Abstract
Key message
Using leaf osmotic potential and plant survival rate as chilling-tolerant trait indices, we identified two major quantitative trait loci qLOP2 and qPSR2 - 1 (39.3-kb region) and Os02g0677300 as the cold-inducible gene for these loci.
Abstract
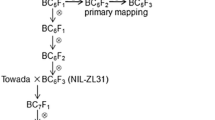
Chilling stress tolerance (CST) at the seedling stage is an important trait affecting rice production in temperate climate and high-altitude areas. To identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with CST, a mapping population consisting of 151 BC2F1 plants was constructed by using chilling-tolerant Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) as a donor parent and chilling-sensitive indica as a recurrent parent. With leaf osmotic potential (LOP) and plant survival rate (PSR) as chilling-tolerant trait indexes, two major QTLs, qLOP2 (LOD = 3.8) and qPSR2-1 (LOD = 3.3), were detected on the long arm of chromosome 2 by composite interval mapping method in QTL Cartographer software, which explained 10.1 and 12.3 % of the phenotypic variation, respectively. In R/QTL analyzed result, their major effects were also confirmed. Using molecular marker RM318 and RM106, qLOP2 and qPSR2-1 have been introgressed into chilling-sensitive varieties (93-11 and Yuefeng) by marker-assisted selection procedure (MAS), which resulted in 16 BC5F3 BILs that chilling tolerance have significantly enhanced compare with wild-type parents (P < 0.01). Therefore, two large segregating populations of 11,326 BC4F2 and 8,642 BC4F3 were developed to fine mapping of qLOP2 and qPSR2-1. Lastly, they were dissected to a 39.3-kb candidate region between marker RM221 and RS8. Expression and sequence analysis results indicated that Os02g0677300 was a cold-inducible gene for these loci. Our study provides novel alleles for improving rice CST by MAS and contributes to the understanding of its molecular mechanisms.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CST:
-
Chilling stress tolerance
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- PSR:
-
Plant survival rate
- LOP:
-
Leaf osmotic potential
- BIL:
-
Backcross introgression lines
- CBF:
-
Calmodulin-binding transcription activator
- DREB:
-
Dehydration-responsive element binding
References
Agarwal P, Agarwal PK, Joshi AJ, Sopory SK, Reddy MK (2010) Overexpression of PgDREB2A transcription factor enhances abiotic stress tolerance and activates downstream stress-responsive genes. Mol Biol Rep 37(2):1125–1135
Alm V, Busso CS, Ergon A, Rudi H, Larsen A, Humphreys MW, Rognli O (2011) A QTL analyses and comparative genetic mapping of frost tolerance, winter survival and drought tolerance in meadow fescue (Festuca pratensis Huds.). Theor Appl Genet 123:369–382
Andaya VC, Mackill DJ (2003a) Mapping of QTLs associated with cold tolerance during the vegetative stage in rice. J Exp Bot 54:2579–2585
Andaya VC, Mackill DJ (2003b) QTLs conferring cold tolerance at the booting stage of rice using recombinant inbred lines from a japonica × indica cross. Theor Appl Genet 106(6):1084–1090
Andaya VC, Tai TH (2006) Fine mapping of the qCTS12 locus, a major QTL for seedling cold tolerance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 113(3):467–475
Andaya VC, Tai TH (2007) Fine mapping of the qCTS4 locus associated with seedling cold tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Breed 20(4):349–358
Arvind K, Hei L, Islam AKMR, Shoshi K (2012) Comparative transcriptome analysis of AP2/EREBP gene family under normal and hormone treatments, and under two drought stresses in NILs setup by Aday Selection and IR64. Mol Genet Genomics 287:1–19
Ashikari M, Matsuoka M (2006) Identification, isolation and pyramiding of quantitative trait loci for rice breeding. Trends Plant Sci 11(7):344–350
Brar DS, Khush GS (1997) Alien introgression in rice. Plant Mol Biol 35:35–47
Caton BP, Foin TC, Gibson KD, Hill JE (1998) A temperature-based model of direct-, water-seeded rice (Oryza sativa) stand establishment in California. Agric For Meteorol 90(1–2):91–102
Chawade A, Lindlëf A, Olsson B, Olsson O (2013) Global expression profiling of low temperature induced genes in the chilling tolerant japonica rice jumli marshi. PLoS ONE 8(12):e81729
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate–phenol–chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold value for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Dai XY, Xu YY, Ma QB, Xu WY, Wang T, Xue YB, Chong K (2007) Overexpression of an R1R2R3 MYB Gene, OsMYB3R-2, increases tolerance to freezing, drought, and salt stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 143:1739–1751
