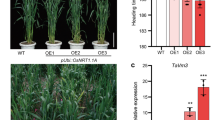
Abstract
In this study, the additive effects of a late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) gene and a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) gene on salt and osmotic stress in Tamarix plants were analyzed. The constructs containing one or both of the LEA and bZIP genes were transformed into tobacco. Northern blot analysis showed the genes were overexpressed under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter in both dual and single gene-transgenic tobacco lines. The effects of salt and osmotic stress in transgenic tobacco plant were investigated. Following exposure to NaCl, mannitol, and PEG6000 stress, dual gene-transgenic lines showed higher seed generation and growth rates than single gene-transgenic lines and the wild-type. In response to NaCl stress, the dual gene-transgenic lines showed lower malondialdehyde and higher leaf chlorophyll content than single gene-transgenic lines and the wild-type. These results suggested that the co-expression of LEA and bZIP resulted in an additive enhancement of stress tolerance in dual gene-transgenic tobacco.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MM, Sharmin S, Nabi Z, Mondal SI, Islam MS, Nayeem SB, Shoyaib M, Khan H (2010) A putative leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase of jute involved in stress response. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28:394–402. doi:10.1007/s11105-009-0166-4
Basyuni M, Kinjo Y, Baba S, Shinzato N, Iwasaki H, Siregar EBM, Oku H (2011) Isolation of salt stress tolerance genes from roots of mangrove plant, Rhizophora stylosa Griff., using PCR-based suppression subtractive hybridization. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:533–543. doi:10.1007/s11105-010-0257-2
Ben Saad R, Zouari N, Ben Ramdhan W, Azaza J, Meynard D, Guiderdoni E, Hassairi A (2010) Improved drought and salt stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco overexpressing a novel A20/AN1 zinc-finger "AlSAP" gene isolated from the halophyte grass Aeluropus littoralis. Plant Mol Biol 72:171–190. doi:10.1007/s11103-009-9560-4
Bohnert HJ, Golldack D, Ishitani M, Kamasani UR, Rammesmayer G, Shen B, Sheleva E, Jensen RG (1996) Salt tolerance engineering requires multiple gene transfer. In: Collins GB, Shepherd RJ (eds) Engineering plants for commercial products and application. Ann NY Acad Sci 792:115–125
Borsani O, Valpuesta V, Botella MA (2001) Evidence for a role of salicylic acid in the oxidative damage generated by NaCl and osmotic stress in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Physiol 126:1024–1030. doi:10.1104/pp. 126.3.1024
Brini F, Hanin M, Lumbreras V, Amara I, Khoudi H, Hassairi A, Pagès M, Masmoudi K (2007) Overexpression of wheat dehydrin DHN-5 enhances tolerance to salt and osmotic stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep 26:2017–2026. doi:10.1007/s00299-007-0412-x
Chen H, Nelson RS, Sherwood JL (1994) Enhanced recovery of transformants of Agrobacterium tumifaciens after freeze–thaw transformation and drug selection. Biotechniques 16:664–668
Davenport SB, Gallego SM, Benavides MP, Tomaro ML (2003) Behaviour of antioxidant defense system in the adaptive response to salt stress in Helianthus annuus L. cells. Plant Growth Regul 40:81–88. doi:10.1023/A:1023060211546
de Nazaré Monteiro Costa C, Brígida ABS, do Nascimento Borges B, de Menezes Neto MA, Carvalho LJCB, de Souza CRB (2011) Levels of MeLEA3, a cDNA sequence coding for an atypical late embryogenesis abundant protein in cassava, increase under in vitro salt stress treatment. Plant Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11105-011-0292-7
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Fujita Y, Fujita M, Satoh R, Maruyama K, Parvez MM, Seki M, Hiratsu K, Ohme-Takagi M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2005) AREB1 is a transcription activator of novel ABRE-dependent ABA signaling that enhances drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17(12):3470–3488. doi:10.1105/tpc.105.035659
Gao C, Wang Y, Liu G, Yang C, Jiang J, Li H (2008) Expression profiling of salinity-alkali stress responses by large-scale expressed sequence tag analysis in Tamarix hispida. Plant Mol Biol 66:245–258. doi:10.1007/s11103-007-9266-4
Gao C, Wang Y, Liu G, Wang C, Jiang J, Yang C (2010) Cloning of ten peroxidase (POD) genes from Tamarix hispida and characterization of their responses to abiotic stress. Plant Mol Biol Rep 28:77–89. doi:10.1007/s11105-009-0129-9
Goyal K, Walton LJ, Tunnacliffe A (2005) LEA proteins prevent protein aggregation due to water stress. Biochem J 388:151–157. doi:10.1042/BJ20041931
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffmann NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227:1229–1231. doi:10.1126/science.227.4691.1229
Kaufmann MR, Eckard AN (1971) Evaluation of water stress control with polyethylene glycols by analysis of guttation. Plant Physiol 47:453–456
Lee SC, Choi HW, Hwang IS, Choi DS, Hwang BK (2006) Functional roles of the pepper pathogen-induced bZIP transcription factor, CAbZIP1, in enhanced resistance to pathogen infection and environmental stresses. Planta 224:1209–1225. doi:10.1007/s00425-006-0302-4
