Abstract
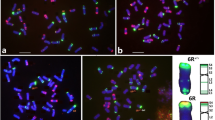
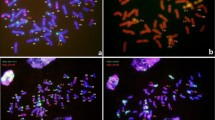
The wild species, Secale africanum Stapf., serves as a valuable germplasm resource for increasing the diversity of cultivated rye (Secale cereale L.) and providing novel genes for wheat improvement. The objective of this study was to identify new wheat-S. africanum chromosome 2Rafr derivatives by molecular markers and in situ hybridization, and to test the effects of centric translocations of S. africanum chromosome 2Rafr on disease resistance and agronomic performance of wheat. The T2RafrS.2DL and T2DS.2RafrL translocations, and other S. africanum chromosome introgressions such as a 2Rafr substitution as well as monotelo-2RafrS and 2RafrL addition lines, were identified by the genomic in situ hybridization and sequential fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Twenty-three molecular markers were localized on chromosome 2Rafr arms which will facilitate future identification of their introgressions into wheat. A comparison of FISH patterns and the molecular marker distribution between the S. africanum chromosome 2Rafr and cultivated rye chromosome 2R indicates differentiation between the wild and cultivated Secale genomes. Tests of disease resistance and agronomic performance of wheat-S. africanum chromosome 2Rafr derivatives indicated that chromosome 2RafrL carried gene(s) for dwarfing and stripe rust resistance, while the 2RafrS translocation line was the most favorable for agronomic performance when compared with the substitution and 2RafrL translocation lines. These results encourage the continued use of novel wheat-S. africanum 2Rafr derivative lines in wheat improvement.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso-Blanco C, Goicoechea PG, Roca A, Giraldez R (1993) Genetic linkage between cytological markers and the seed storage protein loci sec2 (Gli-R2) and sec3 (Glu-R1) in rye. Theor Appl Genet 87:321–327
An DG, Li LH, Li JM, Li HJ, Zhu YG (2006) Introgression of resistance to powdery mildew conferred by chromosome 2R by crossing wheat nullisomic 2D with rye. J Integr Plant Biol 48:838–847
Bariana HS, McIntosh RA (1993) Cytogenetic studies in wheat. XV. Location of rust resistance genes in VPM1 and their genetic linkage with other disease resistance genes in chromosome 2A. Genome 36:476–482
Bennett MD, Gustafson JP, Smith JB (1977) Variation in nuclear DNA in the genus Secale. Chromosoma 61:149–176
Borner A, Plaschke J, Korzun V, Worland AJ (1996) The relationships between the dwarfing genes of wheat and rye. Euphytica 89:69–75
Chen QJ, Yuan ZW, Zhang LQ, Yan ZH, Xiang ZG, Wan YF, Zheng YL, Liu DC (2008) Molecular characterisation and comparative analysis of four new genes from Sec2 locus encoding 75 K gamma secalins of rye species. J Cereal Sci 48:111–116
Cheng ZJ, Murata M (2002) Loss of chromosomes 2R and 5RS in octoploid triticale selected for agronomic traits. Genes Gen Syst 77:23–29
Conley EJ, Nduati V, Gonzalez-Hernandez JL, Mesfin A, Trudeau-Spanjers M, Chao S, Lazo GR, Hummel DD, Anderson OD, Qi LL, Gill BS, Echalier B, Linkiewicz AM, Dubcovsky J, Akhunov ED, Dvorák J, Peng JH, Lapitan NLV, Pathan MS, Nguyen HT, Ma XF, Miftahudin JPG, Greene RA, Sorrells ME, Hossain KG, Kalavacharla V, Kianian SF, Sidhu D, Dilbirligi M, Gill KS, Choi DW, Fenton RD, Close TJ, McGuire PE, Qualset CO, Anderson JA (2004) A 2600-locus chromosome bin map of wheat homoeologous group 2 reveals interstitial gene-rich islands and colinearity with rice. Genetics 168:625–637
