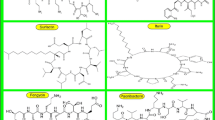
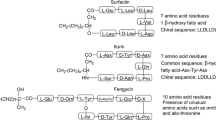
Abstract
As lead molecules, cyclic lipopeptides with antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral properties have garnered a lot of attention in recent years. Because of their potential, cyclic lipopeptides have earned recognition as a significant class of antimicrobial compounds with applications in pharmacology and biotechnology. These lipopeptides, often with biosurfactant properties, are amphiphilic, consisting of a hydrophilic moiety, like a carboxyl group, peptide backbone, or carbohydrates, and a hydrophobic moiety, mostly a fatty acid. Besides, several lipopeptides also have cationic groups that play an important role in biological activities. Antimicrobial lipopeptides can be considered as possible substitutes for antibiotics that are conventional to address the current drug-resistant issues as pharmaceutical industries modify the parent antibiotic molecules to render them more effective against antibiotic-resistant bacteria and fungi, leading to the development of more resistant microbial strains. Bacillus species produce lipopeptides, which are secondary metabolites that are amphiphilic and are typically synthesized by non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs). They have been identified as potential biocontrol agents as they exhibit a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. A further benefit of lipopeptides is that they can be produced and purified biotechnologically or biochemically in a sustainable manner using readily available, affordable, renewable sources without harming the environment. In this review, we discuss the biochemical and functional characterization of antifungal lipopeptides, as well as their various modes of action, method of production and purification (in brief), and potential applications as novel antibiotic agents.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available upon reason request from the corresponding author.
References
Anckaert A, Arias AA, Hoff G, Calonne-Salmon M, Declerck S, Ongena M (2021) The use of Bacillus spp. as bacterial biocontrol agents to control plant diseases. pp 247–300 Doi: https://doi.org/10.19103/as.2021.0093.10
Andrés MT, Viejo-Díaz M, Fierro JF (2008) Human lactoferrin induces apoptosis-like cell death in Candida albicans: critical role of K + -channel-mediated K + efflux. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52(11):4081–4088. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01597-07
Aranda FJ, Teruel JA, Ortiz A (2005) Further aspects on the hemolytic activity of the antibiotic lipopeptide iturin A. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1713(1):51–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2005.05.003
Arima K, Kakinuma A, Tamura G (1968) Surfactin, a crystalline peptide lipid 509 surfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis: Isolation, characterization and its inhibition of fibrin 510 clot formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 31(3):488–494
Arrebola E, Sivakumar D, Korsten L (2010) Effect of volatile compounds produced by Bacillus strains on postharvest decay in citrus. Biol Control 53(1):122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2009.11.010
Arroyave-Toro JJ, Mosquera S, Villegas-Escobar V (2017) Biocontrol activity of Bacillus subtilis EA-CB0015 cells and lipopeptides against postharvest fungal pathogens. Biol Control 114:195–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2017.08.014
Bahar AA, Ren D (2013) Antimicrobial peptides. Pharmaceuticals 6(12):1543–1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6121543
Baindara P, Korpole S (2016) Lipopeptides: Status and strategies to control fungal infection. In: Recent trends in antifungal agents and antifungal therapy. pp 97–121. Springer India. Doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2782-3_4
Balkovec JM, Hughes DL, Masurekar PS, Sable CA, Schwartz RE, Singh SB (2014) Discovery and development of first in class antifungal caspofungin (CANCIDAS®): A case study. Nat Prod Rep 31(1):15–34. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3np70070d
Barale SS, Ghane SG, Sonawane KD (2022) Purification and characterization of antibacterial surfactin isoforms produced by Bacillus velezensis SK. AMB Express 12(1):89. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-022-01348-3
Benedict RG, Langlykke AF (1947) Antibiotic activity of Bacillus polymyxa. J Bacteriol 54(1):24
Benz VF (1974) Echinocandin B, ein neuartiges Polipeptid-Antibiotikum aus Aspergillus nidulans var. echinatus: Isolierung und Bausteine. Heiv Chim Acta 57:2459–2477. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.19740570818
Biniarz P, Łukaszewicz M, Janek T (2016) Screening concepts, characterization and structural analysis of microbial-derived bioactive lipopeptides: a review. Critical Rev Biotechnol 37(3):393–410. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2016.1163324
Bionda N, Pitteloud JP, Cudic P (2013) Cyclic lipodepsipeptides: a new class of antibacterial agents in the battle against resistant bacteria. Fut Med Chem 5(11):1121–1330. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.13.86
Bonmatin J-M, Laprévote O, Peypoux F (2003) Diversity among microbial cyclic lipopeptides: iturins and surfactins activity-structure relationships to design new bioactive agents. Combin Chem High Throughput Screen 6(6):541–556
Bowman JC, Hicks PS, Kurtz MB, Rosen H, Schmatz DM, Liberator PA, Douglas CM (2002) The antifungal echinocandin caspofungin acetate kills growing cells of Aspergillus fumigatus in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46(9):3001–3012. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.46.9.3001-3012.2002
Buda De Cesare G, Cristy SA, Garsin DA, Lorenz MC (2020) Antimicrobial peptides: a new frontier in antifungal therapy. Mbio 11(6):10–1128. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02123-20
Cai Q, Zhang B, Chen B, Zhu Z, Lin W, Cao T (2014) Screening of biosurfactant producers from petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated sources in cold marine environments. Mar Pollut Bull 86(1–2):402–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.06.039
Canepari P, Boaretti M, Lleo MM, Satta G (1990) Lipoteichoic acid as a new target for activity of antibiotics: mode of action of daptomycin (LY146032). Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34(6):1220–1226. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.34.6.1220
Cappelletty D, Eiselstein-McKitrick K (2007) The echinocandins. Pharmacother 27(3):369–388. https://doi.org/10.1592/phco.27.3.369