Dubouzet JG, Sakuma Y, Ito Y, Kasuga M, Dubouzet EG, Miura S, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) OsDREB genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.) encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J 334:751–763
Fowler S, Thomashow MF (2002) Arabidopsis transcriptome profiling indicates that multiple regulatory pathways are activated during cold acclimation in addition to the CBF cold response pathway. Plant Cell 14:1675–1690
Fowler SG, Cook D, Thomashow MF (2005) Low temperature induction of Arabidopsis CBF1, 2, and 3 is gated by the circadian clock. Plant Physiol 137:961–968
Francia E, Barabaschi D, Tondelli A, Laido G, Rizza F, Stanca AM, Busconi M, Fogher C, Stockinger EJ, Pecchioni N (2007) Fine mapping of a HvCBF gene cluster at the frost resistance locus Fr-H2 in barley. Theor Appl Genet 115:1083–1091
Han LZ, Qiao YL, Zhang SY, Zhang YY, Cao GL, Kim JW, Lee K, Koh HJ (2007) Identification of quantitative trait loci for cold response of seedling vigor traits in rice. J Genet Genomics 34(3):239–246
Huang J, Sun SJ, Xu DQ, Yang X, Bao YM, Wang ZF (2009) Increased tolerance of rice to cold, drought and oxidative stresses mediated by the overexpression of a gene that encodes the zinc finger protein ZFP245. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 389:556–561
Huang J, Sun S, Xu D, Lan H, Sun H, Wang Z (2012) A TFIIIA-type zinc finger protein confers multiple abiotic stress tolerances in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 80:337–350
Ji SL, Jiang L, Wang YH, Zhang WW, Liu X, Liu SJ, Chen LM, Zhai HQ, Wan JM (2009) Quantitative trait loci mapping and stability for low temperature germination ability of rice. Plant Breed 128(4):387–392
Jiang L, Xun M, Wang J, Wan J (2008) QTL analysis of cold tolerance at seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using recombination inbred lines. J Cereal Sci 48(1):173–179
Knox AK, Li C, Vagujfalvi A, Galiba G, Stockinger EJ, Dubcovsky J (2008) Identification of candidate CBF genes for the frost tolerance locus Fr-Am 2 in Triticum monococcum. Plant Mol Biol 67:257–270
Koseki M, Kitazawa N, Yonebayashi S, Maehara Y, Wang ZX, Minobe Y (2010) Identification and fine mapping of a major quantitative trait locus originating from wild rice, controlling cold tolerance at the seedling stage. Mol Genet Genomics 284(1):45–54
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Lee SC, Huh KW, An K, An G, Kim SR (2004) Ectopic expression of a cold-inducible transcription factor, CBF1/DREB1b, in transgenic rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Cells 18:107–114
Li F, Guo S, Zhao Y, Chen D, Chong K, Xu Y (2010) Overexpression of a homopeptide repeat-containing bHLH protein gene (OrbHLH001) from Dongxiang Wild Rice confers freezing and salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 29(9):977–986
Lilley JM, Ludlow MM, McCouch SR, O’Toole JC (1996) Locating QTL for osmotic adjustment and dehydration tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 47(302):1427–1436
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander ES (1992) Mapping genes controlling quantitative traits with MAPMAKER/QTL 1.1. Whitehead Institute technical report, 2nd edn. Massachusetts
Liu FX, Xu WY, Song Q, Tan LB, Liu JY, Zhu ZF, Fu YC, Su Z, Sun CQ (2013) Microarray-assisted fine-mapping of quantitative trait loci for cold tolerance in rice. Mol Plant 6(3):757–767
Lou Q, Chen L, Sun Z, Xing Y, Li J, Xu X, Mei H, Luo L (2007) A major QTL associated with cold tolerance at seedling stage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 158(1–2):87–94
Maclean JL, Dawe DC, Hardy B, Hettel GP (2002) In: Rice almanac: source book for the most important economic activity on earth, 3rd edn. The International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, Philippines, p 6–8
Mao DH, Chen CY (2012) Colinearity and similar expression pattern of rice DREB1s reveal their functional conservation in the cold-responsive pathway. PLoS ONE 7(10):e47275
Maruyama K et al (2004) Identification of cold-inducible downstream genes of the Arabidopsis DREB1A/CBF3 transcriptional factor using two microarray systems. Plant J 38:982–993
