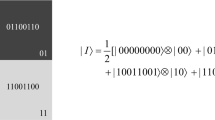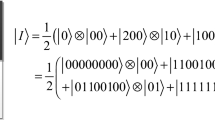Abstract
Based on the NEQR of quantum images, a new quantum gray-scale image watermarking scheme is proposed through Arnold scrambling and least significant bit (LSB) steganography. The sizes of the carrier image and the watermark image are assumed to be \(2n\times 2n\) and \(n\times n\), respectively. Firstly, a classical \(n\times n\) sized watermark image with 8-bit gray scale is expanded to a \(2n\times 2n\) sized image with 2-bit gray scale. Secondly, through the module of PA-MOD N, the expanded watermark image is scrambled to a meaningless image by the Arnold transform. Then, the expanded scrambled image is embedded into the carrier image by the steganography method of LSB. Finally, the time complexity analysis is given. The simulation experiment results show that our quantum circuit has lower time complexity, and the proposed watermarking scheme is superior to others.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feynman, R.: Simulating physics with computers. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 21(6–7), 467–488 (1982)
Deutsch, D.: Quantum theory, the church-turing principle and the universal quantum computer. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 400, 97–117 (1985)
Shor, P.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, 124–134 (1994)
Grover, L.A.: fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceedings of the 28th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, 212–219 (1996)
Venegas-Andraca, S., Bose, S.: Storing, processing, and retrieving an image using quantum mechanics.In: Proceedings of SPIE Conference of Quantum Information and Computation, 5105, 134–147 (2003)
Latorre, J.: Image Compression and Entanglement. arXiv:quant-ph/0510031 (2005)
Le, P., Dong, F., Hirota, K.: A flexible representation of quantum images for polynomial preparation, image compression, and processing operations. Quant. Inf. Process. 10(1), 63–84 (2011)
Zhang, Y., Lu, K., Gao, Y., et al.: NEQR: a novel enhanced quantum representation of digital images. Quant. Inf. Process. 12(8), 2833–2860 (2013)
Zhang, Y., Lu, K., Gao, Y., Xu, K.: A novel quantum representation for log-polar images. Quant. Inf. Process. 12(9), 3103–3126 (2013)
Li, H., Zhu, Q., Lan, S., Shen, C., Zhou, R., Mo, J.: Image storage, retrieval, compression and segmentation in a quantum system. Quant. Inf. Process. 12(6), 2269–2290 (2013)
Li, H., Zhu, Q., Zhou, R., Song, L., Yang, X.: Multi-dimensional color image storage and retrieval for a normal arbitrary quantum superposition state. Quant. Inf. Process. 13(4), 991–1011 (2014)
Yuan, S., Mao, X., Xue, Y., Chen, L., Xiong, Q., Compare, A.: SQR: a simple quantum representation of infrared images. Quant. Inf. Process. 13(6), 1353–1379 (2014)
Sang, J., Wang, S., Li, Q.: A novel quantum representation of color digital images. Quant. Inf. Process 16(2), 42 (2017)
Iliyasu, A.: Towards realising secure and efficient image and video processing applications on quantum computers. Entropy 15, 2874–2974 (2013)
Yan, F., Iliyasu, A.M., Venegas-Andraca, S.E.: A survey of quantum image representations. Quant. Inf. Process 15, 1–35 (2016)
Yan, F.: Quantum Computation Based Image Data Searching, Image Watermarking, and representation of Emotion Space. Ph.D. Thesis, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan (2014)
Yan, F., Iliyasu, A., Jiang, Z.: Quantum computation-based image representation, processing operations and their applications. Entropy 16(10), 5290–5338 (2014)
Le, P.Q., Iliyasu, A.M., Dong, F., et al.: Strategies for designing geometric transformations on quantum images. Theor. Comput. Sci. 412(15), 1406–1418 (2011)
Fan, P., Zhou, R.G., Jing, N., et al.: Geometric transformations of multidimensional color images based on NASS. Inf. Sci. S 340–341, 191–208 (2016)
Le, P.Q., Iliyasu, A.M., Dong, F., et al.: Fast geometric transformations on quantum images. Iaeng Int. J. Appl. Math. 40(3), 113–123 (2010)
Le, P.Q., Iliyasu, A.M., Dong, F., et al.: Efficient color transformations on quantum images. J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inf. 15(6), 698–706 (2011)
Fan, P., Zhou, Rigui: Quantum gray-scale image translation transform. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 11(23), 8763–8770 (2015)
Wang, J., Jiang, N., Wang, L.: Quantum image translation. Quant. Inf. Process. 14(5), 1589–1604 (2015)
Zhou, R.G., Tan, C., Hou, I.: Global and local translation designs of quantum image based on FRQI. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(4), 1382–1398 (2017)