Carolin CF, Kumar PS, Ngueagni PT (2021) A review on new aspects of lipopeptide biosurfactant: Types, production, properties and its application in the bioremediation process. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124827
Chander CS, Lohitnath T, Kumar DM, Kalaichelvan PT (2012) Production and characterization of biosurfactant from Bacillus subtilis MTCC441 and its evaluation to use as bioemulsifier for food bio-preservative. Adv Appl Sci Res 3:1827–1831
Chauhan V, Dhiman VK, Kanwar SS (2022) Purification and characterization of a novel bacterial Lipopeptide(s) biosurfactant and determining its antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties. Process Biochem 120:114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2022.06.005
Chen L, Yue Q, Li Y, Niu X, Xiang M, Wang W, Bills GF, Liu X, An Z (2015a) Engineering of Glarea lozoyensis for exclusive production of the pneumocandin B0 precursor of the antifungal drug caspofungin acetate. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(5):1550–1558. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03256-14
Chen WC, Juang RS, Wei YH (2015b) Applications of a lipopeptide biosurfactant, surfactin, produced by microorganisms. Biochem Eng J 103:158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2015.07.009
Chen X, Lu Y, Shan M, Zhao H, Lu Z, Lu Y (2022) A mini-review: mechanism of antimicrobial action and application of surfactin. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38(8):143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03323-3
Chowdhury T, Baindara P, Mandal SM (2021) LPD-12: a promising lipopeptide to control COVID-19. Int J Antimicrob Agents. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106218
Chtioui O, Dimitrov K, Gancel F, Nikov I (2010) Biosurfactants production by immobilized cells of Bacillus subtilis ATCC 21332 and their recovery by pertraction. Process Biochem 45(11):1795–1799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2010.05.012
Colson AR, Morton A, Årdal C, Chalkidou K, Davies SC, Garrison LP, Xiao Y (2021) Antimicrobial resistance: is health technology assessment part of the solution or part of the problem? Value in Health 24(12):1828–1834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2021.06.002
De Faria AF, Stéfani D, Vaz BG, Silva ÍS, Garcia JS, Eberlin MN, Grossman MJ, Alves OL, Durrant LR (2011) Purification and structural characterization of fengycin homologues produced by Bacillus subtilis LSFM-05 grown on raw glycerol. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38(7):863–871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-011-0980-1
De Lucca AJ, Walsh TJ (1999) Antifungal peptides: novel therapeutic compounds against emerging pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.43.1.1
De Oliveira DWF, Cara AB, Lechuga-Villena M, García-Román M, Melo VMM, Gonçalves LRB, Vaz DA (2017) Aquatic toxicity and biodegradability of a surfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis ICA56. J Environ Sci Health Part A 52(2):174–181. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2016.1240491
De Vuyst L, Vandamme EJ (1992) Influence of the carbon source on nisin production in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis batch fermentations. J Gen Microbiol 138(3):571–578. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-138-3-571
De Zoysa GH, Cameron AJ, Hegde VV, Raghothama S, Sarojini V (2015) Antimicrobial peptides with potential for biofilm eradication: synthesis and structure activity relationship studies of battacin peptides. J Med Chem 58(2):625–639. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm501084q
Deleu M, Paquot M, Nylander T (2008) Effect of fengycin, a lipopeptide produced by Bacillus subtilis, on model biomembranes. Biophys J 94(7):2667–2679. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.107.114090
Dijksteel GS, Ulrich MM, Middelkoop E, Boekema BK (2021) Lessons learned from clinical trials using antimicrobial peptides (AMPs). Front Microbiol 12:616979. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.616979
Dubos RJ (1939) Studies on a bactericidal agent extracted from a soil bacillus: i preparation of the agent: its activity in vitro. J Exp Med 70(1):1
Ebadipour N, Lotfabad TB, Yaghmaei S, RoostAazad R (2016) Optimization of low-cost biosurfactant production from agricultural residues through response surface methodology. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 46(1):30–38. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2014.979204
Ehlert F, Neu HC (1987) In vitro activity of LY146032 (daptomycin), a new peptolide. Eur J Clin Microbiol 6:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02097208
Englerová K, Bedlovičová Z, Nemcová R, Király J, Maďar M, Hajdučková V, Reiffová K (2021) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens—derived lipopeptide biosurfactants inhibit biofilm formation and expression of biofilm-related genes of Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 10(10):1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10101252
Epand RM (1997) Biophysical studies of lipopeptide-membrane interactions. Pept Sci 43(1):15–24. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(1997)43:1%3c15::AID-BIP3%3e3.0.CO;2-3
Fan H, Ru J, Zhang Y, Wang Q, Li Y (2017) Fengycin produced by Bacillus subtilis 9407 plays a major role in the biocontrol of apple ring rot disease. Microbiol Res 199:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2017.03.004
Fechtner J, Koza A, Sterpaio PD, Hapca SM, Spiers AJ (2011) Surfactants expressed by soil pseudomonads alter local soil–water distribution, suggesting a hydrological role for these compounds. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 78(1):50–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01141.x
Fernández de Ullivarri M, Arbulu S, Garcia-Gutierrez E, Cotter PD (2020) Antifungal peptides as therapeutic agents. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:105. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.00105
Fiedler S, Heerklotz H (2015) Vesicle leakage reflects the target selectivity of antimicrobial lipopeptides from Bacillus subtilis. Biophys J 109(10):2079–2089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2015.09.021
Gálvez A, Abriouel H, López RL, Omar NB (2011) Biological control of pathogens and post-processing spoilage microorganisms in fresh and processed fruit and vegetables. In: Protective cultures, antimicrobial metabolites and bacteriophages for food and beverage biopreservation. pp 403–432. Woodhead Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1533/9780857090522.3.403
Gálvez A, Maqueda M, Martínez-Bueno M, Valdivia E (1989) Bactericidal and bacteriolytic action of peptide antibiotic AS-48 against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and other organisms. Res Microbiol 140(1):57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/0923-2508(89)90060-0
