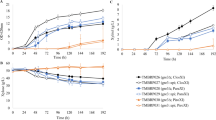
Abstract
In the present study, we modified xylose uptake properties of a recombinant xylose-utilizing yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by expression of heterologous and homologous permease-encoding genes. In a mutant yeast strain with the main seven hexose transporter genes deleted, and engineered for xylose utilization, we screened an expression cDNA library of the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei (Hypocrea jecorina) for enhanced growth on xylose plates. One cDNA clone with significant homology to fungal sugar transporters was obtained, but when the clone was retransformed into the host, it did not support significant growth on xylose. However, during a long liquid culture of the strain carrying the cDNA clone, adaptive mutations apparently occurred in the host, which led to growth on xylose but not on glucose. The new transporter homologue, Trxlt1 thus appears to code for a protein specific for xylose uptake. In addition, xylose-transporting properties of some homologous hexose transporters were studied. All of them, i.e., Hxt1, Hxt2, Hxt4, and Hxt7 were capable of xylose uptake. Their affinities for xylose varied, K m values between 130 and 900 mM were observed. The single-Hxt strains showed a biphasic growth mode on xylose, alike the Trxlt1 harboring strain. The initial, slow growth was followed by a long lag and finally by exponential growth.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Billard P, Ménart S, Blaisonneau J, Bolotin-Fukuhara M, Fukuhara H, Wésolowski-Louvel M (1996) Glucose uptake in Kluyveromyces lactis: role of the HGT1 gene in glucose transport. J Bacteriol 178:5860–5866
Boles E, Hollenberg C (1997) The molecular genetics of hexose transport in yeasts. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21:85–111
Boles E, Gohlmann HW, Zimmermann FK (1996) Cloning of a second gene encoding 5-phosphofructo-2-kinase in yeast, and characterization of mutant strains without fructose-2,6-bisphosphate. Mol Microbiol 20:65–76
Buziol S, Becker J, Baumeister A, Jung S, Mauch K, Reuss M, Boles E (2002) Determination of in vivo kinetics of the starvation-induced Hxt5 glucose transporter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 2:283–291
Cornish-Bowden A, Eisenthal R (1974) Statistical considerations in the estimation of enzyme kinetic parameters by the direct linear plot and other methods. Biochem J 139:721–730
Corpet F (1988) Multiple sequence alignment with hierarchical clustering. Nucleic Acids Res 16:10881–10890
Does AL, Bisson LF (1989) Characterization of xylose uptake in the yeasts Pichia heedie and Pichia stipitis. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:159–164
Eisenthal R, Cornish-Bowden A (1974) The direct linear plot. A new graphical procedure for estimating enzyme kinetic parameters. Biochem J 139:715–720
Eliasson A, Christensson C, Wahlbom CF, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000) Anaerobic xylose fermentation by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae carrying XYL1, XYL2, and XKS1 in mineral medium chemostat cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3381–3386
Gárdonyi M, Jeppsson M, Lidén G, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2002) Control of xylose consumption by xylose transport in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Bioeng 82:818–824
Gárdonyi M, Österberg M, Rodrigues C, Spencer-Martins I, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2003) High capacity xylose transport in Candida intermedia PYCC 4715. FEMS Yeast Res 3:45–52
Gietz D, St Jean A, Woods R, Schiestl R (1992) Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res 20:1425
Goffrini P, Ferrero I, Donnini C (2002) Respiration-dependent utilization of sugars in yeasts: a determinant role for sugar transporters. J Bacteriol 184:427–432
Hamacher T, Becker J, Gárdonyi M, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Boles E (2002) Characterization of the xylose-transporting properties of yeast hexose transporters and their influence on xylose utilization. Microbiology 148:2783–2788
Hill J, Ian KA, Donald G, Griffith DE (1991) DMSO-enhanced whole cell yeast transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5791
Ho NWY, Chen Z, Brainard AP (1998) Genetically engineered Saccharomyces yeast capable of effective cofermentation of glucose and xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1852–1859
Hoffman C, Winston F (1987) A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene 57:267–272
Kotyk A (1967) Properties of the sugar carrier in baker’s yeast. Folia Microbiol 12:121–131
