Abstract
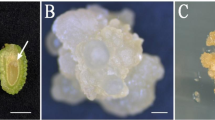
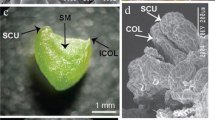
Somatic embryogenesis is a unique method of in vitro regeneration, which can be used in plant reproduction, germplasm conservation, and molecular-assisted breeding. The results showed that the optimum medium for embryogenic callus induction was MS + 6 mg L−1 6-BA + 1.5 mg L−1 TDZ + 0.5 mg L−1 NAA + 30 g L−1 sucrose + 7 g L−1 agar, and the induction rate was 47.45%. The best somatic differentiation medium was MS + 2 mg L−16-BA + 1.5 mg L−1 TDZ + 30 g L−1 sucrose + 7 g L−1 agar, and the induction rate of somatic embryos was 54.45%. The optimum medium for embryoid proliferation was MS + 6 mg L−1 6-BA + 1 mg L−1 NAA + 0.2 mg L−1 TDZ, and the proliferation rate and the multiplication coefficient reached 46.33% and 7.83, respectively. The mature somatic embryos were put into MS, B5, and 1/2MS medium for seedling culture. In MS medium, true leaves grew, complete plants were obtained, and the seedling rate was 88.00%. At the same time, the survival rate of transplanting seedlings in the mixed matrix (peat: organic fertilizer: soil = 1:1:1) was as high as 98%. Cytological observation showed that the somatic embryos underwent globular, heart-shaped, torpedo, and cotyledon stages. This study established a regeneration system of C. × generalis with excellent somatic embryos, and provided basic technical support for the large-scale commercial propagation and germplasm resources protection. It will lay a foundation for further research on gene function and breeding new varieties and ideal research materials for the study of somatic embryogenesis mechanism and genetic transformation of C. × generalis.
Key Message
Somatic embryos was acquired successfully from the embryogenic callus of C. × generalis, cytological observation showed that the somatic embryos underwent globular, heart-shaped, torpedo, and cotyledon stages. Histological analysis confirmed the vascular bundle separation between embryoid and maternal tissue.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
Arnold S, Sabala I, Bozhkov P, Dyachok J, Filonova L (2002) Developmental pathways of somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 69:233–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/10.1023/A:1015673200621
Bailey LH (1923) Various cultigens and transfers in nomenclature. Gentes Herb 1:118–120
Dong X, Yang F, Yang S, Yan C (2019) Subcellular distribution and tolerance of cadmium in Canna indica L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 185:109692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109692
Du YM, Cheng FY, Zhong Y (2020) Induction of direct somatic embryogenesis and shoot organogenesis and histological study in tree peony (Paeonia sect. Moutan). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 141(3):557–570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01815-4
Egertsdotter U, Ahmad I, Clapham D (2019) Automation and scale up of somatic embryogenesis for commercial plant production, with emphasis on conifers. Front Plant Sci 10:109. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00109
Fang H, Dong Y, Zhou R, Wang Q, Duan Q, Wang C, Yang KQ (2022) Optimization of the induction, germination, and plant regeneration system for somatic embryos in apomictic walnut (Juglans regia L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 150:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-022-02266-9
Feher A, Pasternak TP, Dudits D (2003) Transition of somatic plant cells to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 74:201–228. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024033216561
Ferreira JCB, de Araújo S-C, de Oliveira MR, Scherwinski-Pereira JE (2022) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from zygotic embryos of the palm tree Euterpe precatoria Mart. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 148:667–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-022-02227-2
Halperin W, Wetherell DF (1964) Adventive embryony in tissue cultures of the wild carrot, Daucus Carota. Am J Bot 51(3):274–283. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1964.tb06630.x
Henslo G (1911) The origin of monocotyledons from dicotyledons, through self-adaptation to a moist or aquatic habit. Ann Bot 25:717–744. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a089350
Horstman A, Bemer M, Boutilier K (2017) A transcriptional view on somatic embryogenesis. Regen 4(4):201–216. https://doi.org/10.1002/reg2.91
Islam MM, Haque ME, Alam S, Islam MA, Khalekuzzaman M, Sikdar B (2013) Morphological and histological observation of embryogenic calli derived from immature embryo of BRRI dhan28 (Oryza sativa L.) variety. Res Plant Biol 3:21–27
Ji W, Luo YX, Guo RR, Li XX, Zhou Q, Ma XH, Wang YJ (2017) Abnormal somatic embryo reduction and recycling in grapevine regeneration. J Plant Growth Regul 36:912–918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-017-9694-6
Kanchanapoom K, Ponpiboon T, Wirakiat W, Kanchanapoom K (2011) Regeneration of lily (Lilium longiflorum‘Easter lily’) by callus derived from leaf explants cultured in vitro. Sci Asia 37:373. https://doi.org/10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2011.37.373
Kurczynska EU, Gaj MD, Ujczak A, Mazur E (2007) Histological analysis of direct somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Planta 226:619–628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0510-6