Ganesan NG, Rangarajan V (2021) A kinetics study on surfactin production from Bacillus subtilis MTCC 2415 for application in green cosmetics. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 33:102001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102001
Ganesan NG, Singh RD, Rangarajan V (2023) Optimization of processing parameters for the improved production of surfactin from B. subtilis using a statistical approach and demonstration of its imminent potential in cosmetic applications. Mater Today 76:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.09.042
Garcia-Effron G (2020) Rezafungin—mechanisms of action, susceptibility and resistance: similarities and differences with the other echinocandins. J Fungi 6(4):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040262
Gayathiri E, Prakash P, Karmegam N, Varjani S, Awasthi MK, Ravindran B (2022) Biosurfactants: potential and eco-friendly material for sustainable agriculture and environmental safety—a review. Agronomy 12(3):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12030662
Geissler M, Oellig C, Moss K, Schwack W, Henkel M, Hausmann R (2017) High-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) for the simultaneous quantification of the cyclic lipopeptides Surfactin, Iturin A and Fengycin in culture samples of Bacillus species. J Chromatogr B 1044:214–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.11.013
Ghazala I, Charfeddine S, Charfeddine M, Gargouri-Bouzid R, Ellouz-Chaabouni S, Haddar A (2022) Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Bacillus mojavensis I4 lipopeptides and their potential application against the potato dry rot causative Fusarium solani. Arch Microbiol 204(8):484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03098-z
Gond SK, Bergen MS, Torres MS, White JF (2015) Endophytic Bacillus spp. produce antifungal lipopeptides and induce host defence gene expression in maize. Microbiol Res 172:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2014.11.004
Guardado-Valdivia L, Tovar-Pérez E, Chacón-López A, López-García U, Gutiérrez-Martínez P, Stoll A, Aguilera S (2018) Identification and characterization of a new Bacillus atrophaeus strain B5 as biocontrol agent of postharvest anthracnose disease in soursop (Annona muricata) and avocado (Persea americana). Microbiol Res 210:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2018.01.007
Hamley IW (2021) Lipopeptides for vaccine development. Bioconjug Chem 32(8):1472–1490. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.1c00258
Hancock RE, Chapple DS (1999) Peptide antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43(6):1317–1323. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.43.6.1317
Hao B, Cheng S, Clancy CJ, Nguyen MH (2013) Caspofungin kills Candida albicans by causing both cellular apoptosis and necrosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57(1):326–332. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01366-12
Hashimoto S (2009) Micafungin: a sulfated echinocandin. J Antibiot 62(1):27–35. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2008.3
Hawser S, Borgonovi, M, Markus A, Isert D (1999) Mulundocandm, an echinocandin-like lipopeptide antifungal agent: biological activities in vitro. J Antibiot 52(3):305–310. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.52.305
Heinemann B, RD M, IR H (1953) Amphomycin, a new antibiotic. Antibiot Chemother (northfield, Ill) 3(12):1239–1242
Hoenigl M, Sprute R, Egger M, Arastehfar A, Cornely OA, Krause R, Jenks JD (2021) The antifungal pipeline: fosmanogepix, ibrexafungerp, olorofim, opelconazole, and rezafungin. Drugs 81:1703–1729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01611-0
Hoffmann M, Mück D, Grossmann L, Greiner L, Klausmann P, Henkel M, Hausmann R (2021) Surfactin from Bacillus subtilis displays promising characteristics as O/W-emulsifier for food formulations. Colloids Surf B 203:111749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.111749
Hollmann A, Matos PM, Augusto MT, Castanho MA, Santos NC (2013) Conjugation of cholesterol to HIV-1 fusion inhibitor C34 increases peptide-membrane interactions potentiating its action. PLoS ONE 8(4):e60302. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060302
Horn JN, Romo TD, Grossfield A (2013) Simulating the mechanism of antimicrobial lipopeptides with all-atom molecular dynamics. Biochemistry 52(33):5604–5610. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi400773q
Hutchinson JA, Burholt S, Hamley IW (2017) Peptide hormones and lipopeptides: from self-assembly to therapeutic applications. J Pept Sci 23(2):82–94. https://doi.org/10.1002/psc.2954
Hüttel W (2021) Echinocandins: structural diversity, biosynthesis, and development of antimycotics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:55–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-11022-y
Janek T, Łukaszewicz M, Krasowska A (2012) Antiadhesive activity of the biosurfactant pseudofactin II secreted by the Arctic bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens BD5. BMC Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-24
Janek T, Łukaszewicz M, Rezanka T, Krasowska A (2010) Isolation and characterization of two new lipopeptide biosurfactants produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens BD5 isolated from water from the Arctic Archipelago of Svalbard. Biores Technol 101(15):6118–6123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.109
Jha SS, Joshi SJ, SJ G (2016) Lipopeptide production by Bacillus subtilis R1 and its possible applications. Braz J Microbiol 47:955–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2016.07.006
Jia C, Zhang J, Yu L, Wang C, Yang Y, Rong X, Xu K, Chu M (2019) Antifungal activity of coumarin against Candida albicans is related to apoptosis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 8:445. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2018.00445
Jiang YM, Zhu XR, Li YB (2001) Postharvest control of litchi fruit rot by Bacillus subtilis. LWT- Food Sci Technol 34(7):430–436. https://doi.org/10.1006/fstl.2001.0758
Jin H, Li K, Niu Y, Guo M, Hu C, Chen S, Huang F (2015) Continuous enhancement of iturin A production by Bacillus subtilis with a stepwise two-stage glucose feeding strategy. BMC Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-015-0172-6
Jin P, Wang H, Tan Z, Xuan Z, Dahar GY, Li QX, Liu W (2020) Antifungal mechanism of bacillomycin D from Bacillus velezensis HN-2 against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Penz. Pesticide Biochem Physiol 163:102–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2019.11.004
