Abstract
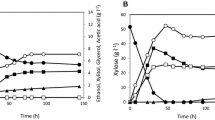
Previously, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain was engineered for xylose assimilation by the constitutive overexpression of the Orpinomyces xylose isomerase, the S. cerevisiae xylulokinase, and the Pichia stipitis SUT1 sugar transporter genes. The recombinant strain exhibited growth on xylose, under aerobic conditions, with a specific growth rate of 0.025 h−1, while ethanol production from xylose was achieved anaerobically. In the present study, the developed recombinant yeast was adapted for enhanced growth on xylose by serial transfer in xylose-containing minimal medium under aerobic conditions. After repeated batch cultivations, a strain was isolated which grew with a specific growth rate of 0.133 h−1. The adapted strain could ferment 20 g l−1 of xylose to ethanol with a yield of 0.37 g g−1 and production rate of 0.026 g l−1 h−1. Raising the fermentation temperature from 30°C to 35°C resulted in a substantial increase in the ethanol yield (0.43 g g−1) and production rate (0.07 g l−1 h−1) as well as a significant reduction in the xylitol yield. By the addition of a sugar complexing agent, such as sodium tetraborate, significant improvement in ethanol production and reduction in xylitol accumulation was achieved. Furthermore, ethanol production from xylose and a mixture of glucose and xylose was also demonstrated in complex medium containing yeast extract, peptone, and borate with a considerably high yield of 0.48 g g−1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amore R, Wilhelm M, Hollenberg CP (1989) The fermentation of xylose—an analysis of the expression of Bacillus and Actinoplanes xylose isomerase genes in yeast. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 30:351–357
Bennett A, Rowe RI, Soch N, Eckhert CD (1999) Boron stimulates yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) growth. J Nutr 129:2236–2238
Chan E, Ueng PP, Chen LF (1989) Metabolism of d-xylose in Schizosaccharomyces pombe cloned with a xylose isomerase gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31:524–528
Chandrakant P, Bisaria VS (1998) Simultaneous bioconversion of cellulose and hemicellulose to ethanol. Crit Rev Biotechnol 18:295–331
Chandrakant P, Bisaria VS (2000) Simultaneous bioconversion of glucose and xylose to ethanol by Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the presence of xylose isomerase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:301–309
Chapelle S, Verchere J (1988) A 11B and 13C NMR determination of the structures of borate complexes of pentoses and related sugars. Tetrahedron 44:4469–4482
Chiang L, Gong C, Chen L, Tsao GT (1981) d-Xylulose fermentation to ethanol by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 42:284–289
Dische Z, Borenfreund E (1951) A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J Biol Chem 192:583–587
Dmytruk OV, Voronovsky AY, Abbas CA, Dmytruk KV, Ishchuk OP, Sibirny AA (2008) Overexpression of bacterial xylose isomerase and yeast host xylulokinase improves xylose alcoholic fermentation in the thermotolerant yeast Hansenula polymorpha. FEMS Yeast Res 8:165–173
Eckhert CD, Bennett A, Becker K, Luo D (2000) Homing in on the molecular basis of boron essentiality using differential display, gene arrays, and northern blots. In: Roussel AM, Anderson RA, Favier AE (eds) Trace elements in man and animals 10. Kluwer Academic/Plenum, New York, USA, pp 1049–1052
Gárdonyi M, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2003) The Streptomyces rubiginosus xylose isomerase is misfolded when expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:252–259
Hsiao H, Chiang L, Chen L, Tsao GT (1982) Effects of borate on isomerization and yeast fermentation of high xylulose solution and acid hydrolysate of hemicellulose. Enzyme Microb Technol 4:25–31
Jennings ML, Howren TR, Cui J, Winters M, Hannigan R (2007) Transport and regulatory characteristics of the yeast bicarbonate transporter homolog Bor1p. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 293:C468–C476
Jeppsson M, Träff K, Johansson B, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund M (2003) Effect of enhanced xylose reductase activity on xylose consumption and product distribution in xylose-fermenting recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 3:167–175
Jin Y, Laplaza JM, Jeffries TW (2004) Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered for xylose metabolism exhibits a respiratory response. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6816–6825
Johansson B, Christensson C, Hobley T, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2001) Xylulokinase overexpression in two strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae also expressing xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase and its effect on fermentation of xylose and lignocellulosic hydrolysate. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4249–4255
Karhumaa K, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2005) Investigation of limiting metabolic steps in the utilization of xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae using metabolic engineering. Yeast 22:359–368
Karhumaa K, Fromanger R, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2007a) High activity of xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase improves xylose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:1039–1046
Karhumaa K, Sanchez RG, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF (2007b) Comparison of the xylose reductase-xylitol dehydrogenase and the xylose isomerase pathways for xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 6:5
Katahira S, Fujita Y, Mizuike A, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2004) Construction of a xylan-fermenting yeast strain through codisplay of xylanolytic enzymes on the surface of xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5407–5414
Katahira S, Mizuike A, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2006) Ethanol fermentation from lignocellulosic hydrolysate by a recombinant xylose- and cellooligosaccharide-assimilating yeast strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:1136–1143