Miller AK, Galiba G, Dubcovsky J (2006) A cluster of 11 CBF transcription factors is located at the frost tolerance locus Fr-Am 2 in Triticum monococcum. Mol Genet Genomics 275:193–203
Miura K, Lin SY, Yano M, Nagamine T (2001) Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling low temperature germinability in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed Sci 51(4):293–299
Morsya MR, Almutairia AM, Gibbonsa J, Yunb SJ, Reyes BG (2005) The OsLti6 genes encoding low-molecular-weight membrane proteins are differentially expressed in rice cultivars with contrasting sensitivity to low temperature. Gene 34(3):171–180
Nagamine T (1991) Genetic control of tolerance to chilling injury at seedling in rice, Oryza sativa L. Jpn J Breed 41:35–40
Nakagahra M, Okuno K, Vaughan D (1997) Rice genetic resources: history, conservation, investigative characterization and use in Japan. Plant Mol Biol 35(1–2):69–77
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H (2006) Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 140(2):411–432
Nguyen BD, Brar DS, Bui BC, Nguyen TV, Pham LN, Nguyen HT (2003) Identification and mapping of the QTL for aluminum tolerance introgressed from the new source, Oryza rufipogon Griff., intoindica rice (O. sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 106:583–593
Nguyen TT, Klueva N, Chamareck V, Aarti A, Magpantay G, Millena AC, Pathan MS, Nguyen HT (2004) Saturation mapping of QTL regions and identification of putative candidate genes for drought tolerance in rice. Mol Genet Genomics 272:35–46
Novillo F, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Salinas J (2004) CBF2/DREB1C is a negative regulator of CBF1/DREB1B and CBF3/DREB1A expression and plays a central role in stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. PNAS 101(1):3985–3990
Novillo F, Medina J, Salinas J (2007) Arabidopsis CBF1 and CBF3 have a different function than CBF2 in cold acclimation and define different gene classes in the CBF regulon. PNAS 104:52
Panaud O, Chen X, McCouch SR (1996) Development of microsatellite markers and characterization of simple sequence length polymorphism (SSLP) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Gen Genet 252(5):597–607
Qian Q, Zeng D, He P, Zheng X, Chen Y, Zhu L (2000) QTL analysis of the rice seedling cold tolerance in a double haploid population derived from anther culture of a hybrid between indica and japonica rice. Chin Sci Bull 45(5):448–453
Robin S, Pathan MS, Courtois B, Lafitte R, Carandang S, Lanceras S, Amante M, Nguyen HT, Li Z (2003) apping osmotic adjustment in an advanced back-cross inbred population of rice. Theor Appl Genet 107(7):1288–1296
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1985) Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol 5(2):69–76
Saito K, Hayano-Saito Y, Maruyama-Funatsuki W, Sato Y, Kato A (2004) Physical mapping and putative candidate gene identification of a quantitative trait locus Ctb1 for cold tolerance at the booting stage of rice. Theor Appl Genet 109(3):515–522
Saito K, Hayano-Saito Y, Kuroki M, Sato Y (2010) Map-based cloning of the rice cold tolerance gene Ctb1. Plant Sci 179(1):97–102
Sen S, Churchill GA (2001) A statistical framework for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 159:371–387
Shigyo M, Ito M (2004) Analysis of gymnosperm two-AP2-domain-containing genes. Dev Genes Evolut 214(3):105–114
Sipaseuth BJ, Fukai S, Farrell TC, Senthonghae M, Phamixay S, Linquist B, Chanphengsay M (2007) Opportunities to increasing dry season rice productivity in low temperature affected areas. Field Crops Res 102(2):87–97
Song SY, Chen Y, Chen J, Dai XY, Zhang WH (2011) Physiological mechanisms underlying OsNAC5-dependent tolerance of rice plants to abiotic stress. Planta 234:331–345
Suh JP, Lee CK, Lee JH, Kim JJ, Kim SM, Cho YC, Park SH, Shin JC, Kim YG, Jena KK (2012) Identification of quantitative trait loci for seedling cold tolerance using RILs derived from a cross between japonica and tropical japonica rice cultivars. Euphytica 184(1):101–108
Szabados L, Savoure A (2010) Proline: a multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci 15:89–97
Takesawa T, Ito M, Kanzaki H, Kameya N, Nakamura I (2002) Over-expression of glutathione S-transferase in transgenic rice enhances germination and growth at low temperature. Mol Breed 9(2):93–101
Teng S, Zeng D, Qian Q, Kunihifo Y, Huang D, Zhu L (2001) QTL analysis of rice low temperature germinability. Chin Sci Bull 46(21):1800–1803
