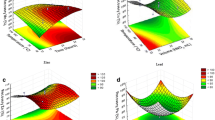
Abstract
The existence of hazardous heavy metals in aquatic settings causes health risks to humans, prompting researchers to devise effective methods for removing these pollutants from drinking water and wastewater. To obtain optimum removal efficiencies and sorption capacities of the contaminants on the sorbent materials, it is normally necessary to optimize the purification technology to attain the optimum value of the independent process variables. This review discusses the most current advancements in using various adsorbents for heavy metal remediation, as well as the modeling and optimization of the adsorption process independent factors by response surface methodology. The remarkable efficiency of the response surface methodology for the extraction of the various heavy metal ions from aqueous systems by various types of adsorbents is confirmed in this critical review. For the first time, this review also identifies several gaps in the optimization of adsorption process factors that need to be addressed. The comprehensive analysis and conclusions in this review should also be useful to industry players, engineers, environmentalists, scientists, and other motivated researchers interested in the use of the various adsorbents and optimization methods or tools in environmental pollution cleanup.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulrahman, O. A., Abd Latiff, A. A., Daud, Z., Saphira Radin Mohamed, R. M., Ismail, N., Ab Aziz, A., Rafatullah, M., Hossain, K., Ahmad, A., & Kamoldeen Abiodun, A. (2019). Adsorption of cadmium and lead from palm oil mill effluent using bone-composite: Optimisation and isotherm studies. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 99(8), 707–725. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1607318
Abedpour, M., Kamyab Moghadas, B., & Tamjidi, S. (2020). Equilibrium and kinetic study of simultaneous removal of Cd (II) and Ni (II) by acrylamide-based polymer as effective adsorbent: Optimisation by response surface methodology (RSM). International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 00(00), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1772768
Adane, T., Haile, D., Dessie, A., Abebe, Y., & Dagne, H. (2020). Response surface methodology as a statistical tool for optimization of removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution by Teff (Eragrostis teff) husk activated carbon. Applied Water Science, 10(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1120-8
Afolabi, F. O., Musonge, P., & Bakare, B. F. (2021). Bio-sorption of a bi-solute system of copper and lead ions onto banana peels: Characterization and optimization. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 19(1), 613–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-021-00632-x
Afroze, S., & Sen, T. K. (2018). A review on heavy metal ions and dye adsorption from water by agricultural solid waste adsorbents. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 229(7). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3869-z
Agarwal, M., Patel, D., & Dinker, A. (2016). Optimization of manganese removal from water using response surface methodology. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transaction a: Science, 40(1), 63–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-016-0013-z
Ahmadi, R., Rezaee, A., Anvari, M., Hossini, H., & Rastegar, S. O. (2016). Optimization of Cr(VI) removal by sulfate-reducing bacteria using response surface methodology. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(24), 11096–11102. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1041055
Ahmady-Asbchin, S., Safari, M., & Varposhti, M. (2015). Biosorption optimization of Cr(VI) using response surface methodology and thermodynamics modeling onto Azolla filiculoides. Separation Science and Technology (philadelphia), 50(4), 554–563. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2014.957313
Ahmady-Asbchin, S., Tabaraki, R., Jafari, N., Allahverdi, A., & Azhdehakoshpour, A. (2013). Study of nickel and copper biosorption on brown algae Sargassum angustifolium: Application of response surface methodology (RSM). Environmental Technology (united Kingdom), 34(16), 2423–2431. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.772643
Ahmaruzzaman, M. (2011). Industrial wastes as low-cost potential adsorbents for the treatment of wastewater laden with heavy metals. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 166(1–2), 36–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2011.04.005
Akinhanmi, T. F., Ofudje, E. A., Adeogun, A. I., Aina, P., & Joseph, I. M. (2020). Orange peel as low-cost adsorbent in the elimination of Cd(II) ion: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and optimization evaluations. Bioresources and Bioprocessing, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-020-00320-y
Alabi, O., Olanrewaju, A. A., & Afolabi, T. J. (2020). Process optimization of adsorption of Cr(VI) on adsorbent prepared from Bauhinia rufescens pod by Box-Behnken Design. Separation Science and Technology (philadelphia), 55(1), 47–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1577436
Alimohammadi, M., Saeedi, Z., Akbarpour, B., Rasoulzadeh, H., Yetilmezsoy, K., Al-Ghouti, M. A., Khraisheh, M., & McKay, G. (2017). Adsorptive removal of arsenic and mercury from aqueous solutions by eucalyptus leaves. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 228(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3607-y
Alimohammady, M., Jahangiri, M., Kiani, F., & Tahermansouri, H. (2017). Highly efficient simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II), Hg(II) and As(III) ions from aqueous solutions by modification of graphene oxide with 3-aminopyrazole: Central composite design optimization. New Journal of Chemistry, 41(17), 8905–8919. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj01450c
Alslaibi, T. M., Abustan, I., Ahmad, M. A., & Abu Foul, A. (2014). Preparation of activated carbon from olive stone waste: Optimization study on the removal of Cu2+, Cd2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, Fe2+, and Zn2+ from aqueous solution using response surface methodology. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 35(7), 913–925. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2013.809506
Anfar, Z., Ait Ahsaine, H., Zbair, M., Amedlous, A., Ait El Fakir, A., Jada, A., & El Alem, N. (2020). Recent trends on numerical investigations of response surface methodology for pollutants adsorption onto activated carbon materials: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 50(10), 1043–1084. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1642835
Aravind, J., Lenin, C., Nancyflavia, C., Rashika, P., & Saravanan, S. (2015). Response surface methodology optimization of nickel (II) removal using pigeon pea pod biosorbent. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 12(1), 105–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-013-0391-0
Arida, C. V. J., de Luna, M. D. G., Futalan, C. M., & Wan, M. W. (2016). Optimization of As(V) removal using chitosan-coated bentonite from groundwater using Box-Behnken design: Effects of adsorbent mass, flow rate, and initial concentration. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(40), 18739–18747. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1094420
Arslanoğlu, H., Orhan, R., & Turan, M. D. (2020). Application of response surface methodology for the optimization of copper removal from aqueous solution by activated carbon prepared using waste polyurethane. Analytical Letters, 53(9), 1343–1365. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2019.1705849
Aslani, H., Kosari, T. E., Naseri, S., Nabizadeh, R., & Khazaei, M. (2018). Hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution using functionalized chitosan as a novel nano-adsorbent: Modeling and optimization, kinetic, isotherm, and thermodynamic studies, and toxicity testing Time X 4 Initial concentration of chromium X i Variabl. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–15.