Juhaniewicz-Dębińska J, Lasek R, Tymecka D, Burdach K, Bartosik D, Sęk S (2020) Physicochemical and biological characterization of novel membrane-active cationic lipopeptides with antimicrobial properties. Langmuir 36(43):12900–12910. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c02135
Jung D, Rozek A, Okon M, Hancock RE (2004) Structural transitions as determinants of the action of the calcium-dependent antibiotic daptomycin. Chem Biol 11(7):949–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.04.020
Kakinuma A, Sugino H, Isono M, Tamura G, Arima K (1969) Determination of fatty acid in surfactin and elucidation of the total structure of surfactin. Agric Biol Chem 33(6):973–976. https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1969.10859409
Karlapudi AP, Venkateswarulu TC, Tammineedi J, Kanumuri L, Ravuru BK, Ramu Dirisala V, Kodali VP (2018) Role of biosurfactants in bioremediation of oil pollution-a review. Petroleum 4(3):241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petlm.2018.03.007
Kelleher TJ, Lai J-J, Decourcey JP, Zenoni M, Tagliani AR (2015) Process for the purification of daptomycin. Eur Patent Appl Bull 5:89
Khelissa S, Chihib NE, Gharsallaoui A (2021) Conditions of nisin production by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis and its main uses as a food preservative. Arch Microbiol 203:465–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-02054-z
Korenblum E, de Araujo LV, Guimarães CR, De Souza LM, Sassaki G, Abreu F, Seldin L (2012) Purification and characterization of a surfactin-like molecule produced by Bacillus sp H2O–1 and its antagonistic effect against sulfate reducing bacteria. BMC Microbiol 12(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-252
Lamoth F (2023) Novel therapeutic approaches to invasive candidiasis: considerations for the clinician. Infect Drug Resist 1087–1097. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S375625
Latoud C, Peypoux F, Michel G, Genet R, Morgat JL (1986) Interactions of antibiotics of the iturin group with human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 856(3):526–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2736(86)90144-6
Lei S, Zhao H, Pang B, Qu R, Lian Z, Jiang C, Shao D, Huang Q, Jin M, Shi J (2019) Capability of iturin from Bacillus subtilis to inhibit Candida albicans in vitro and in vivo. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(11):4377–4392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09805-z
Li G, Liu B, Shang Y, Yu Z, Zhang R (2012) Novel activity evaluation and subsequent partial purification of antimicrobial peptides produced by Bacillus subtilis LFB112. Ann Microbiol 62(2):667–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0303-9
Li Y, Chang W, Zhang M, Li X, Jiao Y, Lou H (2015) Diorcinol D exerts fungicidal action against Candida albicans through cytoplasm membrane destruction and ROS accumulation. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0128693. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128693
Liang C, Xi-Xi X, Yun-Xiang S, Qiu-Hua X, Yang-Yong L, Yuan-Sen H, Ke B (2023) Surfactin inhibits Fusarium graminearum by accumulating intracellular ROS and inducing apoptosis mechanisms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 39(12):340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03790-2
Lin D, Grossfield A (2015) Thermodynamics of micelle formation and membrane fusion modulate antimicrobial lipopeptide activity. Biophys J 109(4):750–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2015.07.011
Lin LZ, Zheng QW, Wei T, Zhang ZQ, Zhao CF, Zhong H, Guo LQ (2020) Isolation and characterization of fengycins produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens JFL21 and its broad-spectrum antimicrobial potential against multidrug-resistant foodborne pathogens. Front Microbiol 11:579621. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.579621
Liu Y, Lu J, Sun J, Lu F, Bie X, Lu Z (2019) Membrane disruption and DNA binding of Fusarium graminearum cell induced by C16-Fengycin A produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Food Control 102:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.03.031
Ludovico P, Sansonetty F, Côrte-Real M (2001) Assessment of mitochondrial membrane potential in yeast cell populations by flow cytometry. Microbiology 147(12):3335–3343. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-147-12-3335
Luo C, Liu X, Zhou X, Guo J, Truong J, Wang X, Chen Z (2015) Unusual biosynthesis and structure of locillomycins from Bacillus subtilis 916. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(19):6601–6609. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01639-15
Ma Z, Hu J (2014) Production and characterization of iturinic lipopeptides as antifungal agents and biosurfactants produced by a marine Pinctada martensii-derived Bacillus mojavensis B0621A. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173:705–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0879-1
Ma H, Zhao X, Yang L, Su P, Fu P, Peng J, Guo G (2020) Antimicrobial peptide AMP-17 affects Candida albicans by disrupting its cell wall and cell membrane integrity. Infect Drug Resis 8:2509–2520. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S250278
Maget-Dana R, Peypoux F (1994) Iturins, a special class of lipopeptides: biological and properties pore-forming physicochemical. Toxicology 87:151–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-483X(94)90159-7
Makovitzki A, Shai Y (2005) pH-dependent antifungal lipopeptides and their plausible mode of action. Biochemistry 44(28):9775–9784. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0502386
Makovitzki A, Avrahami D, Shai Y (2006) Ultrashort antibacterial and antifungal lipopeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103(43):15997–16002. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606129103
Makovitzki A, Baram J, Shai Y (2008) Antimicrobial lipopolypeptides composed of palmitoyl di- and tricationic peptides: in vitro and in vivo activities, self-assembly to nanostructures, and a plausible mode of action. Biochemistry 47(40):10630–10636. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi8011675
Makovitzki A, Viterbo A, Brotman Y, Chet I, Shai Y (2007) Inhibition of fungal and bacterial plant pathogens in vitro and in planta with ultrashort cationic lipopeptides. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(20):6629–6636. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01334-07
Malina A, Shai Y (2005) Conjugation of fatty acids with different lengths modulates the antibacterial and antifungal activity of a cationic biologically inactive peptide. Biochem J 390(3):695–702. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20050520
Martínez-Núñez MA, López VEL (2016) Nonribosomal peptides synthetases and their applications in industry. Sustain Chem Processes. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40508-016-0057-6
