Abstract
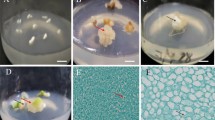
We present here a method for the in vitro propagation of Anthurium andraeanum cv. Fantasia through direct somatic embryogenesis. The embryos were directly formed at the cut end of most of the leaf explants when cultured on MS basal medium supplemented with N6-benzyladenine (BA) plus α-naphthalene acetic acid (NAA). MS basal media supplemented with BA (0.27 μM) and NAA (2.68 μM) induced maximum number of somatic embryos per leaf explant (15.33 ± 1.45) after 28 d of continuous culture. The highest numbers of embryos (12.33 ± 0.88) were matured into plantlets in MS basal medium augmented with 0.27 μM BA and 58.4 mM sucrose. Histology showed the presence of scutellum, coleoptile, well-developed root, and shoot initials at different stages of somatic embryo (SE) development directly on leaf explants. About 85% of the plantlets were successfully acclimatized, and of these, 80.3% plants survived after secondary hardening under greenhouse conditions. The embryo-derived plants successfully flowered. The presence of monomorphic DNA bands in random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) marker analysis confirmed the genetic homogeneity of direct somatic embryo-derived plantlets in respect to their mother plant.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beyramizade E, Azadi P, Mii M (2008) Optimization of factors affecting organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis of Anthurium andraeanum Lind. ‘Tera’. Propaga Ornamental Plants 8:198–203
Borchetia S, Das SC, Handique PJ, Das S (2009) High multiplication frequency and genetic stability for commercialization of the three varieties of micropropagated tea plants (Camellia spp.). Sci Hortic 120:544–550
Dam A, Paul S, Bandyopadhyay TK (2010) Direct somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf explants of Limonium sinensis (Girard) Kuntze. Sci Hortic 126:253–260
Dam A, Paul S, Bhattacharya C, Bandyopadhyay TK (2013) Effects of culture conditions on multiple shoot induction from inflorescence and RAPD analysis of cloned plants in Limonium sinensis (Girard) Kuntze, var. Golden Diamond. Plant Biochem Biotechnol 22:348–352
Denchev P, Velcheva M, Atanassov A (1991) A new approach to direct somatic embryogenesis in Medicago. Plant Cell Rep 10:338–341
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Fehér A (2005) Why somatic plant cells start to form embryos? In: Mujib A, Samaj J (eds) Plant cell monographs (2). Somatic embryogenesis. Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 85–101
Finnie JF, van Staden J (1986) In vitro culture of Anthurium andraeanum. S Afr J Bot 52:343–346
Gantait S, Sinniah UR, Mandal N, Das PK (2012) Direct induction of protocorm-like bodies from shoot tips, plantlet formation, and clonal fidelity analysis in Anthurium andreanum cv. Can. Plant Growth Regul 67:257–270
Geier T (1986) Factors affecting plant regeneration from leaf segments of Anthurium scherzerianum Schott (Araceae) cultured in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 6:115–125
Gow WP, Chen JT, Chang WC (2010) Enhancement of direct somatic embryogenesis and plantlet growth from leaf explants of Phalaenopsis by adjusting culture period and explant length. Acta Physiol Plant 32:621–627
Kubeš M, Drážná N, Konrádová H, Lipavská H (2014) Robust carbohydrate dynamics based on sucrose resynthesis in developing Norway spruce somatic embryos at variable sugar supply. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 50:45–57
Kuehnle AR, Chen FC, Sugii N (1992) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Anthurium andraeanum hybrids. Plant Cell Rep 11:438–442
Kuehnle AR, Sugii N (1991) Callus induction and plantlet regeneration in tissue cultures of Hawaiian Anthuriums. HortSci 26:919–921
Kumari S, Desai JR, Shah RR (2011) Callus mediated plant regeneration of two cutflower cultivars of Anthurium andraeanum Hort. J Appl Hortic 13:37–41
Kunisaki JT (1980) In vitro propagation of Anthurium andraeanum Lind. HortSci 15:508–509
Larkin PJ, Scowcroft WR (1981) Somaclonal variation—a novel source of variability from cell cultures for plant improvement. Theor Appl Genet 60:197–214
Martin KP, Joseph D, Madassey J, Philip VJ (2003) Direct shoot regeneration from lamina explants of two commercial cut flower cultivars of Anthurium andreanum Hort. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 39:500–504
Matsumoto TK, Kuehnle AR (1997) Micropropagation of Anthurium. In: Bajaj YPS (ed) High tech and micropropagation VI. Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry. Springer Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 14–29