Azadegan, F., Bidhendi, M. E., & Badiei, A. (2019). Removal of Hg(II) ions from aqueous environment with the use of modified LUS-1 as new nanostructured adsorbent. International Journal of Environmental Research, 13(3), 557–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-019-00195-8
Babaei, A. A., Bahrami, M., Farrokhian Firouzi, A., Ramazanpour Esfahani, A., & Alidokht, L. (2015). Adsorption of cadmium onto modified nanosized magnetite: Kinetic modeling, isotherm studies, and process optimization. Desalination and Water Treatment, 56(12), 3380–3392. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.972986
Baby, S. R., Saifullah, B., & Rehman, F. U. (2018). Greener method for the removal of toxic metal ions from the wastewater by application of agricultural waste as an adsorbent. Water, 10(10), 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101316
Bandpei, A. M., Mohseni, S. M., Sheikhmohammadi, A., Sardar, M., Sarkhosh, M., Almasian, M., Avazpour, M., Mosallanejad, Z., Atafar, Z., Nazari, S., & Rezaei, S. (2017). Optimization of arsenite removal by adsorption onto organically modified montmorillonite clay: Experimental & theoretical approaches. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 34(2), 376–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-016-0287-z
Bangaraiah, P., & Sarathbabu, B. (2019). Optimization of process parameters in removal of lead from aqueous solution through response surface methodology. Chemical Engineering Communications, 206(8), 986–993. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2018.1541800
Bayuo, J. (2021). Decontamination of cadmium(II) from synthetic wastewater onto shea fruit shell biomass. Applied Water Science, 11(5), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-021-01416-2
Bayuo, J., Abukari, M. A., & Pelig-Ba, K. B. (2020). Optimization using central composite design (CCD) of response surface methodology (RSM) for biosorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous media. Applied Water Science, 10(6), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01213-3
Bayuo, J., Kenneth, B. P., & Abukari, M. A. (2019a). Optimization of adsorption parameters for effective removal of lead (II) from aqueous solution. Physical Chemistry: An Indian Journal Research Article |, 14(1), 123. www.tsijournals.com. Accessed 5 March 2019.
Bayuo, J., Pelig-Ba, K. B., & Abukari, M. A. (2019b). Adsorptive removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution unto groundnut shell. Applied Water Science, 9(4), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0987-8
Bhat, A., Megeri, G. B., Thomas, C., Bhargava, H., Jeevitha, C., Chandrashekar, S., & Madhu, G. M. (2015). Adsorption and optimization studies of lead from aqueous solution using γ-alumina. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 3(1), 30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.11.014
Binaeian, E., Maleki, S., Motaghedi, N., & Arjmandi, M. (2020). Study on the performance of Cd2+ sorption using dimethylethylenediamine-modified zinc-based MOF (ZIF-8-mmen): Optimization of the process by RSM technique. Separation Science and Technology (philadelphia), 55(15), 2713–2728. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1655056
Bingöl, D., & Bozbaş, S. K. (2012). Removal of lead (II) from aqueous solution on multiwalled carbon nanotube by using response surface methodology. Spectroscopy Letters, 45(5), 324–329. https://doi.org/10.1080/00387010.2012.666697
Biswas, S., Meikap, B. C., & Sen, T. K. (2019). Adsorptive removal of aqueous phase copper (Cu2+) and nickel (Ni2+) metal ions by synthesized biochar–biopolymeric hybrid adsorbents and process optimization by response surface methodology (RSM). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 230(8). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4258-y
Çetintaş, S., & Bingöl, D. (2018). Optimization of Pb(II) biosorption with date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) seeds using response surface methodology. Journal of Water Chemistry and Technology, 40(6), 370–378. https://doi.org/10.3103/s1063455x18060103
Chaduka, M., Guyo, U., Zinyama, N. P., Tshuma, P., & Matsinha, L. C. (2020). Modeling and optimization of lead (II) adsorption by a novel peanut hull-g-methyl methacrylate biopolymer using response surface methodology (RSM). Analytical Letters, 53(8), 1294–1311. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2019.1702993
Cheng, J., Gao, J., Zhang, J., Yuan, W., Yan, S., Zhou, J., Zhao, J., & Feng, S. (2021). Optimization of hexavalent chromium biosorption by Shewanella putrefaciens using the Box-Behnken design. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 232(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04947-7
Çiçek, E., Cojocaru, C., Zakrzewska-Trznadel, G., Harasimowicz, M., & Miskiewicz, A. (2012). Response surface methodology for the modelling of 85Sr adsorption on zeolite 3A and pumice. Environmental Technology, 33(1), 51–59. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2010.549514
Cronje, K. J., Chetty, K., Carsky, M., Sahu, J. N., & Meikap, B. C. (2011). Optimization of chromium(VI) sorption potential using developed activated carbon from sugarcane bagasse with chemical activation by zinc chloride. Desalination, 275(1–3), 276–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.03.019
Daoud, W., Ebadi, T., & Fahimifar, A. (2015). Optimization of hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution using acid-modified granular activated carbon as adsorbent through response surface methodology. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 32(6), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0337-3
Dehghani, M. H., Zarei, A., Mesdaghinia, A., Nabizadeh, R., Alimohammadi, M., & Afsharnia, M. (2017). Response surface modeling, isotherm, thermodynamic and optimization study of arsenic (V) removal from aqueous solutions using modified bentonite-chitosan (MBC). Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 34(3), 757–767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-016-0330-0
Demir, D. A., Gülçiçek, O., & Gören, N. (2019). Optimization of adsorption for the removal of cadmium from aqueous solution using Turkish coffee grounds. International Journal of Environmental Research, 13(5), 861–878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-019-00224-6
