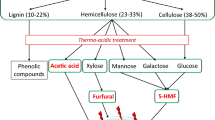
Abstract
Fuel ethanol production from lignocellulosic materials is at a level where commercial biofuel production is becoming a reality. The solubilization of the hemicellulose fraction in lignocellulosic-based feedstocks results in a large variety of sugar mixtures including xylose. However, allowing xylose fermentation in yeast that normally is used for fuel ethanol production requires genetic engineering. Moreover, the efficiency of lignocellulosic pretreatment, together with the release and generation of inhibitory compounds in this step, are some of the new challenges faced during second generation ethanol production. Successful advances in all these aspects will improve ethanol yield, productivity and titer, which will reduce the impact on capital and operating costs, leading to the consolidation of the fermentation of lignocellulosic biomass as an economically feasible option for the production of renewable fuels. Therefore the development of yeast strains capable of fermenting a wide variety of sugars in a highly inhibitory environment, while maintaining a high ethanol yield and production rate, is required. This review provides an overview of the current status in the use of xylose-engineered yeast strains and describes the remaining challenges to achieve an efficient deployment of lignocellulosic-based ethanol production.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers E, Larsson C (2009) A comparison of stress tolerance in YPD and industrial lignocellulose-based medium among industrial and laboratory yeast strains. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1085–1091
Almeida JRM, Bertilsson M, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Gorsich S, Lidén G (2009a) Metabolic effects of furaldehydes and impacts on biotechnological processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:625–638
Almeida JRM, Karhumaa K, Bengtsson O, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2009b) Screening of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with respect to anaerobic growth in non-detoxified lignocellulose hydrolysate. Bioresour Technol 100:3674–3677
Almeida JRM, Runquist D, Sànchez Nogué V, Lidén G, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2011) Stress-related challenges in pentose fermentation to ethanol by the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol J 6:286–299
Alvira P, Tomás-Pejó E, Ballesteros M, Negro MJ (2010) Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: a review. Bioresour Technol 101:4851–4861
Bellissimi E, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT, van Maris AJA (2009) Effects of acetic acid on the kinetics of xylose fermentation by an engineered, xylose-isomerase-based Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. FEMS Yeast Res 9:358–364
Brandberg T, Franzen CJ, Gustafsson L (2004) The fermentation performance of nine strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in batch and fed-batch cultures in dilute-acid wood hydrolysate. J Biosci Bioeng 98:122–125
Brat D, Boles E, Wiedemann B (2009) Functional expression of a bacterial xylose isomerase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:2304–2311
Çakar ZP, Turanli-Yildiz B, Alkim C, Yilmaz U (2012) Evolutionary engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for improved industrially important properties. FEMS Yeast Res 12:171–182
Cellulosic biofuels. In: Industry progress report (2012–2013) Advanced Ethanol Council. www.advancedethanol.net. Accessed Oct 2014
Chang SF, Ho NWY (1988) Cloning the yeast xylulokinase gene for the improvement of xylose fermentation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 17:313–318
Demeke MM, Dietz H, Li YY, Foulquie-Moreno MR, Mutturi S, Deprez S, Den Abt T, Bonini BM, Liden G, Dumortier F, Verplaetse A, Boles E, Thevelein JM (2013) Development of a d-xylose fermenting and inhibitor tolerant industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high performance in lignocellulose hydrolysates using metabolic and evolutionary engineering. Biotechnol Biofuel 6:89
Dragosits M, Mattanovich D (2013) Adaptive laboratory evolution - principles and applications for biotechnology. Microb Cell Fact 12:64
Eliasson A, Christensson C, Wahlbom CF, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000) Anaerobic xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae carrying XYL1, XYL2, and XKS1 in mineral medium chemostat cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3381–3386
