Abstract
To explore the effect of terephthalic acid/glycerol interaction on the performance of poly (butanediol sebacate—butanediol terephthalate) (PBSeT) copolyesters, the puncture, tearing, and degradation properties of PBSeT copolyesters with different terephthalic acid content and glycerol content 0 ~ 0.1 mol were investigated. The results showed that the puncture and tear strength of the copolyesters were improved with the content of terephthalic acid but first rose and then declined with the increase of glycerol content, which glycerol and terephthalic acid exhibited synergistic mechanism in puncture and tearing performance within a certain range. Compared with LDPE, the optimal puncture and tearing strength of the copolyesters were 1.82 and 2.49 times, respectively. As far as hydrolysis was concerned, a greater weight loss was observed under alkaline conditions than acidic conditions. Moreover, higher terephthalic acid and glycerol content exhibited a synergistic effect to hinder the hydrolysis under alkaline conditions. Surprisingly, the addition of a certain content of glycerol promoted the enzymatic degradation of all copolyesters except for the 0.04 mol content, and the weight loss of enzyme degradation reached the maximum at 0.06 mol content; however, the high terephthalic acid content made the enzyme degradation performance deteriorates. Therefore, inhibitory mechanism in enzymatic degradation was showed by terephthalic acid and glycerol. To sum up, this suggested a potential utility and application prospect in the field of agriculture, packaging, and engineering materials.
Graphical abstract
Synergistic/inhibitory mechanism of terephthalic acid and glycerol on the puncture, tearing, and degradation properties of PBSeT copolyesters.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan T, Deng W, Gang Y, Du Z, Li Y (2021) Degradation of hazardous organics via cathodic flow-through process using a spinel FeCo2O4/CNT decorated stainless-steel mesh. ES Materials & Manufacturing. https://doi.org/10.30919/esmm5f417
Jadhav P, Shinde S, Suryawanshi SS, Teli SB, Patil PS, Ramteke AA, Hiremath NG, Prasad NR (2020) Green AgNPs decorated ZnO nanocomposites for dye degradation and antimicrobial applications. Engineered Science. https://doi.org/10.30919/es8d1138
Chang B, Li Y, Wang W, Song G, Lin J, Murugadoss V, Naik N, Guo Z (2021) Impacts of chain extenders on thermal property, degradation, and rheological performance of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate). J Mater Res 36(15):3134–3144. https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-021-00308-0
Naz F, Zuber M, Mehmood Zia K, Salman M, Chakraborty J, Nath I, Verpoort F (2018) Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-based waterborne polyurethane for textile finishes. Carbohydr Polym 200:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.076
Guidotti G, Soccio M, Gazzano M, Bloise N, Bruni G, Aluigi A, Visai L, Munari A, Lotti N (2020) Biocompatible PBS-based copolymer for soft tissue engineering: introduction of disulfide bonds as winning tool to tune the final properties. Polym Degrad Stab 182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2020.109403
Pan D, Su F, Liu H, Liu C, Umar A, Castañeda LC, Algadi H, Wang C, Guo Z, (2021) Research progress on catalytic pyrolysis and reuse of waste plastics and petroleum sludge. ES Materials & Manufacturing 11:3–15. https://doi.org/10.30919/esmm5f415
Qiu S, Zhou Y, Waterhouse GIN, Gong R, Xie J, Zhang K, Xu J (2021) Optimizing interfacial adhesion in PBAT/PLA nanocomposite for biodegradable packaging films. Food Chem 334:127487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127487
Chen L, Li J, Zhao Y, Li M, Li L, Hou H, Chen L (2020) Numerical simulation and optimization of indirect squeeze casting process. Engineered Science 13:65–70
Wu H, Zhong Y, Tang Y, Huang Y, Liu G, Sun W, Xie P, Pan D, Liu C, Guo Z (2021) Precise regulation of weakly negative permittivity in CaCu3Ti4O12 metacomposites by synergistic effects of carbon nanotubes and grapheme. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00378-y
Qi G, Liu Y, Chen L, Xie P, Pan D, Shi Z, Quan B, Zhong Y, Liu C, Fan R, Guo Z (2021) Lightweight Fe3C@Fe/C nanocomposites derived from wasted cornstalks with high-efficiency microwave absorption and ultrathin thickness. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials 4(4):1226–1238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00368-0
