Abstract
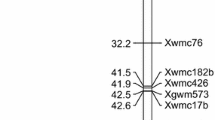
Quality, specifically protein content and gluten strength are among the main objectives of a durum wheat breeding program. The aim of this work was to validate quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with grain protein content (GPC) and gluten strength measured by SDS sedimentation volume (SV) and to find additional QTLs expressed in Argentinean environments. Also, epistatic QTL and QTL x environmental interactions were analyzed. A mapping population of 93 RILs derived from the cross UC1113 x Kofa showing extreme values in gluten quality was used. Phenotypic data were collected along six environments (three locations, two years). Main effect QTLs associated with GPC were found in equivalent positions in two environments on chromosomes 3BS (R2 = 21.0-21.6%) and 7BL (R2 = 12.1-13%), and in one environment on chromosomes 1BS, 2AL, 2BS, 3BL, 4AL, 5AS, 5BL and 7AS. The most important and stable QTL affecting SV was located on chromosome 1BL (Glu-B1) consistently detected over the six environments (R2 = 20.9- 54.2%). Additional QTLs were found in three environments on chromosomes 6AL (R2 = 6.4-12.5%), and in two environments on chromosomes 6BL (R2 = 11.5-12.1%), 7AS (R2 = 8.2-10.2%) and 4BS (R2 = 11–16.4%). In addition, pleiotropic effects were found affecting grain yield, test weight, thousand-kernel- weight and days to heading in some of these QTLs. Epistatic QTLs and QTL x environment interactions were found for both quality traits, mostly for GPC. The flanking markers of the QTLs detected in this work could be efficient tools to select superior genotypes for the mentioned traits.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GPC:
-
Grain protein content
- SV:
-
SDS sedimentation volume
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- GY:
-
Grain yield
- TKW:
-
Thousand kernel weight
- TW:
-
Test weight
References
Blanco A, and De Giovanni C (1995) Triticum dicoccoides for qualitative improvement of durum wheat: Associations of protein loci to grain traits in recombinant inbred lines. p. 149–159. In N. di Fonzo et al. (ed.) Durum wheat quality in the Mediterranean region.CIHEAM/ICARDA/CIMMYT,Zaragoza, Spain. 17–19Nov. 1993. Mediterranean Agronomic Institute, Chania, Greece
Blanco A, Simeone R, Laddomada B, Pascualone A, Troccoli A, Di Fonzo N (2000) Variation for grain protein content and identification of QTLs by molecular markers in tetraploid wheats. En: Durum wheat improvement in the Mediterranean region: New challenges. pp. 455–461. Royo C, Nachit, MM, DiFonzo N, y Arauz, JL. (eds). International Centre for Advanced Mediterranean Agronomic Studies (CIHEAM), Zaragoza
Blanco A, Pasqualone A, Troccoli A, Di Fonzo N, Simeone R (2002) Detection of grain protein content QTLs across environments in tetraploid wheats. Plant Mol Biol 48:615–623
Blanco A, Simeone R, Gadaleta A (2006) Detection of QTLs for grain protein content in durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 112:1195–1204
Boggini G, Pogna NE (1989) The breedmaking quality and storage proteins composition of italian durum wheat. J Cereal Sci 9:131–138
Campbell KG, Finney PL, Bergman CJ, Gualberto DG, Anderson JA, Giroux MJ, Siritunga D, Zhu J, Gendre F, Roué C, Vérel A, Sorrells ME (2001) Quantitative trait loci associated whit milling and baking quality in a soft x hard wheat cross. Crop Sci 41:1275–1285
Carrillo JM, Vázquez JF, Ruiz M, Albuquerque MM (1991) Relationships between gluten strength and protein components in spanish durum wheat landraces. pp. 268–276. En: Gluten Proteins 1990. W. Bushuk y R. Tkachuk (eds.). Am. Assoc. Cereal Chem. St. Paul, MN
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Clarke JM, Clarke FR, Ames NP, McCaig TN, Knox RE (2000) Evaluation of predictors of quality for use in early generation selection. In: Royo C, Nachit MM, Di Fonzo N, Araus JL (eds) Durum Wheat Improvement In The Mediterranean Region: New Chalenges. International Centre for Advanced Mediterranean Agronomic Studies (CIHEAM), Zaragoza, pp 439–446
Conti V, Cervigni G, Miranda R, Wehrhahne L, Jensen C, Bariffi J, Echenique V (2008) Utilidad de marcadores moleculares asociados a fuerza de gluten en la selección asistida de trigo candeal. VII National Wheat Conference. 2–4 July. La Pampa, Argentina. http://rian.inta.gov.ar/trabajoscongresotrigo2008/
Cruz CD (1997) Programa Genes: aplicativo computacional em genética e estatística. p. 442. Viçosa: Editora UFV
Cruz CD and Regazzi AJ (1997) Modelos biométricos aplicados ao melhoramento genético. 2ª edición. Editora UFV, Universidade Federal de Viçosa. Brasil