Marx R, Stein T, Entian KD, Glaser SJ (2001) Structure of the Bacillus subtilis peptide antibiotic subtilosin A determined by 1H-NMR and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Protein Chem 20:501–506. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012562631268
Matos PM, Gonçalves S, Santos NC (2008) Interaction of peptides with biomembranes assessed by potential-sensitive fluorescent probes. J Pept Sci 14(4):407–415. https://doi.org/10.1002/psc.1005
Mba EI, Nweze IE (2022) Antimicrobial peptides therapy: an emerging alternative for treating drug-resistant bacteria. Yale J Biol Med 95(4):445
McIntosh JA, Donia MS, Schmidt EW (2009) Ribosomal peptide natural products: bridging the ribosomal and nonribosomal worlds. Nat Prod Rep 26(4):537–559. https://doi.org/10.1039/B714132G
Meena KR, Kanwar SS (2015) Lipopeptides as the antifungal and antibacterial agents: applications in food safety and therapeutics. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/473050
Meleney FL, Johnson BA (1949) Bacitracin. Am J Med 7(6):794–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(49)90418-0
Mello EO, Ribeiro SFF, Carvalho AO, Santos IS, Da Cunha M, Santa-Catarina C, Gomes VM (2011) Antifungal activity of PvD1 defensin involves plasma membrane permeabilization, inhibition of medium acidification, and induction of ROS in fungi cells. Curr Microbiol 62(4):1209–1217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9847-3
Melander RJ, Zurawski DV, Melander C (2018) Narrow-spectrum antibacterial agents. Medchemcomm 9(1):12–21. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MD00528H
Mohid SA, Biswas K, Won T, Mallela LS, Gucchait A, Butzke L, Sarkar R, Barkham T, Reif B, Leipold E, Roy S, Misra AK, Lakshminarayanan R, Lee D, Bhunia A (2022) Structural insights into the interaction of antifungal peptides and ergosterol containing fungal membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1864(10):183996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2022.183996
Morrison DC, Jacobs DM (1976) Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry 13(10):813–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6
Motta AS, Flores FS, Souto AA, Brandelli A (2008) Antibacterial activity of a bacteriocin-like substance produced by Bacillus sp P34 that targets the bacterial cell envelope: antonie van Leeuwenhoek. Int J General Mol Microbiol 93(3):275–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-007-9202-2
Moyne AL, Cleveland TE, Tuzun S (2004) Molecular characterization and analysis of the operon encoding the antifungal lipopeptide bacillomycin D. FEMS Microbiol Lett 234(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2004.tb09511.x
Mulligan CN (2005) Environmental applications for biosurfactants. Environ Pollut 133(2):183–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.06.009
Munusamy S, Conde R, Bertrand B, Munoz-Garay C (2020) Biophysical approaches for exploring lipopeptide-lipid interactions. Biochimie 170:173–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2020.01.009
Nanjundan J, Ramasamy R, Uthandi S, Ponnusamy M (2019) Antimicrobial activity and spectroscopic characterization of surfactin class of lipopeptides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SR1. Microb Pathog 128:374–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2019.01.037
Naruse N, Tenmyo O, Kobaru S, Kamei H, Miyaki T, Konishi M, Oki T (1990) Pumilacidin, a complex of new antiviral antibiotics production, isolation, chemical properties, structure and biological activity. J Antibiot 43(3):267–280. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.43.267
Nasir MN, Besson F (2012) Interactions of the antifungal mycosubtilin with ergosterol-containing interfacial monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1818(5):1302–1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.01.020
Nation RL, Li J (2009) Colistin in the 21st century. Curr Opin Infect Dis 22(6):535.
Naughton PJ, Marchant R, Naughton V, Banat IM (2019) Microbial biosurfactants: current trends and applications in agricultural and biomedical industries. J Appl Microbiol 127(1):12–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14243
Neu TR, Härtner T, Poralla K (1990) Surface active properties of viscosin: a peptidolipid antibiotic. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 32:518–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173720
Nybroe O, Sørensen J (2004) Production of Cyclic Lipopeptides by Fluorescent Pseudomonads: in Pseudomonas: Biosynthesis of Macromolecules and Molecular Metabolism, pp 147–172. Boston, MA: Springer US. Doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9088-4_5
Ongena M, Jacques P (2008) Bacillus lipopeptides: versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends Microbiol 16(3):115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2007.12.009
Oppenheimer-Shaanan Y, Steinberg N, Kolodkin-Gal I (2013) Small molecules are natural triggers for the disassembly of biofilms. Trends Microbiol 21(11):594–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2013.08.005
Pacwa-Płociniczak M, Płaza GA, Piotrowska-Seget Z, Cameotra SS (2011) Environmental applications of biosurfactants: recent advances. Int J Mol Sci 12(1):633–654. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12010633
Parmanik A, Das S, Kar B, Bose A, Dwivedi GR, Pandey MM (2022) Current treatment strategies against multidrug-resistant bacteria: a review. Curr Microbiol 79(12):388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-03061-7
Parulekar RS, Sonawane KD (2018) Insights into the antibiotic resistance and inhibition mechanism of aminoglycoside phosphotransferase from Bacillus cereus: In silico and in vitro perspective. J Cell Biochem 119(11):9444–9461. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27261
Patel S, Ahmed S, Eswari JS (2015) Therapeutic cyclic lipopeptides mining from microbes: latest strides and hurdles. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31:1177–1193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1880-8
Pathak KV, Keharia H (2014) Identification of surfactins and iturins produced by potent fungal antagonist, Bacillus subtilis K1 isolated from aerial roots of banyan (Ficus benghalensis) tree using mass spectrometry. 3 Biotech 4(3):283–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-013-0151-3
Pathak KV, Keharia H, Gupta K, Thakur SS, Balaram P (2012) Lipopeptides from the banyan endophyte, Bacillus subtilis K1: mass spectrometric characterization of a library of fengycins. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 23(10):1716–1728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-012-0437-4
