Abstract
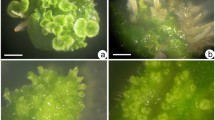
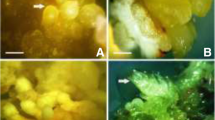
A reproducible protocol for direct and indirect somatic embryogenesis was established in a small aromatic tree, Murraya koenigii. Embryogenic callus was obtained from 90% zygotic embryonic axis (ZE) and 70% cotyledon (COT) explants in Murashige and Skoog (MS) basal medium supplemented with 8.88 μM 6-benzyladenine (BA) and 2.675 μM α-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA). Globular somatic embryos were induced and further matured from such embryogenic callus by subsequent culture on the same basal media containing thidiazuron (TDZ) (2.27–9.08 μM). The highest frequency of somatic embryos (14.58 ± 0.42) was recovered from ZE-derived callus after 6 weeks. The age and type of explant and concentration of TDZ played an important role in the development of somatic embryos. Explants excised from 60-day-old seed differentiated from 96.67% of ZE explants and 86.67% from COT explants when cultured on MS basal medium supplemented with 4.54 and 9.08 μM TDZ, respectively, after 4 weeks. The best result obtained for the average frequency of somatic embryos (11.28 ± 0.32) was from ZE explants, which was significantly higher than COT explants (7.34 ± 0.97). Most of the somatic embryos (above 95%), irrespective of their origin, germinated after 4 weeks in 1/2 MS basal media containing 2.32 μM kinetin (KN) and 1.07 μM NAA. Well-rooted plantlets were successfully acclimatized. Histological analysis and scanning electron micrographs confirmed the initiation, development, and germination of somatic embryos from both explants.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebajo AC, Ayoola OF, Iwalewa EO, Akindahunsi AA, Omisore NO, Adewunmi CO et al (2006) Anti-trichomonal, biochemical and toxicological activities of methanolic extract and some carbazole alkaloids isolated from the leaves of Murraya koenigii growing in Nigeria. Phytomedicine 13:246–254
Bhuyan AK, Pattanaik S, Chand PK (1997) Micropropagation of curry leaf tree [Murraya koenigii (L.) Spreng.] by axillary proliferation using intact seedlings. Plant Cell Rep 16:779–782
Bilyeu KD, Cole JL, Laskey JG, Riekhof WR, Esparza TJ, Kramer MD et al (2001) Molecular and biochemical characterization of a cytokinin oxidase from maize. Plant Physiol 125:378–386
Carimi F, De Pasquale F, Crescimanno FG (1995) Somatic embryogenesis in Citrus from styles culture. Plant Sci 105:81–86
Carra A, De Pasquale F, Ricci A, Carimi F (2006) Diphenylurea derivatives induce somatic embryogenesis in Citrus. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 87:41–48
Chakrabarty M, Nath AC, Khasnobis S, Chakrabarty M, Konda Y, Harigaya Y et al (1997) Carbazole alkaloids from Murraya koenigii. Phytochemistry 46:751–755
Da Silva ML, Pinto DLP, Guerra MP, Iochevet E, Floh S, Bruckner CH et al (2009) A novel regeneration system for a wild passion fruit species (Passiflora cincinnata Mast.) based on somatic embryogenesis from mature zygotic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 99:47–54
Dam A, Paul S, Bandyopadhyay TK (2010) Direct somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf explants of Limonium sinensis (Girard) Kuntze. Sci Hortic 126:253–260
Etienne H, Montoro P, Michaux-Ferriere N, Carron MP (1993) Effects of desiccation, medium osmolarity and abscisic acid on the maturation of Hevea brasiliensis somatic embryos. J Exp Bot 44:1613–1619
Fan GQ, Zhai XQ, Zhai CJ, Bi HT (2001) Callus induction from leaves of different Paulownia species and its plantlet regeneration. J For Res 12:209–214
Gaj MD (2004) Factors influencing somatic embryogenesis induction and plant regeneration with particular reference to Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant Growth Regul 43:27–47
Gupta GL, Nigam SS (1970) Chemical examination of the leaves of Murraya koenigii. Planta Med 19:83–86
Ito C, Itoigawa M, Nakao K, Murata T, Tsuboi M, Kaneda N et al (2006) Induction of apoptosis by carbazole alkaloids isolated from Murraya koenigii. Phytomedicine 13:359–365
Jiménez VM, Bangerth F (2001) Endogenous hormone levels in explants and in embryogenic and non-embryogenic cultures of carrot. Physiol Plant 111:389–395
Jumin HB, Nito N (1996) Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from protoplasts of six plant species related to Citrus. Plant Cell Rep 15:332–336
Kesari AN, Kesari S, Singh SK, Gupta RK, Watal G (2007) Studies on the glycemic and lipidemic effect of Murraya koenigii in experimental animals. J Ethnopharmacol 112:305–311