Cuadrado A, Jouve N (2002) Evolutionary trends of different repetitive DNA sequences during speciation in the genus Secale. J Hered 93:339–345
Devos KM, Atkinson MD, Chinoy CN, Francis HA, Harcourt RL, Koebner RMD, Liu CJ, Masojc P, Xie DX, Gale MD (1993) Chromosomal rearrangements in the rye genome relative to that of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 85:673–680
Friebe B, Hatchett JH, Sears RG, Gill BS (1990) Transfer of Hessian fly resistance from ‘Chaupon’ rye to hexaploid wheat via a 2BS/2RL wheat-rye chromosome translocation. Theor Appl Genet 79:385–389
Friebe B, Hatchett JH, Gill BS, Mukai Y, Sebesta EE (1991) Transfer of Hessian fly resistance from rye to wheat via radiation-induced terminal and intercalary chromosomal translocations. Theor Appl Genet 83:33–40
Gale MD, Youssefian S (1985) Dwarfing genes in wheat. In: Russell GE (ed) Progress in plant breeding. Butterworth, London, pp 1–35
Hammer K, Khoshbakht K (2005) Towards a ‘red list’ for crop plant species. Genet Resour Crop Evol 52:249–265
Hatchett JH, Sears RG, Cox TS (1993) Inheritance of resistance to Hessian fly in rye and wheat-rye translocation lines. Crop Sci 33:730–734
Hysing SC, Hsam SLK, Singh RP, Huerta-Espino J, Boyd LA, Koebner RMD, Cambron S, Johnson JW, Bland DE, Liljeroth E, Merker A (2007) Agronomic performance and multiple disease resistance in T2BS.2RL wheat-rye translocation lines. Crop Sci 47:254–260
Ishikawa G, Nakamura T, Ashida T, Saito M, Nasuda S, Endo T, Wu J, Matsumoto T (2009) Localization of anchor loci representing five hundred annotated rice genes to wheat chromosomes using PLUG markers. Theor Appl Genet 118:499–514
Khush GS, Stebbins GL (1961) Cytogenetic and evolutionary studies in Secale, I. Some new data on the ancestry of S. cereale. Am J Bot 48:723–730
Lei MP, Li GR, Zhang SF, Liu C, Yang ZJ (2011) Molecular cytogenetic characterization of a new wheat-Secale africanum 2Ra(2D) substitution line for resistant to stripe rust. J Genet 90:283–287
Lei MP, Li GR, Liu C, Yang ZJ (2012) Characterization of new wheat-Secale africanum derivatives reveals evolutionary aspects of chromosome 1R in rye. Genome 55:765–774
Liu C, Li GR, Sehgal SK, Jia JQ, Yang ZJ, Friebe B, Gill BS (2010) Genomic relationships in the genus Dasypyrum: evidence from molecular phylogenetic analysis and in situ hybridization. Plant Syst Evol 288:149–156
Lukaszewski AJ, Gustafson JP (1983) Translocations and modifications of chromosomes in triticale × wheat hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 64:239–248
Lukaszewski AJ, Gustafson JP (1987) Cytogenetics of triticale. In: Janick J (ed) Plant breeding reviews, vol 5. AVI, NY, pp 41–93
Lukaszewski AJ, Rybka K, Korzun V, Malyshev SV, Lapinski B, Whitkus R (2004) Genetic and physical mapping of homoeologous recombination points involving wheat chromosome 2B and rye chromosome 2R. Genome 47:36–45
Merker A, Forsström P (2000) Isolation of mildew resistant wheat-rye translocation lines from a double substitution line. Euphytica 115:167–172
Miedaner T, Müller BU, Piepho HP, Falke KC (2011) Genetic architecture of plant height in winter rye introgression libraries. Plant Breed 130:209–216
Montero M, Sanz J, Jouve N (1986) Meiotic pairing and alpha-amylase phenotype in a 5B/5Rm Triticum aestivum-Secale montanum translocation line in common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 73:122–128
Nkongolo KK, Comeau A (1998) Development and characterization of a genetic stock tolerant to the barley yellow dwarf virus. Crop Sci 38:1413–1414