Dhoble, R. M., Maddigapu, P. R., Bhole, A. G., & Rayalu, S. (2018). Development of bark-based magnetic iron oxide particle (BMIOP), a bio-adsorbent for removal of arsenic (III) from water. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(20), 19657–19674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1792-x
Ecer, Ü., Yılmaz, Ş, & Şahan, T. (2020). Investigation of mercury(II) and arsenic(V) adsorption onto sulphur functionalised pumice: A response surface approach for optimisation and modelling. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 00(00), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1838495
Egirani, D., Latif, M. T., Wessey, N., Poyi, N. R., & Shehata, N. (2021). Preparation and characterization of powdered and granular activated carbon from Palmae biomass for mercury removal. Applied Water Science, 11(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01343-8
Emenike, P. C., Omole, D. O., Ngene, B. U., & Tenebe, I. T. (2016). Potentiality of agricultural adsorbent for the sequestering of metal ions from wastewater. Global Journal Environment Science Management, 2(4), 411–442. https://doi.org/10.22034/gjesm.2016.02.04.010
Essa, A. M. M. (2012). The effect of a continuous mercury stress on mercury reducing community of some characterized bacterial strains. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 6(18), 4006–4012. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR11.1472
Ezechi, E. H., Kutty, S. R., & bin M., Isa, M. H., and Liew, M. S. (2016). Application of response surface methodology for the optimization of hexavalent chromium removal using a new low-cost adsorbent. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(47), 22507–22518. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1129506
Fakhri, A. (2015). Investigation of mercury (II) adsorption from aqueous solution onto copper oxide nanoparticles: Optimization using response surface methodology. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 93(Ii), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2014.06.003
Farnane, M., Machrouhi, A., Elhalil, A., Abdennouri, M., Qourzal, S., Tounsadi, H., & Barka, N. (2018). New sustainable biosorbent based on recycled deoiled carob seeds : Optimization of heavy metals remediation. Journal of Chemistry, 2018, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5748493
Fooladgar, S., Teimouri, A., & Ghanavati Nasab, S. (2019). Highly efficient removal of lead ions from aqueous solutions using chitosan/rice husk ash/nano alumina with a focus on optimization by response surface methodology: Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 27(5), 1025–1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-019-01385-3
Foroutan, R., Mohammadi, R., Adeleye, A. S., Farjadfard, S., Esvandi, Z., Arfaeinia, H., Sorial, G. A., Ramavandi, B., & Sahebi, S. (2019). Efficient arsenic(V) removal from contaminated water using natural clay and clay composite adsorbents. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(29), 29748–29762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06070-5
Gabor, A., Davidescu, C. M., Negrea, A., Ciopec, M., Grozav, I., Negrea, P., & Duteanu, N. (2017). Optimizing the lanthanum adsorption process onto chemically modified biomaterials using factorial and response surface design. Journal of Environmental Management, 204, 839–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.01.046
Garba, Z. N., Bello, I., Galadima, A., & Lawal, A. Y. (2016). Optimization of adsorption conditions using central composite design for the removal of copper (II) and lead (II) by defatted papaya seed. Karbala International Journal of Modern Science, 2(1), 20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kijoms.2015.12.002
Ghanavati, N. S., Teimouri, A., Hemmasi, M., Jafari Harandi, Z., & Javaheran, Y. M. (2020). Removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous solutions by nanodiopside as a novel and green adsorbent: Optimisation by response surface methodology. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 00(00), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1699917
Ghasemi, S. M., Ghaderpoori, M., Moradi, B., Taghavi, M., Karimyan, K., & Mehdipour, F. (2020). Optimization of Cr(VI) adsorption by modified sesame hull from aqueous solutions using response surface methodology. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1763972
Ghosh, A., & Das, P. (2014). Optimization of copper adsorption by soil of polluted wasteland using response surface methodology. Indian Chemical Engineer, 56(1), 29–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/00194506.2014.883728
Ghosh, A., & Saha, P. D. (2012). Optimization of copper adsorption by chemically modified fly ash using response surface methodology modeling. Desalination and Water Treatment, 49(1–3), 218–226. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.719324
Ghosh, R. K., Ray, D. P., Chakraborty, S., Saha, B., Manna, K., Tewari, A., & Sarkar, S. (2020). Cadmium removal from aqueous medium by jute stick activated carbon using response surface methodology: Factor optimisation, equilibrium, and regeneration. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2019.1700964
Gupta, A., & Balomajumder, C. (2017). Statistical optimization of process parameters for the simultaneous adsorption of Cr(VI) and phenol onto Fe-treated tea waste biomass. Applied Water Science, 7(8), 4361–4374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-017-0582-9
Gupta, G. K., & Mondal, M. K. (2020). Mechanism of Cr(VI) uptake onto sagwan sawdust derived biochar and statistical optimization via response surface methodology. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, Vi, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-01082-5
Han, C., Pu, H., Li, H., Deng, L., Huang, S., He, S., & Luo, Y. (2013). The optimization of As(V) removal over mesoporous alumina by using response surface methodology and adsorption mechanism. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 254–255(1), 301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.04.008
He, S., Li, Y., Weng, L., Wang, J., He, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, K., Wu, Q., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, Z. (2018). Competitive adsorption of Cd(II), Pb(II) and Ni(II) onto Fe(III)−modified argillaceous limestone: Influence of pH, ionic strength and natural organic matters. The Science of the Total Environment, 69–78.
