Abstract
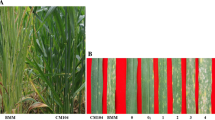
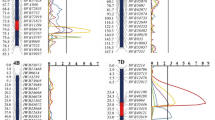
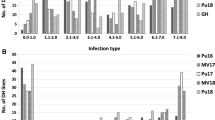
The increasing severity and prevalence of powdery mildew aided by extensive use of semi-dwarf cultivars and high levels of nitrogenous fertilizers are causing significant yield losses in wheat. Resistant cultivars are the most cost-effective and environmentally friendly approach to manage the disease. The objective of this study was to identify quantitative trait loci (QTL) for powdery mildew resistance in a doubled haploid (DH) population from a cross between leading Chinese cultivars, Yangmai 16 and Zhongmai 895. A high-density genetic map comprising of 14,480 non-redundant markers (equal to 148,179 SNPs) in 21 wheat chromosomes was constructed by genotyping the population with the Wheat 660 K SNP array. The DH population was phenotyped for powdery mildew resistance at the adult plant stage in multiple field trials, including four environments in the 2016–2017 cropping season and two environments in 2017–2018. Composite interval mapping detected six stable QTL explaining 3.8–23.6% of the phenotypic variance across environments. QPmyz.caas-5DS, QPmyz.caas-6BL and QPmyz.caas-7BS, are probably new QTL for powdery mildew resistance. One SNP marker closely linked to QPmyz.caas-6BL, the most stable QTL, was converted into a Kompetitive Allele-Specific PCR marker (K_AX-94973433) and validated on 103 commercial wheat cultivars. Significantly lower maximum disease severities of cultivars with the resistance-associated allele than those with the susceptibility-associated allele at QPmyz.caas-6BL in some environments indicated partial effectiveness of the marker. The novel QTL and their closely linked markers identified in the present study should facilitate development of cultivars with improved powdery mildew resistance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen AM, Winfield MO, Burridge AJ et al (2017) Characterization of a Wheat Breeders’ Array suitable for high-throughput SNP genotyping of global accessions of hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum). Plant Biotechnol J 15:390–401. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12635
Asad MA, Bai B, Lan CX et al (2012) Molecular mapping of quantitative trait loci for adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Italian wheat cultivar Libellula. Crop Pasture Sci 63:539–546. https://doi.org/10.1071/cp12174
Börner A, Schumann E, Fürste A et al (2002) Mapping of quantitative trait loci determining agronomic important characters in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 105:921–936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-0994-1
Bougot Y, Lemoine J, Pavoine MT et al (2006) A major QTL effect controlling resistance to powdery mildew in winter wheat at the adult plant stage. Plant Breed 125:550–556. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2006.01308.x
Bradbury P, Zhang Z, Kroon D et al (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Broman KW, Hao W, Saunak S et al (2003) R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19:889–890. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg112
Cavanagh CR, Shiaoman C, Shichen W et al (2013) Genome-wide comparative diversity uncovers multiple targets of selection for improvement in hexaploid wheat landraces and cultivars. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:8057–8062. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1217133110
Cui F, Zhang N, Fan XL et al (2017) Utilization of a Wheat 660 K SNP array-derived high-density genetic map for high-resolution mapping of a major QTL for kernel number. Sci Rep 7:3788. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04028-6
Doyle J, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure from small quantities of fresh leaf tissues. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Draeger R, Gosman N, Steed A et al (2007) Identification of QTLs for resistance to Fusarium head blight, DON accumulation and associated traits in the winter wheat variety Arina. Theor Appl Genet 115:617–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-007-0592-3
Figueroa M, Hammond-Kosack KE, Solomon PS (2018) A review of wheat diseases: a field perspective. Mol Plant Pathol 19:1523–1536. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12618
Friebe B, Heun M, Tuleen N et al (1994) Cytogenetically monitored transfer of powdery mildew resistance from rye into wheat. Crop Sci 34:621–625. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1994.0011183X003400030003x
