
Objectives
Since uptake of xylose limits its fermentation, we aimed to identify novel sugar transporters from Scheffersomyces stipitis that allow xylose uptake and fermentation by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Results
An hxt-null S. cerevisiae strain, lacking the major hexose transporters (hxt1Δ-hxt7Δ and gal2Δ) but having high xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase and xylulokinase activities, was transformed with a genomic DNA library from S. stipitis. Four plasmids allowing growth on xylose contained three genes encoding sugar transporters: the previously characterized XUT1 permease, and two new genes (HXT2.6 and QUP2) not previously identified as xylose transporters. High cell density fermentations with the recombinant strains showed that the XUT1 gene allowed ethanol production from xylose or xylose plus glucose as carbon sources, while the HXT2.6 permease produced both ethanol and xylitol, and the strain expressing the QUP2 gene produced mainly xylitol during xylose consumption.
Conclusions
Cloning novel sugar transporters not previously identified in the S. stipitis genome using an hxt-null S. cerevisiae strain with a high xylose-utilizing pathway provides novel promising target genes for improved lignocellulosic ethanol production by yeasts.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1995) Short protocols in molecular biology, 3rd edn. Wiley & Sons, New York
Bertilsson M, Andersson J, Líden G (2008) Modeling simultaneous glucose and xylose uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from kinetics and gene expression of sugar transporters. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 31:369–377
Cadete RM, Santos RO, Melo MA, Mouro A, Golçalves DL, Stambuk BU, Rosa CA (2009) Spathaspora arborariae sp. nov., a d-xylose fermenting yeast species isolated from rotting wood in Brazil. FEMS Yeast Res 9:1338–1342
Cadete RM, Melo MA, Zilli JE, Vital MJ, Mouro A, Prompt AH, Gomes FC, Stambuk BU, Lachance MA, Rosa CA (2013) Spathaspora brasiliensis sp. nov., Spathaspora sushii sp. nov., Spathaspora roraimanensis sp. Nov. and Spathaspora xylofermentans sp. nov., four novel (d)-xylose-fermenting yeast species from Brazilian Amazonian forest. Anton Leeuw 103:421–431
Cai Z, Zhang B, Li Y (2012) Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient anaerobic xylose fermentation: reflections and perspectives. Biotechnol J 7:34–36
Caspeta L, Buijs NAA, Nielsen J (2013) The role of biofuels in the future energy supply. Energy Environ Sci 6:1077–1082
Diao L, Liu Y, Qian F, Yang J, Jiang Y, Yang S (2013) Construction of fast xylose-fermenting yeast based on industrial ethanol-producing diploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae by rational design and adaptive evolution. BMC Biotechnol 13:1–9
Does AL, Bisson LF (1989) Characterization of xylose uptake in the yeasts Pichia heedie and Pichia stipitis. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:159–164
Du J, Li S, Zhao H (2010) Discovery and characterization of novel d-xylose-specific transporters from Neurospora crassa and Pichia stipitis. Mol BioSyst 6:2150–2156
Farias DR, de Andrade R, Maugeri-Filho F (2014) Kinetic modeling of ethanol production by Scheffersomyces stipitis from xylose. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:361–379
Gárdonyi M, Jeppsson M, Lidén G, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2003) Control of xylose consumption by xylose transport in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 82:818–824
Gonçalves DL, Matsushika A, Sales BB, Goshima T, Bon EPS, Stambuk BU (2014) Xylose and xylose/glucose co-fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing individual hexose transporters. Enzyme Microb Technol 63:13–20
Ha SJ, Kim H, Lin Y, Jang UM, Galazka JM, Kim TJ, Cate JHM, Jin YS (2013) Single amino acid substitutions in Hxt2.4 from Scheffersomyces stipitis lead to improved cellobiose fermentation by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:1500–1507
Hamacher T, Becker J, Gardonyi M, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Boles E (2002) Characterization of the xylose-transporting properties of yeast hexose transporters and their influence on xylose utilization. Microbiology 148:2783–2788
Hector RE, Qureshi N, Hughes SR, Cotta MA (2008) Expression of a heterologous xylose transporter in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain engineered to utilize xylose improves aerobic xylose consumption. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:675–684
