Abstract
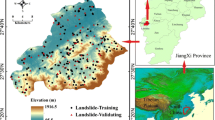
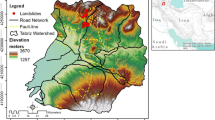
The main purpose of this study is to produce reliable susceptibility maps using GIS-based support vector machine (SVM) models and compare their performances for the Qianyang County of Baoji City, Shaanxi Province, China. In this paper, with kernel classifiers of linear, polynomial, radial basis function and sigmoid, the four various types were applied in landslide susceptibility mapping. The important input parameters for the landslide susceptibility assessment were acquired from different sources. Firstly, 81 landslide sites were obtained by aerial photographs, earlier reports and field surveys. Then, the landslide inventory was randomly classified into two datasets: 70 % (56 landslides) for training the models and 30 % (25 landslides) for validation purpose. Secondly, 15 landslide conditioning factors were selected (i.e., slope angle, slope aspect, altitude, plan curvature, profile curvature, distance to faults, distance to rivers, distance to roads, NDVI, STI, SPI, TWI, geomorphology, rainfall, and lithology). Subsequently, with four types of kernel function classifiers based on landslide conditioning factors, landslide susceptibility parameters were obtained using SVM models. Finally, the rationality of landslide susceptibility maps was verified using the receiver operating characteristics with both success rate curve and prediction rate curve. The validation results showed that success rates for the four SVM models were 83.15 % (RBF-SVM), 82.72 % (PL-SVM), 81.77 % (LN-SVM), and 79.99 % (SIG-SVM). The prediction rates for the four SVM models were 77.98 % (RBF-SVM), 77.50 % (PL-SVM), 77.07 % (LN-SVM), and 76.08 % (SIG-SVM), respectively. The results showed that the RBF-SVM model had the highest overall performance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akgun A (2012) A comparison of landslide susceptibility maps produced by logistic regression, multi-criteria decision, and likelihood ratio methods: a case study at İzmir, Turkey. Landslides 9:93–106
Akgun A, Dag S, Bulut F (2008) Landslide susceptibility mapping for a landslide-prone area (Findikli, NE of Turkey) by likelihood-frequency ratio and weighted linear combination models. Environ Geol 54(6):1127–1143
Akgun A, Sezer EA, Nefeslioglu HA, Gokceoglu C, Pradhan B (2012) An easy-to-use MATLAB program (MamLand) for the assessment of landslide susceptibility using a Mamdani fuzzy algorithm. Comput Geosci 38(1):23–34
Bai SB, Wang J, Lü GN, Zhou PG, Hou SS, Xu SN (2010) GIS-based logistic regression for landslide susceptibility mapping of the Zhongxian segment in the Three Gorges area, China. Geomorphology 115(1):23–31
Brenning A (2005) Spatial prediction models for landslide hazards: review, comparison and evaluation. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 5(6):853–862
Bui DT, Tuan TA, Klempe H, Pradhan B, Revhaug I (2015) Spatial prediction models for shallow landslide hazards: a comparative assessment of the efficacy of support vector machines, artificial neural networks, kernel logistic regression, and logistic model tree. Landslides. doi:10.1007/s10346-015-0557-6
Chauhan S, Sharma M, Arora M, Gupta N (2010) Landslide susceptibility zonation through ratings derived from artificial neural network. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 12:340–350
Choi J, Oh HJ, Lee HJ, Lee C, Lee S (2012) Combining landslide susceptibility maps obtained from frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network models using ASTER images and GIS. Eng Geol 124:12–23
Chung CJF, Fabbri AG (2003) Validation of spatial prediction models for landslide hazard mapping. Nat Hazards 30(3):451–472
Conforti M, Aucelli PP, Robustelli G, Scarciglia F (2011) Geomorphology and GIS analysis for mapping gully erosion susceptibility in the Turbolo stream catchment (Northern Calabria, Italy). Nat Hazards 56(3):881–898
Constantin M, Bednarik M, Jurchescu MC, Vlaicu M (2011) Landslide susceptibility assessment using the bivariate statistical analysis and the index of entropy in the Sibiciu Basin (Romania). Environ Earth Sci 63(2):397–406
