Abstract
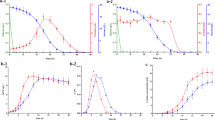
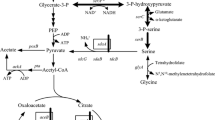
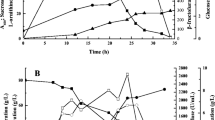
The direct fermentative production of l-serine by Corynebacterium glutamicum from sugars is attractive. However, superfluous by-product accumulation and low l-serine productivity limit its industrial production on large scale. This study aimed to investigate metabolic and bioprocess engineering strategies towards eliminating by-products as well as increasing l-serine productivity. Deletion of alaT and avtA encoding the transaminases and introduction of an attenuated mutant of acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) increased both l-serine production level (26.23 g/L) and its productivity (0.27 g/L/h). Compared to the parent strain, the by-products l-alanine and l-valine accumulation in the resulting strain were reduced by 87 % (from 9.80 to 1.23 g/L) and 60 % (from 6.54 to 2.63 g/L), respectively. The modification decreased the metabolic flow towards the branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and induced to shift it towards l-serine production. Meanwhile, it was found that corn steep liquor (CSL) could stimulate cell growth and increase sucrose consumption rate as well as l-serine productivity. With addition of 2 g/L CSL, the resulting strain showed a significant improvement in the sucrose consumption rate (72 %) and the l-serine productivity (67 %). In fed-batch fermentation, 42.62 g/L of l-serine accumulation was achieved with a productivity of 0.44 g/L/h and yield of 0.21 g/g sucrose, which was the highest production of l-serine from sugars to date. The results demonstrated that combined metabolic and bioprocess engineering strategies could minimize by-product accumulation and improve l-serine productivity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartek T, Zönnchen E, Klein B, Gerstmeir R, Makus P, Lang S, Oldiges M (2010) Analysing overexpression of l-valine biosynthesis genes in pyruvate-dehydrogenase-deficient Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 37:263–270
Blombach B, Hans S, Bathe B, Eikmanns BJ (2009) Acetohydroxyacid synthase, a novel target for improvement of L-lysine production by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:419–427
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chen Q, Wang Q, Wei G, Liang Q, Qi Q (2011) Production in Escherichia coli of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) with differing monomer compositions from unrelated carbon sources. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:4886–4893
Eggeling L (2007) L-Serine and glycine. In: Amino acid biosynthesis—pathways, regulation and metabolic engineering. Springer, Berlin 5:259–272
Elišáková V, Pátek M, Holátko J, Nešvera J, Leyval D, Goergen J-L, Delaunay S (2005) Feedback-resistant acetohydroxy acid synthase increases valine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:207–213
Gu P, Yang F, Su T, Li F, Li Y, Qi Q (2014) Construction of an L-serine producing Escherichia coli via metabolic engineering. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:1443–1450
Hou X, Chen X, Zhang Y, Qian H, Zhang W (2012) L-Valine production with minimization of by-products’ synthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum and Brevibacterium flavum. Amino Acids 43:2301–2311
Hsiao HY, Wei T (1986) Enzymatic production of L-serine with a feedback control system for formaldehyde addition. Biotechnol Bioeng 28:1510–1518
Ikeda M, Takeno S (2013) Amino acid production by Corynebacterium glutamicum. In: Yukama H, Inui M (eds) Microbiology monographs 23, Corynebacterium glutamicum. Springer, Berlin, pp 107–147
Izumi Y, Yoshida T, Miyazaki SS, Mitsunaga T, Ohshiro T, Shimao M, Miyata A, Tanabe T (1993) L-Serine production by a methylotroph and its related enzymes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:427–432
Jojima T, Fujii M, Mori E, Inui M, Yukawa H (2010) Engineering of sugar metabolism of Corynebacterium glutamicum for production of amino acid L-alanine under oxygen deprivation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:159–165
Kennedy M, Krouse D (1999) Strategies for improving fermentation medium performance: a review. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23:456–475
Lai S, Zhang Y, Liu S, Liang Y, Shang X, Chai X, Wen T (2012) Metabolic engineering and flux analysis of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-serine production. Sci China Life Sci 55:283–290
Leuchtenberger W, Huthmacher K, Drauz K (2005) Biotechnological production of amino acids and derivatives: current status and prospects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:1–8
Leyval D, Uy D, Delaunay S, Goergen J, Engasser J (2003) Characterisation of the enzyme activities involved in the valine biosynthetic pathway in a valine-producing strain of Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biotechnol 104:241–252
Li Y, Chen G-K, Tong X-W, Zhang H-T, Liu X-G, Liu Y-H, Lu F-P (2012) Construction of Escherichia coli strains producing L-serine from glucose. Biotechnol Lett 34:1525–1530
Marienhagen J, Eggeling L (2008) Metabolic function of Corynebacterium glutamicum aminotransferases AlaT and AvtA and impact on L-valine production. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7457–7462
Marienhagen J, Kennerknecht N, Sahm H, Eggeling L (2005) Functional analysis of all aminotransferase proteins inferred from the genome sequence of Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Bacteriol 187:7639–7646
Netzer R, Peters-Wendisch P, Eggeling L, Sahm H (2004) Cometabolism of a nongrowth substrate: L-serine utilization by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7148–7155
Peters-Wendisch P, Stolz M, Etterich H, Kennerknecht N, Sahm H, Eggeling L (2005) Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for L-serine production. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7139–7144
Schäfer A, Tauch A, Jäger W, Kalinowski J, Thierbach G, Pühler A (1994) Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene 145:69–73
Stolz M, Peters-Wendisch P, Etterich H, Gerharz T, Faurie R, Sahm H, Fersterra H, Eggeling L (2007) Reduced folate supply as a key to enhanced L-serine production by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:750–755
Van der Rest M, Lange C, Molenaar D (1999) A heat shock following electroporation induces highly efficient transformation of Corynebacterium glutamicum with xenogeneic plasmid DNA. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:541–545
Wieschalka S, Blombach B, Eikmanns BJ (2012) Engineering Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of pyruvate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:449–459
Xu G, Jin X, Guo W, Dou W, Zhang X, Xu Z (2014) Characterization, modification, and overexpression of 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase in Corynebacterium glutamicum for enhancing L-serine production. Ann Microbiol. doi:10.1007/s13213-014-0936-6
Zhang X, Xu G, Li H, Dou W, Xu Z (2014) Effect of cofactor folate on the growth of Corynebacterium glutamicum SYPS-062 and L-serine accumulation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173:1607–1617
Zhang X, Zhang R, Bao T, Rao Z, Yang T, Xu M, Xu Z, Li H, Yang S (2014b) The rebalanced pathway significantly enhances acetoin production by disruption of acetoin reductase gene and moderate-expression of a new water-forming NADH oxidase in Bacillus subtilis. Metab Eng 23:34–41
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the High Tech Development Program of China (863 Project, No. 2012AA022102) and the production project of Ministry of Education of Guangdong province (No. 2012B091000083).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Q., Zhang, X., Luo, Y. et al. l-Serine overproduction with minimization of by-product synthesis by engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 1665–1673 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6243-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6243-0