Jeffries TW, Van Vleet JRH (2009) Pichia stipitis genomics, transcriptomics, and gene clusters. FEMS Yeast Res 9:793–807
Jeffries TW, Grigoriev IV, Grimwood J, Laplaza JM, Aertis A, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Lindquist E, Dehal P, Shapiro H, Jin YSU, Passoth V, Richardson PM (2007) Genome sequence of the lignocellulose-bioconverting and xylose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Nat Biotechnol 25:319–326
Jin Y, Alper H, Yang Y, Stephanopoulos G (2005) Improvement of xylose uptake and ethanol production in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae through an inverse metabolic engineering approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8249–8256
Kang Y, Kane J, Kujan J, Stadel JM, Tipper DJ (1990) Effects of expression of mammalian GeL and hybrid mammalian-yeast Ga proteins on the yeast pheromone response signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol 10:2582–2590
Katahira S, Ito M, Takema H, Fujita Y, Tanino T, Tanaka T, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2008) Improvement of ethanol productivity during xylose and glucose co-fermentation by xylose-assimilating S. cerevisiae via expression of glucose transporter Sut1. Enzyme Microb Technol 43:115–119
Kilian SG, Van Uden N (1988) Transport of xylose and glucose in the xylose fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27:545–548
Kim SR, Ha SJ, Wei N, Oh EJ, Jin YS (2012) Simultaneous co-fermentation of mixed sugars: a promising strategy for producing cellulosic ethanol. Trends Biotechnol 30:274–282
Kötter P, Ciriacy M (1993) Xylose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:776–783
Laluce C, Schenberg ACG, Gallardo JCM, Coradello LFC, Pombeiro-Sponchiado SR (2012) Advances and developments in strategies to improve strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and processes to obtain the lignocellulosic ethanol—a review. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:1908–1926
Lee WJ, Kim MD, Ryu YW, Bisson LF, Seo JH (2002) Kinetic studies on glucose and xylose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:186–191
Lin S, Tanaka S (2006) Ethanol fermentation from biomass resources: current state and prospects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:627–642
Lobo FP, Gonçalves DL, Alves SL Jr, Gerber AL, Vasconcelos ATR, Basso LC, Franco GR, Soares MA, Cadete RM, Rosa CA, Stambuk BU (2014) Draft genome sequence of the d-xylose-fermenting yeast Spathaspora arborariae UFMG-HM19.1AT. Genome Announc 2:e01163-13
Madhavan A, Tamalampudi S, Srivastava A, Fukuda H, Bisaria VS, Kondo A (2009) Alcoholic fermentation of xylose and mixed sugars using recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered for xylose utilization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:1037–1047
Matsushika A, Inoue H, Kodaki T, Sawayama S (2009) Ethanol production from xylose in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:37–53
Moon J, Liu ZL, Ma M, Slininger PJ (2013) New genotypes of industrial yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered with YXI and heterologous xylose transporters improve xylose utilization and ethanol production. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 2:247–254
Nielsen J, Larsson C, van Maris A, Pronk J (2013) Metabolic engineering of yeast for production of fuels and chemicals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24:398–404
Nigam JN (2001) Ethanol production from wheat straw hemicelluloses by Pichia stipitis. J Biotechnol 87:17–27
Nogueira LAH, Moreira JR, Schuchardt U, Goldemberg J (2013) The rationality of biofuels. Energy Policy 61:595–598
Parachin NS, Bergdahl B, van Niel EW, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2011) Kinetic modelling reveals current limitations in the production of ethanol from xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 13:508–517
Parambil LK, Sarkar D (2014) Probing the bioethanol production potential of Scheffersomyces (Pichia) stipitis using validated genome-scale model. Biotechnol Lett 36:2443–2451
Runquist D, Fonseca C, Radstrom P, Spencer-Martins I, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2009) Expression of the Gxf1 transporter from Candida intermedia improves fermentation performance in recombinant xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:123–130
