Abstract
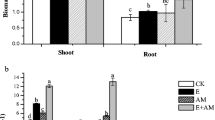
The interactive impacts of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF, Glomus intraradices) and earthworms (Aporrectodea trapezoides) on maize (Zea mays L.) growth and nutrient uptake were studied under near natural conditions with pots buried in the soil of a maize field. Treatments included maize plants inoculated vs. not inoculated with AMF, treated or not treated with earthworms, at low (25 mg kg−1) or high (175 mg kg−1) P fertilization rate. Wheat straw was added as feed for earthworms. Root colonization, mycorrhiza structure, plant biomass and N and P contents of shoots and roots, soil available P and NO −3 –N concentrations, and soil microbial biomass C and N were measured at harvest. Results indicated that mycorrhizal colonization increased markedly in maize inoculated with AMF especially at low P rate, which was further enhanced by the addition of earthworms. AMF and earthworms interactively increased maize shoot and root biomass as well as N and P uptake but decreased soil NO −3 –N and available P concentrations at harvest. Earthworm and AMF interaction also increased soil microbial biomass C, which probably improved root N and P contents and indirectly increased the shoot N and P uptake. At low P rate, soil N mobilization by earthworms might have reduced potential N competition by arbuscular mycorrhizal hyphae, resulting in greater plant shoot and root biomass. Earthworms and AMF interactively enhanced soil N and P availability, leading to greater nutrient uptake and plant growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato M, Ladd JN (1988) Assay for microbial biomass based on ninhydrin-reactive N in extracts of fumigated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 20:107–114
Artursson V, Finlay RD, Jansson JK (2006) Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and bacteria and their potential for stimulating plant growth. Environ Microbiol 8:1–10
Axmann H, Sebastianelli A, Arrillaga JL (1990) Sample preparation techniques of biological material for isotope analysis. In: Hardarson G (ed) Use of nuclear techniques in studies of soil-plant relationship. International Atomic Energy Agency, Viena, pp 41–53
Azcon R, Azcon-Aguilar C, Barea JM (1978) Effect of plant hormones present in bacterial cultures on the formation and responses to VA endomycorrhiza. New Phytol 80:359–364
Bago B, PfefferP E, Shachar-Hill Y (2000) Carbon metabolism and transport in arbuscular mycorrhizas. Plant Physiol 124:924–957
Bardgett RD, Bowman WD, Kaufmann R, Schmidt SK (2005) A temporal approach to linking aboveground and belowground ecology. Trends Ecology Evol 20:634–641
Bonkowski M, Griffiths BS, Ritz K (2000) Food preferences of earthworms for soil fungi. Pedobiologia 44:666–676
Bradford MA, Jones TH, Bardgett RD, Black HIJ, Boag B, Bonkowski M, Cook R, Eggers T, Gange AC, Grayston SJ, Kandeler E, McCaig AE, Newington JE, Prosser JI, Setälä H, Staddon PL, Tordoff GM, Tscherko D, Lawton JH (2002) Impacts of soil faunal community composition on model grassland ecosystems. Science 298:615–618
Brookes PC, Kragt JF, Powlson DS, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and release of soil N: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass N in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842
Brown GG, Barois I, Lavelle P (2000) Regulation of soil organic matter dynamics and microbial activity in the drilosphere and the role of interactions with other edaphic functional domains. Eur J Soil Biol 36:177–198
Brussaard L, Pulleman MM, Ouédraogo E, Mando A, Six J (2007) Soil fauna and soil function in the fabric of the food web. Pedobiologia 50:447–462
Calvet C, Pera J, Barea JM (1993) Growth response of Marigold (Tagetes erecta L.) to inoculation with Glomus mosseae, Trichoderma aureoviridae and Pythium ultimum in a peat–perlite mixture. Plant Soil 148:1–6
Campbell CA, Lafond GP, Leyshon AJ, Zentner RP, Janzen HH (1991) Effect of cropping practices on the initial potential rate of nitrogen mineralization in a thin Black Chernozem. Can J Soil Sci 71:43–53
Campbell CA, Biederbeck VO, Wen G, Zentner RP, Schoenau J, Hahn D (1999) Seasonal trends in soil biochemical attributes: effects of crop rotations in the semi-arid prairie. Can J Soil Sci 79:73–84
Cao Z-P, Qiao Y-H, Wang B-Q, Qin X (2006) Influence of agricultural intensification on the earthworm community in arable farmland in the North China Plain. Eur J Soil Biol 42:362–366
Cheng J-M, Yu X-Z, Wong M-H (2005) Roles of earthworm–mycorrhiza interactions on phytoremediation of Cd contaminated soil. Aata Ecologica Sinica 25:1256–1263
Cheng J-M, Yu X-Z, Wong M-H (2006) Effect of earthworm-mycorrhiza interaction on available nutrients and ryegrass growth in Cd contaminated soil. J Agro-Environ Sci 25:685–689
Cui ZL, Zhang FS, Chen XP (2008) On-farm estimation of indigenous nitrogen supply for site-specific nitrogen management in the North China plain. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 81:37–47
Curry JP, Byrne D (1992) The role of earthworms in straw decomposition and nitrogen turn over in arable land inIreland. Soil Biol Biochem 24:1409–1412