Emonson NS, Eyckens DJ, Allardyce BJ, Hendlmeier A, Stanfield MK, Soulsby LC, Stojcevski F, Henderson LC (2020) Using in situ polymerization to increase puncture resistance and induce reversible formability in silk membranes. Materials (Basel) 13 (10). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102252
Chuang YC, Bao L, Lin MC, Lou CW, Lin T (2019) Mechanical and static stab resistant properties of hybrid-fabric fibrous planks: manufacturing process of nonwoven fabrics made of recycled fibers. Polymers (Basel) 11 (7). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11071140
Li T-T, Wang R, Lou C-W, Lin J-H (2014) Static and dynamic puncture behaviors of compound fabrics with recycled high-performance Kevlar fibers. Compos B Eng 59:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.10.063
Ma Y, Zhuang Z, Ma M, Yang Y, Li W, Dong M, Wu S, Ding T, Guo Z (2019) Solid polyaniline dendrites consisting of high aspect ratio branches self-assembled using sodium lauryl sulfonate as soft templates: synthesis and electrochemical performance. Polymer 182:121808
Gürgen S, Kuşhan MC (2017) The ballistic performance of aramid based fabrics impregnated with multi-phase shear thickening fluids. Polym Testing 64:296–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2017.11.003
Chuang YC, Bao L, Lin MC, Lin TA, Lou CW (2019) Fabric composites reinforced with thermally bonded and irregularly aligned filaments: preparation and puncture resistant performance. polymers (Basel) 11 (4). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11040706
Kashfipour MA, Mehra N, Dent RS, Zhu J (2019) Regulating intermolecular chain interaction of biopolymer with natural polyol for flexible, optically transparent and thermally conductive hybrids. Engineered Science 8:11–18. https://doi.org/10.30919/es8d508
Chen L-Q, Zhao Y (2021) From classical thermodynamics to phase-field method. Prog Mater Sci:100868
Zhao Y-H, Ying J-H, Chen L-W, Hou H (2021) Current research status of interface of ceramic-metal laminated composite material for armor protection. Acta Metall Sin
Feng S, Yue Y, Chen J, Zhou J, Li Y, Zhang Q (2020) Biodegradation mechanism of polycaprolactone by a novel esterase MGS0156: a QM/MM approach. Environ Sci Process Impacts 22(12):2332–2344. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0em00340a
Haider TP, Volker C, Kramm J, Landfester K, Wurm FR (2019) Plastics of the future? The impact of biodegradable polymers on the environment and on society. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 58(1):50–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201805766
Hajighasemi M, Nocek BP, Tchigvintsev A, Brown G, Flick R, Xu X, Cui H, Hai T, Joachimiak A, Golyshin PN, Savchenko A, Edwards EA, Yakunin AF (2016) Biochemical and structural insights into enzymatic depolymerization of polylactic acid and other polyesters by microbial carboxylesterases. Biomacromol 17(6):2027–2039. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00223
García JM (2016) Catalyst: design challenges for the future of plastics recycling. Chem 1(6):813–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2016.11.003
Vinod B, Suresh S, Sudhakara D (2020) Investigation of biodegradable hybrid composites: effect of fibers on tribo-mechanical characteristics. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials 3(2):194–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-020-00148-2
Ma Y, Hou C, Zhang H, Qiao M, Chen Y, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Guo Z (2017) Morphology-dependent electrochemical supercapacitors in multi-dimensional polyaniline nanostructures. J Mater Chem A 5(27):14041–14052. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta03279j
Zhuang Z, Wang W, Wei Y, Li T, Ma M, Ma Y (2021) Preparation of polyaniline nanorods/manganese dioxide nanoflowers core/shell nanostructure and investigation of electrochemical performances. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-42021-00225-42110