Runquist D, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Radstrom P (2010) Comparison of heterologous xylose transporters in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:5
Saloheimo A, Rauta J, Stasyk OV, Sibirny AA, Penttilä M, Ruohonen L (2007) Xylose transport studies with xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing heterologous and homologous permeases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:1041–1052
Sànchez Nogué V, Karhumaa K (2015) Xylose fermentation as a challenge for commercialization of lignocellulosic fuels and chemicals. Biotechnol Lett 37:761–772
Sarkar N, Ghosh SK, Bannerjee S, Aikat K (2011) Bioethanol production from agricultural wastes: an overview. Renew Energy 37:19–23
Sedlak M, Ho NWY (2004) Characterization of the effectiveness of hexose transporters for transporting xylose during glucose and xylose co-fermentation by a recombinant Saccharomyces yeast. Yeast 21:671–684
Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen DG, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, Mcwilliam H, Remmert M, Soding J, Thomson JD, Higgins D (2011) Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 7:1–6
Stambuk BU, Eleutherio ECA, Florez-Pardo LM, Souto-Maior AM, Bon EPS (2008) Brazilian potential for biomass ethanol: challenge of using hexose and pentose cofermenting yeast strains. J Sci Ind Res 67:918–926
Sun L, Zeng X, Yan C, Sun X, Gong X, Rao Y, Yan N (2012) Crystal structure of a bacterial homologue of glucose transporters GLUT1–4. Nature 490:361–368
Tamura K, Peterson D, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tanino T, Ito T, Ogino C, Ohmura N, Ohshima T, Kondo A (2012) Sugar consumption and ethanol fermentation by transporter-overexpressed xylose-metabolizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae harboring a xylose isomerase pathway. J Biosci Bioeng 114:209–211
Toivola A, Yarrow D, Van Den Bosch E, Van Dijken JP, Scheffers WA (1984) Alcoholic fermentation of d-xylose by yeasts. Appl Environ Microbiol 47:1221–1223
Watanabe T, Watanabe I, Yamamoto Y, Ando A, Nakamura TA (2011) UV-induced mutant of Pichia stipitis with increased ethanol production from xylose and selection of a spontaneous mutant with increased ethanol tolerance. Bioresour Technol 102:1844–1848
Weierstall T, Hollenberg CP, Boles E (1999) Cloning and characterization of three genes (SUT1-3) encoding glucose transporters of the yeast Pichia stipitis. Mol Microbiol 31:871–883
Wohlbach DJ, Kuo A, Sato TK, Potts KM, Salamov AA, Labutti KM, Sun H, Clum A, Pangilinan JL, Lindquist EA, Lucas S, Lapidus A, Jin M, Gunawan C, Balan V, Dale BD, Jeffries TW, Zinkel R, Barry KW, Grigoriev C, Gash AP (2011) Comparative genomics of xylose-fermenting fungi for enhanced biofuel production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:13212–13217
Young E, Lee SM, Alper H (2010) Optimizing pentose utilization in yeast: the need for novel tools and approaches. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:24
Young E, Poucher A, Comer A, Bailey A, Alper H (2011) Functional survey for heterologous sugar transport proteins, using Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a host. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:3311–3319
Young ME, Comer AD, Huang H, Alper HS (2012) A molecular transporter engineering approach to improving xylose catabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 14:401–411
Young E, Tong A, Bui H, Spofford C, Alper HS (2014) Rewiring yeast sugar transporter preference through modifying a conserved protein motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:131–136
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants and fellowships from the Brazilian agencies CNPq (Process Nos. 490029/2009-4, 551392/2010-0, 307290/2012-3, and 478841/2013-2), FINEP (Process No. 01.09.0566.00/1421-08) and FAPESC (Process No. 17293/2009-6), and by the Japanese International Cooperation Agency (JICA).
Supporting information
Supplementary Table 1—Growth rates and ethanol yields of the recombinant yeast strains grown on synthetic SC medium with the indicated sugars.
Supplementary Fig. 1—Amino acid sequence alignment of S. stipites sugar transporters.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Sales, B.B., Scheid, B., Gonçalves, D.L. et al. Cloning novel sugar transporters from Scheffersomyces (Pichia) stipitis allowing d-xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Biotechnol Lett 37, 1973–1982 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1893-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1893-2