D’Egidio MG, Marian BM, Nardi S, Novaro P, Cubadda R (1990) Chemical and technological variables and their relationships: a predictive equation for pasta cooking quality. Cereal Chem 67:275–281
Dick JW, Quick JS (1983) A modified screening test for rapid estimation of gluten strength in early generation durum wheat breeding lines. AACC. Vol. 60, Nº 4
Distelfeld A, Uauy C, Fahima T, Dubcovsky J (2006) Physical map of the wheat high-grain protein content gene Gpc-B1 and development of a high-throughput molecular marker. New Phytol 169:753–763
Elouafi I, Nachit MM, Elsaleh A, Asbati A, Mather DE (2000) QTL-mapping of genomic regions controlling gluten strength in durum (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum). En: Durum wheat improvement in the Mediterranean region: New challenges. Options mediterranéennes 40: 455–461. Royo, C, Nachit, MM, DiFonzo, N. y Arauz, JL (eds) International Centre for Advanced Mediterranean Agronomic Studies (CIHEAM), Zaragoza
Gianibelli MC, Larroque OR, MacRitchie F, Wrigley CW (2001) Biochemical, genetic, and molecular characterization of wheat endosperm proteins. Cereal Chem 78:635–646
Groos C, Robert N, Bervas E, Charmet G (2003) Genetic analysis of grain protein-content, grain yield and thousand-kernel weight in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 106:1032–1040
Huang XQ, Cloutier S, Lycar L, Radovanovic N, Humphreys DG, Noll JS, Somers DJ, Brown PD (2006) Molecular detection of QTL for agronomic and quality traits in a doubled haploid population derived from two Canadian wheats (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 113:753–766
Joppa LR, Cantrell RG (1990) Chromosomal location of genes for grain protein in content of wild tetraploid wheat. Crop Sci 30:1059–1064
Joppa LR, Khan K, Williams ND (1983) Chromosomal location of genes for gliadin polypeptides in durum wheat Triticum turgidum. Theor Appl Genet 64:289–293
Kerfal S, Giraldo P, Rodríguez-Quijano M, Vázquez JF, Adams K, Lukow OM, Röder MS, Somers DJ, Carrillo JM (2010) Mapping quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with dough quality in a soft x hard bread wheat progeny. J Cereal Sci 52:46–52
Kunert A, Naz AA, Dedeck O, Pillen K, Leon J (2007) AB-QTL analysis in winter wheat: I. Synthetic hexaploid wheat (T. turgidum ssp. dicoccoides · T. tauschii) as a source of favourable alleles for milling and baking quality traits. Theor Appl Genet 115:683–695
Lafiandra D, Sanguineti MC, Maccaferri M. and DeAmbrogio E (2007) Molecular markers and qtl analysis for grain quality improvement in wheat. Chapter 2. R.K. Varshney and R. Tuberosa (eds.), Genomics Assisted Crop Improvement:Vol. 2: Genomics Applications in Crops, 25–50
Lerner SE, Cogliatti M, Ponzio NR, Seghezzo ML, Molfese ER, Rogers WJ (2004) Genetic variation for grain protein components and industrial quality of durum wheat cultivars sown in Argentina. J Cereal Sci 40:161–166
Li Y, Song Y, Zhou R, Branlard G, Jia J (2009) Detection of QTLs for bread-making quality in wheat using a recombinant inbred line population. Plant Breed 128:235–243
Mann G, Diffey S, Cullis B, Azanza F, Martin D, Kelly A, McIntyre L, Schmidt A, Ma W, Nath Z, Kutty I, Leyne EP, Rampling L, Quail KJ, Morell MK (2009) Genetic control of wheat quality: interactions between chromosomal regions determining protein content and composition, dough rheology, and sponge and dough baking properties. Theor Appl Genet 118:1519–1537
Martínez MC, Ruiz M, Carrillo JM (2005) Effects of different prolamin alleles on durum wheat quality properties. J Cereal Sci 41:123–131
McCartney CA, Somers DJ, Lukow O, Ames N, Noll J, Cloutier S, Humphreys DG, McCallum BD (2006) QTL analysis of quality traits in the spring wheat cross RL4452 x AC Domain. Plant Breed 125:565–575
Mcintosh RA, Yamazaki Y, Devos KM, Dubcovsky J, Rogers WJ, Appels R (2003) Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat. In: International Wheat Genetics Symposium. (10º, 1–6 September, 2003, Instituto Sperimentale per la Cerealicoltura, Rome, Paestum, Italy). 2003, vol. 4, 77 p
Olmos S, Distelfeld A, Chicaiza O, Schlatter AR, Fahima T, Echenique V, Dubcovsky J (2003) Precise mapping of a locus affecting grain protein content in durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 107:1243–1251
Patil RM, Oak MD, Tamhankar SA, Rao VS (2009) Molecular mapping of QTLs for gluten strength as measured by sedimentation volume and mixograph in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. ssp durum). J Cereal Sci 49:378–386
Payne PI (1987) Genetics of wheat storage proteins and the effect of allelic variation on bread-making quality. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 38:141–153