Matsumoto TK, Webb DT, Kuehnle AR (1996) Histology and origin of somatic embryos derived from Anthurium andraeanum Linden ex André Lamina. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 121:404–407
Matsumoto TK, Kuehnle AR, Webb DT (1998) Zygotic embryogenesis in Anthurium (Araceae). Am J Bot 85:560–568
Mordhorst AP, Toonen MAJ, de Vries SC (1997) Plant embryogenesis. Crit Rev Plant Sci 16:535–576
Mujib A, Banerjee S, Maqsood M, Ghosh PD (2013) Somatic embryogenesis of some member ornamental genera of Amaryllidaceae and allied families: the similarities and differences. Open Hort J 6:9–18
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Paul S, Dam A, Bhattacharyya A, Bandyopadhyay TK (2011) An efficient regeneration system via direct and indirect somatic embryogenesis for the medicinal tree Murraya koenigii. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 105:271–283
Pedroso CM, Pais MS (1995) Factors controlling somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 43:147–154
Pierik RLM, Steegmans HHM, Van Der Meys JAJ (1974) Plantlet formation in callus tissue of Anthurium andraeanum Lind. Sci Hortic 2:193–198
Pinheiro MVM, Martins FB, da Cruz ACF, de Carvalho ACPP, Ventrella MC, Otoni WC (2013) Maturation of Anthurium andraeanum cv. Eidibel somatic embryos from nodal segments. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 49:304–312
Pinheiro MVM, Martins FB, da Cruz ACF, de Carvalho ACPP, Ventrella MC, Otoni WC (2014) Somatic embryogenesis in anthurium (Anthurium andraeanum cv. Eidibel) as affected by different explants. Acta Sci Agron 36:87–98
Punyarani K, Devi KD, Singh CH, Singh NS, Singh HH, Singh TD, Moirangthem S, Devi HS (2013) In vitro production of genetically stable and virus free plantlets of Musa sp. var. Meitei Hei using male inflorescence as explant. Sci Hortic 164:440–447
Rout GR, Das P, Goel S, Raina SN (1998) Determination of genetic stability of micropropagated plants of ginger using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. Bot Bull Acad Sin 39:23–27
Skirvin RM, Mcpheeters KD, Norton M (1994) Sources and frequency of somaclonal variation. HortSci 29:1232–1237
Smulders MJM, de Klerk GJ (2011) Epigenetics in plant tissue culture. Plant Growth Regul 63:137–146
Teixeira da Silva JA, Dobránszkib J, Winarto B, Zeng S (2015) Anthurium in vitro: a review. Sci Hortic 186:266–298
Vasil V, Hauptmann RM, Morrish FM, Vasil IK (1988) Comparative analysis of free DNA delivery and expression into protoplasts of Panicum maximum Jacq. (Guinea grass) by electroporation and polyethylene glycol. Plant Cell Rep 7:499–503
Viégas J, Rocha MTR, Ferreira-Moura I, Rosa DL, Souza JA, Corrêa MGS, Silva JAT (2007) Anthurium andraeanum (Linden ex André) culture: in vitro and ex vitro. Floric Ornam Biotechnol 1:61–65
Winarto B, da Silva JAT (2012) Influence of isolation technique of half-anthers and of initiation culture medium on callus induction and regeneration in Anthurium andreanum. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 110:401–411
Winarto B, Rachmawati F, Pramanik D, Teixeira da Silva J (2011a) Morphological and cytological diversity of regenerants derived from half-anther cultures of anthurium. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 105:363–374
Winarto B, Rachmawati F, Teixeira da Silva J (2011b) New basal media for half-anther culture of Anthurium andreanum Linden ex André cv. Tropical. Plant Growth Regul 65:513–529
Zhang Q, Chen J, Henny RJ (2006) Regeneration of Syngonium podophyllum ‘Variegatum’ through direct somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 84:181–188
Zhao J, Cui J, Liu J, Liao F, Henny RJ, Chen J (2012) Direct somatic embryogenesis from leaf and petiole explants of Spathiphyllum ‘Supreme’ and analysis of regenerants using flow cytometry. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 110:239–249
Acknowledgments
The financial assistance from DST-PURSE Programme, University of Kalyani, and Personal Research Grants (PRGs) for teachers provided by the University of Kalyani, Kalyani, West Bengal, India, are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Ewen Mullins
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11627-016-9777-2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, C., Dam, A., Karmakar, J. et al. Direct somatic embryogenesis and genetic homogeneity assessment of regenerated plants of Anthurium andraeanum Linden cv. Fantasia. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 52, 512–519 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-016-9763-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-016-9763-8