Pfaller MA, Boyken L, Hollis RJ, Kroeger J, Messer SA, Tendolkar S, Diekema DJ (2008) In vitro susceptibility of invasive isolates of Candida spp. to anidulafungin, caspofungin, and micafungin: six years of global surveillance. J Clin Microbiol 46(1):150–156. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01901-07
Poursoleiman A, Karimi-Jafari MH, Zolmajd-Haghighi Z, Bagheri M, Haertlé T, Behbehani GR, Ghasemi A, Stroylova YY, Muronetz VI, Saboury AA (2019) Polymyxins interaction to the human serum albumin: a thermodynamic and computational study. Spectrochim Acta Part A 217:155–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.03.077
Ramachandran R, Chalasani AG, Lal R, Roy U (2014) A broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity of Bacillus subtilis RLID 12.1. Sci World J 194:1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/968487
Ramachandran R, Shrivastava M, Narayanan NN, Thakur RL, Chakrabarti A, Roy U (2018) Evaluation of antifungal efficacy of three new cyclic lipopeptides of the class bacillomycin from Bacillus subtilis RLID 12.1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 62(1):10–1128. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.01457-17
Ramchandran R, Ramesh SAA, Thakur R, Chakrabarti A, Roy U (2020) Improved production of two anti candida lipopeptide homologues co- produced by the wild-type Bacillus subtilis RLID 12.1 under optimized conditions. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 21(5):438–450. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389201020666191205115008
Ramesh S, Madduri M, Rudramurthy SM, Roy U (2023a) Functional characterization of a Bacillus-derived novel broad-spectrum antifungal lipopeptide variant against Candida tropicalis and Candida auris and unravelling its mode of action. Microbiol Spectr 11(2):e01583-e1622. https://doi.org/10.1128/spectrum.01583-22
Ramesh S, Shaw D, Madhuri M, Rudramurthy SM, Roy U (2023b) In vitro evaluation of novel Bacillus-derived lipopeptide on clinically prevalent Trichophyton spp. in dermatophytosis. Acta microbiol. Bulg 39(1):83–86
Ramesh S, Roy U, Sushashish R, Rudramurthy SM (2024) A natural lipopeptide from Bacillus subtilis RLID12.1 with promising antifungal activity: its partial characterization and insight into the mode of action. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 108:161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12976-5
Ray A, Aayilliath KA, Banerjee S, Chakrabarti A, Denning DW (2022) Burden of serious fungal infections in India. Open Forum Infect Dis 9(12):603. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofac603
Reddy KVR, Yedery RD, Aranha C (2004) Antimicrobial peptides: premises and promises. Int J Antimicrob Agents 24(6):536–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2004.09.005
Redza-Dutordoir M, Averill-Bates DA (2016) Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1863(12):2977–2992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.09.012
Roberts KD, Zhu Y, Azad MA, Han ML, Wang J, Wang L, Li J (2022) A synthetic lipopeptide targeting top-priority multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens. Nat Commun 13(1):1625. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29234-3
Rodrigues LR, Teixeira JA (2010) Biomedical and therapeutic applications of biosurfactants. Biosurfactants 5:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-5979-9_6
Rodríguez-López L, López-Prieto A, Lopez-Álvarez M, Pérez-Davila S, Serra J, González P, Moldes AB (2020) Characterization and cytotoxic effect of biosurfactants obtained from different sources. ACS Omega 5(48):31381–31390. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c04933
Romero D, De Vicente A, Olmos JL, Dávila JC, Pérez-García A (2007a) Effect of lipopeptides of antagonistic strains of Bacillus subtilis on the morphology and ultrastructure of the cucurbit fungal pathogen Podosphaera fusca. J Appl Microbiol 103(4):969–976. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03323.x
Romero D, De Vicente A, Rakotoaly RH, Dufour SE, Veening JW, Arrebola E, Pérez-García A (2007b) The iturin and fengycin families of lipopeptides are key factors in antagonism of Bacillus subtilis toward Podosphaera fusca. Mol Plant-Microbe Int 20(4):430–440. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-20-4-0430
Rossolini GM, Arena F, Pecile P, Pollini S (2014) Update on the antibiotic resistance crisis. Curr Opin Pharmacol 18:56–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2014.09.006
Roy K, Mukhopadhyay, Reddy T, GCS, Desikan, KR, Ganguli BN (1987) Mulundocandin, a new lipopeptide antibiotic I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, and characterization. J Antibiot 40(3):275–280. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.40.275
Sabnis A, Hagart KL, Klöckner A, Becce M, Evans LE, Furniss RCD, Edwards AM (2021) Colistin kills bacteria by targeting lipopolysaccharide in the cytoplasmic membrane. Elife 10:e65836. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.65836
Saini HS, Barragán-Huerta BE, Lebrón-Paler A, Pemberton JE, Vázquez RR, Burns AM, Maier RM (2008) Efficient purification of the biosurfactant viscosin from Pseudomonas libanensis strain M9–3 and its physicochemical and biological properties. J Nat Products 71(6):1011–1015. https://doi.org/10.1021/np800069u
Sajid M, Khan MSA, Cameotra SS, Al-Thubiani AS (2020) Biosurfactants: potential applications as immunomodulator drugs. Immunol Lett 223:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2020.04.003
Santos DKF, Rufino RD, Luna JM, Santos VA, Sarubbo LA (2016) Biosurfactants: multifunctional biomolecules of the 21st century. Int J Mol Sci 17(3):401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17030401
Settanni L, Corsetti A (2008) Application of bacteriocins in vegetable food biopreservation. Int J Food Microbiol 121(2):123–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.09.001
Schneider T, Müller A, Miess H, Gross H (2014) Cyclic lipopeptides as antibacterial agents–potent antibiotic activity mediated by intriguing mode of actions. Int J Med Microbiol 304(1):37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2013.08.009
Shafi J, Tian H, Ji M (2017) Bacillus species as versatile weapons for plant pathogens: a review. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 31(3):446–459. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2017.1286950
Sharma D, Mandal SM, Manhas RK (2014) Purification and characterization of a novel lipopeptide from Streptomyces amritsarensis sp. nov. active against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. AMB Express 4(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-014-0050-y
