Abstract
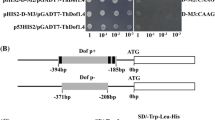
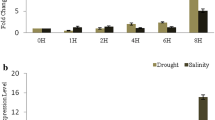
Zinc finger proteins (ZFPs) play important roles in growth and development in both animals and plants. Recently, some Arabidopsis genes encoding distinct ZFPs have been identified. However, the physiological role of their homologues with putative zinc finger motif remains unclear. In the present study, a novel gene, ThZF1, was characterized from salt stressed cress (Thellungiella halophila, Shan Dong), encoding a functional transcription factor. ThZF1 contains two conserved C2H2 regions and shares conserved domains, including DNA-binding motif, with Arabidopsis thaliana ZFP family members. The transcript of the ThZF1 gene was induced by salinity and drought. Transient expression analysis of ThZF1–GFP fusion protein revealed that ThZF1 was localized preferentially in nucleus. A gel-shift assay showed that ThZF1 specially bind to the wild-type (WT) EP2 element, a cis-element present in the promoter regions of several target genes regulated by ZFPs. Furthermore, a functional analysis demonstrated that ThZF1 was able to activate HIS marker gene in yeast. Finally, ectopic expression of ThZF1 in Arabidopsis mutant azf2 suggested that ThZF1 may have similar roles as Arabidopsis AZF2 in plant development as well as regulation of downstream gene.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- cDNA:
-
complementary DNA
- EST:
-
expressed sequence tags
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RACE:
-
rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends
- ZFPs:
-
zinc finger proteins
References
Bressan RA, Zhang CQ (2001) Learning from the Arabidopsis experience. The next gene search paradigm. Plant Physiol 127:1354–1360
Chen W, Provart NJ, Glazebrook J, Katagiri F, Chang HS, Eulgem T, Mauch F, Luan S, Zou G, Whitham SA (2002) Expression profile matrix of Arabidopsis transcription factor genes suggests their putative functions in response to environmental stresses. Plant Cell 14:559–574
Choo Y, Klug A (1997) Physical basis of a protein–DNA recognition code. Curr Opin Struc Biol 7:117–125
Davis SJ, Vierstra RD (1998) Soluble, highly fluorescent variants of green fluorescent protein (GFP) for use in higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 36:521–528
Herman KM (1995) The shikimate pathway, early steps in the biosynthesis of aromatic compounds. Plant Cell 7:907–919
Inan G, Zhang Q, Li PH, Wang ZL (2004) Salt Cress, a halophyte and cryophyte Arabidopsis relative model system and its applicability to molecular genetic analyses of growth and development of extremophiles. Plant Physiol 135:1718–1735
Kobayashi A, Sakamoto A, Kubo K, Rybka Z, Kanno Y, Takatsuji H (1998) Seven zinc-finger transcription factors are expressed sequentially during the development of anthers in petunia. Plant J 13:571–576
Kozak M (1996) Interpreting cDNA sequences, some insights from studies on translation. Mammalian Genome 7:563–574
Kubo K, Sakamoto A, Kobayashi A, Rybka Z, Kanno Y, Nakagawa H, Nishino T, Takatsuji H (1998) Cys2/His2 zinc-finger protein family of petunia, evolution and general mechanism of target-sequence recognition. Nucleic Acids Res 26:608–615
Lippuner V, Cyert MS, Gasser CS (1996) Two classes of plant cDNA clones differentially complement yeast calcineurin mutants and increase salt tolerance of wild-type yeast. J Biol Chem 271:12859–12866
Liu L, White MJ, MacRae TH (1999) Transcription factors and their genes in higher plants, functional domains, evolution and regulation. Eur J Biochem 262:247–257
Liu Q, Kasuga M, Sakuma Y, Abe H, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1998) Two transcription factors, DREB1and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:1391–1406
Montiel G, Gantet P, Jay-Allemand C, Breton C (2004) Transcription factor networks. Pathways to the knowledge of root development. Plant Physiol 136:3478–3485
Pabo CO, Peisach E, Grant RA (2001) Design and selection of novel Cys2His2 zinc finger proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 70:313–340
Randy DD, Christina P, Glenn BC (2003) Expression and deletion analysis of an Arabidopsis SUPERMAN-like zinc finger gene. Plant Sci 165:33–41
