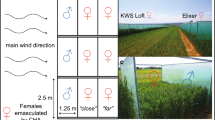
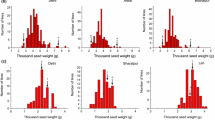
Abstract
Previously identified alleles at quantitative trait loci (QTL) for hybrid seed yield were re-evaluated in the same genetic background (in hybrid combination with the same tester) as the original QTL mapping study and also evaluated in a different genetic background (in hybrid combination with two different testers). The QTL were identified from wide crosses of exotic germplasm sources with spring-type Brassica napus L., in which alleles from the exotic germplasm sources increased hybrid seed yield. Results from the re-evaluation of six QTL, in the same genetic background and hybrid combination, indicate that several of the exotic donor QTL alleles did increase hybrid seed yield and could be successfully used for improving the original single-cross hybrid. However, results from the evaluation of seven QTL (including the same six previous QTL) in a new genetic background, in combination with two new testers, indicate that the exotic QTL alleles were often no different or produced significantly lower hybrid seed yield than the spring QTL alleles. In all studies, the QTL were also very sensitive to environmental interactions. Thus, our results indicate that although these exotic sources contain favorable QTL alleles when introgressed into one spring hybrid background, the effects are not predictive of other genetic backgrounds or hybrid combinations. Although QTL affecting hybrid seed yield have been identified, comparisons of multiple QTL alleles are needed to determine the most favorable allele at each locus. Characterization of QTL complementation across testers will be required to predict their effects in multiple hybrid combinations.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CMS:
-
Cytoplasmic male sterility
- DH:
-
Double haploid
- IBL:
-
Inbred backcross line
- LOD:
-
Logarithm of odds
- MAS:
-
Marker-assisted selection
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- RCBD:
-
Randomized complete block design
- RFLP:
-
Restriction fragment length polymorphism
- SI:
-
Self incompatibility
- STS:
-
Sequence-tagged sites
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeats
- SSCP:
-
Single-strand conformation polymorphism
References
Bartkowiak-Broda I, Rousselle P, Renard M (1979) Investigations of two kinds of cytoplasmic male-sterility in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Genetica Pol 20:487–497
Beavis WD (1994) The power and deceit of QTL experiments: lessons from comparative QTL studies. In: Wilkinson DB (ed) Proceedings of the 49th Annual Corn and Sorghum Industry Research Conference, Dec 7–8, Chicago (IL). American Seed Trade Association, Washington (DC), pp 250–266
Bouchez A, Hospital F, Causse M, Gallais A, Charcosset A (2002) Marker-assisted introgression of favorable alleles at quantitative trait loci between maize elite lines. Genetics 162:1945–1959
Brandle JE, McVetty PBE (1990) Geographical diversity, parental selection and heterosis in oilseed rape. Can J Plant Sci 70:935–940
Butruille DV (1998) Introgression of winter germplasm and use of molecular markers to document its effects on agronomic traits of spring inbreds and hybrids of Brassica napus (Ph.D. dissertation). Madison (WI): University of Wisconsin, Madison, 195 pp
Butruille DV, Guries RP, Osborn TC (1999a) Increasing yield of spring oilseed rape hybrids through introgression of winter germplasm. Crop Sci 39:1491–1496
Butruille DV, Guries RP, Osborn TC (1999b) Linkage analysis of molecular markers and quantitative trait loci in populations of inbred backcross lines of Brassica napus L. Genetics 153:949–964
Buzza GC (1995) Plant breeding. In: Kimber DS, McGregor DI (eds) Brassica oilseeds: production and utilization. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 153–175
Campbell BT, Baenziger PS, Eskridge KM, Budak H, Streck NA, Weiss A, Gill KS, Erayman M (2004) Using environmental covariates to explain genotype × environment and QTL × environment interactions for agronomic traits on chromosome 3A of wheat. Crop Sci 44:620–627