Payne PI, Holt LM, Jackson EA, Law CN (1984) Wheat storage proteins: their genetics and their potential for manipulation by plant breeding. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 304:359–371
Peña RJ, Zarco-Hernandez J, Amaya-Celis A, Mujeed-Kazi A (1994) Relationships between chromosome 1B-encoded glutenin subunit compositions and bread-making quality characteristics of some durum wheat (Triticum turgidum) cultivars. J Cereal Sci 19:243–249
Pogna NE, Dal Belin Peruffo A, Mellini F (1984) Genetic aspects of gliadin bands 40 and 43.5 associated with gluten strength. Genet Agrar 39:101–108
Pogna NE, Autran JC, Mellini F, Lafiandra D, Feillet P (1990) Chromosome 1B-encoded gliadins and glutenin subunits in durum wheat: genetics and relationship to gluten strength. J Cereal Sci 11:15–34
Prasad M, Kumar N, Kulwal PL, Röder MS, Balyan HS, Dhaliwal HS, Gupta PK (2003) QTL analysis for grain protein content using SSR markers and validation studies using NILs in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 106:659–667
Ruiz M, Carrillo JM (1995) Separate effects on gluten strength of Gli-1 and Glu-3 prolamin genes on chromosomes 1A and 1B in durum wheat. J Cereal Sci 21:137–144
Shewry PR, Halford NG, Lafiandra D (2003) Genetics of wheat gluten proteins. Adv Genet 49:111–184
Suprayogi Y, Pozniak CJ, Clarke FR, Clarke JM, Knox RE, Singh AK (2009) Identification and validation of quantitative trait loci for grain protein concentration in adapted Canadian durum wheat populations. Theor Appl Genet 119:437–448
Uauy C, Distelfeld A, Fahima T, Blechl A, Dubcovsky J (2006) A NAC gene regulating senescence improves grain protein, zinc, and iron content in wheat. Science 314:1298–1301
Van Ooijen JW (1992) Accuracy of mapping quantitative trait loci in autogamous species. Theor Appl Genet 84:803–811
Wang DL, Zhu J, Li ZK, Paterson AH (1999) Mapping QTLs with epistatic effects and QTL x environment interactions by mixed linear model approaches. Theor Appl Genet 99:1255–1264
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng Z (2004) Windows QTL cartographer. V2.0 Program in statistical genetics. North Carolina State University, North Carolina. http://www.statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Zanetti S, Winzeler M, Feuillet C, Keller B, Messmer M (2001) Genetic analysis of bread-making quality in wheat and spelt. Plant Breed 120:13–19
Zhang W, Chao S, Manthey F, Chicaiza O, Brevis JC, Echenique V, Dubcovsky J (2008) QTL analysis of pasta quality using a composite microsatellite and SNP map of durum wheat. Theor Appl Genet 117:1361–1377
Zhao L, Zhang KP, Zhi-ying Deng BL, Qu HL, Tian JC (2010) A comparison of grain protein content QTLs and flour protein content QTLs across environments in cultivated wheat. Euphytica 174:325–335
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Jorge Dubcovsky for providing us with the molecular map and the mapping population to conduct the present analysis. This project was granted by the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), the Universidad Nacional del Sur (UNS) and the Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Tecnológica (ANPCyT). We thank Pablo Mandolesi for technical support and José H. Bariffi, Liliana Wehrhahne, Pavan Akkiraju and Partricia Gomez for helping us with the field experiments. We also thank very much Dr. John Rogers from Universidad Nacional del Centro, Bs. As., Argentina for reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Veronica Conti and Pablo F. Roncallo contributed equally to this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Grain protein content (GPC) and SDS sedimentation volume (SV) values from eight Argentinean cultivars of durum wheat growing in six environments of Argentina (DOC 132 kb)
Table S2
Threshold LOD values in each environment and using the mean data of the six environments at 5% and 10% of probability for type I error (DOC 28 kb)
Table S3
Pearson simple correlation coefficients (r) among environments for grain protein content (GPC) and SDS sedimentation volume (SV) in the UC1113 x Kofa RILs mapping population (DOC 32 kb)
Table S4
Fertilization practices performed in each environment (DOC 30 kb)
Table S5
Rainfall condition and monthly temperatures (minimum, mean and maximum) in the six growing environments used in the QTL mapping analyses (DOC 77 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conti, V., Roncallo, P.F., Beaufort, V. et al. Mapping of main and epistatic effect QTLs associated to grain protein and gluten strength using a RIL population of durum wheat. J Appl Genetics 52, 287–298 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-011-0045-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-011-0045-1