Hosseini, S. S. S., Khosravi, A., Tavakoli, H., Esmhosseini, M., & Khezri, S. (2016). Natural zeolite for nickel ions removal from aqueous solutions: Optimization and modeling using response surface methodology based on central composite design. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(36), 16898–16906. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1082508
Hossini, H., Esmaeili Taheri, H., Arab Markadeh, A., Rezaee, A., & Rastegar, S. O. (2016). Optimization of effective parameters in the biosorption of Cr(VI) using acid treated date palm fiber from aqueous solution. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(11), 4994–5003. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.995716
Hymavathi, D., & Prabhakar, G. (2017). Studies on the removal of cobalt(II) from aqueous solutions by adsorption with Ficus benghalensis leaf powder through response surface methodology. Chemical Engineering Communications, 204(12), 1401–1411. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2017.1365063
Iftekhar, S., Ramasamy, D. L., Srivastava, V., Asif, M. B., & Sillanpää, M. (2018). Understanding the factors affecting the adsorption of Lanthanum using different adsorbents: A critical review. Chemosphere, 204, 413–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.053
Igberase, E., Osifo, P., & Ofomaja, A. (2017). Chromium (VI) ion adsorption by grafted cross-linked chitosan beads in aqueous solution–a mathematical and statistical modeling study. Environmental Technology (united Kingdom), 38(24), 3156–3166. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1290152
Ince, O. K., Ince, M., Karaaslan, N. M., & Yonten, V. (2016). Optimization of cadmium removal from water by hydroxyapatite using experimental design methodology. Analytical Letters, 49(15), 2513–2524. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2016.1151022
Iqbal, M., Iqbal, N., Bhatti, I. A., Ahmad, N., & Zahid, M. (2016). Response surface methodology application in optimization of cadmium adsorption by shoe waste: A good option of waste mitigation by waste. Ecological Engineering, 88, 265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.12.041
Ittrat, P., Chacho, T., Pholprayoon, J. S., Charoenpanich, N., & J. (2014). Application of agriculture waste as a support for lipase immobilization. Biocatalysis, 3(3), 77–82.
Jahangiri, K., Yousefi, N., Ghadiri, S. K., Fekri, R., Bagheri, A., & Talebi, S. S. (2019). Enhancement adsorption of hexavalent chromium onto modified fly ash from aqueous solution; optimization; isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic study. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 40(8), 1147–1158. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2018.1496841
Jain, M., Garg, V. K., & Kadirvelu, K. (2011). Investigation of Cr(VI) adsorption onto chemically treated Helianthus annuus: Optimization using response surface methodology. Bioresource Technology, 102(2), 600–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.08.001
Jamileh, K., Ghorbani, M. H., Aghaie, H., & Fazaeli, R. (2020). Investigation of Zn(II) Adsorption from aqueous solution onto copper oxide with different morphologies: Optimization using response surface methodology. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 94(9), 1921–1929. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024420090149
Javid, A., Roudbari, A., Yousefi, N., Fard, M. A., Barkdoll, B., Talebi, S. S., Nazemi, S., Ghanbarian, M., & Ghadiri, S. K. (2020). Modeling of chromium (VI) removal from aqueous solution using modified green-graphene: RSM-CCD approach, optimization, isotherm, and kinetic studies. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 18(2), 515–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00479-8
Jjagwe, J., Olupot, P. W., Menya, E., & Kalibbala, H. M. (2021). Synthesis and application of granular activated carbon from biomass waste materials for water treatment: A review. Journal of Bioresources and Bioproducts, April. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobab.2021.03.003
Kaakani, M. (2012). Heavy metal removal from wastewater using novel adsorbent. American University of Sharjah.
