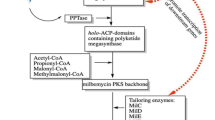
Abstract
Milbemycins and their semisynthetic derivatives are recognized as effective and eco-friendly pesticides, whereas the high price limits their widespread applications in agriculture. One of the pivotal questions is the accumulation of milbemycin-like by-products, which not only reduces the yield of the target products milbemycin A3/A4, but also brings difficulty to the purification. With other analogous by-products abolished, α9/α10 and β-family milbemycins remain to be eliminated. Herein, we solved these issues by engineering of post-modification steps. First, Cyp41, a CYP268 family cytochrome P450, was identified to participate in α9/α10 biosynthesis. By deleting cyp41, milbemycin α9/α10 was eliminated with an increase of milbemycin A3/A4 titer from 2382.5 ± 55.7 mg/L to 2625.6 ± 64.5 mg/L. Then, MilE, a CYP171 family cytochrome P450, was determined to be responsible for the generation of the furan ring between C6 and C8a of milbemycins. By further overexpression of milE, the production of β-family milbemycins was reduced by 77.2%. Finally, the titer of milbemycin A3/A4 was increased by 53.1% to 3646.9 ± 69.9 mg/L. Interestingly, overexpression of milE resulted in increased transcriptional levels of milbemycin biosynthetic genes and production of total milbemycins, which implied that the insufficient function of MilE was a limiting factor to milbemycin biosynthesis. Our research not only provides an efficient engineering strategy to improve the production of a commercially important product milbemycins, but also offers the clues for future study about transcriptional regulation of milbemycin biosynthesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chamberland S, LEE M, Lomovskaya O (1997) Fungal efflux pump inhibitors. International Patent: PCT/US98/20916
Child SA, Naumann EF, Bruning JB, Bell SG (2018) Structural and functional characterisation of the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP268A2 from Mycobacterium marinum. Biochem J 475(4):705–722. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20170946
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39(4):783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Goegelman RT (1985) Antihelmintic macrocyclic lactones and their production by fermentation. Eur Pat 86303294:2
Hayes B, Schnitzler B, Wiseman S, Snyder DE (2015) Field evaluation of the efficacy and safety of a combination of spinosad and milbemycin oxime in the treatment and prevention of naturally acquired flea infestations and treatment of intestinal nematode infections in dogs in Europe. Vet Parasitol 207(1):99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.11.011
He H, Ye L, Li C, Wang H, Guo X, Wang X, Zhang Y, Xiang W (2018) SbbR/SbbA, an important ArpA/AfsA-like system, regulates milbemycin production in Streptomyces bingchenggensis. Front Microbiol 9:1064. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01064
Horbal L, Marques F, Nadmid S, Mendes MV, Luzhetskyy A (2018) Secondary metabolites overproduction through transcriptional gene cluster refactoring. Metab Eng 49:299–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.09.010
Huang J, Zha W, An T, Dong H, Huang Y, Wang D, Yu R, Duan L, Zhang X, Peters RJ, Dai Z, Zi J (2019) Identification of RoCYP01 (CYP716A155) enables construction of engineered yeast for high-yield production of betulinic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(17):7029–7039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10004-z
Ikeda H, Omura S (1997) Avermectin biosynthesis. Chem Rev 97(7):2591–2610. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr960023p
Kasey CM, Zerrad M, Li Y, Cropp TA, Williams GJ (2018) Development of transcription factor-based designer macrolide biosensors for metabolic engineering and synthetic biology. ACS Synth Biol 7(1):227–239. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.7b00287
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical streptomyces genetics, vol 412 John Innes Foundation Norwich
Kim MS, Cho WJ, Song MC, Park SW, Kim K, Kim E, Lee N, Nam SJ, Oh KH, Yoon YJ (2017) Engineered biosynthesis of milbemycins in the avermectin high-producing strain Streptomyces avermitilis. Microb Cell Factories 16(1):9–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0626-8
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Li L, Wei K, Liu X, Wu Y, Zheng G, Chen S, Jiang W, Lu Y (2019) aMSGE: advanced multiplex site-specific genome engineering with orthogonal modular recombinases in actinomycetes. Metab Eng 52:153–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.12.001
Liu W, Zhang Q, Guo J, Chen Z, Li J, Wen Y, Elliot MA (2015) Increasing avermectin production in Streptomyces avermitilis by manipulating the expression of a novel TetR-family regulator and its target gene product. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(15):5157–5173. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00868-15
McKellar QA, Benchaoui HA (1996) Avermectins and milbemycins. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 19(5):331–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2885.1996.tb00062.x
Merola VM, Eubig PA (2018) Toxicology of avermectins and milbemycins (macrocyclic lactones) and the role of P-glycoprotein in dogs and cats. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 48(6):991–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvsm.2018.07.002
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, New York
Nelson DR (2009) The cytochrome p450 homepage. Hum Genomics 4(1):59–65
Niu G, Chater KF, Tian Y, Zhang J, Tan H (2016) Specialised metabolites regulating antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces spp. FEMS Microbiol Rev 40(4):554–573. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuw012
Nonaka K, Kumasaka C, Okamoto Y, Maruyama F, Yoshikawa H (1999) Bioconversion of milbemycin-related compounds: biosynthetic pathway of milbemycins. J Antibiot 52(2):109–116. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.52.109