Sharma D, Singh SS, Baindara P, Sharma S, Khatri N, Grover V, Korpole S (2020) Surfactin like broad spectrum antimicrobial lipopeptide co-produced with sublancin from Bacillus subtilis strain A52: dual reservoir of bioactives. Front Microbiol 11:1167. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01167
Sikora K, Jaśkiewicz M, Neubauer D, Migoń D, Kamysz W (2020) The role of counter-ions in peptides: an overview. Pharmaceuticals 13(12):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13120442
Silverman JA, Perlmutter NG, Shapiro HM (2003) Correlation of daptomycin bactericidal activity and membrane depolarization in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47(8):2538–2544. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.47.8.2538-2544.2003
Singh AK, Sharma P (2020) Disinfectant-like activity of lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by Bacillus tequilensis strain SDS21. Colloids Surf B 185:110514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110514
Singh S, Sequeira RA, Kumar P, Ghadge VA, Vaghela P, Mohanty KA, Ghosh A, Prasad K, Shinde PB (2022) Selective partition of lipopeptides from fermentation broth: a green and sustainable approach. ACS Omega 7(50):46646–46652. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c05587
Sivapathasekaran C, Mukherjee S, Samanta R, Sen R (2009) High-performance liquid chromatography purification of biosurfactant isoforms produced by a marine bacterium. Anal Bioanal Chem 395(3):845–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3023-2
Soares da Silva R, de C. F., Almeida, D. G., Meira, H. M., Silva, E. J., Farias, C. B. B., Rufino, R. D., Luna, J. M., & Sarubbo, L. A. (2017) Production and characterization of a new biosurfactant from Pseudomonas cepacia grown in low-cost fermentative medium and its application in the oil industry. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 12:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2017.09.004
Soares GMS, Figueiredo LC, Faveri M, Cortelli SC, Duarte PM, Feres M (2012) Mechanisms of action of systemic antibiotics used in periodontal treatment and mechanisms of bacterial resistance to these drugs. J Appl Oral Sci 20:295–309. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1678-77572012000300002
Sofjan AK, Mitchell A, Shah DN, Nguyen T, Sim M, Trojcak A, Garey KW (2018) Rezafungin (CD101), a next-generation echinocandin: A systematic literature review and assessment of possible place in therapy. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 14:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2018.02.013
Sreedharan SM, Rishi N, Singh R (2023) Microbial lipopeptides: Properties, mechanics, and engineering for novel lipopeptides. Microbiol Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2023.127363
Stachelhaus T, Marahiel MA (1995) Modular structure of genes encoding multifunctional peptide synthetases required for non-ribosomal peptide synthesis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 125(1):3–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1995.tb07328.x
Stansly PG (1949) The polymyxins; a review and assessment. Am J Med 7(6):807–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-9343(49)90419-2
Sucher AJ, Chahine EB, Balcer HE (2009) Echinocandins: the newest class of antifungals. Ann Pharmacother 43(10):1647–1657. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1M237
Sumi CD, Yang BW, Yeo IC, Hahm YT (2015) Antimicrobial peptides of the genus Bacillus: A new era for antibiotics. Can J Microbiol 61(2):93–103. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2014-0613
Sur S, Grossfield A (2022) Effects of cholesterol on the mechanism of fengycin, a biofungicide. Biophys J 121(10):1963–1974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2022.04.006
Szymański M, Chmielewska S, Czyżewska U, Malinowska M, Tylicki A (2022) Echinocandins–structure, mechanism of action and use in antifungal therapy. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 37(1):876–894. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2022.2050224
Talapko J, Meštrović T, Juzbašić M, Tomas M, Erić S, Horvat Aleksijević L, Škrlec I (2022) Antimicrobial peptides Mechanisms of action, antimicrobial effects and clinical applications. Antibiotics 11(10):1417. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11101417
Tang J, He J, Liu T, Xin X, Hu H (2017) Removal of heavy metal from sludge by the combined application of a biodegradable biosurfactant and complexing agent in enhanced electrokinetic treatment. Chemosphere 189:599–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.104
Tanwar J, Das S, Fatima Z, Hameed S (2014) Multidrug resistance: an emerging crisis. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/541340
Thimon L, Peypoux F, Wallach J, Michel G (1995) Effect of the lipopeptide antibiotic, iturin A, on morphology and membrane ultrastructure of yeast cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett 128(2):101–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1995.tb07507.x
Thompson GR, Soriano A, Honore PM, Bassetti M, Cornely OA, Kollef M, Pappas PG (2023) Efficacy and safety of rezafungin and caspofungin in candidaemia and invasive candidiasis: pooled data from two prospective randomised controlled trials. Lancet Infect Dis. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00551-0
Tossi A, Tarantino C, Romeo D (1997) Design of synthetic antimicrobial peptides based on sequence analogy and amphipathicity. Eur J Biochem 250(2):549–558. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.0549a.x
Tran C, Cock IE, Chen X, Feng Y (2022) Antimicrobial Bacillus: metabolites and their mode of action. Antibiotics 11(1):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11010088
Tran PN, Yen MR, Chiang CY, Lin HC, Chen PY (2019) Detecting and prioritizing biosynthetic gene clusters for bioactive compounds in bacteria and fungi. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:3277–3287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09708-z
Tsai PW, Yang CY, Chang HT, Lan CY (2011) Human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 inhibits adhesion of Candida albicans by interacting with yeast cell-wall carbohydrates. PLoS ONE 6(3):e17755. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017755
Tsuge K, Akiyama T, Shoda M (2001) Cloning, sequencing, and characterization of the iturin A operon. J Bacteriol 183(21):6265–6273. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.183.21.6265-6273.2001
Varjani SJ, Upasani VN (2017) Critical review on biosurfactant analysis, purification and characterization using rhamnolipid as a model biosurfactant. Biores Technol 232:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.047