Li W, Wang D, Jin T, Chang Q, Yin D, Xu S, Liu B, Liu L (2011) The vacuolar Na+/H + antiporter gene SsNHX1 from the halophyte Salsola soda confers salt tolerance in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:278–290. doi:10.1007/s11105-010-0224-y
Liang CY, Xi Y, Shu J, Li J, Yang JL, Che KP, Jin DM, Liu XL, Weng ML, He YK, Wang B (2004) Construction of a BAC library of Physcomitrella patens and isolation of a LEA gene. Plant Sci 167:491–498. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.04.015
Liao Y, Zou HF, Wei W, Hao YJ, Tian AG, Huang J, Liu YF, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2008) Soybean GmbZIP44, GmbZIP62 and GmbZIP78 genes function as negative regulator of ABA signaling and confer salt and freezing tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 228:225–240. doi:10.1007/s00425-008-0731-3
Mukherjee K, Choudhury AR, Gupta B, Gupta S, Sengupta DN (2006) An ABRE-binding factor, OSBZ8, is highly expressed in salt tolerant cultivars than in salt sensitive cultivars of indica rice. BMC Plant Biol 6:1–14. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-6-18
Prabu G, Kawar PG, Pagariya MC, Prasad DT (2011) Identification of water deficit stress upregulated genes in sugarcane. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:291–304. doi:10.1007/s11105-010-0230-0
Shao HB, Liang ZS, Shao MA (2005) LEA proteins in higher plants: structure, function, gene expression and regulation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 45:131–135. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2005.07.017
Singh S, Cornilescu CC, Tyler RC, Cornilescu G, Tonelli M, Lee MS, Markley JL (2005) Solution structure of a late embryogenesis abundant protein (LEA14) from Arabidopsis thaliana, a cellular stress-related protein. Protein Sci 14:2601–2609. doi:10.1110/ps.051579205
Stolf-Moreira R, Lemos EGM, Carareto-Alves L et al (2011) Transcriptional profiles of roots of different soybean genotypes subjected to drought stress. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:19–34. doi:10.1007/s11105-010-0203-3
Sunkar R, Bartels D, Kirch HH (2003) Overexpression of a stress-inducible aldehyde dehydrogenase gene from Arabidopsis thaliana in transgenic plants improves stress tolerance. Plant J 35:452–464. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01819.x
Wang Y, Jiang J, Zhao X, Liu G, Yang C, Zhan L (2006) A novel LEA gene from Tamarix androssowii confers drought tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Sci 171:655–662. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2006.06.011
Wang Y, Gao C, Liang Y, Wang C, Yang C, Liu G (2010) A novel bZIP gene from Tamarix hispida mediates physiological responses to salt stress in tobacco plants. J Plant Physiol 167:222–230. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2009.09.008
Xu S, Wang X, Chen J (2007) Zinc finger protein 1 (ThZF1) from salt cress (Thellungiella halophila) is a Cys-2/His-2-type transcription factor involved in drought and salt stress. Plant Cell Rep 26:497–506. doi:10.1007/s00299-006-0248-9
Xu C, Zheng L, Gao C, Wang C, Liu G, Jiang J, Wang Y (2011) Overexpression of a vacuolar H+−ATPase c subunit gene mediates physiological changes leading to enhanced salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:424–430. doi:10.1007/s11105-010-0247-4
Yang O, Popova OV, Süthoff U, Lüking I, Dietz KJ, Golldack D (2009) The Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factor AtbZIP24 regulates complex transcriptional networks involved in abiotic stress resistance. Gene 436:45–55. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2009.02.010
Zhang X, Wollenweber B, Jiang D, Liu F, Zhao J (2008) Water deficits and heat shock effects on photosynthesis of a transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana constitutively expressing ABP9, a bZIP transcription factor. J Exp Bot 59:839–848. doi:10.1093/jxb/erm364
Zhou S, Chen X, Zhang X, Li Y (2008) Improved salt tolerance in tobacco plants by co-transformation of a betaine synthesis gene BADH and a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene SeNHX1. Biotechnol Lett 30:369–376. doi:10.1007/s10529-007-9548-6
Zhou GA, Chang RZ, Qiu LJ (2010) Overexpression of soybean ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene GmUBC2 confers enhanced drought and salt tolerance through modulating abiotic stress-responsive gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 72:357–367. doi:10.1007/s11103-009-9575-x
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Genetically Modified Organisms Breeding Major Project (2009ZX08009-098B), the National Natural Science Foundation (31070595) of China, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (DL10EA01-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, GZ., Zang, L., Xilin, H. et al. Co-transfer of LEA and bZip Genes from Tamarix Confers Additive Salt and Osmotic Stress Tolerance in Transgenic Tobacco. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30, 512–518 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-011-0371-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-011-0371-9