Li YM, Zhang HC, Jiang H, Fu ZZ, Zhang J, Yuan X, Wang HJ, Gao J, Dong XY, Wang LM (2021) Callus induction and somatic embryogenesis of peony anthers. Acta Bot Sin 056(004):443–450. https://doi.org/10.11983/CBB20195
Li Q, Shu ML, Gan ZY, Zhao J, Zhao T, Zhang WE, Pan XJ (2022) Establishment of efficient seed germination and in vitro rapid propagation system of Canna × generalis. Plant Physiol J 58(4):667–676. https://doi.org/10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.100077
Lu D, Wei W, Zhou W, McGuigan LD, Ji F, Li X, Xing Y, Zhang Q, Fang K, Cao Q, Qin L (2017) Establishment of a somatic embryo regeneration system and expression analysis of somatic embryogenesis-related genes in Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 130:601–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1250-3
Maadon SN, Rohani ER, Ismail I, Baharum SN, Normah MN (2016) Somatic embryogenesis and metabolic differences between embryogenic and non-embryogenic structures in mangosteen. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 127:443–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1068-4
Mahmoud TN, El-Maadawy WH, Kandil ZA, Khalil H, EI-Fiky NM, EI Alfy TSMA (2021) Canna × generalis LH Bailey rhizome extract ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via modulating intestinal mucosal dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and TLR4/ NF-kB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 269:113670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.113670
Martínez MT, San-Jose MDC, Arrillaga I, Cano V, Morcillo M, Cernadas MJ, Corredoira E (2019) Holmoak somatic embryogenesis: current status and future perspectives. Front Plant Sci 10:239. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00239
Martins JS, Correia G, Pinto J, Canhoto (2022) Cloning adult trees of Arbutus unedo L. through somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 150:611–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-022-02314-4
Miroshnichenko D, Chaban I, Chernobrovkina M, Dolgov S (2017) Protocol for efficient regulation of in vitro morphogenesis in einkorn (Triticum monococcum L.), a recalcitrant diploid wheat species. PLoS ONE 12:e0173533. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173533
Mishra T, Goyal AK, Sen A (2015) Somatic embryogenesis and genetic fidelity study of the micropropagated medicinal species, Canna indica. Horticulturae 1:3–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae1010003
Mitrofanova IV, Tevfik AS, Mitrofanova OV, Brailko VA, Lesnikova-Sedoshenko NP (2017) Features of canna regeneration in vitro and plantlets adaptation in vivo. Acta Hortic 1155:447–454. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2017.1155.66
Murashige T, Nakano R (1965) Morphogenetic behavior of tobacco tissue cultures and implication of plant senescence. Amer J Bot 52:819–827. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1965.tb07253.x
Natarajan N, Sundararajan S, Ramalingam S, Chellakan PS (2020) Efficient and rapid in-vitro plantlet regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in ornamental bananas (Musa spp.). Biologia 75:317–326. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-019-00358-0
Nirmal SA, Shelke SM, Gagare PB, Jadhav PR, Dethe PM (2007) Antinociceptive and anthelmintic activity of Canna indica. Nat Prod Res 21(12):1042–1047. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786410701526016
Oh MJ, Na HR, Choi HK, Liu JR, Kim SW (2010) High frequency plant regeneration system for Nymphoides coreana via somatic embryogenesis from zygotic embryo derived embryogenic cell suspension cultures. Plant Biotech Rep 4:125–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-010-0126-3
Pereira C, Castander-Olarieta A, Montalbán IA, Pěnčík A, Petřík I, Pavlović I, De Medeiros OE, De Freitas Fraga HP, Guerra MP, Novák O, Strnad M, Canhoto J, Moncaleán P (2020) Embryonal masses induced at high temperatures in Aleppo pine: cytokinin profile and cytological characterization. Forests 11:807. https://doi.org/10.3390/F11080807
Piovan A, Caniato R, Filippini R (2014) Somatic embryogenesis and glucosinolate/myrosinase system in vulnerable Brassica repanda subsp. glabrescens (Poldini) GómezCampo. Sci Hortic 172:317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.04.027
Purshottam DK, Srivastava RK, Misra P (2019) Low-cost shoot multiplication and improved growth in different cultivars of Canna indica. 3 Biotech 9(3):67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1583-1
Quinga LAP, Heringer AS, Fraga HPDF, Vieira L, Silveira V, Steinmacher D, Guerra M (2018) Insights into the conversion potential of Theobroma cacao L. somatic embryos using quantitative proteomic analysis. Sci Horticult 229:65–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.10.005
Raju CS, Kathiravan K, Aslam A, Shajahan A (2013) An efficient regeneration system via somatic embryogenesis in mango ginger (Curcuma amada Roxb.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 112:387–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-012-0244-4
Sakai T, Imai K (2007) The influences of growth regulators and culture medium composition on shoot-tip cultures of edible canna. Environ Control Biol 45(3):155–163. https://doi.org/10.2525/ecb.45.155
Shchukin A, Ben-Bassat D, Israeli Y (1997) Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in Grand Nain banana and its effect on somaclonal variation. Acta Hortic 447:317–318. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.1997.447.62