Eliasson A, Hofmeyr JHS, Pedler S, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2001) The xylose reductase/xylitol dehydrogenase/xylulokinase ratio affects product formation in recombinant xylose-utilising Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enz Microb Technol 29:288–297
Erdei B, Barta Z, Sipos B, Reczey K, Galbe M, Zacchi G (2010) Ethanol production from mixtures of wheat straw and wheat meal. Biotechnol Biofuel 3:16
Erdei B, Franko B, Galbe M, Zacchi G (2012) Separate hydrolysis and co-fermentation for improved xylose utilization in integrated ethanol production from wheat meal and wheat straw. Biotechnol Biofuel 5:12
Erdei B, Franko B, Galbe M, Zacchi G (2013a) Glucose and xylose co-fermentation of pretreated wheat straw using mutants of S. cerevisiae TMB3400. J Biotechnol 164:50–58
Erdei B, Hancz D, Galbe M, Zacchi G (2013b) SSF of steam-pretreated wheat straw with the addition of saccharified or fermented wheat meal in integrated bioethanol production. Biotechnol Biofuel 6:169
Farwick A, Bruder S, Schadeweg V, Oreb M, Boles E (2014) Engineering of yeast hexose transporters to transport d-xylose without inhibition by d-glucose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:5159–5164
Fujitomi K, Sanda T, Hasunuma T, Kondo A (2012) Deletion of the PHO13 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae improves ethanol production from lignocellulosic hydrolysate in the presence of acetic and formic acids, and furfural. Bioresour Technol 111:161–166
Galbe M, Zacchi G (2012) Pretreatment: the key to efficient utilization of lignocellulosic materials. Biomass Bioenergy 46:70–78
Galbe M, Sassner P, Wingren A, Zacchi G (2007) Process engineering economics of bioethanol production. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 108:303–327
Gao L, Xia LM (2012) Sm-like protein enhanced tolerance of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae to inhibitors in hemicellulosic hydrolysate. Bioresour Technol 124:504–507
Gao DH, Uppugundla N, Chundawat SPS, Yu XR, Hermanson S, Gowda K, Brumm P, Mead D, Balan V, Dale BE (2011) Hemicellulases and auxiliary enzymes for improved conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to monosaccharides. Biotechnol Biofuel 4:5
Gírio FM, Fonseca C, Carvalheiro F, Duarte LC, Marques S, Bogel-Lukasik R (2010) Hemicelluloses for fuel ethanol: a review. Bioresour Technol 101:4775–4800
GranBio. Press release 24 Sept 2014. “GranBio begins producing second-generation ethanol”. www.granbio.com.br. Accessed Oct 2014
Graves T, Narendranath NV, Dawson K, Power R (2006) Effect of pH and lactic or acetic acid on ethanol productivity by Saccharomyces cerevisiae in corn mash. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33:469–474
Gu F, Wang W, Jing L, Jin Y (2013) Sulfite-formaldehyde pretreatment on rice straw for the improvement of enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour Technol 142:218–224
Hahn-Hägerdal B, Karhumaa K, Larsson CU, Gorwa-Grauslund M, Görgens J, van Zyl WH (2005) Role of cultivation media in the development of yeast strains for large scale industrial use. Microb Cell Fact 4:31
Hamacher T, Becker J, Gardonyi M, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Boles E (2002) Characterization of the xylose-transporting properties of yeast hexose transporters and their influence on xylose utilization. Microbiology 148:2783–2788
Han SH, Cho DH, Kim YH, Shin SJ (2013) Biobutanol production from 2-year-old willow biomass by acid hydrolysis and acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation. Energy 61:13–17
Hasunuma T, Sung K, Sanda T, Yoshimura K, Matsuda F, Kondo A (2011) Efficient fermentation of xylose to ethanol at high formic acid concentrations by metabolically engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:997–1004
Hasunuma T, Ismail KSK, Nambu Y, Kondo A (2014) Co-expression of TAL1 and ADH1 in recombinant xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae improves ethanol production from lignocellulosic hydrolysates in the presence of furfural. J Biosci Bioeng 117:165–169
Heer D, Sauer U (2008) Identification of furfural as a key toxin in lignocellulosic hydrolysates and evolution of a tolerant yeast strain. Microb Biotechnol 1:497–506
Inbicon. Press release 4 December 2013. “DONG Energy and DSM prove cellulosic bio-ethanol fermentation on industrial scale with 40 % higher yield”. www.inbicon.com. Accessed Oct 2014