Gao H, Zhu F, Jiang Y et al (2012) Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of a new powdery mildew resistant gene Pm46 in common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 125:967–973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1886-7
Hao Y, Parks R, Cowger C et al (2015) Molecular characterization of a new powdery mildew resistance gene Pm54 in soft red winter wheat. Theor Appl Genet 128:465–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2445-1
He R, Chang Z, Yang Z et al (2009) Inheritance and mapping of powdery mildew resistance gene Pm43 introgressed from Thinopyrum intermedium into wheat. Theor Appl Genet 118:1173–1180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-0971-z
He X, Singh PK, Dreisigacker S et al (2016) Dwarfing genes Rht-B1b and Rht-D1b are associated with both type I FHB susceptibility and low anther extrusion in two bread wheat populations. PLoS ONE 11:e0162499. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0162499
Huang XQ, Röder MS (2004) Molecular mapping of powdery mildew resistance genes in wheat: a review. Euphytica 137:203–223. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:euph.0000041576.74566.d7
Huang J, Zhao Z, Song F et al (2012) Molecular detection of a gene effective against powdery mildew in the wheat cultivar Liangxing 66. Mol Breed 30:1737–1745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-012-9757-0
International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium (IWGSC) (2018) Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science 361:eaar7191. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar7191
Järve K, Peusha H, Tsymbalova J et al (2000) Chromosomal location of a Triticum timopheevii-derived powdery mildew resistance gene transferred to common wheat. Genome 43:377–381
Jia A, Ren Y, Gao F et al (2018) Mapping and validation of a new QTL for adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Chinese elite bread wheat line Zhou8425B. Theor Appl Genet 131:1063–1071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3058-x
Keller M, Keller B, Schachermayr G et al (1999) Quantitative trait loci for resistance against powdery mildew in a segregating wheat × spelt population. Theor Appl Genet 98:903–912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051149
Lan C, Ni X, Yan J et al (2010) Quantitative trait loci mapping of adult-plant resistance to powdery mildew in Chinese wheat cultivar Lumai 21. Mol Breed 25:615–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9358-8
Li G, Fang T, Zhu J et al (2009) Molecular identification of a powdery mildew resistance gene from common wheat cultivar Brock. Acta Agron Sin 35:1613–1619. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1006.2009.01613
Lillemo M, Asalf B, Singh RP et al (2008) The adult plant rust resistance loci Lr34/Yr18 and Lr46/Yr29 are important determinants of partial resistance to powdery mildew in bread wheat line Saar. Theor Appl Genet 116:1155–1166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0743-1
Lillemo M, Bjørnstad Å, Skinnes H (2012) Molecular mapping of partial resistance to powdery mildew in winter wheat cultivar Folke. Euphytica 185:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0620-x
Lu Q, Bjornstad A, Ren Y et al (2012) Partial resistance to powdery mildew in German spring wheat ‘Naxos’ is based on multiple genes with stable effects in diverse environments. Theor Appl Genet 125:297–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1834-6
Lu Q, Lillemo M, Skinnes H et al (2013) Anther extrusion and plant height are associated with Type I resistance to Fusarium head blight in bread wheat line ‘Shanghai-3/Catbird’. Theor Appl Genet 126:317–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1981-9
Ma Q, Luo PG, Ren ZL et al (2007) Genetic analysis and chromosomal location of two new genes for resistance to powdery mildew in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Acta Agron Sin 33:1–8
Ma H, Kong Z, Fu B et al (2011) Identification and mapping of a new powdery mildew resistance gene on chromosome 6D of common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 123:1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1651-3
Ma P, Xu H, Luo Q et al (2014) Inheritance and genetic mapping of a gene for seedling resistance to powdery mildew in wheat line X3986-2. Euphytica 200:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1178-1
Ma P, Xu H, Xu Y et al (2015) Molecular mapping of a new powdery mildew resistance gene Pm2b in Chinese breeding line KM2939. Theor Appl Genet 128:613–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2457-5