Kawai F, Oda M, Tamashiro T, Waku T, Tanaka N, Yamamoto M, Mizushima H, Miyakawa T, Tanokura M (2014) A novel Ca(2)(+)-activated, thermostabilized polyesterase capable of hydrolyzing polyethylene terephthalate from Saccharomonospora viridis AHK190. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(24):10053–10064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5860-y
Ma Y, Hou C, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Liu H, Wu S, Guo Z (2019) Three-dimensional core-shell Fe3O4/polyaniline coaxial heterogeneous nanonets: Preparation and high performance supercapacitor electrodes. Electrochim Acta 315:114–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.05.073
Perz V, Bleymaier K, Sinkel C, Kueper U, Bonnekessel M, Ribitsch D, Guebitz GM (2016) Substrate specificities of cutinases on aliphatic-aromatic polyesters and on their model substrates. N Biotechnol 33(2):295–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2015.11.004
Marten E, Müller R-J, Deckwer W-D (2005) Studies on the enzymatic hydrolysis of polyesters. II. Aliphatic–aromatic copolyesters. Polymer Degradation and Stability 88 (3):371–381. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2004.12.001
Shanmugam L, Kazemi ME, Qiu C, Rui M, Yang L, Yang J (2020) Influence of UHMWPE fiber and Ti6Al4V metal surface treatments on the low-velocity impact behavior of thermoplastic fiber metal laminates. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials 3(4):508–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-020-00189-7
Perz V, Hromic A, Baumschlager A, Steinkellner G, Pavkov-Keller T, Gruber K, Bleymaier K, Zitzenbacher S, Zankel A, Mayrhofer C, Sinkel C, Kueper U, Schlegel K, Ribitsch D, Guebitz GM (2016) An esterase from anaerobic clostridium hathewayi can hydrolyze aliphatic-aromatic polyesters. Environ Sci Technol 50(6):2899–2907. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04346
Biundo A, Hromic A, Pavkov-Keller T, Gruber K, Quartinello F, Haernvall K, Perz V, Arrell MS, Zinn M, Ribitsch D, Guebitz GM (2016) Characterization of a poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)- hydrolyzing lipase from Pelosinus fermentans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(4):1753–1764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7031-1
Shah AA, Kato S, Shintani N, Kamini NR, Nakajima-Kambe T (2014) Microbial degradation of aliphatic and aliphatic-aromatic co-polyesters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(8):3437–3447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5558-1
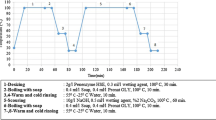
Z Li Y Li X Dong W Wang Y-C Zhu V Murugadoss G Song N Naik D Pan Z Guo 2021 Synthesis, characterization and properties of poly(butanediol sebacate–butanediol terephthalate) (PBSeT) copolyesters using glycerol as cross-linking agent Materials Today Communications 28 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102557
Heidarzadeh N, Rafizadeh M, Taromi FA, del Valle LJ, Franco L, Puiggalí J (2017) Biodegradability and biocompatibility of copoly(butylene sebacate-co-terephthalate)s. Polym Degrad Stab 135:18–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2016.11.013
Lu J, Wu L, Li B-G (2017) Long chain branched poly(butylene succinate-co-terephthalate) copolyesters using pentaerythritol as branching agent: Synthesis, thermo-mechanical, and rheological properties. J. Appl Polym Sci 134 (9). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44544
Lu J, Wu L, Li B-G (2017) High molecular weight polyesters derived from bio-based 1,5-pentanediol and a variety of aliphatic diacids: Synthesis, characterization and thermo-mechanical properties. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering
Lai L, Wang S, Li J, Liu P, Wu L, Wu H, Xu J, Severtson SJ, Wang WJ (2020) Stiffening, strengthening, and toughening of biodegradable poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) with a low nanoinclusion usage. Carbohydr Polym 247:116687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116687
Sultan M, Islam A, Gull N, Bhatti HN, Safa Y (2014) Structural variation in soft segment of waterborne polyurethane acrylate nanoemulsions. J Appl Polym Sci 132(12):41706. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41706
Nissen KE, Stuart BH, Stevens MG, Baker AT (2008) The tensile and tear properties of a biodegradable polyester film. Int J Polym Anal Charact 13(3):190–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/10236660802070538