Kruckeberg AL, Ye L, Berden JA, van Dam K (1999) Functional expression, quantification and cellular localization of the Hxt2 hexose transporter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tagged with the green fluorescent protein. Biochem J 339:299–307
Kuyper M, Hartog MMP, Toirkens MJ, Almering MJH, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2005a) Metabolic engineering of a xylose-isomerase-expressing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for rapid anaerobic xylose fermentation. FEMS Yeast Res 5:399–409
Kuyper M, Toirkens MJ, Diderich JA, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2005b) Evolutionary engineering of mixed-sugar utilization by a xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. FEMS Yeast Res 5:925–934
Kötter P, Ciriacy M (1993) Xylose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38:776–783
Kötter P, Amore R, Hollenberg C, Ciriacy M (1990) Isolation and characterization of the Pichia stipitis xylitol dehydrogenase gene, XYL2, and construction of a xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae transformant. Curr Genet 18:493–500
Leandro MJ, Conçalves P, Spencer-Martins I (2006) Two glucose/xylose transporter genes from the yeast Candida intermedia: first molecular characterization of a yeast xylose-H+ symporter. Biochem J 395:543–549
Lee W-J, Kim M-D, Ryu Y-W, Bisson LF, Seo J-H (2002) Kinetic studies on glucose and xylose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:186–191
Lichtenberg H, Heyer M, Höfer M (1999) Tpr1, a Schizosaccharomyces pombe protein involved in potassium transport. FEBS Lett 457:363–368
Lowry O, Rosebrough N, Farr A, Randall R (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lucas C, van Uden N (1986) Transport of hemicellulose monomeres in the xylose-fermenting yeast Candida shehatae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 23:491–495
Maier A, Völker B, Boles E, Fuhrmann GF (2002) Characterisation of glucose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with plasma membrane vesicles (countertransport) and intact cells (initial uptake) with single Hxt1, Hxt2, Hxt3, Hxt4, Hxt6, Hxt7 or Gal2 transporters. FEMS Yeast Res 2:539–550
Makuc J, Cappellaro C, Boles E (2004) Co-expression of a mammalian accessory trafficking protein enables functional expression of the rat MCT1 monocarboxylate transporter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 4:795–801
Margolles-Clark E, Tenkanen M, Nakari-Setälä T, Penttilä M (1996) Cloning of genes encoding alpha-l-arabinofuranosidase and beta-xylosidase from Trichoderma reesei by expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3840–3846
Nobre A, Lucas C, Leão C (1999) Transport and utilization of hexoses and pentoses in the halotolerant yeast Debaryomyces hansenii. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3594–3598
Özcan S, Johnston M (1999) Function and regulation of yeast hexose transporters. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:554–569
Pitkänen J-P, Rintala E, Aristidou A, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2005) Xylose chemostat isolates of Saccharomyces cerevisiae show altered metabolite and enzyme levels compared with xylose, glucose, and ethanol metabolism of the original strain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:827–837
Prior C, Fukuhara H, Blaisonneau J, Wésolowski-Louvel M (1993) Low-affinity glucose carrier gene LGT1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, a homologue of the Kluyveromyces lactis RAG1 gene. Yeast 9:1373–1377
Reifenberger E, Freidel K, Ciriacy M (1995) Identification of novel HXT genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals the impact of individual hexose transporters on glycolytic flux. Mol Microbiol 16:157–167
Reifenberger E, Boles E, Ciriacy M (1997) Kinetic characterization of individual hexose transporters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and their relation to the triggering mechanisms of glucose repression. Eur J Biochem 245:324–333
Richard P, Toivari M, Penttilä M (2000) The role of xylulokinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae xylulose catabolism. FEMS Microbiol Lett 190:39–43
Richard P, Verho R, Putkonen M, Londesborough J, Penttilä M (2003) Production of ethanol from l-arabinose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae containing a fungal L-arabinose pathway. FEMS Yeast Res 3:185–189
Ruohonen L, Aalto M, Keränen S (1995) Modifications to the ADH1 promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient production of heterologous proteins. J Biotechnol 39:193–203
Saloheimo A, Henrissat B, Hoffrén A, Teleman O, Penttilä M (1994) A novel, small endoglucanase gene, egl5, from Trichoderma reesei isolated by expression in yeast. Mol Microbiol 13:219–228