Marone D, Russo MA, Laidò G et al (2013) Genetic basis of qualitative and quantitative resistance to powdery mildew in wheat: from consensus regions to candidate genes. BMC Genom 14:562. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-562
McIntosh RA, Yamazaki Y, Dubcovsky J et al (2013) Gene symbol: catalogue of gene symbols for wheat. In: Proceedings of 12th International wheat genetics symposium, vol 57, 8–13 Sept, Yokohama, Japan, pp 303–321
McIntosh RA, Dubcovsky J, Rogers WJ et al (2018) Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat: 2018 supplement. Annu Wheat Newsl 63:73–93
Meng L, Li H, Zhang L et al (2015) QTL IciMapping: integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J 3:269–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2015.01.001
Mesterházy A (1995) Types and components of resistance to Fusarium head blight of wheat. Plant Breed 114:377–386. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.1995.tb00816.x
Moore JW, Herrera-Foessel S, Lan C et al (2015) A recently evolved hexose transporter variant confers resistance to multiple pathogens in wheat. Nat Genet 47:1494–1498. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3439
Nyquist WE, Baker RJ (1991) Estimation of heritability and prediction of selection response in plant populations. Crit Rev Plant Sci 10:235–322. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689109382313
Qiu YC, Sun XL, Zhou RH et al (2006) Identification of microsatellite markers linked to powdery mildew resistance gene Pm2 in wheat. Cereal Res Commun 34:1267–1273. https://doi.org/10.1556/CRC.34.2006.4.268
Ramirez-Gonzalez RH, Segovia V, Bird N et al (2015a) RNA-Seq bulked segregant analysis enables the identification of high-resolution genetic markers for breeding in hexaploid wheat. Plant Biotechnol J 13:613–624. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12281
Ramirez-Gonzalez RH, Uauy C, Caccamo M (2015b) PolyMarker: a fast polyploid primer design pipeline. Bioinformatics 31:2038–2039. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv069
Rasheed A, Xia X (2019) From markers to genome-based breeding in wheat. Theor Appl Genet. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03286-4
Rasheed A, Wen W, Gao F et al (2016) Development and validation of KASP assays for genes underpinning key economic traits in bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 129:1843–1860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2743-x
Rimbert H, Darrier B, Navarro J et al (2018) High throughput SNP discovery and genotyping in hexaploid wheat. PLoS ONE 13:e0186329. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186329
Saville RJ, Gosman N, Burt CJ et al (2012) The ‘Green Revolution’ dwarfing genes play a role in disease resistance in Triticum aestivum and Hordeum vulgare. J Exp Bot 63:1271–1283. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err350
Semagn K, Babu R, Hearne S et al (2014) Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP): overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement. Mol Breed 33:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9917-x
Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, Rajaram S (2000) Achieving near-immunity to leaf and stripe rusts in wheat by combining slow rusting resistance genes. Acta Phytopathol Entomol Hung 35:133–139
Singh RP, Singh PK, Rutkoski J et al (2016) Disease impact on wheat yield potential and prospects of genetic control. Annu Rev Phytopathol 54:303–322. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-phyto-080615-095835
Srinivasachary GN, Steed A et al (2008) Susceptibility to Fusarium head blight is associated with the Rht-D1b semi-dwarfing allele in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 116:1145–1153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0742-2
Stam P (1993) Construction of integrated genetic linkage maps by means of a new computer package: JOINMAP. Plant J 3:739–744. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.1993.00739.x
Sun Y, Zou J, Sun H et al (2015) PmLX66 and PmW14: new alleles of Pm2 for resistance to powdery mildew in the Chinese winter wheat cultivars Liangxing 66 and Wennong 14. Plant Dis 99:1118–1124. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-10-14-1079-RE
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/93.1.77
Voss HH, Holzapfel J, Hartl L et al (2008) Effect of the Rht-D1 dwarfing locus on Fusarium head blight rating in three segregating populations of winter wheat. Plant Breed 127:333–339. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2008.01518.x