Pogorevc D, Panter F, Schillinger C, Jansen R, Wenzel SC, Muller R (2019) Production optimization and biosynthesis revision of corallopyronin A, a potent anti-filarial antibiotic. Metab Eng 55:201–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.07.010
Rudolf JD, Chang C, Ma M, Shen B (2017) Cytochromes P450 for natural product biosynthesis in Streptomyces: sequence, structure, and function. Nat Prod Rep 34(9):1141–1172. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7np00034k
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (3-volume set)
Sherwood EJ, Bibb MJ (2013) The antibiotic planosporicin coordinates its own production in the actinomycete Planomonospora alba. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(27):E2500–E2509. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1305392110
Sun P, Zhao Q, Yu F, Zhang H, Wu Z, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Liu W (2013) Spiroketal formation and modification in avermectin biosynthesis involves a dual activity of AveC. J Am Chem Soc 135(4):1540–1548. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja311339u
Takiguchi Y, Mishima H, Okuda M, Terao M, Aoki A, Fukuda R (1980) Milbemycins, a new family of macrolide antibiotics: fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical properties. J Antibiot 33(10):1120–1127. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.33.1120
Tatsuta K (2016) Celebrating the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine of Dr Satoshi Omura. J Antibiot 69(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2015.113
Wang X, Wang X, Xiang W (2009) Improvement of milbemycin-producing Streptomyces bingchenggensis by rational screening of ultraviolet-and chemically induced mutants. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(6):1051–1056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-9986-5
Wang X, Wang C, Sun X, Xiang W (2010a) 5-ketoreductase from Streptomyces bingchengensis: overexpression and preliminary characterization. Biotechnol Lett 32(10):1497–1502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0320-y
Wang X, Yan Y, Zhang B, An J, Wang J, Tian J, Jiang L, Chen Y, Huang S, Yin M, Zhang J, Gao A, Liu C, Zhu Z, Xiang W (2010b) Genome sequence of the milbemycin-producing bacterium Streptomyces bingchenggensis. J Bacteriol 192(17):4526–4527. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00596-10
Wang X, Zhang B, Yan Y, An J, Zhang J, Liu C, Xiang W (2013) Characterization and analysis of an industrial strain of Streptomyces bingchenggensis by genome sequencing and gene microarray. Genome 56(11):677–689. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2013-0098
Wang H, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Zhang B, Liu C, He H, Wang X, Xiang W (2014) Combined application of plasma mutagenesis and gene engineering leads to 5-oxomilbemycins A3/A4 as main components from Streptomyces bingchenggensis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(23):9703–9712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5970-6
Wang W, Li S, Li Z, Zhang J, Fan K, Tan G, Ai G, Lam SM, Shui G, Yang Z, Lu H, Jin P, Li Y, Chen X, Xia X, Liu X, Dannelly HK, Yang C, Yang Y, Zhang S, Alterovitz G, Xiang W, Zhang L (2020) Harnessing the intracellular triacylglycerols for titer improvement of polyketides in Streptomyces. Nat Biotechnol 38(1):76–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0335-4
Wei K, Wu Y, Li L, Jiang W, Hu J, Lu Y, Chen S (2018) MilR2, a novel TetR family regulator involved in 5-oxomilbemycin A3/A4 biosynthesis in Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(20):8841–8853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9280-2
Zhang J, An J, Wang J, Yan Y, He H, Wang X, Xiang W (2013) Genetic engineering of Streptomyces bingchenggensis to produce milbemycins A3/A4 as main components and eliminate the biosynthesis of nanchangmycin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5255-5
Zhang Y, He H, Liu H, Wang H, Wang X, Xiang W (2016) Characterization of a pathway-specific activator of milbemycin biosynthesis and improved milbemycin production by its overexpression in Streptomyces bingchenggensis. Microb Cell Factories 15(1):152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0552-1
Zhu T, Cheng X, Liu Y, Deng Z, You D (2013) Deciphering and engineering of the final step halogenase for improved chlortetracycline biosynthesis in industrial Streptomyces aureofaciens. Metab Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2013.06.003
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Professor Mervyn Bibb (John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK) for providing S. coelicolor M1146, Professor Mark Buttner (John Innes Centre, Norwich, UK) for providing plasmid pIJ10500, and Doctor Weishan Wang (Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China) for providing promoter pKasO*.
Funding
This work received financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31601701 and 31572070) and General Financial Grant from China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2016 M600152).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Haiyan Wang, Xu Cheng, Xiangjing Wang, and Wensheng Xiang designed the research. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Xu Cheng, Haiyan Wang, and Yuqing Liu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Haiyan Wang and Xu Cheng. Shanshan Li and Yanyan Zhang modified the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have filed a provisional patent for this work to the China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA). W. X., X.C., H.W., Y.L., and X.W. are inventors on the provisional patent application (CN202010032599.2, filed 13 January 2020).
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 518 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Cheng, X., Liu, Y. et al. Improved milbemycin production by engineering two Cytochromes P450 in Streptomyces bingchenggensis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 2935–2946 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10410-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10410-8