Salusjärvi L, Pitkänen J-P, Aristidou A, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2006) Gene expression analysis of recombinant xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals novel responses to xylose as a carbon source. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 128:237–261
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, USA
Sedlak M, Ho NWY (2004) Characterisation of the effectiveness of hexose transporters for transporting xylose during glucose and xylose co-fermentation by a recombinant Saccharomyces yeast. Yeast 21:671–684
Sherman F, Fink G, Hicks JB (1983) Methods in yeast genetics. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, USA
Sherwood PW, Katic I, Sanz P, Carlson M (2000) A glucose transporter chimera confers a dominant negative glucose starvation phenotype in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 155:989–992
Sonderegger M, Sauer U (2003) Evolutionary engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for anaerobic growth on xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1990–1998
Stambuk BU, Franden MA, Singh A, Zhang M (2003) d-Xylose transport by Candida succiphila and Kluyveromyces marxianus. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 105–108:255–263
Toivari M, Aristidou A, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2001) Conversion of xylose to ethanol by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae: importance of xylulokinase (XKS1) and oxygen availability. Metab Eng 3:236–249
Tokai M, Kawasaki H, Kikuchi Y, Ouchi K (2000) Cloning and characterization of the CSF1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is required for nutrient uptake at low temperature. J Bacteriol 182:2865–2868
Varma A, Singh BB, Karnani N, Lichtenberg-Frate H, Hofer M, Magee BB, Prasad R (2000) Molecular cloning and functional characterisation of a glucose transporter, CaHGT1, of Candida albicans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 182:15–21
Wahlbom CF, Cordero Otero RR, van Zyl WH, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Jönsson LJ (2003) Molecular analysis of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant with improved ability to utilize xylose shows enhanced expression of proteins involved in transport, initial xylose metabolism and the pentose phosphate pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:740–746
Walfridsson M, Hallborn J, Penttilä M, Keränen S, Hahn-Hägerdal B (1995) Xylose-metabolizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains overexpressing the TKL1 and TAL1 genes encoding the pentose phosphate pathway enzymes transketolase and transaldolase. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4184–4190
Weierstall T, Hollenberg CP, Boles E (1999) Cloning and characterization of three genes (SUT1-3) encoding glucose transporters of the yeast Pichia stipitis. Mol Microbiol 31:871–883
Wieczorke R, Krampe S, Weierstall T, Freidel K, Hollenberg CP, Boles E (1999) Concurrent knock-out of at least 20 transporter genes is required to block uptake of hexoses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 464:123–128
Ye L, Kruckeberg AL, Berden JA, van Dam K (1999) Growth and glucose repression are controlled by glucose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells containing only one glucose transporter. J Bacteriol 181:4673–4675
Zhang Y, Lee H (1997) Site-directed mutagenesis of the cysteine residues in the Pichia stipitis xylose reductase. FEMS Microbiol Lett 147:227–232
Acknowledgements
We want to acknowledge John Londesborough for his advice on the uptake studies and analysis of the results, for instructive discussions, as well as important comments on the manuscript. Virve Vidgren is thanked for the help in cloning of the hexose transporter genes and Carmen Limon for the help in sequencing of the xylose transporter. Technical assistance of Seija Rissanen, Aila Siltala, Eila Leino, and Titta Manninen is warmly thanked. This work is part of the research program “VTT Industrial Biotechnology” (Academy of Finland; Finnish Centre of Excellence program, 2000–2005, Project no. 64330). The financial support of Technology Agency of Finland (Project no. Tekes 40416/01) is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saloheimo, A., Rauta, J., Stasyk, O.V. et al. Xylose transport studies with xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing heterologous and homologous permeases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74, 1041–1052 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0747-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0747-1