Kalantari, K., Ahmad, M. B., Masoumi, H. R. F., Shameli, K., Basri, M., & Khandanlou, R. (2014). Rapid adsorption of heavy metals by Fe3O4/talc nanocomposite and optimization study using response surface methodology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(7), 12913–12927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150712913
Kanaujia, S., Singh, B., & Singh, S. K. (2015). Removal of fluoride from groundwater by carbonised Punica granatum carbon bio-adsorbent. Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 03(04), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2015.34001
Karmaker, S. C., Eljamal, O., & Saha, B. B. (2021). Response surface methodology for strontium removal process optimization from contaminated water using zeolite nanocomposites. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14503-3
Kashi, N., Elmi Fard, N., & Fazaeli, R. (2017). Empirical modeling and CCD-based RSM optimization of Cd(II) adsorption from aqueous solution on clinoptilolite and bentonite. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 90(6), 977–992. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427217060210
Khandanlou, R., Ahmad, M. B., Masoumi, H. R. F., Shameli, K., Basri, M., & Kalantari, K. (2015). Rapid adsorption of copper(II) and lead(II) by rice straw/Fe3O4 nanocomposite: Optimization, equilibrium isotherms, and adsorption kinetics study. PLoS ONE, 10(3), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120264
Khani, R., Sobhani, S., & Beyki, M. H. (2016). Highly selective and efficient removal of lead with magnetic nano-adsorbent: Multivariate optimization, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 466, 198–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.12.027
Khelifi, O., Affoune, A. M., Nacef, M., Chelaghmia, M. L., & Laksaci, H. (2021). Response surface modeling and optimization of Ni(II) and Cu(II) ions competitive adsorption capacity by sewage sludge activated carbon. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, Ii, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05534-6
Kishore, K. K., Krishna, M. M., Rama, L. G., & Murthy, C. V. R. (2013). Studies on biosorption of cadmium on grape pomace using response surface methodology. Desalination and Water Treatment, 51(28–30), 5592–5598. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.769666
Korrapati, N., & Y, P. S. (2015). Optimization studies on biosorption of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) from wastewater in a packed bed bioreactor. Desalination and Water Treatment, 53(8), 2167–2176. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.862870
Kumar, D., Pandey, L. K., & Gaur, J. P. (2016). Metal sorption by algal biomass: From batch to continuous system. Algal Research, 18, 95–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.05.026
Kumar, M. P. S., & Phanikumar, B. R. (2013). Response surface modelling of Cr6+ adsorption from aqueous solution by neem bark powder: Box-Behnken experimental approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(3), 1327–1343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-0981-2
Kumar, P., Ramalingam, S., Sathyaselvabala, V., Kirupha, S., Murugesan, A., & Sivanesan, S. (2012). Removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solution by agricultural waste cashew nut shell. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 43(29), 756–768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0259-2
Kumari, B., Tiwary, R. K., Yadav, M., & Singh, K. M. P. (2021). Nonlinear regression analysis and response surface modeling of Cr (VI) removal from synthetic wastewater by an agro-waste Cocos nucifera: Box-Behnken design (BBD). International Journal of Phytoremediation, 23(8), 791–808. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2020.1858399
Kushwaha, D., & Dutta, S. (2017). Experiment, modeling and optimization of liquid phase adsorption of Cu(II) using dried and carbonized biomass of Lyngbya majuscula. Applied Water Science, 7(2), 935–949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0304-0
Lamzougui, G., Es-Said, A., Nafai, H., Chafik, D., Bouhaouss, A., & Bchitou, R. (2021). Optimization and modeling of Pb(II) adsorption from aqueous solution onto phosphogypsum by application of response surface methodology. Phosphorus, Sulfur and Silicon and the Related Elements, 196(6), 521–529. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426507.2020.1860985
Langeroodi, N. S., Farhadravesh, Z., & Khalaji, A. D. (2018). Optimization of adsorption parameters for Fe (III) ions removal from aqueous solutions by transition metal oxide nanocomposite. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 11(4), 404–413. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2018.1526329
Lingamdinne, L. P., Koduru, J. R., Chang, Y. Y., & Karri, R. R. (2018). Process optimization and adsorption modeling of Pb(II) on nickel ferrite-reduced graphene oxide nano-composite. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 250(Ii), 202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.11.174
Liu, X., Han, B., Su, C., & li, Han, Q., Chen, K. jie, and Chen, Z. qiong. (2019). Optimization and mechanisms of biosorption process of Zn(II) on rape straw powders in aqueous solution. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(31), 32151–32164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06342-0
Lyonga, F. N., Hong, S. H., Cho, E. J., Kang, J. K., Lee, C. G., & Park, S. J. (2021). As(III) adsorption onto Fe-impregnated food waste biochar: Experimental investigation, modeling, and optimization using response surface methodology. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43(9), 3303–3321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00739-4
Mahmoud, A. S., Mohamed, N. Y., Mostafa, M. K., & Mahmoud, M. S. (2021). Effective chromium adsorption from aqueous solutions and tannery wastewater using bimetallic Fe/Cu nanoparticles: Response surface methodology and artificial neural network. Air, Soil and Water Research, 14. https://doi.org/10.1177/11786221211028162
Maiti, S., Prasad, B., & Minocha, A. K. (2020). Optimization of copper removal from wastewater by fly ash using central composite design of response surface methodology. SN Applied Sciences, 2(12), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03892-8
Mbugua, M., Mbuvi, H., & Muthengia, J. (2014). Rice husk ash derived zeolite blended with water hyacinth ash for enhanced adsorption of cadmium ions. Current World Environment, 9(2), 280–286. https://doi.org/10.12944/cwe.9.2.08
Memon, A. Q., Ahmed, S., Bhatti, Z. A., Maitlo, G., Shah, A. K., Mazari, S. A., Muhammad, A., Jatoi, A. S., & Kandhro, G. A. (2021). Experimental investigations of arsenic adsorption from contaminated water using chemically activated hematite (Fe2O3) iron ore. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(10), 12898–12908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11208-x
Mohd, I., Ahamed, I., & Lichtfouse, E. (2021). Water pollution and remediation: Heavy metals. In Environmental Chemistry for a Sustainable World (vol. 53). http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-030-54723-3. Accessed 14 January 2021.