Shekhawat MS, Kannan N, Manokari M, Priyadharshini S (2021) Regeneration of shoots via direct somatic embryogenesis from the leaf surface of Scaevola taccada (Gaertn.) Roxb.—a climate resilient species of coastal areas. S Afr J Bot 140:276–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2020.05.006
Singh R, Dubey AK, Sanyal I (2019) Optimisation of adventitious shoot regeneration and agrobacterium-mediated transformation in Canna × generalis (Canna Lily). Hortic Plant J 5(01):39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpj.2018.11.002
Soundar Raju C, Kathiravan K, Aslam A, Surhajahan A (2013) An efficient regeneration system via somatic embryogenesis in mango ginger (Ccuma amada Roxb.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 112:387–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-012-0244-4
Srivastava J, Vankar PS (2010) Canna indica flower: new source of anthocyanins. Plant Physiol Bioch 48(12):1015–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.011
Stasolla C, Yeung EC (2003) Recent advances in conifer somatic embryogenesis: improving somatic embryo quality. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 74(1):15–35. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023345803336
Tomiczak K, Mikuła A, Niedziela A, Wójcik-Lewandowska A, Domżalska L, Rybczyński JJ (2019) Somatic embryogenesis in the family Gentianaceae and its biotechnological application. Front Plant Sci 10:762. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00762
Vahdati K, Bayat S, Ebrahimzadeh H, Jariteh M, Mirmasoumi M (2008) Effect of exogenous ABA on somatic embryo maturation and germination in Persian walnut (Juglans regia L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 93:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-008-9355-3
Wafa SN, Mat Taha R, Mohajer S, Mahmad N, Ali Ahmed Abdul B (2016) Organogenesis and ultrastructural features of in vitro grown Canna indica L. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2820454
Wang Y, Li H, Zhou Y, Guo D, Zhu J, Peng S (2021) Transcriptomes analysis reveals novel insight into the molecular mechanisms of somatic embryogenesis in Hevea brasiliensis. BMC Genomics 22(1):183. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-021-07501-9
Woradulayapinij W, Soonthornchareonnon N, Wiwat C (2005) In vitro HIV type 1 reverse transcriptase inhibitory activities of Thai medicinal plants and Canna indica L. rhizomes. J Ethnopha Rmacol 101(1–3):84–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2005.03.030
Yan R, Wang C, Wang J, Nie R, Sun H (2020) High-efficiency somatic embryogenesis techniques for different hybrids of cut lilies. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 143(1):145–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01904-4
Yang X, Zhang X (2010) Regulation of somatic embryogenesis in higher plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 29(1):36–57. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680903436291
Zhang W, Pan X, Zhao Q, Zhao T (2021) Plant growth, antioxidant enzymes and response to cadmium stress. Hortic Plant J 007(003):256–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hpj.2021.03.003
Zhao W, Zheng S, Ling HQ (2011) An efficient regeneration system and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Chinese upland rice cultivar Handao297. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 106(3):475–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9946-2
Zhao T, Pan X, Ou Z, Li Q, Zhang W (2022) Comprehensive evaluation of waterlogging tolerance of eleven canna cultivars at flowering stage. Sci Hortic 296:110890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2022.110890
Zhou HC, Li M, Zhao X, Fan XC, Guo AG (2012) Plant regeneration from in vitro leaves of the peach rootstock ‘Nemaguard’ (Prunus persica×P. davidiana). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 101:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9666-z
Zou SY, Xiao HZ, Cai HL, Wang DW, Huang ZP, Hong W (2019) Recurrent somatic embryogenesis and development of somatic embryos in Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz (Lardizabalaceae). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 139(3):493–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01686-4
Funding
Application and industrialization project of scientific and technological achievements in Guizhou Province (2021 General 009) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (31460371).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception. Material preparation was performed by ZYG, FY and GFW. Data collection was accomplished by ZYG and MLS. Data analysis, experiment design and supervision were performed by XJP, WEZ and FY. The draft of the manuscript was written by ZYG and WEZ revised the article. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript and all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Yan Liu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, Zy., Shu, Ml., Yang, F. et al. Somatic embryo induction and plantlet regeneration of Canna × generalis from immature zygotic embryo. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 155, 681–692 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-023-02588-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-023-02588-2