Theocharis A, Clément C, Barka EA (2012) Physiological and molecular changes in plants at low temperatures. Planta 235:1091–1105
Tian F, Zhu Z, Zhang B, Tan L, Fu Y, Wang X, Sun CQ (2006) Fine mapping of a quantitative trait locus for grain number per panicle from wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Theor Appl Genet 113:619–629
Verbruggen N, Hermans C (2008) Proline accumulation in plants: a review. Amino Acids 35:753–759
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2007) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics. North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Wang Q, Guan Y, Wu Y, Chen H, Chen F, Chu C (2008) Overexpression of a rice OsDREB1F gene increases salt, drought, and low temperature tolerance in both Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol Biol 676:589–602
Wang ZF, Wang FH, Zhou R, Wang JF, Zhang HS (2011) Identification of quantitative trait loci for cold tolerance during the germination and seedling stages in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 183(3):405–413
Xiao N, Sun G, Hong Y, Xia R, Zhang C, Su Y, Chen J (2011) Cloning of genome-specific repetitive DNA sequences in wild rice (O. rufipogon Griff.), and the development of Ty3-gypsy retrotransposon-based SSAP marker for distinguishing rice (O. sativa L.) indica and japonica subspecies. Genet Resour Crop Evol 58(8):1177–1186
Xiao N, Huang WN, Zhang XX, Gao Y, Li AL, Dai Y, Yu L, Liu GQ, Pan CH, Li YH, Dai ZY, Chen JM (2014) Fine Mapping of qRC10-2, a quantitative trait locus for cold tolerance of rice roots at seedling and mature stages. PLoS ONE 9(5):e96046
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1994) A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low-temperature, or high-salt stress. Plant Cell Online 6(2):251–264
Yoshida R, Kanno A, Sato T, Kameya T (1996) Cool temperatureinduced chlorosis in rice plants. Plant Physiol 110:997–1005
Yun KY, Park MR, Mohanty B, Herath V, Xu FY, Mauleon R, Wijaya E, Bajic VB, Bruskiewich R, Reyes BGL (2010) Transcriptional regulatory network triggered by oxidative signals configures the early response mechanisms of japonica rice to chilling stress. BMC Plant Biol 10:16
Zhang J, Zheng HG, Aarti A, Pantuwan G, Nguyen TT, Tripathy JN, Sarial AK, Robin S, Babu RC, Nguyen BD, Sarkarung S, Blum A, Nguyen HT (2001) Locating genomic regions associated with components of drought resistance in rice: comparative mapping within and across species. Theor Appl Genet 103:19–29
Zhang ZH, Su L, Li W, Chen W, Zhu YG (2005) A major QTL conferring cold tolerance at the early seedling stage using recombinant inbred lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci 168(2):527–534
Zhang CQ, Nishiuchi S, Liu S, Takano T (2008) Characterization of two plasma membrane protein 3 genes (PutPMP3) from the alkali grass, Puccinellia tenuiflora, and functional comparison of the rice homologues, OsLti6a/b from rice. BMB Rep 41(6):448–454
Zhang Y, Chen C, Jin XF, Xiong AS, Peng RH, Hong YH, Yao QH, Chen JM (2009) Expression of a rice DREB1 gene, OsDREB1D, enhances cold and high-salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. BMB Rep 428:486–492
Zhang T, Zhao XQ, Wang WS, Pan YJ, Huang LY, Liu XY, Zong Y, Zhu LH, Yang DC, Fu BY (2012) Comparative transcriptome profiling of chilling stress responsiveness in two contrasting rice genotypes. PLoS ONE 7(8):e43274
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31401365), Natural Science Foundation (BK2011426 and BK2011427) of Jiangsu Province, National Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System Special Fund (CARS-01-45), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions and International Atomic Energy Agency (12228/RO).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Matthias Wissuwa.
N. Xiao and W. Huang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2014_2420_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 3 Expression analysis of OsLti6a, OsLti6b, and P5CS by real-time PCR for plants maintained at 4°C for different durations. *Significant difference from Nanjing 11 with a P value = 0.01 (TIFF 4690 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, N., Huang, Wn., Li, Ah. et al. Fine mapping of the qLOP2 and qPSR2-1 loci associated with chilling stress tolerance of wild rice seedlings. Theor Appl Genet 128, 173–185 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2420-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2420-x