Mohubedu, R. P., Diagboya, P. N., Abasi, C. Y., Dikio, E. D., & Mtunzi, F. (2019). Magnetic valorization of biomass and biochar of a typical plant nuisance for toxic metals contaminated water treatment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 209, 1016–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.215
Mondal, N. K., Basu, S., & Das, B. (2019a). Decontamination and optimization study of hexavalent chromium on modified chicken feather using response surface methodology. Applied Water Science, 9(3), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0930-z
Mondal, N. K., Basu, S., Sen, K., & Debnath, P. (2019b). Potentiality of mosambi (Citrus limetta) peel dust toward removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution: An optimization study. Applied Water Science, 9(4), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0997-6
Mondal, N. K., Samanta, A., Roy, P., & Das, B. (2019c). Optimization study of adsorption parameters for removal of Cr(VI) using magnolia leaf biomass by response surface methodology. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 5(4), 1627–1639. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-019-00322-5
Naga, B. A., Raja, S. T., Srinivasa, R. D., Suresh, K. G., & Krishna, M. G. V. (2021). Experimental and statistical analysis of As(III) adsorption from contaminated water using activated red mud doped calcium-alginate beads. Environmental Technology (united Kingdom), 42(12), 1810–1825. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1681520
Nazari, A., Nakhaei, M., & Yari, A. R. (2021). Arsenic adsorption by TiO2 nanoparticles under conditions similar to groundwater: Batch and column studies. International Journal of Environmental Research, 15(1), 79–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-020-00298-7
Nikraftar, N., & Ghorbani, F. (2016). Adsorption of As(V) Using modified magnetic nanoparticles with ascorbic acid: Optimization by response surface methodology. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 227(6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2876-1
Okolo, B. I., Oke, E. O., Agu, C. M., Adeyi, O., Nwoso-Obieogu, K., & Akatobi, K. N. (2020). Adsorption of lead(II) from aqueous solution using Africa elemi seed, mucuna shell and oyster shell as adsorbents and optimization using Box-Behnken design. Applied Water Science, 10(8), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01242-y
Özdemir, E., Duranoĝlu, D., Beker, Ü., & Avci, A. Ö. (2011). Process optimization for Cr(VI) adsorption onto activated carbons by experimental design. Chemical Engineering Journal, 172(1), 207–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.091
Park, D., Yun, Y., & Park, J. (2014). The past, present, and future trends of biosorption. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 15, 86–102.
Prabhu, A. A., Chityala, S., Jayachandran, D., Deshavath, N. N., & Veeranki, V. D. (2021). A two step optimization approach for maximizing biosorption of hexavalent chromium ions (Cr (VI)) using alginate immobilized Sargassum sp in a packed bed column. Separation Science and Technology (philadelphia), 56(1), 90–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2019.1708933
Premkumar, M., & Shanthakumar, S. (2015). Process optimization for Cr(VI) removal by Mangifera indica seed powder: A response surface methodology approach. Desalination and Water Treatment, 53(6), 1653–1663. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.857615
Pyrzynska, K. (2019). Removal of cadmium from wastewaters with low-cost adsorbents. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 7(1), 102795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.11.040
Rahdar, S., Taghavi, M., Khaksefidi, R., & Ahmadi, S. (2019). Adsorption of arsenic (V) from aqueous solution using modified saxaul ash: Isotherm and thermodynamic study. Applied Water Science, 9(4), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0974-0
Rahman, N., & Nasir, M. (2018). Application of Box-Behnken design and desirability function in the optimization of Cd(II) removal from aqueous solution using poly(o-phenylenediamine)/hydrous zirconium oxide composite: Equilibrium modeling, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(26), 26114–26134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2566-1
Rangabhashiyam, S., Giri Nandagopal, M. S., Nakkeeran, E., Keerthi, R., & Selvaraju, N. (2016). Use of Box-Behnken design of experiments for the adsorption of chromium using immobilized macroalgae. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(54), 26101–26113. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1163514
Rashid, K., Suresh Kumar Reddy, K., Shoaibi, A. Al, & Srinivasakannan, C. (2013). Sulfur-impregnated porous carbon for removal of mercuric chloride: Optimization using RSM. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 15(6), 1041–1048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0564-4
Roy, P., Dey, U., Chattoraj, S., Mukhopadhyay, D., & Mondal, N. K. (2017). Modeling of the adsorptive removal of arsenic(III) using plant biomass: A bioremedial approach. Applied Water Science, 7(3), 1307–1321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0339-2
Roy, P., Mondal, N. K., & Das, K. (2014). Modeling of the adsorptive removal of arsenic: A statistical approach. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2(1), 585–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.10.014
Sabah, H., Thouraya, T., Melek, H., & Nadia, M. (2018). Application of response surface methodology for optimization of cadmium ion removal from an aqueous solution by eggshell powder. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities, 34(2), 302–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-018-7163-9
Sadeghalvad, B., Azadmehr, A. R., & Motevalian, H. (2017). Statistical design and kinetic and thermodynamic studies of Ni(II) adsorption on bentonite. Journal of Central South University, 24(7), 1529–1536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3557-y