Sang, J., Wang, S., Niu, X.: Quantum realization of the nearest-neighbor interpolation method for FRQI and NEQR. Quant. Inf. Process. 15(1), 37–64 (2016)
Jiang, N., Wang, L.: Quantum image scaling using nearest neighbor interpolation. Quant. Inf. Process. 14(5), 1559–1571 (2015)
Jiang, N., Wang, J., Mu, Y.: Quantum image scaling up based on nearest-neighbor interpolation with integer scaling ratio. Quant. Inf. Process. 14(11), 4001–4026 (2015)
Jiang, N., Wu, W.Y., Wang, L.: The quantum realization of Arnold and Fibonacci image scrambling. Quant. Inf. Process. 13(5), 1223–1236 (2014)
Jiang, N., Wang, L.: Analysis and improvement of the quantum Arnold image scrambling. Quant. Inf. Process. 13(7), 1545–1551 (2014)
Jiang, N., Wang, L., Wu, W.Y.: Quantum Hilbert image scrambling. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53(7), 2463–2484 (2014)
Zhou, RiGui, Sun, YaJuan, Fan, Ping: Quantum image Gray-code and bit-plane scrambling. Quant. Inf. Process. 14, 1717–1734 (2015)
Sang, J., Wang, S., Shi, X., Li, Qiong: Quantum realization of Arnold scrambling for IFRQI. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(8), 3706–3721 (2016)
Caraiman, S., Manta, V.I.: Image segmentation on a quantum computer. Quant. Inf. Process. 14(5), 1693–1715 (2015)
Zhang, Y., Lu, K., Xu, K., et al.: Local feature point extraction for quantum images. Quant. Inf. Process. 14(5), 1573–1588 (2015)
Zhang, Y., Lu, K., Gao, Y.H.: QSobel: a novel quantum image edge extraction algorithm. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 58(1), 1–13 (2015)
Jiang, N., Dang, Y., Wang, J.: Quantum image matching. Quant. Inf. Process. 15(9), 3543–3572 (2016)
Zhang, W.W., Gao, F., Liu, B., Wen, Q.Y., Chen, H.: A watermark strategy for quantum images based on quantum Fourier transform. Quant. Inf. Process. 12(2), 793–803 (2013)
Song, X.H., Wang, S., Liu, S., et al.: A dynamic watermarking scheme for quantum images using quantum wavelet transform. Quant. Inf. Process. 12(12), 3689–3706 (2013)
Song, X., Wang, S., El-Latif, A.A.A., Niu, X.: Dynamic watermarking scheme for quantum images based on Hadamard transform. Multimed. Syst. 20(4), 379–388 (2014)
Miyake, S., Nakamael, K.: A quantum watermarking scheme using simple and small-scale quantum circuits. Quant. Inf. Process. 15, 1849–1864 (2016)
Heidari, S., Naseri, M.: A novel LSB based quantum watermarking. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(10), 1–14 (2016)
Tirkel, A.Z., Rankin, G.A., VanSchyndel, R.M et al.: Electronic watermark. In: Proceedings of Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications, Macquarie University. 666–672 (1993)
Arnold, V.I., Avez, A.: Ergodic Problems of Classical Mechanics. Benjamin, New York (1968)
Dyson, F.J., Falk, H.: Period of a discrete cat mapping. Am. Math. Mon. 99(7), 603–614 (1992)
Islam, M.S., Rahman, M.M., Begum, Z., et al.: Low cost quantum realization of reversible multiplier circuit. Inf. Technol. J. 8(2), 208–213 (2009)
Thapliyal, H., Ranganathan, N.A .: New design of the reversible subtractor circuit. In: 11th IEEE Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), 2011. IEEE. pp. 1430–1435 (2011)
Kotiyal, S., Thapliyal, H., Ranganathan, N.: Circuit for reversible quantum multiplier based on binary tree optimizing ancilla and garbage bits. In: 2014 27th International Conference on VLSI Design and 2014 13th International Conference on Embedded Systems. IEEE. 545–550 (2014)
Weinfurter, H., Smolin, J.A.: Elementary gates for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 52, 3457 (1995)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61463016, Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University under Grant No. NCET-13-0795, Training program of Academic and technical leaders of Jiangxi Province under Grant No. 20153BCB22002, and the advantages of scientific and technological innovation team of Nanchang City under Grant No. 2015CXTD003. Project of Science and Technology of Jiangxi province Grant No. 20161BAB202065. Project of International Cooperation and Exchanges of Jiangxi Province under Grant No. 20161BBH80034. Project of Humanities and Social Sciences in colleges and universities of Jiangxi Province under Grant No. JC161023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, RG., Hu, W. & Fan, P. Quantum watermarking scheme through Arnold scrambling and LSB steganography. Quantum Inf Process 16, 212 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1640-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-017-1640-9