Wang JP (2017) Genetic dissection of key traits and functional marker development in common wheat. Ph.D, Shandong Agricultural University
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Wang S, Wong D, Forrest K et al (2014) Characterization of polyploid wheat genomic diversity using a high-density 90,000 single nucleotide polymorphism array. Plant Biotechnol J 12:787–796. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12183
Wang Y, Wang C, Quan W et al (2016) Identification and mapping of PmSE5785, a new recessive powdery mildew resistance locus, in synthetic hexaploid wheat. Euphytica 207:619–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1560-7
Windju SS, Malla K, Belova T et al (2017) Mapping and validation of powdery mildew resistance loci from spring wheat cv. Naxos with SNP markers. Mol Breed 37:61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0655-3
Winfield MO, Allen AM, Burridge AJ et al (2016) High-density SNP genotyping array for hexaploid wheat and its secondary and tertiary gene pool. Plant Biotechnol J 14:1195–1206. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12485
Wu Y, Bhat PR, Close TJ et al (2008) Efficient and accurate construction of genetic linkage maps from the minimum spanning tree of a graph. PLoS Genet 4:e1000212. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000212
Xiao M, Song F, Jiao J et al (2013) Identification of the gene Pm47 on chromosome 7BS conferring resistance to powdery mildew in the Chinese wheat landrace Hongyanglazi. Theor Appl Genet 126:1397–1403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2060-6
Xie W, Ben-David R, Zeng B et al (2012) Identification and characterization of a novel powdery mildew resistance gene PmG3M derived from wild emmer wheat, Triticum dicoccoides. Theor Appl Genet 124:911–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1756-8
Xu H, Yi Y, Ma P et al (2015) Molecular tagging of a new broad-spectrum powdery mildew resistance allele Pm2c in Chinese wheat landrace Niaomai. Theor Appl Genet 128:2077–2084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2568-z
Zadoks JC, Chang TT, Konzak CF (1974) A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res 14:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3180.1974.tb01084.x
Zhang R, Fan Y, Kong L et al (2018) Pm62, an adult-plant powdery mildew resistance gene introgressed from Dasypyrum villosum chromosome arm 2VL into wheat. Theor Appl Genet 131:2613–2620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3176-5
Zhang D, Zhu K, Dong L et al (2019) Wheat powdery mildew resistance gene Pm64 derived from wild emmer (Triticum turgidum var. dicoccoides) is tightly linked in repulsion with stripe rust resistance gene Yr5. Crop J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2019.03.003
Zhong S, Ma L, Fatima SA et al (2016) Collinearity analysis and high-density genetic mapping of the wheat powdery mildew resistance gene Pm40 in PI 672538. PLoS ONE 11:e0164815. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0164815
Zhou R, Zhu Z, Kong X et al (2005) Development of wheat near-isogenic lines for powdery mildew resistance. Theor Appl Genet 110:640–648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1889-0
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Prof. R. A. McIntosh, Plant Breeding Institute, University of Sydney, for critical review of this manuscript. This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFE0108600 and 2016YFD0101802) and CAAS Science and Technology Innovation Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaoting Xu performed the experimental work and data analysis, and wrote the paper. Zhanwang Zhu, Aolin Jia, Yelun Zhang, Chao Fu and Xianchun Xia participated in field trials. Fengju Wang constructed the DH population. Jinping Wang contributed to genotyping the DH lines. Zhanwang Zhu and Luping Fu helped with genetic map construction. Guihua Bai helped with the genetic map construction and KASP development. Yuanfeng Hao and Zhonghu He designed the experiment. Yuanfeng Hao, Zhonghu He and Xianchun Xia assisted in writing and revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animal performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Zhu, Z., Jia, A. et al. Mapping of QTL for partial resistance to powdery mildew in two Chinese common wheat cultivars. Euphytica 216, 3 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-019-2537-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-019-2537-8