Sagharloo, N. G., Rabani, M., Salimi, L., Ghafourian, H., & Sadatipour, S. M. T. (2021). Immobilized ZnO/TiO2 activated carbon (I ZnO/TiO2 AC) to removal of arsenic from aqueous environments: Optimization using response surface methodology and kinetic studies. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 1, 12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01741-1
Şahan, T., Erol, F., & Yılmaz, Ş. (2018). Mercury(II) adsorption by a novel adsorbent mercapto-modified bentonite using ICP-OES and use of response surface methodology for optimization. Microchemical Journal, 138, 360–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.01.028
Şahan, T., & Öztürk, D. (2014). Investigation of Pb(II) adsorption onto pumice samples: Application of optimization method based on fractional factorial design and response surface methodology. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 16(5), 819–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-013-0673-8
Sahmoune, M. N., Louhab, K., & Boukhiar, A. (2011). Advanced biosorbents materials for removal of chromium from water and wastewaters. Environmental Progress and Sustainable Energy, 30(3), 284–293. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.10473
Sahu, J. N., Acharya, J., Sahoo, B. K., & Meikap, B. C. (2016). Optimization of lead (II) sorption potential using developed activated carbon from tamarind wood with chemical activation by zinc chloride. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(5), 2006–2017. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.979446
Sahu, U., Mahapatra, S. S., & Patel, R. K. (2018). Application of Box-Behnken design in response surface methodology for adsorptive removal of arsenic from aqueous solution using CeO2/Fe2O3/graphene nanocomposite. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 207, 233–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.11.042
Sahu, U. K., Sahu, M. K., Mahapatra, S. S., & Patel, R. K. (2017). Removal of As(III) from aqueous solution using Fe3O4Nanoparticles: Process modeling and optimization using statistical design. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 228(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3224-1
Saini, S., Chawla, J., Kumar, R., & Kaur, I. (2019). Environmental biotechnology for soil and wastewater implications on ecosystems. Environmental Biotechnology for Soil and Wastewater Implications on Ecosystems, 61–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-6846-2
Salah, A. S. (2015). Assessing the potential of laterite in adsorbing cadmium from mine leachate and surrogate cadmium solutions a case study at Anglogold Ashanti Iduaperiem Gold Mine Ltd, Tarkwa. http://hdl.handle.net/123456789/6810. Accessed 10 October 2015.
Saleh, T. A., Sari, A., & Tuzen, M. (2017). Optimization of parameters with experimental design for the adsorption of mercury using polyethylenimine modified-activated carbon. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5(1), 1079–1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.01.032
Samuel, S. M., Abigail M, E. A., & Chidambaram, R. (2015). Isotherm modelling, kinetic study and optimization of batch parameters using response surface methodology for effective removal of Cr(VI) using fungal biomass. PLoS ONE, 10(3), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116884
Saravanan, A., Senthil Kumar, P., & Preetha, B. (2016). Optimization of process parameters for the removal of chromium(VI) and nickel(II) from aqueous solutions by mixed biosorbents (custard apple seeds and Aspergillus niger) using response surface methodology. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(31), 14530–14543. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1064034
Shafaghat, J., & Ghaemi, A. (2021). Comparison of Pb(II) adsorption by ground granulated blast-furnace and phosphorus slags; Exploitation of RSM. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transaction a: Science, 45(3), 899–911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-021-01075-7
Sharifi, S., Nabizadeh, R., Akbarpour, B., Azari, A., Ghaffari, H., Nazmara, S., Mahmoudi, B., Shiri, L., & Yousefi, M. (2019). Modeling and optimizing parameters affecting hexavalent chromium adsorption from aqueous solutions using Ti-XAD7 nanocomposite: RSM-CCD approach, kinetic, and isotherm studies. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 17(2), 873–888. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00405-7
Shojaeimehr, T., Rahimpour, F., Khadivi, M. A., & Sadeghi, M. (2014). A modeling study by response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) on Cu2+ adsorption optimization using light expended clay aggregate (LECA). Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 20(3), 870–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.06.017
Simsek, E. B., Özdemir, E., Tuna, A. O. A., & Beker, U. (2014). Factorial design analysis of As(V) adsorption onto iron-aluminum binary oxide-doped clinoptilolite. Desalination and Water Treatment, 52(40–42), 7812–7821. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.831783
Sivamani, S., Prasad, B. S. N., Nithya, K., Sivarajasekar, N., & Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A. (2021). Back-propagation neural network: Box-Behnken design modelling for optimization of copper adsorption on orange zest biochar. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03411-1
Srivastava, V., Sharma, Y. C., & Sillanpää, M. (2015). Response surface methodological approach for the optimization of adsorption process in the removal of Cr(VI) ions by Cu 2 (OH) 2 CO 3 nanoparticles. In Applied Surface Science (vol. 326, Issue Vi). Elsevier B.V. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.11.097
Sugashini, S., & Begum, K. M. M. S. (2013). Optimization using central composite design (CCD) for the biosorption of Cr(VI) ions by cross linked chitosan carbonized rice husk (CCACR). Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 15(2), 293–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-012-0512-3
Sujatha, S., Venkatesan, G., & Sivarethinamohan, R. (2020). Optimization of lead removal in exhausting Manilkara zapota based activated carbon: Application of response surface methodology. Environmental Technology (united Kingdom), 41(19), 2478–2493. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2019.1570347