Quraishi UM, Abrouk M, Bolot S, Pont C, Throude M, Guilhot N, Confolent C, Bortolini F, Praud S, Murigneux A, Charmet G, Salse J (2009) Genomics in cereals: from genome-wide conserved orthologous set (COS) sequences to candidate genes for trait dissection. Funct Integr Genomics 9:473–484
Rabinovich SV (1998) Importance of wheat-rye translocations for breeding modern cultivars of Triticum aestivum L. Euphytica 100:323–340
Rayburn AL, Gill BS (1986) Isolation of a D-genome species repeated DNA sequence from Aegilpos squarrosa. Plant Mol Biol Rep 4:102–109
Sears RG, Hatchett JH, Cox TS, Gill BS (1992) Registration of Hamlet, a Hessian fly resistant hard red winter wheat germplasm. Crop Sci 32:506
Shewry PR, Parmar S, Miller TE (1985) Chromosomal location of the structural genes for the Mr 75,000 γ-secalins in Secale montanum Guss: evidence for a translocation involving chromosomes 2R and 6R in cultivated rye (Secale cereale L.). Heredity 54:381–383
Shewry PR, Miles MJ, Tatham AS (1994) The prolamin storage proteins of wheat and related cereals. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 61:37–59
Szakács E, Molnár-Láng M (2010) Molecular cytogenetic evaluation of chromosome instability in Triticum aestivum–Secale cereale disomic addition lines. J Appl Genet 51:149–152
Tang ZX, Ross K, Ren ZL, Yang ZJ, Zhang HY, Chikmawati T, Miftahudin, Gustafson JP (2011) Wealth of wild species: role in plant genome elucidation and improvement: Secale. In: Kole C (ed) Wild crop relatives: genomic and breeding resources cereals. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 367–395
Xue S, Zhang Z, Lin F, Kong Z, Cao Y, Li C, Yi H, Mei M, Zhu H, Wu J, Xu H, Zhao D, Tian D, Zhang C, Ma Z (2008) A high-density intervarietal map of the wheat genome enriched with markers derived from expressed sequence tags. Theor Appl Genet 117:181–189
Yang ZJ, Li GR, Ren ZL (2000) Identification of amphiploid between Triticum durum cv. Ailanmai native to Sichuan, China and Secale africanum. Wheat Inf Serv 91:20–24
Yang ZJ, Li GR, Ren ZL (2001) Identification of Triticum durum-Secale africanum amphiploid and its crossability with common wheat. J Genet Breed 55:45–50
Yang ZJ, Li GR, Jia JQ, Zeng X, Lei MP, Zeng ZX, Zhang T, Ren ZL (2009) Molecular cytogenetic characterization of wheat-Secale africanum amphiploids and derived introgression lines with stripe rust resistance. Euphytica 167:197–202
Zhou JP, Yang ZJ, Li GR, Liu C, Tang ZX, Zhang Y, Ren ZL (2010) Diversified chromosomal distribution of tandemly repeated sequences revealed evolutionary trends in Secale (Poaceae). Plant Syst Evol 287:49–56
Zhuang L, Sun L, Li A, Chen T, Qi Z (2011) Identification and development of diagnostic markers for a powdery mildew resistance gene on chromosome 2R of Chinese rye cultivar Jingzhouheimai. Mol Breed 27:455–465
Acknowledgments
We particularly thank Dr. I. Dundas at University of Adelaide, Australia for reviewing the manuscript. We are thankful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30871518, 31171542 and 31101143), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (ZYGX2010J099, ZYGX2011J101) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. P. Lei and G. R. Li contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, MP., Li, GR., Zhou, L. et al. Identification of wheat-Secale africanum chromosome 2Rafr introgression lines with novel disease resistance and agronomic characteristics. Euphytica 194, 197–205 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-0913-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-0913-3