Abstract
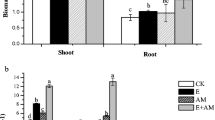
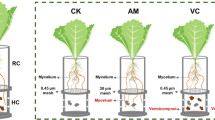
The interactive impacts of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus (AMF; Glomus intraradices) and an earthworm species (Aporrectodea trapezoides) on N uptake by maize growing during wheat straw decomposition was studied with a modified up–down two-compartment root containers incorporating an air gap system. Soil was sterilized and root compartments inoculated with AMF inoculum in each treatment. Treatments comprised hyphal compartments (HC) with or without AMF hyphae and with or without earthworms. Wheat straw labeled with 15N was added to the HC. We determined maize yield, 15N content of shoots and roots, concentration of inorganic 15N in soil, percent of 15N transfer, and soil microbial biomass and community composition as indicated by phospholipid fatty acid profiles of HC soil at harvest. Earthworms enhanced 15N mineralization by 47.7 % from wheat straw compared to the control but did not directly increase N mineralization or transfer N from mycorrhizae to plant. AMF hyphae increased shoot and root 15N uptake by 117.9 and 87.4 %, respectively. Interaction between the AMF and earthworms increased shoot and root 15N uptake by 22.0 and 36.2 %, respectively, (compared to hyphae alone) and decreased soil 15N content by 28.9 % (compared to earthworms alone). The AMF hyphae assisted maize in the uptake of 15N mineralized from wheat straw by earthworms. Interactions between earthworms and AMF may help plants to take up N mineralized from crop residues.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames RN, Reid CPP, Porter LK, Cambardella C (1983) Hyphal uptake and transport of nitrogen from two 15N-labeled sources by Glomus mosseae, a vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. New Phytol 95:381–396
Atul-Nayyar A, Hamel C, Hanson K, Germida J (2009) The arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis links N mineralization to plant demand. Mycorrhiza 19:239–246
Bais HP, Weir TL, Perry LG, Gilroy S, Vivanco JM (2006) The role of root exudates in rhizosphere interactions with plants and other organisms. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:233–266
Bardgett RD, Hobbs PJ, Frostegård Å (1996) Changes in soil fungal: bacterial biomass ratios following reductions in the intensity of management of an upland grassland. Biol Fert Soils 22:261–264
Bardgett RD, Bowman WD, Kaufmann R, Schmidt SK (2005) A temporal approach to linking aboveground and belowground ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 20:634–641
Blair JM, Parmelee RW, Allen MF, McCartney DA, Stinner BR (1997) Changes in soil N pools in response to earthworm population manipulations in agroecosystems with different N sources. Soil Biol Biochem 29:361–367
Bossio DA, Scow KM (1998) Impact of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns. Microbial Ecol 35:265–278
Brown GG, Barois I, Lavelle P (2000) Regulation of soil organic matter dynamics and microbial activity in the drilosphere and the role of interactions with other edaphic functional domains. Eur J Soil Biol 36:177–198
Brussaard L, Pulleman MM, Ouédraogo E, Mando A, Six J (2007) Soil fauna and soil function in the fabric of the food web. Pedobiologia 50:447–462
Butenschoen O, Marhan S, Langel R, Scheu S (2009) Carbon and nitrogen mobilisation by earthworms of different functional groups as affected by soil sand content. Pedobiologia 52:263–272
Calvet C, Pera J, Barea JM (1993) Growth response of marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) to inoculation with Glomus mosseae, Trichoderma aureoviridae and Pythium ultimum in a peat–perlite mixture. Plant Soil 148:1–6
Cao ZP, Qiao YH, Wang BQ, Qin X (2006) Influence of agricultural intensification on the earthworm community in arable farmland in the North China plain. Eur J Soil Biol 42:362–366
Cheng XM, Baumgartner K (2006) Effects of mycorrhizal roots and extraradical hyphae on 15N uptake from vineyard cover crop litter and the soil microbial community. Soil Biol Biochem 38:2665–2675
Cortez J, Billes G, Bouché MB (2000) Effect of climate, soil type and earthworm activity on nitrogen transfer from a nitrogen-15-labelled decomposing material under field conditions. Biol Fert Soils 30:318–327
Costello DM, Lamberti GA (2009) Biological and physical effects of non-native earthworms on nitrogen cycling in riparian soils. Soil Biol Biochem 41:2230–2235
Cruz C, Egsgaard H, Trujillo C, Ambus P, Requena N, Martins-Loução MA, Jakobsen I (2007) Enzymatic evidence for the key role of arginine in nitrogen translocation by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Plant Physiol 144:782–792
Cui ZL, Zhang FS, Chen XP (2008) On-farm estimation of indigenous nitrogen supply for site-specific nitrogen management in the North China plain. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 81:37–47