Concibido VC, La Vallee B, Mclaird P, Pineda N, Meyer J, Hummel L, Yang J, Wu K, Delannay X (2003) Introgression of a quantitative trait locus for yield from Glycine soja into commercial soybean cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 106:575–582
Crossa J, Vargas M, van Eeuwijk FA, Jiang C, Edmeades GO, Hoisington D (1999) Interpreting genotype × environment interaction in tropical maize using linked molecular markers and environmental covariables. Theor Appl Genet 99:611–625. doi:10.1007/s001220051276
Diers BW, Osborn TC (1994) Genetic diversity of oilseed Brassica napus germplasm based on restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Theor Appl Genet 88:662–668. doi:10.1007/BF01253968
Ferreira ME, Williams PH, Osborn TC (1994) RFLP mapping of Brassica napus using doubled haploid lines. Theor Appl Genet 89:615–621. doi:10.1007/BF00222456
Grant I, Beversdorf WD (1985) Heterosis and combining ability estimates in spring-planted oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Can J Genet Cytol 27:472–478
Hospital F, Charcosset A (1997) Marker-assisted introgression of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 147:1469–1485
Kandemir N, Jones BL, Wesenberg DM, Ullrich SE, Kleinhofs A (2000) Marker-assisted analysis of three grain yield QTL in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) using near isogenic lines. Mol Breed 6:157–167. doi:10.1023/A:1009602514106
Kidwell KK, Osborn TC (1992) Simple plant DNA isolation procedures. In: Beckman J, Osborn TC (eds) Plant genomes: methods for genetic and physical mapping. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 1–13
Lande R, Thompson R (1990) Efficiency of marker-assisted selection in the improvement of quantitative traits. Genetics 124:743–756
Lefort-Buson M, Guillot-Lemoine B, Dattee Y (1987) Heterosis and genetic distance in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): crosses between European and Asiatic selfed lines. Genome 29:413–418
Li Z, Pinson SRM, Park WD, Paterson AH, Stansel JW (1997) Epistasis for three grain yield components in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genetics 145:453–465
Lübberstedt T, Melchinger AE, Schön CC, Utz HF, Klein D (1997) QTL mapping in testcrosses of European flint lines of maize: I. Comparison of different testers for forage yield traits. Crop Sci 37:921–931
Lukens LN, Pires JC, Leon E, Vogelzang R, Oslach L, Osborn T (2006) Patterns of sequence loss and cytosine methylation within a population of newly resynthesized Brassica napus allopolyploids. Plant Physiol 140:336–348. doi:10.1104/pp.105.066308
Melchinger AE, Utz HF, Schon CC (1998) Quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping using different testers and independent population samples in maize reveals low power of QTL detection and large bias in estimates of QTL effects. Genetics 149:383–403
Michaels SD, Amasino RM (2001) High throughput isolation of DNA and RNA in 96-well format using a paint shaker. Plant Mol Biol Rep 19:227–233. doi:10.1007/BF02772894
Muangprom A, Thomas SG, Sun T, Osborn TC (2005) A novel dwarfing mutation in a green revolution gene from Brassica rapa. Plant Physiol 137:931–938. doi:10.1104/pp.104.057646
Paterson AH, Damon S, Hewitt JD, Zamir D, Rabinowitch HD, Lincoln SE, Lander ES, Tanksley SD (1991) Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits in tomato: comparison across species, generations, and environments. Genetics 127:181–197
Quijada PA (2003) Introgression of germplasm from winter into spring Brassica napus: detection and confirmation of quantitative trait loci (Ph.D. dissertation). Madison (WI): University of Wisconsin, Madison, 222 pp
Quijada PA, Maureira IJ, Osborn TC (2004a) Confirmation of QTL controlling seed yield in spring canola (Brassica napus L.) hybrids. Mol Breed 13:193–200. doi:10.1023/B:MOLB.0000018774.72965.2a
Quijada PA, Udall JA, Polewicz H, Vogelzang RD, Osborn TC (2004b) Phenotypic effects of introgressing French winter germplasm into hybrid spring canola. Crop Sci 44:1982–1989