Curry JP, Schmidt O (2007) The feeding ecology of earthworms—a review. Pedobiologia 50:463–477
Devliegher W, Verstraete W (1997) The effect of Lumbricus terrestris on soil in relation to plant growth: effects of nutrient-enrichment processes (NEP) and gut-associated processes (GAP). Soil Biol Biochem 29:341–346
Edwards CA (2004) Earthworm ecology. CRC, Boca Raton, p 441
Edwards CA, Bohlen PJ (1996) Biology and ecology of earthworms, 3rd edn. Chapman and Hall, London
Eisenhaue N, Konig S, Renker ACW (2009) Impacts of earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomus intraradices) on plant performance are not interrelated. Soil Biol Biochem 41:561–567
Eisenhauer N, Scheu S (2008a) Earthworms as drivers of the competition between grasses and legumes. Soil Biol Biochem 40:2650–2659
Eisenhauer N, Scheu S (2008b) Invasibility of experimental grassland communities: the role of earthworms, plant functional group identity and seed size. Oikos 117:1026–1036
Gange AC, Brown VK, Sinclair GS (1993) Vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: a determinant of plant community structure in early succession. Funct Ecol 7:616–622
Gormsen D, Olsson P, Hedlund K (2004) The influence of collembolans and earthworms on AM fungal mycelium. Appl Soil Ecol 27:211–220
Jakobsen I, Abbott LK, Robson AD (1992) External hyphae of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with trifolium-subterraneum L. 1. Spread of hyphae and phosphorus inflow into roots. New Phytol 120:371–380
Jeffries P, Gianinazz S, Perotto S, Turnau K, Barea JM (2003) The contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in sustainable maintenance of plant health and soil fertility. Biol Fert Soils 37:1–16
Jenkinson DS, Ladd JN (1981) Microbial biomass in soil: measurement and turnover. In: Paul EA, Ladd JN (eds) Soil biochemistry, vol 5. Decker, New York, pp 415–417
Johansson JF, Paul LR, Finlay RD (2004) Microbial interactions in the mycorrhizosphere and their significance for sustainable agriculture. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:1–13
Jordan D, Kremer RJ, Bergfield WA, Kim KY, Cacnio VN (1995) Evaluation of microbial methods as potential indicators of soil quality in historical agricultural fields. Biol Fertil Soil 19:297–302
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen—inorganic forms. In: Page Al (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part 1. 2nd ed. Agron. Monogr. 9. ASA and SSSA, Madison, pp 643–698
Koerselman W, Meuleman AFM (1996) The vegetation N:P ratio: a new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J Appl Ecol 33:1441–1450
Laossi KR, Ginot A, Noguera DC, Blouin M, Barot S (2010) Earthworm effects on plant growth do not necessarily decrease with soil fertility. Plant Soil 328:109–118
Lavelle P, Melendez G, Pashanasi B, Schaefer R (1992) Nitrogen mineralization and reorganization in casts of the geophagous tropical earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus (Glossoscolecidae). Biol Fert Soil 14:49–53
Lawrence B, Fisk MC, Fahey TJ (2003) Influence of nonnative earthworms on mycorrhizal colonization of sugar maple (Acer saccharum). New Phytol 157:145–153
Lussenhop J (1996) Collembola as mediators of microbial symbiont effects upon soybean. Soil Biol Biochem 28:363–369
Ma Y, Dickinson NM, Wong MH (2006) Beneficial effect of earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on establishment of leguminous trees on Pb/Zn mine tailings. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1403–1412
Magdoff F, Weil RR (2004) Soil organic matter in sustainable agriculture. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 15–21
McGonigle TP, Miller MH, Evans DG, Fairchild GL, Swan JA (1990) A new method which gives an objective-measure of colonization of roots by vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 115:495–501
McLean MA, Migge-Kleian S, Parkinson D (2006) Earthworm invasions of ecosystems devoid of earthworms: effects on soil microbes. Biol Invasions 8:1257–1273
Milcu A, Partsch S, Scherber C, Weisser WW, Scheu S (2008) Earthworms and legumes control litter decomposition in a plant diversity gradient. Ecology 89:1872–1882
Milleret R, Renée-Claire LB, Jean-Michel G (2009) Root, mycorrhiza and earthworm interactions: their effects on soil structuring processes, plant and soil nutrient concentrations and plant biomass. Plant Soil 316:1–12
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Newman EI (1966) A method of estimating total length of root in a sample. J Appl Ecol 3:139–145
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorous in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA Circular 939:1–8
Ortiz-Ceballos AI, Pena-cabriales JJ, Fragoso C (2007) Mycorrhizal colonization and nitrogen uptake by maize: combined effect of tropical earthworms and velvetbean mulch. Biol Fert Soil 44:181–186
Patron JC, Sanchez P, Brown GG (1999) Phosphorus in soil and Brachialis decumbens plants as affected by the geophagous earthworm Pontoscolex corethrurus and P fertilization. Pedobiologia 43:547–556
Pattinson GS, Smith SE, Doube BM (1997) Earthworm Aporrectodea trapezoides had no effect on the dispersal of a vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi Globus intraradices. Soil Biol Biochem 29:1079–1088