Dai FC, Lee CF (2001) Terrain-based mapping of landslide susceptibility using a geographical information system: a case study. Can Geotech J 38(5):911–923
Demir G, Aytekin M, Akgün A, İkizler SB, Tatar O (2013) A comparison of landslide susceptibility mapping of the eastern part of the North Anatolian Fault Zone (Turkey) by likelihood-frequency ratio and analytic hierarchy process methods. Nat Hazards 65(3):1481–1506
Devkota KC, Regmi AD, Pourghasemi HR, Yoshida K, Pradhan B, Ryu IC, Dhital MR, Althuwaynee OF (2013) Landslide susceptibility mapping using certainty factor, index of entropy and logistic regression models in GIS and their comparison at Mugling-Narayanghat road section in Nepal Himalaya. Nat Hazards 65(1):135–165
Ercanoglu M, Gokceoglu C (2002) Assessment of landslide susceptibility for a landslide-prone area (north of Yenice, NW Turkey) by fuzzy approach. Environ Geol 41:720–730
Ercanoglu M, Gokceoglu C (2004) Use of fuzzy relations to produce landslide susceptibility map of a landslide prone area (West Black Sea Region, Turkey). Eng Geol 75(3):229–250
Guettouche MS (2013) Modeling and risk assessment of landslides using fuzzy logic. Application on the slopes of the Algerian Tell (Algeria). Arab J Geosci 6:3163–3173
Guinau M, Pallàs R, Vilaplana JM (2005) A feasible methodology for landslide susceptibility assessment in developing countries: a case-study of NW Nicaragua after Hurricane Mitch. Eng Geol 80(3):316–327
He S, Pan P, Dai L, Wang H, Liu J (2012) Application of kernel-based Fisher discriminant analysis to map landslide susceptibility in the Qinggan River delta, Three Gorges, China. Geomorphology 171:30–41
Jaafari A, Najafi A, Pourghasemi HR, Rezaeian J, Sattarian A (2014) GIS-based frequency ratio and index of entropy models for landslide susceptibility assessment in the Caspian forest, northern Iran. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11(4):909–926
Kannan M, Saranathan E, Anabalagan R (2013) Landslide vulnerability mapping using frequency ratio model: a geospatial approach in Bodi-Bodimettu Ghat section, Theni district, Tamil Nadu, India. Arab J Geosci 6(8):2901–2913
Kanungo DP, Sarkar S, Sharma S (2011) Combining neural network with fuzzy, certainty factor and likelihood ratio concepts for spatial prediction of landslides. Nat Hazards 59(3):1491–1512
Kavzoglu T, Sahin EK, Colkesen I (2014) Landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis, support vector machines, and logistic regression. Landslides 11(3):425–439
Kayastha P, Dhital MR, De Smedt F (2013) Application of analytical hierarchy process (AHP) for landslide susceptibility mapping: a case study from the Tinau watershed, west Nepal. Comput Geosci 52:398–408
Kritikos T, Davies T (2014) Assessment of rainfall-generated shallow landslide/debris-flow susceptibility and runout using a GIS-based approach: application to western Southern Alps of New Zealand. Landslides. doi:10.1007/s10346-014-0533-6
Lee S, Pradhan B (2007) Landslide hazard mapping at Selangor, Malaysia using frequency ratio and logistic regression models. Landslides 4(1):33–41
Marjanović M, Kovačević M, Bajat B, Voženílek V (2011) Landslide susceptibility assessment using SVM machine learning algorithm. Eng Geol 123:225–234
Melchiorre C, Abella EC, van Westen CJ, Matteucci M (2011) Evaluation of prediction capability, robustness, and sensitivity in non-linear landslide susceptibility models, Guantánamo, Cuba. Comput Geosci 37(4):410–425
Mihaela C, Martin B, Marta CJ, Marius V (2011) Landslide susceptibility assessment using the bivariate statistical analysis and the index of entropy in the Sibiciu Basin (Romania). Environ Earth Sci 63:397–406
Oh HJ, Pradhan B (2011) Application of a neuro-fuzzy model to landslide-susceptibility mapping for shallow landslides in a tropical hilly area. Comput Geosci 37(9):1264–1276
Ozdemir A, Altural T (2013) A comparative study of frequency ratio, weights of evidence and logistic regression methods for landslide susceptibility mapping: Sultan Mountains, SW Turkey. J Asian Earth Sci 64:180–197