Curry JP, Byrne D (1992) The role of earthworms in straw decomposition and nitrogen turn over in arable land in Ireland. Soil Biol Biochem 24:1409–1412
Curry JP, Schmidt O (2007) The feeding ecology of earthworms - a review. Pedobiologia 50:463–477
De Goede RGM, Brussaard L, Akkermans ADL (2003) On-farm impact of cattle slurry manure management on biological soil quality. Njas-Wagening J Life Sci 51:103–133
Edwards CA, Fletcher KE (1988) Interactions between earthworms and microorganisms in organic matter breakdown. Agric Ecosyst Environ 24:235–247
Eisenhauer N, Scheu S (2008) Earthworms as drivers of the competition between grasses and legumes. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2650–2659
Eisenhauer N, Konig S, Renker ACW (2009) Impacts of earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomus intraradices) on plant performance are not interrelated. Soil Biol Biochem 41:561–567
Eriksen-Hamel NS, Whalen JK (2008) Earthworms, soil mineral nitrogen and forage production in grass-based hayfields. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1004–1010
Ernst G, Henseler I, Felten D, Emmerling C (2009) Decomposition of energy crop residues governed by earthworms. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1548–1554
Gormsen D, Olsson P, Hedlund K (2004) The influence of collembolans and earthworms on AM fungal mycelium. Appl Soil Ecol 27:211–220
Govindarajulu M, Pfeffer PE, Jin H, Abubaker J, Douds DD, Allen JW, Bucking PJ, Shachar-Hill Y (2005) Nitrogen transfer in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Nature 435:819–823
Guether M, Volpe V, Balestrini R, Requena N, Wipf D, Bonfante P (2011) LjLHT1.2—a mycorrhiza-inducible plant amino acid transporter from Lotus japonicus. Biol Fert Soils 47:925–936
Hawkins HJ, Johansen A, George E (2000) Uptake and transport of organic and inorganic nitrogen by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Plant Soil 226:275–285
Henriksen TM, Breland TA (1999) Nitrogen availability effects on carbon mineralization, fungal and bacterial growth, and enzyme activities during decomposition of wheat straw in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 31:1121–1134
Hodge A, Fitter AH (2010) Substantial nitrogen acquisition by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi from organic material has implications for N cycling. P Natl Acad Sci USA 107:13754–13759
Hodge A, Campbell CD, Fitter AH (2001) An arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus accelerates decomposition and acquires nitrogen directly from organic material. Nature 413:297–299
Hodge A, Helgason T, Fitter AH (2010) Nutritional ecology of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Fungal Ecol 3:267–273
Johansen A, Jakobsen I, Jensen ES (1992) Hyphal transport of 15N-labeled nitrogen by a vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and its effect on depletion of inorganic soil N. New Phytol 122:281–288
Johansen A, Jakobsen I, Jensen ES (1994) Hyphal N transport by a vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus associated with cucumber grown at three nitrogen levels. Plant Soil 160:1–9
Laossi KR, Ginot A, Noguera DC, Blouin M, Barot S (2010) Earthworm effects on plant growth do not necessarily decrease with soil fertility. Plant Soil 328:109–118
Lavelle P (1997) Faunal activities and soil processes: adaptive strategies that determine ecosystem function. Adv Ecol Res 27:93–122
Lawrence B, Fisk MC, Fahey TJ, Suarez ER (2003) Influence of non-native earthworms on mycorrhizal colonization of sugar maple (Acer saccharum Marsh). New Phytol 157:145–153
Leigh J, Hodge A, Fitter AH (2009) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi can transfer substantial amounts of nitrogen to their host plant from organic material. New Phytol 181:199–207
Li XL, George E, Marschner H (1991) Phosphorus depletion and pH decrease at the root–soil and hyphae–soil interfaces of VA-mycorrhizal white clover fertilized with ammonium. New Phytol 119:397–404
Li H, Li XL, Dou ZX, Zhang JL, Wang C (2012) Earthworm (Aporrectodea trapezoides)–mycorrhiza (Glomus intraradices) interaction and nitrogen and phosphorus uptake by maize. Biol Fert Soils 48:75–85
Liu YL, Zhang B, Li CL, Hu F, Velde B (2008) Long-term fertilization influences on clay mineral composition and ammonium adsorption in a rice paddy soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 72:1580–1590
Lubbers IM, Brussaard L, Otten W, Van Groenigen JW (2011) Earthworm-induced N mineralization in fertilized grassland increases both N2O emission and crop N uptake. Eur J Soil Sci 62:152–161
Mary B, Recous S, Darwis D, Robin D (1996) Interactions between decomposition of plant residues and nitrogen cycling in soil. Plant Soil 181:71–82
McLean MA, Migge-Kleian S, Parkinson D (2006) Earthworm invasions of ecosystems devoid of earthworms: effects on soil microbes. Biol Invasions 8:1257–1273
Milleret R, Renée-Claire LB, Jean-Michel G (2009) Root, mycorrhiza and earthworm interactions: their effects on soil structuring processes, plant and soil nutrient concentrations and plant biomass. Plant Soil 316:1–12