Jin MJ, Gunawan C, Balan V, Lau MW, Dale BE (2012) Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation (SSCF) of AFEX pretreated corn stover for ethanol production using commercial enzymes and Saccharomyces cerevisiae 424A(LNH-ST). Bioresour Technol 110:587–594
Jin MJ, Sarks C, Gunawan C, Bice BD, Simonett SP, Narasimhan RA, Willis LB, Dale BE, Balan V, Sato TK (2013) Phenotypic selection of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of AFEX pretreated corn stover. Biotechnol Biofuel 6:108
Jordan S, Fatland-Bloom B, Li L (2012) Xylose isomerase and xylitol dehydrogenase combination for xylose fermentation to ethanol and B. fragilis xylose isomerase. Patent application WO/2012/087601
Karhumaa K, Sànchez i Nogué V Biorenewables at C5LT. In: Dominguez P (ed) Industrial biorenewables. Wiley (in press)
Karhumaa K, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2005) Investigation of limiting metabolic steps in the utilization of xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae using metabolic engineering. Yeast 22:359–368
Karhumaa K, Garcia Sanchez R, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2007) Comparison of the xylose reductase-xylitol dehydrogenase and the xylose isomerase pathways for xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 6:5
Khattab SMR, Saimura M, Kodaki T (2013) Boost in bioethanol production using recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae with mutated strictly NADPH-dependent xylose reductase and NADP(+)-dependent xylitol dehydrogenase. J Biotechnol 165:153–156
Kim SR, Ha SJ, Wei N, Oh EJ, Jin YS (2012) Simultaneous co-fermentation of mixed sugars: a promising strategy for producing cellulosic ethanol. Trends Biotechnol 30:274–282
Kim SR, Park YC, Jin YS, Seo JH (2013) Strain engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for enhanced xylose metabolism. Biotechnol Adv 31:851–861
Klaassen P, Kolen C, Van Maris A, Pronk J (2014) Yeast strains engineered to produce ethanol from acetate. Patent application WO2014033018 A1
Klimacek M, Kirl E, Krahulec S, Longus K, Novy V, Nidetzky B (2014) Stepwise metabolic adaption from pure metabolization to balanced anaerobic growth on xylose explored for recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 13:37
Klinke HB, Thomsen AB, Ahring BK (2004) Inhibition of ethanol-producing yeast and bacteria by degradation products produced during pre-treatment of biomass. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:10–26
Koppram R, Albers E, Olsson L (2012) Evolutionary engineering strategies to enhance tolerance of xylose utilizing recombinant yeast to inhibitors derived from spruce biomass. Biotechnol Biofuel 5:32
Koppram R, Nielsen F, Albers E, Lambert A, Wannstrom S, Welin L, Zacchi G, Olsson L (2013) Simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation for bioethanol production using corncobs at lab, PDU and demo scales. Biotechnol Biofuel 6:2
Kötter P, Ciriacy M (1993) Xylose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:776–783
Kuyper M, Harhangi HR, Stave AK, Winkler AA, Jetten MS, de Laat WT, den Ridder JJ, Op den Camp HJ, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2003) High-level functional expression of a fungal xylose isomerase: the key to efficient ethanolic fermentation of xylose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae? FEMS Yeast Res 4:69–78
Laadan B, Almeida JRM, Rådström P, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund M (2008) Identification of an NADH-dependent 5-hydroxymethylfurfural-reducing alcohol dehydrogenase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 25:191–198
Laluce C, Schenberg ACG, Gallardo JCM, Coradello LFC, Pombeiro-Sponchiado SR (2012) Advances and developments in strategies to improve strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and processes to obtain the lignocellulosic ethanol—a review. Appl Biochem Biotech 166:1908–1926
Lee SM, Jellison T, Alper HS (2012) Directed evolution of xylose isomerase for improved xylose catabolism and fermentation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microb 78:5708–5716
Li BZ, Balan V, Yuan YJ, Dale BE (2010a) Process optimization to convert forage and sweet sorghum bagasse to ethanol based on ammonia fiber expansion (AFEX) pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 101:1285–1292