Riechmann JL, Heard J, Martin G, Reuber L, Jiang C, Keddie J, Adam L, Pineda O, Ratcliffe OJ, Samaha RR (2000) Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 290:2105–2110
Sakai H, Medrano LJ, Meyerowitz EM (1995) Role of SUPERMAN in maintaining Arabidopsis floral whorl boundaries. Nature 378:199–203
Sakamoto A, Omirulleh S, Nakayama T, Iwabuchi M (1996) A zinc-finger-type transcription factor WZF1 that binds to a novel cis-acting element of histone gene promoters represses its own promoter. Plant Cell Physiol 37:557–562
Sakamoto H, Araki T, Meshi T, Iwabuchi M (2000) Expression of a subset of the Arabidopsis Cys2/His2-type zinc-finger protein gene family under water stress. Gene 248:23–32
Sakamoto H, Maruyama K, Sakuma Y (2004) Arabidopsis Cys2/His2-type zinc-finger proteins function as transcription repressors under drought, cold, and high-salinity stress conditions. Plant Physiol 136:2734–46
Seki M, Narusaka M, Ishida J, Nanjo T, Fujita M, Oono Y, Kamiya A, Nakajima M, Enju A, Sakurai T, Satou M, Akiyama K, Taji T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Carninci P, Kawai J, Hayashizaki Y, Shinozaki K (2002) Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold, and high-salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant J 31:279–292
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozakiy K, Seki M (2003) Regulatory network of gene expression in the drought and cold stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:410–417
Stockinger EJ, Gilmour SJ, Thomashow MF (1997) Arabidopsis thaliana CBF1 encodes an AP2 domain-containing transcriptional activator that binds to the C-repeat/ DRE, a cis-acting DNA regulatory element that stimulates transcription in response to low temperature and water deficit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1035–1040
Sugano S, Kaminaka H, Rybka Z, Catala R, Salinas J, Matsui K, Ohme-Takagi M, Takatsuji H (2003) Stress-responsive zinc finger gene ZPT2–3 plays a role in drought tolerance in petunia. Plant J 36:830–841
Tague BW, Gallant P, Goodman HM (1997) Expression analysis of an Arabidopsis C2H2 zinc finger protein gene. Plant Mol Biol 32:785–796
Takatsuji H, Mori M, Benfey PN, Ren L, Cua NH (1992) Characterization of a zinc finger DNA-binding protein expressed specifically in Petunia petals and seedlings. EMBO J 11:241–249
Takatsuji H, Matsumoto T (1996) Target-sequence recognition by separate-type Cys2/His2 zinc finger proteins in plants. J Biol Chem 271:23368–23373
Takatsuji H (1998) Zinc-finger transcription factors in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 54:582–596
Takatsuji H (1999) Zinc-finger proteins, the classical zinc finger emerges in contemporary plant science. Plant Mol Biol 39:1073–1078
van Der Krol AR, van Poecke Remco MP, Vorst Oscar FJ, Voogt C, van Leeuwen W, Borst-Vrensen Tanja WM, Takatsuji H, van der Plas Linus HW (1999) Developmental and wound-, cold-, desiccation-, ultraviolet-b-stress-induced modulations in the expression of the petunia zinc finger transcription factor gene ZPT2–2. Plant Physiol 121:1153–1162
Volkov RA, Panchuk II, Schoffl F (2003) Heat-stress-dependency and developmental modulation of gene expression: the potential of house-keeping genes as internal standards in mRNA expression profiling using real-time RT-PCR. J Exp Bot 54:2343–2349
Wang GL, Fang HY (2002) Gene engineering in plant. 2nd edn. Press of Science, Beijing, pp 734–736
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6:66–71
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the grants of the State Key Basic Research and Development Plan of China (G1999011700 and 2003CB114300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30170088 and 30370120). We also thank Professor S. Y. Chen and Dr. Jian Huang (The Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China) for bounteous offering of the BD-Vector and yeast lines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W.-H. Wu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, S., Wang, X. & Chen, J. Zinc finger protein 1 (ThZF1) from salt cress (Thellungiella halophila) is a Cys-2/His-2-type transcription factor involved in drought and salt stress. Plant Cell Rep 26, 497–506 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-006-0248-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-006-0248-9