Newman EI (1966) A method of estimating total length of root in a sample. J Appl Ecol 3:139–145
Nichols P, Stulp BK, Jones JG, White DC (1986) Comparison of fatty-acid content and DNA homology of the filamentous gliding bacteria Vitreoscilla, Flexibacter, and Filibacter. Arch Microbiol 146:1–6
Oldenburg E, Kramer S, Schrader S, Weinert J (2008) Impact of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris on the degradation of Fusarium-infected and desoxynivalenol-contaminated wheat straw. Soil Biol Biochem 40:3049–3053
Olsson PA, Wilhelmsson P (2000) The growth of external AM fungal mycelium in sand dunes and in experimental systems. Plant Soil 226:161–169
Olsson PA, Baath E, Jakobsen I, Soderstrom B (1995) The use of phospholipid and neutral lipid fatty acids to estimate biomass of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in soil. Mycol Res 99:623–629
Olsson PA, Baath E, Jakobsen I (1997) Phosphorus effects on the mycelium and storage structures of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus as studied in the soil and roots by analysis of fatty acid signatures. Appl Environ Microb 63:3531–3538
Ortiz-Ceballos AI, Pena-cabriales JJ, Fragoso C (2007) Mycorrhizal colonization and nitrogen uptake by maize: combined effect of tropical earthworms and velvet bean mulch. Biol Fert Soils 44:181–186
Pattinson GS, Smith SE, Doube BM (1997) Earthworm Aporrectodea trapezoides had no effect on the dispersal of a vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus, Glomus intraradices. Soil Biol Biochem 29:1079–1088
Six J, Feller C, Denef K, Ogle SM, Sa JCD, Albrecht A (2002) Soil organic matter, biota and aggregation in temperate and tropical soils-effects of no-tillage. Agronomie 22:755–775
Staddon PL, Ramsey CB, Ostle N, Ineson P, Fitter AH (2003) Rapid turnover of hyphae of mycorrhizal fungi determined by AMS microanalysis of 14C. Science 300:1138–1140
Subler S, Baranski CM, Edwards CA (1997) Earthworm additions increased short-term nitrogen availability and leaching in two grain crop agro-ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 29:413–421
Tiunov AV, Scheu S (2004) Carbon availability controls the growth of detritivores (Lumbricidae) and their effect on nitrogen mineralization. Oecologia 138:83–90
Tu C, Booker FL, Watson DM, Chen X, Rufty TW, Shi W, Hu SJ (2006) Mycorrhizal mediation of plant N acquisition and residue decomposition: impact of mineral N inputs. Global Chang Biol 12:793–803
Tuffen F, Eason WR, Scullion J (2002) The effect of earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth of and 32P transfer between Allium porrum plants. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1027–1036
Van Vliet PCJ, Van der Stelt B, Rietberg PI, De Goede RGM (2007) Effects of organic matter content on earthworms and nitrogen mineralization in grassland soils. Eur J Soil Biol 43:222–229
Wang B, Qiu YL (2006) Phylogenetic distribution and evolution of mycorrhizas in land plants. Mycorrhiza 16:299–363
Wurst S, Dugassa-Gobena D, Langel R, Bonkoski M, Scheu S (2004) Combined effects of earthworms and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas on plant and aphid performance. New Phytol 163:169–173
Zarea MJ, Ghalavand A, Goltapeh EM (2009) Effects of mixed cropping, earthworms (Pheretima sp.), and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomus mosseae) on plant yield, mycorrhizal colonization rate, soil microbial biomass, and nitrogenase activity of free-living rhizosphere bacteria. Pedobiologia 4:223–235
Zareitalabad P, Heinze S, Rottmann N, Potthoff M, Dyckmans J, Joergensen RG (2010) Decomposition of 15N labelled maize leaf residues in soil affected by the feeding activity of endogeic geophagous Aporrectodea caliginosa. Soil Biol Biochem 42:276–282
Zelles L (1997) Phospholipid fatty acid profiles in selected member of soil microbial communities. Chemosphere 35:275–294
Zhang LD, Zhang JL, Christie P, Li XL (2008) Pre-inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi suppresses root knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) on cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Biol Fert Soils 45:205–211
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Special Scientific Fund for Non-profit Public Industry (Chinese Ministry of Agriculture, 201103003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Projects 31172037 and 30890132) and the Innovative Group Grant of NSFC (31121062), and the Scientific Research Foundation of China Agricultural University (Project 2010JS112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Wang, C., Li, X. et al. Impact of the earthworm Aporrectodea trapezoides and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices on 15N uptake by maize from wheat straw. Biol Fertil Soils 49, 263–271 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0716-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0716-z