Li CL, Knierim B, Manisseri C, Arora R, Scheller HV, Auer M, Vogel KP, Simmons BA, Singh S (2010b) Comparison of dilute acid and ionic liquid pretreatment of switchgrass: biomass recalcitrance, delignification and enzymatic saccharification. Bioresour Technol 101:4900–4906
Li YC, Gou ZX, Liu ZS, Tang YQ, Akamatsu T, Kida K (2014) Synergistic effects of TAL1 over-expression and PHO13 deletion on the weak acid inhibition of xylose fermentation by industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. Biotechnol Lett 36:2011–2021
Long TM, Su YK, Headman J, Higbee A, Willis LB, Jeffries TW (2012) Cofermentation of glucose, xylose, and cellobiose by the beetle-associated yeast Spathaspora passalidarum. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5492–5500
Lu Y, Warner R, Sedlak M, Ho N, Mosier NS (2009) Comparison of glucose/xylose cofermentation of poplar hydrolysates processed by different pretreatment technologies. Biotechnol Prog 25:349–356
Madhavan A, Tamalampudi S, Ushida K, Kanai D, Katahira S, Srivastava A, Fukuda H, Bisaria VS, Kondo A (2009) Xylose isomerase from polycentric fungus Orpinomyces: gene sequencing, cloning, and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for bioconversion of xylose to ethanol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:1067–1078
Madhavan A, Srivastava A, Kondo A, Bisaria VS (2012) Bioconversion of lignocellulose-derived sugars to ethanol by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Crit Rev Biotechnol 32:22–48
Martin-Sampedro R, Revilla E, Villar JC, Eugenio ME (2014) Enhancement of enzymatic saccharification of Eucalyptus globulus: steam explosion versus steam treatment. Bioresour Technol 167:186–191
Nghiem NP, Kim TH, Yoo CG, Hicks KB (2013) Enzymatic fractionation of SAA-pretreated barley straw for production of fuel ethanol and astaxanthin as a value-added co-product. Appl Biochem Biotech 171:341–351
Olofsson K, Wiman M, Liden G (2010) Controlled feeding of cellulases improves conversion of xylose in simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation for bioethanol production. J Biotechnol 145:168–175
Olofsson K, Runquist D, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Liden G (2011) A mutated xylose reductase increases bioethanol production more than a glucose/xylose facilitator in simultaneous fermentation and co-fermentation of wheat straw. AMB Express 1:4
Pampulha ME, Loureiro-Dias MC (2000) Energetics of the effect of acetic acid on growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Microbiol Lett 184:69–72
Rana V, Eckard AD, Teller P, Ahring BK (2014) On-site enzymes produced from Trichoderma reesei RUT-C30 and Aspergillus saccharolyticus for hydrolysis of wet exploded corn stover and loblolly pine. Bioresour Technol 154:282–289
Runquist D, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Bettiga M (2010) Increased ethanol productivity in xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae via a randomly mutagenized xylose reductase. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:7796–7802
Sakihama Y, Hasunuma T, Kondo A (2014) Improved ethanol production from xylose in the presence of acetic acid by the overexpression of the HAA1 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biosci Bioeng. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.09.004
Sato TK, Liu TJ, Parreiras LS, Williams DL, Wohlbach DJ, Bice BD, Ong IM, Breuer RJ, Qin L, Busalacchi D, Deshpande S, Daum C, Gasch AP, Hodge DB (2014) Harnessing genetic diversity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for fermentation of xylose in hydrolysates of alkaline hydrogen peroxide-pretreated biomass. Appl Environ Microb 80:540–554
Sedlak M, Ho NW (2004) Production of ethanol from cellulosic biomass hydrolysates using genetically engineered Saccharomyces yeast capable of cofermenting glucose and xylose. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 113–116:403–416
Shao Q, Chundawat SPS, Krishnan C, Bals B, Sousa LD, Thelen KD, Dale BE, Balan V (2010) Enzymatic digestibility and ethanol fermentability of AFEX-treated starch-rich lignocellulosics such as corn silage and whole corn plant. Biotechnol Biofuel 3:12
Smith J, van Rensburg E, Görgens JF (2014) Simultaneously improving xylose fermentation and tolerance to lignocellulosic inhibitors through evolutionary engineering of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae harbouring xylose isomerase. BMC Biotechnol 14:41