Kim DH, Faull KF, Norris AJ, Eckhert CD (2004) Borate-nucleotide complex formation depends on charge and phosphorylation state. J Mass Spectrom 39:743–751
Kuyper M, Harhangi HR, Stave AK, Winkler AA, Jetten MSM, de Laat WTAM, den Ridder JJJ, Op den Camp HJM, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2003) High-level functional expression of a fungal xylose isomerase: the key to efficient ethanolic fermentation of xylose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae? FEMS Yeast Res 4:69–78
Kuyper M, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2004) Minimal metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient anaerobic xylose fermentation: a proof of principle. FEMS Yeast Res 4:655–664
Kuyper M, Hartog MMP, Toirkens MJ, Almering MJH, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2005a) Metabolic engineering of a xylose-isomerase-expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for rapid anaerobic xylose fermentation. FEMS Yeast Res 5:399–409
Kuyper M, Toirkens MJ, Diderich JA, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2005b) Evolutionary engineering of mixed-sugar utilization by a xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. FEMS Yeast Res 5:925–934
Lönn A, Träff-Bjerre KL, Cordero Otero RR, van Zyl WH, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2003) Xylose isomerase activity influences xylose fermentation with recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing mutated xylA from Thermus thermophilus. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:567–573
Madhavan A, Tamalampudi S, Ushida K, Kanai D, Katahira S, Srivastava A, Fukuda H, Bisaria VS, Kondo A (2008) Xylose isomerase from polycentric fungus Orpinomyces: gene sequencing, cloning and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for bioconversion of xylose to ethanol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1794-6
Moes CJ, Pretorius IS, van Zyl WH (1996) Cloning and expression of the Clostridium thermosulfurogenesd-xylose isomerase gene (xylA) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Lett 18:269–274
Palmqvist E, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000) Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. I: inhibition and detoxification. Bioresour Technol 74:17–24
Pitkänen J, Aristidou A, Salusjärvi L, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2003) Metabolic flux analysis of xylose metabolism in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae using continuous culture. Metab Eng 5:16–31
Pitkänen J, Rintala E, Aristidou A, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2005) Xylose chemostat isolates of Saccharomyces cerevisiae show altered metabolite and enzyme levels compared with xylose, glucose, and ethanol metabolism of the original strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:827–837
Rao K, Chelikani S, Relue P, Varanasi S (2008) A novel technique that enables efficient conduct of simultaneous isomerization and fermentation (SIF) of xylose. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 146:101–117
Richard P, Toivari MH, Penttilä M (2000) The role of xylulokinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae xylulose catabolism. FEMS Microbiol Lett 190:39–43
Roca C, Olsson L (2003) Increasing ethanol productivity during xylose fermentation by cell recycling of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:560–563
Sarthy AV, McConaughy BL, Lobo Z, Sundstrom JA, Furlong CE, Hall BD (1987) Expression of the Escherichia coli xylose isomerase gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1996–2000
Shamanna DK, Sanderson KE (1979) Uptake and catabolism of d-xylose in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol 139:64–70
Sherman F (1991) Getting started with yeast. Meth Enzymol 194:3–21
Sun Y, Cheng J (2002) Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresour Technol 83:1–11
Träff KL, Cordero RRO, van Zyl WH, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2001) Deletion of the GRE3 aldose reductase gene and its influence on xylose metabolism in recombinant strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing the xylA and XKS1 genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5668–5674
van Bastelaere P, Vangrysperre W, Kersters-Hilderson H (1991) Kinetic studies of Mg2+-, Co2+- and Mn2+-activated d-xylose isomerases. Biochem J 278:285–292
van Zyl WH, Eliasson A, Hobley T, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1999) Xylose utilization by recombinant strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on different carbon sources. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:829–833
Wahlbom CF, Otero RRC, van Zyl WH, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Jönsson LJ (2003) Molecular analysis of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant with improved ability to utilize xylose shows enhanced expression of proteins involved in transport, initial xylose metabolism, and the pentose phosphate pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:740–746
Walfridsson M, Bao X, Anderlund M, Lilius G, Bülow L, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1996) Ethanolic fermentation of xylose with Saccharomyces cerevisiae harboring the Thermus thermophilus xylA gene, which expresses an active xylose (glucose) isomerase. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4648–4651
Wong HC, Ting Y, Lin H, Reichert F, Myambo K, Watt KWK, Toy PL, Drummond RJ (1991) Genetic organization and regulation of the xylose degradation genes in Streptomyces rubiginosus. J Bacteriol 173:6849–6858
Yamanaka K (1969) Inhibition of d-xylose isomerase by pentitols and D-lyxose. Arch Biochem Biophys 131:502–506
Acknowledgment
The author Anjali Madhavan was supported by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madhavan, A., Tamalampudi, S., Srivastava, A. et al. Alcoholic fermentation of xylose and mixed sugars using recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered for xylose utilization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82, 1037–1047 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1818-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1818-2