Velkov T, Roberts KD, Nation RL, Thompson PE, Li J (2013) Pharmacology of polymyxins: new insights into an ‘old class’ of antibiotics. Future Microbiol 8(6):711–724. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb.13.39
Vertesy L, Ehlers E, Kogler H, Kurz M, Meiwes J, Seibert G, Hammann P (2000) Friulimicins: novel lipopeptide antibiotics with peptidoglycan synthesis inhibiting activity from Actinoplanes friuliensis sp. nov. II: Isolation and structural characterization. J Antibiot 53(8):816–827. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.53.816
Vigneshwaran C, Vasantharaj K, Krishnanand N, Sivasubramanian V (2021) Production optimization, purification and characterization of lipopeptide biosurfactant obtained from Brevibacillus sp. AVN13. J Environ Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104867
Wan C, Fan X, Lou Z, Wang H, Olatunde A, Rengasamy KR (2022) Iturin: cyclic lipopeptide with multifunction biological potential. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 62(29):7976–7988. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2021.1922355
Wang K, Dang W, Xie J, Zhu R, Sun M, Jia F, Wang R (2015) Antimicrobial peptide protonectin disturbs the membrane integrity and induces ROS production in yeast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1848(10):2365–2373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.07.008
Wang Q, Pan L, Han Y, Zhou Z (2022) Antimicrobial mechanisms of enterocin CHQS against Candida albicans. Curr Microbiol 79(7):191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02878-6
Weddle R (1968) Purification of polymyxin application great britain. Claims 78:424–123
Wei YH, Wang LC, Chen WC, Chen SY (2010) Production and characterization of fengycin by indigenous Bacillus subtilis F29–3 originating from a potato farm. Int J Mol Sci 11(11):426–4538. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11114526
Woodworth JR, Nyhart EH Jr, Brier GL, Wolny JD, Black HR (1992) Single-dose pharmacokinetics and antibacterial activity of daptomycin, a new lipopeptide antibiotic, in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 36(2):318–325. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.36.2.318
Wu YS, Ngai SC, Goh BH, Chan KG, Lee LH, Chuah LH (2017) Anticancer activities of surfactin and potential application of nanotechnology assisted surfactin delivery. Front Pharmacol 8:761. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00761
Xiao J, Guo X, Qiao X, Zhang X, Chen X, Zhang D (2021) Activity of fengycin and iturin a isolated from Bacillus subtilis Z-14 on gaeumannomyces graminis var tritici and soil microbial diversity. Front Microbiol 12:682437. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.682437
Yakimov MM, Timmis KN, Wray V, Fredrickson HL (1995) Characterization of a new lipopeptide surfactant produced by thermotolerant and halotolerant subsurface Bacillus licheniformis BAS50. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(5):1706–1713. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.61.5.1706-1713.1995
Yamasaki K, Sakurama K, Nish K, Watanabe H, Maruyama T, Seo H, Taguchi K (2020) Characterization of the interaction of daptomycin with site II on human serum albumin. J Pharm Sci 109(9):2919–2924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2020.06.011
Yan F, Li C, Ye X, Lian Y, Wu Y, Wang X (2020) Antifungal activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MG3 against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in loquat fruits. Biol Control 146:104281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2020.104281
Yaraguppi DA, Bagewadi ZK, Patil NR, Mantri N (2023) Iturin: a promising cyclic lipopeptide with diverse applications. Biomolecules 13(10):1515. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13101515
Yocum RR, Rasmussen JR, Strominger JL (1980) The mechanism of action of penicillin: Penicillin acylates the active site of Bacillus stearothermophilus D-alanine carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem 255(9):3977–3986. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)85621-1
Zasloff M (2002) Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 415(6870):389–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/415389a
Zaman M, Toth I (2013) Immunostimulation by synthetic lipopeptide-based vaccine candidates: structure-activity relationships. Front Immunol 4:318. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2013.00318
Zhan Y, Ma N, Liu R, Wang N, Zhang T, He L (2019) Polymyxin B and polymyxin E induce anaphylactoid response through mediation of Mas-related G protein–coupled receptor X2. Chem Biol Interact 308:304–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2019.05.014
Zhao Q, Mei X, Xu Y (2016) Isolation and Identification of antifungal compounds produced by Bacillus Y-IVI for suppressing Fusarium wilt of muskmelon. Plant Protect Sci 52(3):167–175. https://doi.org/10.17221/70/2015-PPS
Zhao X, Kuipers OP (2016) Identification and classification of known and putative antimicrobial compounds produced by a wide variety of Bacillales species. BMC Genomics 17(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-3224-y
Zhao Y, Perlin DS (2020) Review of the novel echinocandin antifungal rezafungin: animal studies and clinical data. J Fungi 6(4):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040192
Zhou S, Liu G, Zheng R, Sun C, Wu S (2020) Structural and functional insights into iturin W, a novel lipopeptide produced by the deep-sea bacterium Bacillus sp. strain wsm-1. Appl Environ Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01597-20
Acknowledgements
First authors (S.K.P. & M.M.) sincerely acknowledge the funding agencies Department of Biotechnology (DBT)-Builder File no. BT/INF/22/SP2543/2021), and Science & Engineering Research Board (SERB) (File no. EMR/2017/000572), Govt. of India for the fellowships. S.R. acknowledges the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), Govt. of India, New Delhi for the senior research fellowship. V.R. and U.R. sincerely acknowledge the DBT-Builder.
Funding
Authors sicerely acknowledge the funding from the DBT-Builder (File no.BT/INF/22/SP2543/2021). First co-author and the second author acknowledge the funding agencies SERB (File no. EMR/2017/000572) and ICMR for the fellowships respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SKP and MM drafted the main manuscript text and SKP, MM, and SR prepared figures and graphical abstracts, VR and UR reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sreelakshmi, K.P., Madhuri, M., Swetha, R. et al. Microbial lipopeptides: their pharmaceutical and biotechnological potential, applications, and way forward. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 135 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-03908-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-03908-0