Abstract
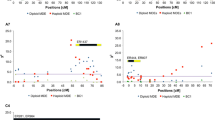
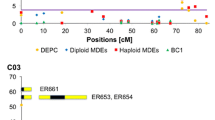
The combined use of doubled haploid lines and molecular markers can provide new genetic information for use in breeding programs. An F1-derived doubled haploid (DH) population of Brassica napus obtained from a cross between an annual canola cultivar (‘Stellar’) and a biennial rapeseed (‘Major’) was used to construct a linkage map of 132 restriction fragment length polymorphism loci. The marker loci were arranged into 22 linkage groups and six pairs of linked loci covering 1016 cM. The DH map was compared to a partial map constructed with a common set of markers for an F2 population derived from the same F1 plant, and the overall maps were not significantly different. Comparisons of maps in Brassica species suggest that less recombination occurs in B. napus (n = 19) than expected from the combined map distances of the two hypothesized diploid progenitors, B. oleracea (n = 9) and B. rapa (n=10). A high percentage (32%) of segregating marker loci were duplicated in the DH map, and conserved linkage arrangements of some duplicated loci indicated possible intergenome homoeology in the amphidiploid or intragenome duplications from the diploid progenitors. Deviation from Mendelian segregation ratios (P < 0.05) was observed for 30% of the marker loci in the DH population and for 24% in the F2 population. Deviation towards each parent occurred at equal frequencies in both populations and marker loci that showed deviation clustered in specific linkage groups. The DH lines and molecular marker map generated for this study can be used to map loci for agronomic traits segregating in this population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Bentolilas Hardy T, Gui Hon C, Freyssinet G (1992) Comparative genetic analysis of F2 plants and anther culture-derived plants of maize. Genome 35:575–582
Burke TJ, Callis J, Vierstra RD (1988) Characterization of a polyubiquitin gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 213:435–443
Burr B, Burr FA, Thompson KH, Albertson MC, Stuber CW (1987) Gene mapping with recombinant inbreds in maize. Genetics 118:519–526
Chen JL, Beversdorf WD (1990) A comparison of traditional and haploid-derived breeding populations of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) for fatty acid composition of the seed oil. Euphytica 51:59–65
Chyi Y-S, Hoenecke ME, Sernyk JL (1992) A genetic linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphism loci for Brassica rapa (syn. campestris). Genome 35:746–757
Coventry J, Kott L, Beversdorf WD (1988) Manual for microspore culture technique for Brassica napus. Department of Crop Science, University of Guelph Canada, Technical Bulletin AC Publ 0489
Downey RK, Rakow GFW (1987) Rapeseed and mustard. In: Fehr WR (ed) Principles of cultivar development, vol 2. Crop species. Macmillan Publ, London, pp 437–486
Edwards MD, Helentjaris T, Wright S, Stuber CW (1992) Molecular-marker-facilitated investigations of quantitative trait loci in maize 4. Theor Appl Genet 83:765–774
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction fragments to a high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Harper JF, Manney L, DeWitt ND, Yoo Mi H, Sussman MR (1990) The Arabidopsis thaliana plasma membrane H+-ATPase multigene family. J Biol Chem 265:13601–13608
Helentjaris T, Weber D, Wright S (1988) Identification of the genomic locations of duplicate nucleotide sequences in maize by analysis of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Genetics 118:353–363
Keller WA, Armstrong KC (1978) High frequency production of microspore-derived plants from Brassica napus anther cultures. Z Pflanzenzucht 80:100–108
Kianian SF, Quiros CF (1992) Generation of a Brassica oleracea composite RFLP map: linkage arrangements among various populations and evolutionary implications. Theor Appl Genet 84:544–554
Kidwell KK, Osborn TC (1992) Simple plant DNA isolation procedures. In: Beckmann J, Osborn TC (eds) Plant genomes: methods for genetic and physical mapping. Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, p 1–13
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly M, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) Mapmaker: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Landry B, Hubert N, Etoh T, Harada JJ, Lincoln SE (1991) A genetic map of Brassica napus based on restriction fragment length polymorphism detected with expressed DNA sequences. Genome 34:543–552
Landry B, Hubert N, Crete R, Chang MS, Lincoln SE, Etoh T (1992) A genetic map of Brassica oleracea based on RFLP markers detected with expressed DNA sequences and mapping of resistance genes to race 2 of Plasmodiophora Brassicae (Woronin). Genome 35:409–420
Lin C, Thomashow MF (1992) A cold-regulated Arabidopsis gene encodes a polypeptide having potent cryoprotective activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 183:1103–1108
Murray M, Thompson WF (1983) Rapid isolation of high-molecularweight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Olin-Fatih M, Heneen WK (1992) C-banded karyotypes of Brassica campestris, B. oleracea and B. napus. Genome 35:583–589
Orkin SH (1986) Reverse genetics and human disease. Cell 47:845–850
Paterson AH, Lander ES, Hewitt JD, Peterson S, Lincoln SE, Tanksley SD (1988) Resolution of quantitative traits into mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature 335:721–726
Powell W, Ellis RP, Macaulay M, McNicol J, Forster BP (1990) The effect of selection for protein and isozyme loci on quantitative traits in a doubled haploid population of barley. Heredity 65:115–122
Sahidi F (ed) (1990) Canola and rapeseed: production chemistry nutrition and processing technology. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Simon AE, Tenbarge KM, Scofield SR, Finkelstein RR, Crouch ML (1985) The nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone of Brassica napus 12S storage protein shows homology with legumin from Pisum sativum. Plant Mol Biol 5:191–201
Slocum MK, Figdore SS, Kennard WC, Suzuki JY, Osborn TC (1990) Linkage arrangement of restriction fragment length polymorphism loci in Brassica oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 80:57–64
Song KM, Osborn TC, Williams PH (1988) Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). I. Genome evolution of diploid and amphidiploid species. Theor Appl Genet 75:784–794
Song KM, Suzuki JY, Slocum MK, Williams PH, Osborn TC (1991) A linkage map of Brassica rapa (syn. campestris) based on restriction fragment length polymorphism loci. Theor Appl Genet 82:296–304
Thormann CE, Ferreira ME, Camargo LEA, Tvang JG, Osborn TC (1994) Comparison of genetic relationship estimates within and among cruciferous species based on RFLPs and RAPDs. Theor Appl Genet (in press)
Uknes S, Mauch-Mani B, Moyer M, Potter S, Williams S, Dincher S, Chandler D, Slusarenko A, Ward E, Ryals J (1992) Acquired resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 4:645–656
Verma SC, Rees H (1974) Nuclear DNA and the evolution of allotetraploid Brassicae. Heredity 33:61–68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. E. Hart
Present address Embrapa/Cenargen, C.P. 0.2372, CEP 70.770, Brasilia DF, Brazil
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, M.E., Williams, P.H. & Osborn, T.C. RFLP mapping of Brassica napus using doubled haploid lines. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 89, 615–621 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222456
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222456