Park S, Choi C, Kim B, Kim J (2013) Landslide susceptibility mapping using frequency ratio, analytic hierarchy process, logistic regression, and artificial neural network methods at the Inje area, Korea. Environ Earth Sci 68:1443–1464
Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C (2012a) Application of fuzzy logic and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) to landslide susceptibility mapping at Haraz watershed, Iran. Nat Hazards 63:965–996
Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C, Moezzi KD (2012b) Landslide susceptibility mapping using a spatial multicriteria evaluation model at Haraz Watershed, Iran. Terrigenous mass movements. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 23–49
Pourghasemi HR, Mohammady M, Pradhan B (2012c) Landslide susceptibility mapping using index of entropy and conditional probability models in GIS: Safarood Basin, Iran. Catena 97:71–84
Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C, Mohammadi M, Moradi HR (2013a) Application of weights-of-evidence and certainty factor models and their comparison in landslide susceptibility mapping at Haraz watershed, Iran. Arab J Geosci 6(7):2351–2365
Pourghasemi HR, Jirandeh AG, Pradhan B, Xu C, Gokceoglu C (2013b) Landslide susceptibility mapping using support vector machine and GIS at the Golestan Province, Iran. J Earth Syst Sci 122(2):349–369
Pouydal CP, Chang C, Oh HJ, Lee S (2010) Landslide susceptibility maps comparing frequency ratio and artificial neural networks: a case study from the Nepal Himalaya. Environ Earth Sci 61:1049–1064
Pradhan B (2010) Landslide susceptibility mapping of a catchment area using frequency ratio, fuzzy logic and multivariate logistic regression approaches. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 38(2):301–320
Pradhan B (2011) Manifestation of an advanced fuzzy logic model coupled with geoinformation techniques coupled with geoinformation techniques for landslide susceptibility analysis. Environ Ecol Stat 18(3):471–493
Pradhan B (2013) A comparative study on the predictive ability of the decision tree, support vector machine and neuro-fuzzy models in landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS. Comput Geosci 51:350–365
Pradhan B, Buchroithner MF (2010) Comparison and validation of landslide susceptibility maps using an artificial neural network model for three test areas in Malaysia. Environ Eng Geosci 16(2):107–126
Pradhan AMS, Kim YT (2014) Relative effect method of landslide susceptibility zonation in weathered granite soil: a case study in Deokjeok-ri Creek, South Korea. Nat Hazards 72(2):1189–1217
Pradhan B, Lee S (2010) Landslide susceptibility assessment and factor effect analysis: back-propagation artificial neural networks and their comparison with frequency ratio and bivariate logistic regression modeling. Environ Modell Softw 25(6):747–759
Pradhan B, Oh HJ, Buchroithner M (2010) Weights-of-evidence model applied to landslide susceptibility mapping in a tropical hilly area. Geomat Nat Hazards Risk 1(3):199–223
Raman R, Punia M (2012) The application of GIS-based bivariate statistical methods for landslide hazards assessment in the upper Tons river valley, Western Himalaya, India. Georisk: Assess Manag Risk Eng Syst Geohazards 6(3):145–161
Regmi AD, Devkota KC, Yoshida K, Pradhan B, Pourghasemi HR, Kumamoto T, Akgun A (2014) Application of frequency ratio, statistical index, and weights-of-evidence models and their comparison in landslide susceptibility mapping in Central Nepal Himalaya. Arab J Geosci 7(2):725–742
San BT (2014) An evaluation of SVM using polygon-based random sampling in landslide susceptibility mapping: The Candir catchment area (western Antalya, Turkey). Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 26:399–412
Schölkopf B, Smola AJ, Williamson RC, Bartlett PL (2000) New support vector algorithms. Neural Comput 12(5):1207–1245
Sezer EA, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C (2011) Manifestation of an adaptive neuro-fuzzy model on landslide susceptibility mapping: Klang Valley, Malaysia. Expert Syst Appl 38:8208–8219