Sonderegger M, Sauer U (2003) Evolutionary engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for anaerobic growth on xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1990–1998
Subtil T, Boles E (2012) Competition between pentoses and glucose during uptake and catabolism in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuel 5:14
Tanaka K, Ishii Y, Ogawa J, Shima J (2012) Enhancement of acetic acid tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by overexpression of the HAA1 gene, encoding a transcriptional activator. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:8161–8163
Tantirungkij M, Nakashima N, Seki T, Yoshida T (1993) Construction of xylose-assimilating Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ferment Bioeng 75:83–88
Taylor MP, Mulako I, Tuffin M, Cowan D (2012) Understanding physiological responses to pre-treatment inhibitors in ethanologenic fermentations. Biotechnol J 7:1169–1181
Uppugundla N, Sousa LD, Chundawat SPS, Yu XR, Simmons B, Singh S, Gao XD, Kumar R, Wyman CE, Dale BE, Balan V (2014) A comparative study of ethanol production using dilute acid, ionic liquid and AFEX pretreated corn stover. Biotechnol Biofuel 7:72
Van Vleet JH, Jeffries TW, Olsson L (2008) Deleting the para-nitrophenyl phosphatase (pNPPase), PHO13, in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae improves growth and ethanol production on d-xylose. Metab Eng 10:360–369
Viell J, Wulfhorst H, Schmidt T, Commandeur U, Fischer R, Spiess A, Marquardt W (2013) An efficient process for the saccharification of wood chips by combined ionic liquid pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 146:144–151
Viikari L, Vehmaanpera J, Koivula A (2012) Lignocellulosic ethanol: from science to industry. Biomass Bioenerg 46:13–24
Walfridsson M, Bao XM, Anderlund M, Lilius G, Bulow L, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1996) Ethanolic fermentation of xylose with Saccharomyces cerevisiae harboring the Thermus thermophilus xylA gene, which expresses an active xylose (glucose) isomerase. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4648–4651
Wallace-Salinas V, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2013) Adaptive evolution of an industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for combined tolerance to inhibitors and temperature. Biotechnol Biofuel 6:151
Wang ZJ, Zhu JY, Zalesny RS, Chen KF (2012) Ethanol production from poplar wood through enzymatic saccharification and fermentation by dilute acid and SPORL pretreatments. Fuel 95:606–614
Watanabe S, Saleh AA, Pack SP, Annaluru N, Kodaki T, Makino K (2007) Ethanol production from xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing protein engineered NADP+-dependent xylitol dehydrogenase. J Biotechnol 130:316–319
Wei N, Xu H, Kim SR, Jin YS (2013) Deletion of FPS1, encoding aquaglyceroporin Fps1p, improves xylose fermentation by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:3193–3201
Wiman M, Dienes D, Hansen MA, van der Meulen T, Zacchi G, Liden G (2012) Cellulose accessibility determines the rate of enzymatic hydrolysis of steam-pretreated spruce. Bioresour Technol 126:208–215
Wright J, Bellissimi E, de Hulster E, Wagner A, Pronk JT, van Maris AJ (2011) Batch and continuous culture-based selection strategies for acetic acid tolerance in xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 11:299–306
Zelle R, Shaw A, Van Dijken J (2014) Method for acetate consumption during ethanolic fermentation of cellulosic feedstocks. Patent application WO2014074895 A2
Zhang HD, Wu SB (2014) Dilute ammonia pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse followed by enzymatic hydrolysis to sugars. Cellulose 21:1341–1349
Zhao J, Xia LM (2010) Bioconversion of corn stover hydrolysate to ethanol by a recombinant yeast strain. Fuel Process Technol 91:1807–1811
Zhou H, Cheng JS, Wang BL, Fink GR, Stephanopoulos G (2012) Xylose isomerase overexpression along with engineering of the pentose phosphate pathway and evolutionary engineering enable rapid xylose utilization and ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 14:611–622
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sànchez Nogué, V., Karhumaa, K. Xylose fermentation as a challenge for commercialization of lignocellulosic fuels and chemicals. Biotechnol Lett 37, 761–772 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1756-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1756-2