Raghubanshi AS, Srivastava SC, Singh RS, Singh JS (1990) Nutrient release in leaf litter. Nature 346:227
Scheu S (1987) Microbial activity and nutrient dynamics in earthworm casts (Lumbricidae). Biology and Fertility of Soils 5:230–234
Scheu S (1994) There is an earthworm mobilizable nitrogen pool in soil. Pedobiologia 38:243–249
Scheu S (2003) Effects of earthworms on plant growth: patterns and perspectives. Pedobiologia 47:846–856
Singh JS, Singh DP, Kashyap AK (2009) A comparative account of the microbial biomass-N and N-mineralization of soils under natural forest, grassland and crop field from dry tropical region. India Plant Soil Environ 55:223–230
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic, San Diego
Soils Laboratory Staff, Royal Tropical Institute (1984) Analytical methods of the service laboratory for soil, plant and water analysis. Part 1: methods for soil analysis. Royal Tropical Institute, Amsterdam
Sparling GP, Feltham CW, Reynolds J, West AW, Singleton P (1990) Estimation of soil microbial carbon by fumigation–extraction method. Use on soils of high organic matter content, and a reassessment of the KEc-factors. Soil Biol Biochem 22:301–307
Subler S, Baranski CM, EdwardsC A (1997) Earthworm additions increased short-term nitrogen availability and leaching in two grain crop agro-ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 29:413–421
Svensson K, Friberg H (2007) Changes in active microbial biomass by earthworms and grass amendments in agricultural soil. Biol Fertil Soils 44:223–228
Tiunov AV, Dobrovolskaya TG (2002) Fungal and bacterial communities in Lumbricus terrestris burrow walls: a laboratory experiment. Pedobiologia 46:595–605
Tuffen F, Eason WR, Scullion J (2002) The effect of earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on rowth of and 32P transfer between Allium porrum plants. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1027–1036
Van Aarle IM, Soderstrom B, Olsson PA (2003) Growth and interactions of arbuscula rmycorrhizal fungi in soils from limestone and acid rock habitats. Soil Biol Biochem 35:1557–1564
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Walkley A (1947) A critical examination of a rapid method for determining organic carbon in soils—effect of variations in digestion conditions and of inorganic soil constituents. Soil Sci 63:251–264
Wardle DA (2002) Communities and ecosystems: linking the aboveground and belowground components. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Wardle DA (2006) The influence of biotic interactions on soil biodiversity. Ecol Lett 9:870–886
Wardle DA, Bardgeet RD, Klironomos JN, Setäl H, Van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2004) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science 304:1629–1633
Welke SE, Parkinson D (2003) Effect of Aporrectodea trapezoides activity on seedling growth of Pseudotsuga menziesii, nutrient dynamics and microbial activity in different soils. Forest Ecol Manag 173:169–186
Wurst S, Dugassa-Gobena D, Langel R, Bonkoski M, Scheu S (2004) Combined effects of earthworms and vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhizas on plant and aphid performance. New Phytol 163:169–173
Wurst S, Allema B, Duyts H, Van der Putten WH (2008) Earthworms counterbalance the negative effect of microorganisms on plant diversity and enhance the tolerance of grasses to nematodes. Oikos 117:711–718
Zarea MJ, Ghalavand A, Goltapeh EM (2009) Effects of mixed cropping, earthworms (Pheretima sp.), and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomus mosseae) on plant yield, mycorrhizal colonization rate, soil microbial biomass, and nitrogenase activity of free-living rhizosphere bacteria. Pedobiologia 4:223–235
Zhang L, Zhang J, Christie P, Li X (2008) Pre-inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi suppresses root knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) on cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Biol Fertil Soils 45:205–211
Zhang B, Liu Y, Li C, Hu F, Velde B (2010) Long-term fertilization influences on clay mineral composition and ammonium adsorption in a rice paddy soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 74:1239–1247
Zhang H, Wu X, Li G, Qin P (2011) Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate-solubilizing fungus (Mortierella sp.) and their effects on Kostelelzkya virginica growth and enzyme activities of rhizosphere and bulk soils at different salinities. Biol Fertil Soils 47:543–554
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Special Scientific Fund for Non-profit Public Industry (MOA, 201103003) and the Project Sponsored by the Scientific Research Foundation in China Agricultural University (Project 2010JS112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ll, H., Li, X., Dou, Z. et al. Earthworm (Aporrectodea trapezoides)–mycorrhiza (Glomus intraradices) interaction and nitrogen and phosphorus uptake by maize. Biol Fertil Soils 48, 75–85 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-011-0610-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-011-0610-0