Chen C, Xu R, Chen X, Xie J, Zhang F, Yang Y, Lei C (2016) Influence of cocrystallization behavior on structure and properties of HDPE/LLDPE microporous membrane. J Polym Res 23(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-016-0935-3
Tabatabaei SH, Carreau PJ, Ajji A (2009) Structure and properties of MDO stretched polypropylene. Polymer 50(16):3981–3989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2009.06.059
Kijchavengkul T, Auras R, Rubino M, Selke S, Ngouajio M, Fernandez RT (2010) Biodegradation and hydrolysis rate of aliphatic aromatic polyester. Polym Degrad Stab 95(12):2641–2647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.07.018
Peng S, Wu L, Li B-G, Dubois P (2017) Hydrolytic and compost degradation of biobased PBSF and PBAF copolyesters with 40–60 mol% BF unit. Polym Degrad Stab 146:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.07.016
Hbaieb S, Kammoun W, Delaite C, Abid M, Abid S, El Gharbi R (2015) New copolyesters containing aliphatic and bio-based furanic units by bulk copolycondensation. Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part A 52(5):365–373. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2015.1018807
Mohanan N, Montazer Z, Sharma PK, Levin DB (2020) Microbial and enzymatic degradation of synthetic plastics. Front Microbiol 11:580709. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.580709
Li F, Xu X, Yu J, Cao A (2007) The morphological effects upon enzymatic degradation of poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene terephthalate)s (PBST). Polym Degrad Stab 92(6):1053–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2007.02.008
De Hoe GX, Zumstein MT, Getzinger GJ, Ruegsegger I, Kohler HE, Maurer-Jones MA, Sander M, Hillmyer MA, McNeill K (2019) Photochemical transformation of poly(butylene adipate- co-terephthalate) and its effects on enzymatic hydrolyzability. Environ Sci Technol 53(5):2472–2481. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b06458
Aarthy M, Puhazhselvan P, Aparna R, George AS, Gowthaman MK, Ayyadurai N, Masaki K, Nakajima-Kambe T, Kamini NR (2018) Growth associated degradation of aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters by Cryptococcus sp. MTCC 5455. Polym Degrad Stab 152:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.03.021
Nikolić MAL, Gauthier E, Colwell JM, Halley P, Bottle SE, Laycock B, Truss R (2017) The challenges in lifetime prediction of oxodegradable polyolefin and biodegradable polymer films. Polym Degrad Stab 145:102–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.07.018
Zhou W, Wang X, Yang B, Xu Y, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Ji J (2013) Synthesis, physical properties and enzymatic degradation of bio-based poly(butylene adipate-co-butylene furandicarboxylate) copolyesters. Polym Degrad Stab 98(11):2177–2183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.08.025
Saadi Z, Cesar G, Bewa H, Benguigui L (2013) Fungal degradation of poly(butylene adipate-Co-terephthalate) in soil and in compost. J Polym Environ 21(4):893–901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-013-0582-2
Bag PP (2021) Introduction of plasticity to change mechanical behaviour of pharmaceutical crystals by co-crystallization: a solution of long standing problem in isoniazid. Engineered Science 15:129–137
Lv X, Tang Y, Tian Q, Wang Y, Ding T (2020) Ultra-stretchable membrane with high electrical and thermal conductivity via electrospinning and in-situ nanosilver deposition. Compos Sci Technol 200:108414
Kang X, Lu Z, Feng W, Wang J, Fang X, Xu Y, Wang Y, Liu B, Ding T, Ma Y (2021) A novel phosphorous and silicon-containing benzoxazine: highly efficient multifunctional flame-retardant synergist for polyoxymethylene. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials 4(1):127–137
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Maoyong He of Taiyuan Institute of Technology for his help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Li, Y., Lei, H. et al. The effect of synergistic/inhibitory mechanism of terephthalic acid and glycerol on the puncture, tearing, and degradation properties of PBSeT copolyesters. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5, 1335–1349 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00405-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-021-00405-y