Sun, Y., Zhang, J. P., Guo, F., & Zhang, L. (2016). Hydrochar preparation from black liquor by CO2 assisted hydrothermal treatment: Optimization of its performance for Pb2+ removal. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 33(9), 2703–2710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-016-0152-0
Tabatabaee, G. S. M., Aminzadeh, R., & Abarzani, M. (2014). Use of response surface methodology to study the combined effect of various parameters on hexavalent chromium adsorption. Chemical Engineering Communications, 201(2), 191–208. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2013.766602
Taha, G. M., Arifien, A. E., & El-Nahas, S. (2011). Removal efficiency of potato peels as a new biosorbent material for uptake of Pb(Ii) Cd(Ii) and Zn(Ii) from their aqueous solutions. The Journal of Solid Waste Technology and Management, 37(2), 128–140. https://doi.org/10.5276/JSWTM.2011.128
Tajernia, H., Ebadi, T., Nasernejad, B., & Ghafori, M. (2014). Arsenic removal from water by sugarcane bagasse: An application of response surface methodology (RSM). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 225(7). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2028-4
Taşdemir, R., Yiğitarslan, S., & Erzengin, S. G. (2021). Optimization of lead (II) Adsorption onto cross-linked polycarboxylate-based adsorbent by response surface methodology. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 46(7), 6287–6301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05029-w
Tuna, A. Ö. A., Özdemir, E., Simsek, E. B., & Beker, U. (2013). Optimization of process parameters for removal of arsenic using activated carbon-based iron-containing adsorbents by response surface methodology. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 224(9). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1685-z
Turkyilmaz, H., Kartal, T., & Yildiz, S. Y. (2014). Optimization of lead adsorption of mordenite by response surface methodology: Characterization and modification. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 12(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2052-336X-12-5
Uddin, M. K., & Salah, M. M. (2018). Statistical analysis of Litchi chinensis’s adsorption behavior toward Cr(VI). Applied Water Science, 8(5), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0784-9
Van Thuan, T., Quynh, B. T. P., Nguyen, T. D., Ho, V. T. T., & Bach, L. G. (2017). Response surface methodology approach for optimization of Cu2+, Ni2+ and Pb2+ adsorption using KOH-activated carbon from banana peel. Surfaces and Interfaces, 6, 209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2016.10.007
Wen, Y., & Wu, Y. (2012). Optimizing adsorption of Co(II) and Ni(II) by 13× molecular sieves using response surface methodology. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223(9), 6095–6107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1343-x
Xavier, A. L. P., Adarme, O. F. H., Furtado, L. M., Ferreira, G. M. D., da Silva, L. H. M., Gil, L. F., & Gurgel, L. V. A. (2018). Modeling adsorption of copper(II), cobalt(II) and nickel(II) metal ions from aqueous solution onto a new carboxylated sugarcane bagasse. Part II: Optimization of monocomponent fixed-bed column adsorption. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 516, 431–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.01.068
Xu, M., Yin, P., Liu, X., Dong, X., Yang, Y., Wang, Z., & Qu, R. (2013). Optimization of biosorption parameters of Hg(II) from aqueous solutions by the buckwheat hulls using respond surface methodology. Desalination and Water Treatment, 51(22–24), 4546–4555. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.770591
Yılmaz, Ş, Şahan, T., & Karabakan, A. (2017). Response surface approach for optimization of Hg(II) adsorption by 3-mercaptopropyl trimethoxysilane-modified kaolin minerals from aqueous solution. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 34(8), 2225–2235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-017-0116-z
Yusuff, A. S. (2018). Optimization of adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by Leucaena leucocephala seed shell activated carbon using design of experiment. Applied Water Science, 8(8), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0850-3
Yusuff, A. S., Owolabi, J. O., & Igbomezie, C. O. (2021). Optimization of process parameters for adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by alumina-onion skin composite. Chemical Engineering Communications, 208(1), 14–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2019.1680371
Zhang, J., Yang, T., Wang, H., & Yang, K. (2016). Optimization of process variables by dried Bacillus cereus for biosorption of nickel(II) using response surface method. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(34), 16096–16103. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1091995
Zhao, J., Yu, L., Ma, H., Zhou, F., Yang, K., & Wu, G. (2020). Corn stalk-based activated carbon synthesized by a novel activation method for high-performance adsorption of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 578, 650–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.06.031
Zhu, H., Fu, Y., Jiang, R., Yao, J., Xiao, L., & Zeng, G. (2014). Optimization of copper(II) adsorption onto novel magnetic calcium alginate/maghemite hydrogel beads using response surface methodology. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 53(10), 4059–4066. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie4031677
Zolgharnein, J., Shahmoradi, A., Zolgharnein, P., & Amani, S. (2016). Multivariate optimization and adsorption characterization of as(III) removal by using fraxinus tree leaves. Chemical Engineering Communications, 203(2), 210–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2014.988330
Funding
The authors acknowledge the funding from the Partnership for Applied Sciences, Engineering, and Technology (PASET), which allowed them to conduct this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayuo, J., Rwiza, M. & Mtei, K. Response surface optimization and modeling in heavy metal removal from wastewater—a critical review. Environ Monit Assess 194, 351 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09994-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09994-7