Sharma LP, Patel Nilanchal, Ghose MK, Debnath P (2013) Synergistic application of fuzzy logic and geo-informatics for landslide vulnerability zonation-a case study in Sikkim Himalayas, India. Appl Geomat 5:271–284
Solaimani K, Mousavi SZ, Kavian A (2013) Landslide susceptibility mapping based on frequency ratio and logistic regression models. Arab J Geosci 6(7):2557–2569
Sujatha ER, Rajamanickam GV, Kumaravel P (2012) Landslide susceptibility analysis using probabilistic certainty factor approach: a case study on Tevankarai stream watershed, India. J Earth Syst Sci 121(5):1337–1350
Sujatha ER, Kumaravel P, Rajamanickam GV (2014) Assessing landslide susceptibility using Bayesian probability-based weight of evidence model. Bull Eng Geol Environ 73(1):147–161
Tehrany MS, Pradhan B, Mansor S, Ahmad N (2015) Flood susceptibility assessment using GIS-based support vector machine model with different kernel types. Catena 125:91–101
Vahidnia MH, Alesheikh AA, Alimohammadi A, Hosseinali F (2010) A GIS-based neuro-fuzzy procedure for integrating knowledge and data in landslide susceptibility mapping. Comput Geosci 36(9):1101–1114
Van Westen CJ, Van Asch TW, Soeters R (2006) Landslide hazard and risk zonation—why is it still so difficult? Bull Eng Geol Environ 65(2):167–184
Vapnick VN (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Vapnik VN (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Vijith H, Madhu G (2008) Estimating potential landslide sites of an upland sub-watershed in Western Ghat’s of Kerala (India) through frequency ratio and GIS. Environ Geol 55(7):1397–1405
Wu X, Ren F, Niu R (2014) Landslide susceptibility assessment using object mapping units, decision tree, and support vector machine models in the Three Gorges of China. Environ Earth Sci 71(11):4725–4738
Xu C, Dai F, Xu X, Lee YH (2012) GIS-based support vector machine modeling of earthquake-triggered landslide susceptibility in the Jianjiang River watershed, China. Geomorphology 145:70–80
Yalcin A, Bulut F (2007) Landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS and digital photogrammetric techniques: a case study from Ardesen (NE-Turkey). Nat Hazards 41(1):201–226
Yalcin A, Reis S, Cagdasoglu A, Yomralioglu T (2011) A GIS-based comparative study of frequency ratio, analytical hierarchy process, bivariate statistics and logistics regression methods for landslide susceptibility mapping in Trabzon, NE Turkey. Catena 85:274–287
Yao X, Tham LG, Dai FC (2008) Landslide susceptibility mapping based on support vector machine: a case study on natural slopes of Hong Kong, China. Geomorphology 101(4):572–582
Yilmaz I (2010a) Comparison of landslide susceptibility mapping methodologies for Koyulhisar, Turkey: conditional probability, logistic regression, artificial neural networks, and support vector machine. Environ Earth Sci 61(4):821–836
Yilmaz I (2010b) The effect of the sampling strategies on the landslide susceptibility mapping by conditional probability and artificial neural networks. Environ Earth Sci 60(3):505–519
Youssef AM, Al-Kathery M, Pradhan B (2015a) Landslide susceptibility mapping at Al-Hasher area, Jizan (Saudi Arabia) using GIS-based frequency ratio and index of entropy models. Geosci J 19(1):113–134
Youssef AM, Pradhan B, Jebur MN, El-Harbi HM (2015b) Landslide susceptibility mapping using ensemble bivariate and multivariate statistical models in Fayfa area, Saudi Arabia. Environ Earth Sci 73(7):3745–3761
Acknowledgments
The authors want to express their gratitude to anonymous reviewers and editors for their valuable comments which were very useful in bringing the manuscript into the present form. The study is supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41302276) and Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2012JM5008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Chai, H., Zhao, Z. et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on GIS and support vector machine models for the Qianyang County, China. Environ Earth Sci 75, 474 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5093-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5093-0