Langhansová L, Konrádová H, Vaněk T (2004) Polyethylene glycol and abscisic acid improve maturation and regeneration of Panax ginseng somatic embryos. Plant Cell Rep 22:725–730
Martin KP, Madassery J (2005) Direct and indirect somatic embryogenesis on cotyledon explants of Quassia amara L., an antileukaemic drug plant. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 41:54–57
Mauri PV, Manzanera JA (2004) Effect of abscisic acid and stratification on somatic embryo maturation and germination of holm oak (Quercus ilex L.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 40:495–498
McCown B, Amos R (1979) Initial trials with commercial micropropagation of birch selections. Comb Proc Int Plant Prop Soc 29:387–393
Mechanda SM, Baum BR, Johnson DA, Arnason JT (2003) Direct shoot regeneration from leaf segments of mature plants of Echinacea purpurea (L.) moench. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 39:505–509
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Murthy BNS, Murch SJ, Saxena PK (1998) Thidiazuron: a potent regulator of in vitro plant morphogenesis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 34:268–276
Nanda RM, Rout GR (2003) In vitro somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Acacia arabica. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 73:131–135
Ningappa MB, Dinesha R, Srinivas L (2008) Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of polyphenol-enriched curry leaf (Murraya koenigii L.) extracts. Food Chem 106:720–728
Nirmal Babu K, Anu A, Remashree AB, Praveen K (2000) Micropropagation of curry leaf tree. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 61:199–203
Nutan MTH, Hasnat A, Rashid MA (1998) Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities of Murraya koenigii. Fitoterapia 69:173–175
Okamura M, Taniguchi T, Kondo T (2001) Efficient embryogenic callus induction and plant regeneration from embryonic axis explants in Quercus acutissima. J For Res 6:63–66
Prakash MG, Gurumurthi K (2010) Effects of type of explant and age, plant growth regulators and medium strength on somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 100:13–20
Rahman MM, Gray AI (2005) A benzoisofuranone derivative and carbazole alkaloids from Murraya koenigii and their antimicrobial activity. Phytochemistry 66:1601–1606
Rao LJM, Ramalakshmi K, Borse BB, Raghavan B (2007) Antioxidant and radical-scavenging carbazole alkaloids from the oleoresin of curry leaf (Murraya koenigii Spreng.). Food Chem 100:742–747
Roy MK, Thalang VN, Trakoontivakorn G, Nakahara K (2004) Mechanism of mahanine-induced apoptosis in human leukemia cells (HL-60). Biochem Pharmacol 67:41–51
Sakai WS (1973) Simple method for differential staining of paraffin embedded plant material using toluidine blue O. Stain Technol 48:247–249
Shaw G (1994) Chemistry of adenine cytokinins. In: Mok DWS, Mok MC (eds) Cytokinins: chemistry, activity, and function. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 15–34
Shee C, Islam A, Ahmad F, Sharma AK (2007) Structure–function studies of Murraya koenigii trypsin inhibitor revealed a stable core beta sheet structure surrounded by α-helices with a possible role for α-helix in inhibitory function. Int J Biol Macromol 41(4):410–414
Shudo K (1994) Chemistry of diphenylurea cytokinins. In: Mok DWS, Mok MC (eds) Cytokinins: chemistry, activity, and function. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 35–42
Tachibana Y, Kikuzaki H, Lajis NH, Nakatani N (2003) Antioxidative activity of carbazoles from Murraya koenigii leaves. J Agric Food Chem 49:5589–5594
Vila SK, Rey HY, Mroginski LA (2007) Factors affecting somatic embryogenesis induction and conversion in “paradise tree” (Melia azedarach L.). J Plant Growth Regul 26:268–277
Woo SH, Nair A, Adachi T, Campbell CG (2000) Plant regeneration from cotyledon tissues of common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 36:358–361
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. S. Banerjee, Editor, Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, for suggesting the necessary modifications to the manuscript. We thank Dr. P. S. Basu and Mr. K. Mukherjee for their valuable suggestions during the manuscript revision. Personal research grants (PRGs) provided by the University of Kalyani, Kalyani, West Bengal, India, are also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, S., Dam, A., Bhattacharyya, A. et al. An efficient regeneration system via direct and indirect somatic embryogenesis for the medicinal tree Murraya koenigii . Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 105, 271–283 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9864-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9864-8