Quijada PA, Udall JA, Lambert B, Osborn TC (2006) Quantitative trait analysis of seed yield and other complex traits in hybrid spring rapeseed (Brassica napus L): 1. Identification of genomic regions from winter germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 113:549–561. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0323-1
Reyna N, Sneller CH (2001) Evaluation of marker-assisted introgression of yield QTL alleles into adapted soybean. Crop Sci 41:1317–1321
Ribaut J-M, Ragot M (2007) Marker-assisted selection to improve drought adaptation in maize: the backcross approach, perspectives, limitations, and alternatives. J Exp Bot 58:351–360. doi:10.1093/jxb/erl214
SAS Institute Inc (2004) SAS OnlineDoc® 9.1.3. SAS Institute Inc, Cary
Sernyk JL, Stefansson BR (1983) Heterosis in summer rape (Brassica napus L.). Can J Plant Sci 63:407–413
Slafer GA (2003) Genetic basis of yield as viewed from a crop physiologist’s perspective. Ann Appl Biol 142:117–128. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7348.2003.tb00237.x
Stuber CW (1994) Successes in the use of molecular markers for yield enhancement in corn. In: Wilkinson DB (ed) Proceedings of the 49th Annual Corn and Sorghum Industry Research Conference, Dec 7–8, Chicago (IL). American Seed Trade Association, Washington (DC), pp 232–238
Stuber CW, Polacco M, Senior ML (1999) Synergy of empirical breeding, marker-assisted selection, and genomics to increase crop yield potential. Crop Sci 39:1571–1583
Thurling N (1993) Physiological constraints and their genetic manipulation. In: Labana KS, Banga SS, Banga SK (eds) Breeding oilseed brassicas. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 44–66
Udall JA (2003) A genetic study of oilseed Brassica napus: mapping chromosome rearrangements and quantitative trait loci (Ph.D. dissertation). Madison (WI): University of Wisconsin, Madison, 240 pp
Udall JA, Quijada PA, Polewicz H, Vogelzang R, Osborn TC (2004) Phenotypic effects of introgressing Chinese winter and resynthesized Brassica napus L. germplasm into hybrid spring canola. Crop Sci 44:1990–1996
Udall JA, Quijada PA, Lambert B, Osborn TC (2006) Quantitative trait analysis of seed yield and other complex traits in hybrid spring rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): 2. Identification of alleles from unadapted germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 113:597–609. doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0324-0
Utz HF, Melchinger AE, Schon CC (2000) Bias and sampling error of the estimated proportion of genotypic variance explained by quantitative trait loci determined from experimental data in maize using cross validation and validation with independent samples. Genetics 154:1839–1849
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78. doi:10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Yan W, Hunt LA (1998) Genotype by environment interaction and crop yield. Plant Breed Rev 16:135–178
Zhu H, Briceño G, Dovel R, Hayes PM, Liu BH, Liu CT, Ullrich SE (1999) Molecular breeding for grain yield in barley: an evaluation of QTL effects in a spring barley cross. Theor Appl Genet 98:772–779. doi:10.1007/s001220051134
Acknowledgments
We thank Robert Gaeta, Federico Iniguez-Luy, Ivan Maureira, Joy Muangprom, Chris Pires, Tim Pruski, Pablo Quijada, Dena Tellefsen, Josh Udall, Robert Vogelzang, and Jianwei Zhao for technical assistance and discussion. Funding to TCO was provided by the USDA North Central Canola Research Program. CCK was supported in part by the Gabelman-Shippo Distinguished Graduate Fellowship in Plant Breeding & Plant Genetics and the Pioneer Plant Breeding Graduate Fellowship, University of Wisconsin, Madison.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kramer, C.C., Polewicz, H. & Osborn, T.C. Evaluation of QTL alleles from exotic sources for hybrid seed yield in the original and different genetic backgrounds of spring-type Brassica napus L.. Mol Breeding 24, 419–431 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9303-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9303-x